It's always scary to hear an incomprehensible diagnosis. Especially if it was diagnosed by a mammologist. Calcification in the mammary gland is an example of a frightening conclusion. To understand how quickly it forms and whether it requires treatment, you need to understand what it is.
Calcifications are neoplasms of calcium salts that can accumulate in all human organs. It is believed that their presence is not a disease, but a consequence of some disease, including oncology. In 20% of cases, it is malignant processes that are the factor of calcification. Therefore, it is necessary to undergo a thorough examination if this problem is detected.
Causes of breast calcification
In addition to oncological processes, the causes of calcium accumulation can be:
- Excess calcium in the body caused by:
- uncontrolled intake of vitamin complexes;
- vitamin D content in the body is at the top of the reference values;
- deterioration of kidney function;
- excess body weight;
- endocrine diseases.
- Body changes during menopause.
- Death of adipose tissue or fibrotic changes in the mammary glands.
- Inflammation of the mammary glands (including lactostasis), which results in an acidic environment that promotes the precipitation of calcium salts.
- Injuries, conditions after operations.
Some doctors associate calcifications with the protective functions of the body - they protect neighboring tissues from damage.
Surgery
Removal of neoplasms by surgical intervention is not carried out, since when the accumulations are removed, the calcified breast cavity can be filled with growing connective tissue, which threatens to start a malignant process.
Surgical intervention is used:
- in case of diagnosis of any stage of cancer;
- with nodular mastopathy;
- for fibroadenomas.
The strategy of surgical intervention is determined by a breast surgeon, taking into account the stage of the pathological process, type of neoplasm, and complications. Removal is performed using sectoral resection or partial mastectomy. To suppress the development of malignant changes, antibacterial therapy, radiation and chemotherapy sessions are additionally prescribed.
Detection of calcium accumulations in the mammary gland is a signal for further, more global medical examination. It is important for women to know what it is and what consequences a late diagnosis can lead to. In order to prevent neoplasms, as well as for early diagnosis of serious diseases, it is necessary to consult a mammologist a couple of times a year .
Article design: Oleg Lozinsky
Types of calcifications
Calcifications in the breast are usually distinguished according to different criteria.
The most important sign is their localization.
| Types of calcifications | Characteristic |
| Ductal | Calcium clots are located in the ducts of the mammary glands. The most unsafe type of location, as it can be a consequence of breast cancer. Additional examination is required. If mammography shows dense and approximately identical formations, then they are considered benign. Blurred neoplasms in the form of segments or dots indicate oncology. |
| Lobular | Upon examination, painful round formations are found in the glandular tissue. Often, they are benign, but to exclude oncology, it is necessary to undergo a biopsy. Characteristic of breast cysts. |
| Stromal | Single calcifications in the mammary gland are observed on mammography, which are localized in the connective tissue. The safest type of calcifications. |
Then the specialist studies the distribution of formations:
| Distribution type | Characteristic |
| Diffuse | Calcifications are located over the entire area of the chest. The type is characteristic of benign processes. |
| Regional | Neoplasms involve more than 2 cm of breast tissue. Regional spread does not occur with ductal localization. |
| Segmental | Distributed within the lobule. Sign of ductal localization. May indicate a malignant process. |
| Clustered (grouped) | Groups of neoplasms located within 1-2cm. The presence of one cluster is a sign of cancer. |
| Linear | Calcifications are arranged in tracks or lines with branches. |
It is important to pay attention to the form. Amorphous or clear, ring-shaped or round, dotted, dotted or branching calcifications in the patient.
The combination of all parameters signals the doctor about the presence or absence of the likelihood of developing a malignant process. The criteria help determine the need for additional research, or allow you to immediately make the correct diagnosis.
Diagnostics
Usually, it is difficult to detect such abnormalities during palpation of the breast, so the patient is referred for an X-ray examination or mammogram.
Depending on the location, size and shape of the tumors, the mammologist makes an accurate diagnosis.
Unfortunately, mammography is not always sufficient in this case, since sometimes neoplasms may not appear in the thickness of normal breast tissue. Therefore, such a study for some women is only the initial stage of diagnosis. We should not forget that you should not use antiperspirants or deodorants before checking your breasts with a mammogram.
Large single calcifications in the breast are a sign of a benign disease. Small calcifications that have jagged edges and blurred borders are often a sign of breast cancer. To confirm or refute the diagnosis, histological verification is performed.
How to Diagnose Breast Calcifications
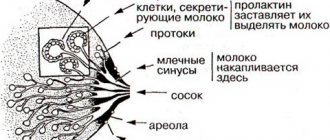
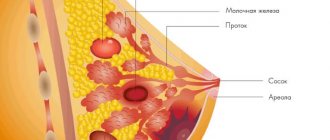
Calcifications in the mammary glands rarely cause discomfort to a woman. Possible pain, discomfort, secretion of fluid from the nipples. More often, the patient accidentally discovers large single formations (up to 0.8-1 cm) on her own. Multiple microcalcifications in the mammary gland cannot be determined by palpation.
The most informative study of microcalcifications is mammography. In X-ray mammography images in several projections, calcifications can be clearly seen, which appear as large white areas of different sizes and shapes. The accuracy of the study reaches 93%. But this method is not suitable for pregnant and lactating women. In this case, electrical impedance mammography is used, although its reliability is already about 75%.
Large single or multiple calcifications can be seen using ultrasound. But in order to establish the differential distribution and nature of the formations, additional research will have to be ordered.
Types of microcalcifications of the mammary glands
Calcium deposits can appear in any part of the mammary glands. There are many types of calcifications. They are classified according to various criteria.
By localization
They are divided into lobular, ductal and stromal (located outside the lobes and ducts). Ductal is a characteristic sign of the formation of intraductal papillomas (internal growths).
By appearance
There are calcifications that are dusty or in the form of separate pieces of different shapes.
Dust-like formations measuring about 600 microns in diameter, scattered throughout the volume, most often occur after inflammatory diseases of the mammary glands, as well as in the presence of benign neoplasms, such as fibroadenoma. But if the particles are small, like powder, these are microcalcifications that occur in the mammary gland with a pathology such as cancer.
Larger particles that resemble chunks of crushed rock, popcorn, cotton wool, or worm-like shapes can also be deposited under various pathological conditions. The degree of their danger can be judged, as a rule, by their number and degree of distribution.
By nature of distribution
Salt deposits can be single or multiple, scattered throughout the volume or located in any part of the female breast.
Single ones appear in the following cases:
- With the formation of intraductal papilloma. In this case, microcalcification of irregular shape appears, its diameter is more than 1 mm.
- The fibroadenoma present in the breast calcifies. This creates an element whose shape resembles “popcorn”.
- Calcium deposits are possible if there are cysts in the breast. Typically, such calcifications are similar in appearance to eggshells.
Multiple grouped. This is the name for point calcium formations located in a group in a volume of less than 2 cubic meters. cm.
Linear calcifications usually form in the presence of postoperative scars or are located along the duct.
Segmental. This type includes calcifications located in one lobe of the gland.
Regional ones are distributed throughout the entire milky lobe.
Diffuse calcifications are distributed throughout the entire volume of the breast.
Oncology or not - methods for checking calcifications
Let us note once again: calcifications themselves are not a sign of a cancerous condition! But they are often the only symptom of breast cancer. The presence and type of tumor can only be determined using hardware diagnostics.
Thermography is suitable for recognizing oncological neoplasm. Cancer cells have a higher temperature relative to the surface of the body, and calcifications will appear as cold clots.
A biopsy diagnoses cancer with 100% certainty. During the study, a section of breast tissue is taken and a histological analysis is performed.
Additionally, studies may be required for tumor markers, total and ionized calcium in the blood plasma, and estrogens.
Methods for detecting microcalcifications and diagnosing diseases
A preventive examination or check of the condition of the breast if pathologies are suspected is carried out by a mammologist. A gynecologist can also refer you for examination (for example, in the presence of mastitis, lactostasis).
Calcifications can be detected using mammography or ultrasound. Ultrasound makes it possible to examine only large individual formations or a group of them. Mammography allows you to take a picture in several projections, assess the size, number and location of calcifications. In most cases, based on the results of mammography, the nature of the neoplasm is determined based on some x-ray signs.
If microcalcifications are detected, the doctor prescribes an in-depth examination using ductography (to detect tumors in the ducts), as well as electrical impedance mammography (based on the fact that healthy and diseased tissues have different electrical conductivity). This makes it possible to detect a malignant tumor at an early stage.
A breast tissue biopsy is performed to study the cellular composition of the tissue and detect cancer cells. A type of such study is pneumocystography (study of the fluid filling the cyst by puncture of its membrane).
Thermography is also one of the methods for detecting tumors, based on the difference in temperature between affected and healthy breast tissue.
CT and MRI are used both to detect calcifications and to determine the type of breast pathology.
Calcifications in the mammary gland and their treatment
Treatment is selected individually, based on the underlying causes of calcification.
Large stromal formations without clinical manifestations of other diseases require only regular visits to a mammologist.
In the presence of benign tumors of the mammary glands, the patient is prescribed hormonal and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. It is also recommended to follow a diet with limited calcium levels to prevent new formations.
If the cause of the pathology is a malignant neoplasm, appropriate therapy is selected based on the stage of the malignant process. The standard of treatment is to perform a mastectomy, after which hormonal agents, radiotherapy and chemotherapy are prescribed.
Treatment methods
Microcalcifications cannot be completely cured . After detecting such neoplasms, the doctor prescribes dynamic monitoring of the patient, during which the woman must be regularly examined by a mammologist.
Drug therapy
As part of drug therapy, drugs are selected to eliminate the provoking factor. For these purposes the following are used:
- Hormone therapy. This method is more often used to treat women during menopause. The choice of drug directly depends on which hormone concentration exceeded the norm (progesterone, estrogen and others). If necessary, a complex of similar medications is prescribed or medications are replaced with treatment with folk remedies.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. These medications are recommended for most pathologies that cause calcium deposits. The need for such treatment is explained by the fact that pain in the mammary glands very often occurs against the background of an inflammatory process.
- Vitamin therapy. This method of treatment is used for the purpose of general strengthening of the body. When choosing medications, you should give preference to those that contain vitamin D and calcium in minimal concentrations.
If the formation of microcalcifications is caused by metabolic disorders, therapy is supplemented with hepatoprotectors. Drugs in this group are prescribed to restore function and protect the liver.
Surgical intervention
Surgeries for microcalcifications are not prescribed due to the low effectiveness of the procedure for such neoplasms. Basically, surgical intervention is used in cases where calcium deposits occur against the background of tumor processes.
The operation is recommended for:
- cancerous tumors;
- fibroadenoma;
- nodular mastopathy;
- festering cysts.
After surgery, a week-long course of antibiotic therapy is prescribed to prevent infection.
Diet food
The diet is developed individually in accordance with the requirements for each case. Most patients need to exclude fried and fatty foods, salty foods and alcoholic beverages from their daily diet. Instead, it is recommended to increase the amount of fresh vegetables and fruits consumed.
In addition, it is recommended to exclude legumes, sweets, sunflower seeds, sesame seeds, yeast products, and cheeses from the diet. They promote the deposition of calcium salts in the body.
Measures to prevent calcium deposits in the chest
And most importantly, do not ignore scheduled visits to the doctor and treat gynecological diseases and hormonal imbalances in a timely manner. If you suspect calcification of the mammary glands, you can make an appointment with a mammologist at our center at any convenient time.
Classification of calcifications
In fact, microcalcifications in the mammary gland are not dangerous formations. They can arise for completely harmless reasons. However, there are situations when the accumulation of calcium salts indicates the presence of serious diseases that are dangerous not only to health, but also to normal life.
Key aspects
Depending on where exactly the calcifications are located, experts distinguish several types of accumulations:
- If the process occurs in glandular tissues, we are talking about lobular lesions. Most often, this form accompanies benign transformations of the mammary glands (fibrocystic pathology of the gland, fibroadenoma, breast cyst);
- If the ducts of the gland are subject to calcification, the diagnostician will note the presence of ductal calcifications. Dense formations of equal size indicate a benign nature (usually, this is a long-term stagnation of secretions). If the structure of the mammary gland is deformed by formations of different shapes and sizes, most likely, the woman’s body is susceptible to an oncological process;
- Stromal calcifications are the most common form. They are located in the thickness of the dermal tissue or the cavity of the blood vessels. Often, cystic elements and benign fibroadenomas undergo calcification. They do not pose any threat to the patient's health. Lying too close to the surface, stromal formations can worsen the appearance of the breast, creating a certain psychological discomfort.
Orientation in relation to shares
Regional calcifications are accumulations of salts that cause deformation of the glandular structures of one lobe. The diffuse form is represented by a whole galaxy of salt accumulations, different in shape and size.
We also recommend viewing: Causes of pain in the mammary glands before menstruation
Depending on exactly how the calcifications are located, diagnosticians put forward the first conclusions regarding the benign nature of the pathological process. The diagnosis of “grouped calcifications” is established if the concentration of salt elements in one lobe is above 3 cubic centimeters.
Main reasons
After carrying out all the diagnostic measures, the attending physician will be able to finally establish both the nature of the occurrence of calcifications and judge the specific reasons that influenced the development of the pathology. Often, at the end of a difficult lactation period, burdened by lactostasis, mastitis of various etiologies, single calcifications may occur in the mammary gland, which do not pose a threat to health.
Long-term treatment can lead to the fact that benign breast tumors, fibroid conditions, adenomatous changes, and cystic formations begin to change under the influence of calcification. Other reasons that inevitably lead to the occurrence of calcifications of various kinds include:
- Age-related changes (menopausal transformations);
- Problems with metabolic status;
- Excess vitamin D (this factor often appears during long-term treatment of fractures and major injuries);
- Sclerosing processes of various origins.
The main mission of the diagnostician is to determine which calcifications are in the mammary gland and whether they are dangerous. What it is and how to eliminate the pathology can be decided by doctors during a consultation.
Symptoms of single calcifications
Every woman who cares about her health should regularly undergo preventive examinations, donate blood for biochemistry and monitor the balance of hormones, especially during menopause.
Due to the poor environmental situation, poor nutrition and sedentary lifestyle, the disease is very common (up to 80%). Since such neoplasms are not characterized by pain, it is necessary to take care of your health and regularly undergo routine examinations so as not to miss the onset of the disease.
The causes of microcalcifications can be:
- Poor nutrition, consumption of foods with a high calcium content in the presence of excess vitamin D in the body. This vitamin accelerates the absorption of calcium. Excess occurs, for example, with the abuse of synthetic vitamin preparations or slow metabolism in the body. Metabolic disorders can be a consequence of diseases of the liver, kidneys, and digestive system.
- Age-related changes in breast tissue during menopause.
- Lactation disturbance and the occurrence of lactostasis (stagnation of milk in the milk ducts) or mastitis (inflammatory process).
- Damage to breast tissue due to breast injuries or during surgery.
- The presence of pathological neoplasms resulting from hormonal disorders.
Calcifications often become a sign of the formation of a malignant tumor.
If large, diffuse, homogeneous calcium deposits appear, this is usually harmless and indicates a benign process. In the presence of malignant tumors, the elements are small (dust-like), heterogeneous in shape (in the form of “crushed stone”, “snake skin”, “lumps of cotton wool” or resemble worms).
There are no symptoms by which a woman can independently notice the formation of calcifications in the breast. Located in deep layers, they do not make themselves felt. They cannot be detected by palpation. Indirect symptoms appear when inflammatory processes or neoplasms occur in a given area of the breast.
Note: The danger does not lie in the appearance of calcifications, which in themselves do not cause any discomfort to the woman. But the fact is that microcalcifications in the mammary gland are neoplasms, the appearance of which is often associated with the presence of a malignant tumor, and in the early stages there are no other signs. Therefore, when calcium deposits are detected in the breast, a diagnostic examination is required.
In order not to provoke the formation of lime deposits in tissues, it is necessary to control the consumption of calcium-containing foods and vitamin preparations. Vitamin D is taken strictly following the dosage.
The chest should be protected from injury. It is not recommended to wear tight underwear.
An important role is played by regular visits to doctors (mammologist and gynecologist) for preventive monitoring of the condition of the female reproductive system and breasts.
Calcifications or calcareous formations are formed:
- in the stroma (connective tissue);
- in lobules (acini);
- in the ducts.
Those that have “made a nest” in lobules (acinar or lobular) are rounded up to 3 mm in diameter, neat, single.
Intraductal calcifications are polymorphs. Because they are formed due to the impregnation of dead cells or tissues with calcium salts. They are uneven, fragmented (visible in pieces on an ultrasound or mammogram).
Types of calcareous formations can be divided not only according to the degree of malignancy of the process that caused them, but also, for example, according to the location of the segments (calcifications):
- Scattered calcifications or diffuse location is when you have calcifications “scattered” throughout the “mammogram” (throughout the entire volume of tissue, but not in the ducts).
- The regional location suggests that the calcifications occupy a decent volume of the gland (up to 2 cm2) and are also not ducts.
- Segmental is the location of calcareous formations in the area of one lobe of the mammary gland or in the acinus (lobule).
- The linear distribution of calcifications indicates the location of calcareous objects along the excretory duct.
The process of early diagnosis and treatment is complicated by the fact that calcifications do not signal themselves with any symptoms. The general condition of the breast is normal; the lump cannot be felt during palpation. Disturbances in the metabolic process, deposits of calcium salts can be seen during mammography. In addition, certain indicators of a biochemical blood test and hormone analysis also indicate possible problems.
There are no obvious symptoms that a woman could notice, the breasts look normal, no pain occurs. Signs can only appear when the deposits reach large sizes, more than 1 cm in diameter, and become noticeable upon palpation. But such cases are rare; usually calcifications in the mammary glands are not large.
Which doctor should I contact?
If lumps appear in the breast or calcifications are detected during mammography, you should contact a mammologist. After conducting a series of examinations (blood tests for hormones, mammography, ultrasound, biopsy, etc.), the doctor will draw up a plan for further treatment and recommend clinical observation. If necessary, the patient is scheduled to consult an endocrinologist or oncologist.
Breast calcifications are accumulations (foci of calcification) of calcium salts that form in soft tissues as a result of various diseases leading to structural damage to glandular and connective tissue cells. In most cases, these formations are practically asymptomatic and can only be palpated when they reach large sizes (1 cm or more). In themselves, they are not dangerous to a woman’s health, but their presence always indicates the need to identify the cause of their appearance and treat the underlying disease.
Rating: (votes - 1 , average: 5.00 out of 5)