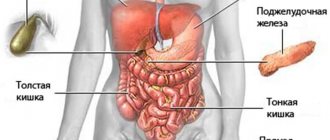
The liver parenchyma is a formative tissue. The liver is of great importance for the body, since it is this organ that neutralizes toxins and toxic substances with the help of special Kupffer cells, which remove harmful elements into the intestines. The functions of this organ include the synthesis and removal of bile through channels, the formation and synthesis of glucose, lipoproteins, globulin, prothrombin, albumin, fibrinogen. The liver helps normalize the metabolic processes of amino acids, proteins, carbohydrates, hormones, fats and vitamins. It accumulates useful substances formed from metabolic products.
Diffuse changes in the organ cause the appearance of serious pathological conditions. Timely detection and treatment of changes in the liver parenchyma, giving up bad habits will help prevent the development of life-threatening diseases.
What it is
The liver is located in the upper right area of the abdomen under the rib. The upper part of the organ reaches the level of the nipples. Parenchyma - the tissue from which the organ is formed, consists of liver lobules. The liver is completely regenerated in about a year. When diffuse changes develop in it, in most cases this is revealed by an increase in parenchymal tissue, less often by its decrease. Violations of this kind can be large-scale or minor. The lobes have a prismatic shape; they are separated from each other by bile ducts, blood vessels and an intermediate substance. This structure allows each cell of the organ to be provided with the required volume of blood; each lobe has an outlet for the synthesis of substances. The width of each lobe reaches from 0.7 to 2 mm. The parenchyma consists of more than a million of these parts.
Structure
To put it simply, parenchyma is the tissue that fills the kidneys, which is a collection of cells. It performs the function of a regulator consisting of the following components:
- removal of toxins, toxic substances obtained as a result of processing waste products, in other ways;
- maintaining water balance throughout the body;
- blood purification;
- normalization of metabolic processes.
An important indicator of the healthy state of kidney tissue is thickness, which changes naturally only with age. From adolescence to old age, the norm is 15–25 mm. Considering the structure of renal tissue on ultrasound, we can distinguish its two layers:
- Cortical. This outer layer consists of glomeruli covered with vessels, each of which produces urine. It is then transmitted to the urinary system. In a healthy kidney, the cortex contains about a million nephrons, but not all of them function at the same time.
- Cerebral. After urine has formed in the outer layer, it is transferred further to the inner layer. In it, the liquid passes through a complex system of pyramids and channels further. The medullary part of the parenchyma is connected to the cortical canals, so the fluid moves freely as it is processed.
Interesting! Scientists are still amazed at the uniqueness of the parenchyma, because, unlike other tissues of the body, it has the unique ability to constantly regenerate.
https://youtu.be/qeb2S8JOKkc
What does the disease look like, photo
The main method for determining diffuse changes in the liver parenchyma is ultrasound. The method allows you to assess the degree of organ transformation. During the study period, the specialist detects the following diffuse changes: heterogeneity in the structure of the organ, an increase in its size, a disturbed pattern of blood vessels, and compaction of the periportal tracts.
Typical liver changes
By conducting a study, a specialist will be able to identify the main typical changes in the parenchyma:
- change of size;
- increased echogenicity;
- changing the clarity of the contour;
- change in the pattern of blood vessels;
- violation of the homogeneity of the structure;
- focal, local or diffuse changes in liver tissue.
Sometimes even an experienced diagnostician will not give you a completely complete picture of the condition of your organs. Minor changes can hide severe pathology. And sometimes the changes are associated with previous illnesses. For a complete clinical picture, it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive examination, an MRI, and a urine and blood test.
Changes in the parenchyma are quite dangerous and lead to diseases such as cirrhosis, hepatitis, and sclerosing cholangitis.
Parenchyma of the liver and pancreas
Diffuse lesions of the liver and pancreas parenchyma are mainly detected during ultrasound diagnostics. A uniform change in tissue density is observed, extending to the entire pancreas and liver. The detection of such changes indicates the presence of pathology of these organs.
Diffuse changes in the liver and pancreas parenchyma often occur together and can be reactive. For example, in case of liver pathologies, reactive pancreatitis is diagnosed. The detection of concomitant pathology makes it possible to exclude the presence of a tumor, cyst or stones in the patient, since such formations cause focal changes in tissue density.
If the echogenicity and density of the pancreas decreases against the background of an increase in its size, acute pancreatitis is suspected. If the size of the liver is unchanged, then there is a possibility that pancreatitis is chronic. When inflammation causes the transformation of the glandular tissue of the pancreas into fibrous tissue, ultrasound reveals a diffuse increase in density against the background of normal or reduced organ size.
Echostructure of the kidney
Ultrasound evaluates organs and tissues based on their ability to reflect or transmit ultrasound waves. If the waves pass freely (the structure is hollow or filled with liquid), then they speak of its anechoicity, echonegativity. The denser the tissue, the better it reflects ultrasound, the better its echogenicity. Stones, for example, show themselves as structures in which the echogenicity is increased (hyperechogenic).
Normal kidney on ultrasound:* Bertin's columns,** pyramids, ***cortex, ***renal sinus
Normally, on ultrasound, the kidney has a heterogeneous structure:
- pyramids are hypoechoic;
- the cortex and columns are isoechoic (identical to each other);
- sinuses are hyperechoic due to connective, fibrous, fatty tissue and the vessels and apexes of the pyramids located there. The pyelocaliceal complex is not normally visualized.
In a healthy kidney, the cortex, pyramids and columns of Bertin are clearly visible. In addition, during ultrasound, the doctor always pays attention to the echogenicity of the renal parenchyma in comparison with the liver parenchyma, since the indicators of this particular organ are taken as the standard of echogenicity. Normally, the echogenicity indicators of a normal kidney are lower than those of a normal liver, and those of the adrenal glands are higher.
Types of changes
Various types of changes can occur in liver tissue: in density, shape and composition.
Pathological deviations are divided into certain types:
- Diffuse. Occur throughout the parenchyma;
- Local. Part of the parenchyma is damaged;
- Focal. There is a compaction or one small lesion.
Focal type
Focal lesions can be multiple, merging or single. Focal changes are diagnosed by echography. The degree of echo-reflection classifies focal lesions as those without echostructure and those with echostructure (weak, strong or mixed). As the pathology worsens, the echogenicity of the lesion may change.
Using echography, it is possible to determine the development of areas of calcification (seals) in the parenchyma. They occur less frequently in children than in adults.
The appearance of focal lesions of the parenchyma is promoted by cirrhosis, chronic hepatitis, tuberculosis, echinococcosis, and hypomotor dyskinesia of the bile ducts. Pathology also develops as a result of stagnation of bile in the liver, malaria, sepsis and parasitic infestations.
Currently reading: What are diffuse changes in the liver and pancreas - types and how to treat
Lesions whose echostructure cannot be identified are parenchymal cysts. It is possible to detect formations using an echogram only when they reach a size of 3–5 mm in width. Formations in the form of cysts are divided into specific types, differing in the cause of formation (congenital or acquired) and methods of appearance (false and true, parasitic and non-parasitic).
Diffuse altered (diffuse - heterogeneous)
Diffuse changes are acute and chronic hepatitis, fat accumulation, cirrhosis, changes under the influence of other diseases. With hepatitis, the patient's liver size increases, but its structure does not change.
Violations of the parenchymal surface appear when the inflammatory process continues to progress. In this case, thickening of the thin wall of the liver is recorded. During the examination, weak echogenicity is determined against the background of increased sound conductivity.
In the presence of hepatitis, unexpressed inflammatory processes in the parenchyma cause a heterogeneous level of echogenicity. When cirrhosis is diagnosed, lesions with impaired echogenicity begin to grow in number as a result of the rapid destruction of a homogeneous structure. The size of the lesions varies from 0.5 cm to 2 cm.
Heterogeneity of the parenchyma can be caused by stagnation in the bile ducts, fatty degeneration of the parenchyma, and impaired metabolism.
Types of parenchyma studies
Despite the ability of the kidneys to regenerate, they are still susceptible to all sorts of pathological formations: cysts, benign, malignant tumors, infections, etc.
The most effective research methods are:
- ultrasonography
- Magnetic resonance imaging
- CT scan
- kidney biopsy
The thickness of the tissue can be used to judge the condition of the organs. If any deviations from the norm are noted, then there is a serious reason to conduct more detailed studies together with testing.
Signs and symptoms
Damage to the liver parenchyma is revealed by certain signs. The patient feels bitterness in the mouth, weakness, nausea and headache, pain in the right hypochondrium. A characteristic symptom of the pathological condition is jaundice. The appearance of one or more symptoms is a cause for concern and requires urgent medical advice. Focal inflammation of the liver occurs with characteristic signs: the formation of calcifications in the liver (seals containing calcium salts) and the formation of cysts.
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out using ultrasound. The study makes it possible to detect various types of damage in the structure of the parenchyma.
Diffuse changes of a mild nature may be a consequence of previous viral diseases or poor nutrition. Such changes cannot be dangerous to human health. When significant changes are recorded that indicate serious illness, it is necessary to undergo laboratory tests to determine the cause of liver damage.
The main symptoms of the disease include:
- The appearance of jaundice in the sclera. Yellowness spreads to the mucous membranes of the palate and skin (a red or green tint may appear);
- Skin inflammation and itching;
- Discoloration of stool and change in urine color (becomes darker);
- Temperature increase;
- Nausea, vomiting;
- Pain in muscles and joints.
Treatment of kidney failure with folk remedies
It is important to know that only the attending physician can prescribe a folk remedy, since self-medication can lead to complications. If a patient is diagnosed with kidney failure, treatment is often carried out with burdock root. To prepare a folk medicine, the ingredient must be crushed, then prepare 250 g of boiling water. Water should be filtered. Then pour boiling water over 1.5 tablespoons of the mixture and leave to infuse for a day. If urine does not flow out in the required quantity, swelling will occur. For this reason, the therapy process should be supervised by the attending physician.
Liver parenchyma with increased echogenicity
If during an ultrasound examination an increased echogenicity of the liver is recorded, then we can talk about the presence of pathological changes, from fatty inclusions, scars, abscesses to acute viral hepatitis, tumors or destruction of hepatocytosis.
The specialist compares the resulting picture with accurate data on the echogenicity of the organ in question and states an increase or decrease. Deviation from standards indicates negative factors that caused damage and malfunction of internal organs - systems.
If an increase in echogenicity is recorded, this means that the organ tissues differ from healthy structures. Deviations are a signal of liver problems. The cause of increased echogenicity can be various diseases:
- Chronic hepatitis or cholangelitis;
- Dystrophy and steatosis;
- Parasitic infestation;
- Liver abscess. The early stage of inflammation is revealed by a small area of reduced echogenicity. However, with the development of an abscess, heterogeneous echo density appears (either decreased or quite increased).
Increased echogenicity is also influenced by the presence of echogenic formations such as hematomas, hemangiomas, adenomas, excess weight or sudden weight loss, alcoholic fibrosis or sclerosis, diabetes mellitus and prolonged use of medications.
Increased echogenicity of the parenchyma is manifested by external signs and symptoms that indicate the presence of serious problems in the liver.
The main symptoms include:
- Periodic pain on the right side below the chest;
- Digestive difficulties;
- Jaundice;
- Changes in the size of the liver, which are detected by palpation;
- Excess weight;
- Decreased immunity;
- Heart problems.
Treatment of increased echogenicity of the liver is aimed at eliminating the pathology that causes the condition. Therapy necessarily includes a diet.
What is parenchyma
The word “parenchyma” literally translated from Greek means “poured around, nearby.” In medicine, this term refers to the main functionally active tissue of all dense (not hollow) organs: for example, the liver, kidneys, lungs, pancreas and prostate glands.
The parenchyma in the liver is represented by glandular epithelium, which in appearance resembles a sponge. Thanks to this structure, the filtration function of the liver is ensured.
- The outside of the gland is covered with stroma: it is a durable capsule that consists of connective tissue fibers. It plays a protective, supportive and organ-forming role. The stroma protects the parenchyma from external influences.
- Partitions (trabeculae) extend from the capsule deep into the liver, dividing the entire organ into lobes and segments. Nutrient blood vessels, bile ducts and nerves pass through their thickness.
- Inside the liver, connective tissue fibers from the stroma branch to form cells. Each of them contains a mass of cells forming parenchyma. In humans, this cellular structure is weakly expressed (but, for example, in the liver of pigs it is highly developed).
Important! Parenchymal organs differ from hollow ones in that they consist of a dense mass of cells, which is covered on top with a strong connective tissue capsule. The processes of the outer shell divide the entire organ into separate structural elements.
Causes of hepatic parenchyma
Liver pathologies occur as a result of improper functioning of liver cells. When the liver is damaged or inflamed, the cells of the organ lose their ability to capture bilirubin, which leads to the accumulation of this pigment in the blood and jaundice appears. The cause of jaundice may also be stagnation of bile.
Currently reading: Normal liver size according to ultrasound - tables and description of the procedure
Liver pathologies mainly appear as a result of:
- Infections with viruses (viral hepatitis);
- Poisoning with toxins and alcohol;
- The appearance of sepsis, which provokes a lack of oxygen in cells;
- Development of autoimmune type of hepatitis.
Pseudopathologies
In some cases, with ultrasound, what, at first glance, seems to be a pathology, is not. Thus, often enlarged Bertin's columns extend quite deeply beyond the parenchyma into the renal sinus. This parenchymal bridge appears to literally divide the kidney in two. However, all of the structures that make up the bridge are normal renal tissue. Often enlarged Bertin's columns or such bridges are mistaken for a tumor.
Various variants of the structure of the pyelocaliceal system should not be classified as pathology. There are a great many options for their configuration, even for one person the structure of the right and left kidneys is individual. This also applies to the anatomical structure of the renal parenchyma.
Partial doubling of the kidney can be considered ambiguously. In this case, the parenchymal constriction divides the sinus into two seemingly separate sections, but complete bifurcation of the pelvis does not occur. This condition is considered a variant of the norm and generally does not cause discomfort.
Ultrasonography
The principle of ultrasound research is based on the fact that human tissues are capable of reflecting ultrasonic waves. Each component of the body reflects ultrasound to a certain extent, each of them has a standard reflection indicator. Violation of indicators indicates the presence of an inflammatory process. Based on the data obtained, the specialist can determine the existence of tumors, stones, abscesses, parasitic infestations in the liver, and parenchymal injuries.
The procedure is non-invasive and quite easy to perform. The patient being examined takes a horizontal position and is asked to lie on his back or left side. The doctor applies a special gel to the skin in the upper right area of the peritoneum and begins to examine the problem area with an ultrasound sensor.
The patient does not need to undergo any preparation before performing an ultrasound. The only requirement is to avoid eating foods that increase gas formation 3 days before the test. Ultrasound is performed on an empty stomach, which allows you to obtain data with high accuracy and a real picture of the disease.
Normal picture of parenchyma on ultrasound
The norm of parenchyma is determined in accordance with the size of the hepatic lobes, the delineation of their contours and structures. The parameters are compared with standard indicators, thus the specialist determines which segment of the liver is affected. If the liver does not show pathological changes, the size of the right section should be about 12.5 cm, and the left – 7 cm. The width of the portal vein with a healthy liver reaches 13 mm, and the common bile duct up to 8 mm. The edges of the liver, in the absence of diffuse changes, should be smooth.
Measurable Indicators
Like any organ, the kidneys have their own health indicators. And if laboratory methods for examining urine and monitoring the rhythm of urination are used to assess the functionality of the kidneys, then the integrity of the organ, its acquired or congenital anomalies can be judged by examination data from ultrasound, CT (computed tomography) or MRI. If the obtained indicators are within the normal range, it means that the kidney tissue has not been damaged, but this does not give reason to talk about the preservation of its functions.
Kidney size on ultrasound. Length – length, width – width, parenchyma – parenchyma
Normally, the size of this organ in an adult reaches 10-120 mm in length and 40-60 mm in width. Often the right kidney is smaller than the left. If you have a non-standard physique (too large or fragile), it is not the size, but the volume of the kidney that is assessed. Its normal value in digital terms should be twice the body weight ±20 ml. For example, with a weight of 80 kg, the volume norm is from 140 to 180 ml.
The thickness of the kidney parenchyma is also assessed in different ways: by direct measurement (the norm is 13-25 mm, of which the cortical layer is 8-10 mm) and by the ratio of the thickness of the parenchyma and the sinus. The norm for this indicator in young people is 1.6, in the group over 30 years old 1.2-1.6, in older people – 1.1.
Other diagnostic methods
To diagnose liver diseases, in addition to ultrasound, other methods are used to obtain a more detailed and accurate picture of the disease. Prescribed:
- Examinations of blood, urine and feces;
- Blood chemistry;
- ELISA, PCR. Examinations can identify antibodies that are able to resist viruses, and thus confirm their role in the development of the disease;
- CT;
- Liver biopsy with histological examination of a sample of the affected area. A study is carried out if cirrhosis is suspected.
Diagnostics
How to measure the size of the parenchyma and diagnose changes? Only doctors can do this using special equipment. Three diagnostic procedures are usually prescribed:
- Ultrasound;
- CT;
- MRI.
Important! CT and MRI have a number of contraindications for use, for example, CT is prohibited during pregnancy, MRI is prohibited in the first trimester.
An examination of both kidneys is always prescribed. If an ultrasound examination reveals diffuse or focal changes in only one, both are considered in further diagnostic procedures. If necessary, a study of nearby organs of the genitourinary system related to kidney function may be prescribed.
By examining the parenchyma, calcifications can be detected - deposits of calcium salts. This pathology is so dangerous that in the absence of timely treatment it can lead to the development of renal failure and other chronic kidney diseases. Also, deposits of calcifications (nefocalcinosis) can cause swelling, which will lead to urinary tract diseases.
Regenerative ability
The liver has regenerative properties, which are activated in response to the death of hepacitosis. Regenerating cells include a supply of glycogen and standard organelles. The regeneration process occurs through accelerated division of liver cells. Due to this, the surface of the liver grows and replaces the necrotic zones. The bile ducts are also subject to restoration.
If the liver is damaged beyond repair, an organ transplant is required to save the patient's life.
What are diffuse changes in the thyroid gland? Symptoms and causes
Diffuse changes in the thyroid gland in women and men represent tissue damage that is detected by ultrasound. This manifests itself in the abnormal reflection of ultrasonic waves by the thyroid gland. In fact, such a change is not a diagnosis, but just a term. Therefore, in the future, additional examination is necessary to detect a specific disease.
Main reasons
The thyroid gland undergoes diffuse changes for several reasons:
- lack of iodine in the body;
- hormonal imbalance in the thyroid gland;
- autoimmune changes, that is, tissue inflammation;
- poor nutrition.
Iodine deficiency is caused primarily by endemic conditions. In every country there are regions in which both soil and water contain quite little iodine, so diffuse changes in the thyroid gland are most common in these areas. Women are especially susceptible to this.
Many people, when eating food, do not even think about the content of iodine substances, but this leads to abnormal disorders. Also, not many people know that there are vegetables that interfere with the production of gland hormones, and this leads to pathology.
With hormonal imbalance, the structure and size of the thyroid gland changes, causing diffuse failure. The most common cause is an autoimmune change. In this case, the immune system becomes aggressive towards the thyroid gland, which is why harmful antibodies and lymphocytes are formed in the organ.
Diffuse change manifests itself in diseases such as endemic goiter, subacute and chronic thyroiditis, toxic and mixed goiter.
Symptoms of disorders
When examined in the clinic, pathological changes manifest themselves in heterogeneity of tissue structure and differences in gland density.
Upon palpation, you can detect an enlargement of the organ, which can lead to the appearance of a goiter, that is, parenchyma. A sick person may notice the following changes:
- dry hair;
- chills;
- fragility of the nail plate in women;
- frequent colds;
- fatigue and lethargy;
- a decrease not only in physical performance, but also in intellectual performance;
- neurosis, depression;
- memory impairment;
- impaired concentration;
- weight change;
- decreased sexual function;
- constipation
If these symptoms appear, you must immediately go to the hospital and undergo appropriate examination. Women need to additionally see a gynecologist.
Organ cell disorders
The parenchyma in a woman is a cellular complex of the thyroid gland, which bears a significant load. It consists of different types of tissue: hematopoietic, epithelial, nervous and others. There is also a stroma in the thyroid gland, thanks to which the organ functions normally. It is the stroma that is the base, and the parenchyma fills all compartments with actively dividing cells.
A diffuse change in the cells of the thyroid gland is a disruption of all parenchyma tissues, resulting in an enlargement of the organ. Such changes can be detected by palpation by an endocrinologist, after which an ultrasound is performed and a final diagnosis is established. As a rule, this is a diffuse change in the parenchyma.
In this case, symptoms may not appear at all, so diffuse failure is often discovered completely by accident. If the pathology is not detected in a timely manner and treatment is not started, the disease will progress with subsequent complications.
Other violations
Diffuse changes in the thyroid gland can be focal and nodular in nature. In the first case, the focus of inflammation may indicate various tumor formations: cyst, cancer, adenoma, and so on. Focal lesions appear due to constant imbalance. This variety is observed in various forms of goiter and tumors. Diagnosis is carried out by ultrasound, after which treatment is prescribed.
Diffuse nodular failure in both women and men is quite easily palpable during examination, because enlarged nodes are located superficially. This form is formed against the background of enlarged follicles, which indicates a parenchymal onset.
It is possible to detect nodal pathologies only during a doctor’s examination, since the disease is completely asymptomatic.
The only thing the patient can pay attention to are signs of suffocation, foreign body sensation and a change in voice. This does not appear at the initial stage. If not treated in time, then the number of nodes increases significantly, which is why a malignant tumor develops.
Treatment of any form is carried out strictly at the individual level, taking into account the characteristics of the patient, the degree of the disease, and other things. The effectiveness of treatment always depends on how quickly the patient responds to the first symptoms of diffuse changes in the thyroid gland.
Diffuse changes in the parenchyma of the thyroid gland are a pathological process that covers all tissues of the organ and is not a separate disease, but only a diagnostic definition. A similar term is used to refer to processes occurring in tissues in certain diseases of the thyroid gland.
What it is
Diffuse lesions are detected by ultrasound of the thyroid gland. The principle of the procedure is based on the assessment of echogenicity. In some pathologies, there is a significant change in the ability of tissues to reflect sound. Diffuse lesions are evenly distributed nodes and compaction of the thyroid gland of various types. The doctor evaluates tissue density and monitors the rate of development of a benign or malignant tumor.
The term includes a large number of pathological conditions accompanied by deformation of thyroid tissue. The entire organ reflects ultrasound differently than it does in its normal state. To prescribe an effective therapeutic technique for identifying diffuse lesions, it is not enough.
Causes
Conditions that contribute to deformation of thyroid tissue are associated with iodine deficiency in the body. This problem is well known to people living in unfavorable environmental conditions. Hypothyroidism or thyrotoxicosis may also be accompanied by diffuse changes in the thyroid gland. These diseases contribute to tissue proliferation and the formation of a thyroid goiter.
Pathological changes are accompanied by autoimmune pathologies that cause inflammation of the thyroid gland. Antibodies destroy healthy organ cells, causing organic and functional disorders. Nutrition has a significant impact on the endocrine system. Diffuse changes may occur due to consumption of foods that interfere with the absorption of iodine.
Moderate signs of thyroid damage can be found in endemic and toxic goiter.
Symptoms
Diffuse changes in the tissues of the thyroid gland are detected accidentally during routine medical examinations and palpation of the organ. Parenchyma is significantly different from stroma, which consists of only one type of tissue. Changes in it are accompanied by deterioration of the skin and nails, chills, and dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract.
In adults there are:
- decreased libido;
- disruptions in the menstrual cycle;
- obesity not related to diet.
In children, pathological conditions are expressed in hyperactivity, retardation in psychophysical development, constant aches in muscles and joints, and a tendency to viral infections. Chronic fatigue is combined with deterioration of memory and attention.
Signs of thyroid disease vary depending on the nature of the disease. In the early stages there may be no symptoms.
Additional research methods are used to make a final diagnosis.
In mature women, thyroid lesions may be accompanied by signs of hormonal imbalances - lack of menstruation, the appearance of benign tumors in the mammary glands.
Diagnostics
Nodular changes in the parenchyma of the organ are detected using ultrasound. Deciphering the result helps confirm or exclude the presence of diseases. Pronounced echo signs of pathology are observed in autoimmune thyroiditis. The patient's examination begins with inspection and palpation.
Structural changes are detected already in the early stages. Additionally, a blood test is prescribed for antibodies to thyroglobulin, the level of triiodityronine, thyroxine and TSH. Slight and moderate enlargement of the thyroid gland is accompanied by an imbalance of these substances. Ultrasound is based on the assessment of echographic signs of tissue. Its violation indicates a heterogeneous structure of the parenchyma. A healthy organ has normal echogenicity, which covers most of both lobes. Sometimes additional diagnostic procedures are used - radiography, CT and MRI.
Sometimes in a patient’s medical record you can see a diagnosis such as a heterogeneous structure of the thyroid gland. Normally, this organ of the endocrine system... Read more >>
Treatment of diffuse changes in the thyroid parenchyma
Therapeutic measures should be carried out under the supervision of the attending physician. Self-medication is not only ineffective, but also dangerous to the life and health of the patient.
Medicines and other methods can be selected only after deciphering the results of diagnostic procedures.
Subsequently, the therapeutic regimen undergoes several adjustments.
Since diffuse lesions of the thyroid gland are accompanied by a disruption in the production of hormones, replacement therapy cannot be avoided. Such treatment is a vital necessity for chronic autoimmune thyroiditis. The amount of thyroid hormones in this case exceeds the maximum permissible values.
If there are moderate signs of damage to the thyroid gland, treatment involves changing the diet and taking iodine-containing medications. If the pathology is accompanied by hypothyroidism, synthetic thyroid hormones are used.
For diffuse nodular lesions of the thyroid gland that contribute to the development of compression syndrome, emergency surgical intervention is prescribed. After the operation, the patient must regularly visit the endocrinologist and undergo all necessary tests. With proper treatment, the prognosis for recovery is favorable. Without treatment, dangerous complications may develop.
Prevention
Measures to prevent the development of diffuse lesions of the thyroid gland are aimed at eliminating iodine deficiency. To do this, you need to introduce foods rich in this substance into your diet, replace table salt with iodized salt and start taking special medications.
It is recommended to avoid stress that contributes to dysfunction of the thyroid gland. It is useful to perform procedures aimed at strengthening the immune system. Older patients need to regularly visit an endocrinologist.
Liver pathologies in children
Symptoms of liver disease in children differ from those in adults. In the first year of life, infants develop diseases that have hereditary causes.
In the first 14 days of life, babies exhibit dysfunction of the hepatobiliary system, in the form of jaundice of the skin. The condition is caused by intrauterine underdevelopment of the canals (atresia), or by feeding the infant with fatty milk. The baby has discolored stool.
Liver damage in an infant is also recorded if a woman suffered an acute infectious disease during pregnancy, regularly drank alcohol, or took hepatotoxic drugs. Signs of liver disease in a child include poor digestion and nervous system problems.
Liver diseases in children at the initial stage are detected by the appearance of pain in the area of the right hypochondrium. Pain increases when eating fatty foods and when running. The pain is cramping, bursting or aching. The duration of pain can reach up to 15 minutes.
The following symptoms indicate the presence of liver pathology in a child:
Currently reading: What is fatty liver - what it can lead to, symptoms and treatment
- Regurgitation after eating;
- Nausea and vomiting mixed with bile;
- Feeling of bitterness in the mouth;
- Change in urine color;
- Diarrhea;
- Weakness and headache;
- Decreased appetite;
- Increased flatulence;
- Yellowness of the mucous membranes and skin.
The child sleeps poorly, becomes capricious and whiny.
The cause of pain and discomfort in the liver area in children can be physical activity, unbalanced nutrition and the predominance of fatty foods in the diet, stretching of the liver capsule due to hepatomegaly, pathology of the bile duct and bladder.
Treatment of the child is organized based on the results of examinations. A diet is prescribed, the purpose of which is to normalize the outflow of bile and reduce the load on the hepatobiliary system.
Drug treatment of the child is carried out using anti-inflammatory drugs to eliminate pain and reduce the severity of the inflammatory process. Antispasmodics are also used to expand the biliary tract, normalize the passage of bile and sedatives. The therapy includes antibacterial, antiviral or antiparasitic drugs to eliminate pathogens; the course also includes choleretic agents to prevent stagnation.
When cholelithiasis is advanced, sometimes they resort to removing the bladder. The intervention is performed using laparoscopic instruments. With atresia of the biliary ducts, anastomoses are formed to restore bile outflow.
Diffuse changes in organs
Diffuse changes in the kidneys are not an independent disease, but a set of signs indicating pathological processes.
On ultrasound, the doctor identifies diffuse lesions (see photo below), which can be mild or severe. The final document describes parenchymal changes as follows:
- Echoten, calculosis. This means the presence of sand or kidney stones.
- Volumetric formations are cysts, tumors, inflammations.
- Echo-positive formations of heterogeneous texture are a cancerous tumor.
- Echo-negative lesions are necrotic lesions.
- Anechoic formation—cyst.
- Hyperechoic zone - lipoma, adenoma.
- Uneven contour of the kidneys, asymmetry in size - pyelonephritis in an advanced stage.
Diffuse changes may manifest themselves with the following symptoms:
- The appearance of blood in the urine.
- Pain when urinating.
- Lower back pain.
- Chills.
- Edema.
If the above symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor for differential diagnosis.
https://youtu.be/bb_uVbGaCMo
Treating Changes
Treatment of liver parenchyma is aimed at identifying the root cause of diffuse changes and eliminating it.
If viral hepatitis is detected, antiviral medications are prescribed. Viferon and Alfaferon are considered effective.
For autoimmune diseases, immunosuppressive drugs are used. Azathioprine and Prednisolone are mainly prescribed
The course of treatment includes amino acids, phospholipids and vitamin complexes. Phospholipids accelerate the regeneration of hepatocides. Amino acids and vitamin compounds compensate for the lack of nutrients in the body.
How is the treatment carried out?
Damage to the parenchyma is a reaction to primary diseases, and general therapy is aimed at eliminating them. Medications are prescribed, the purpose of which is to eliminate the root cause, including the following:
- Antiviral pharmaceuticals. For changes caused by hepatitis, take Reaferon or Viferon.
- Antituberculosis. If the cause was tuberculosis, use Rifampicin or Isoniazid.
- Antibiotics. For infectious diseases of the lungs, the drugs Cycloserine and Ethambutol are prescribed. To eliminate inflammatory processes and improve bile flow, take Tetracycline or Metacycline.
- Hormonal and immunosuppressants. For autoimmune diseases, Medrol and Azathioprine are prescribed.
- Choleretic. To increase secretory functionality, take Allohol and Berberine.
- Hepatoprotectors. Prescribed for gallstone disease and cholecystitis, liver intoxication with drugs or toxins. These are “Essentiale”, “Essliver”, “Hepa-Merz”, “Rezalut”.
- Antispasmodics. To relieve pain, take the drugs “No-shpa”, “Papaverine”, “Mebeverine”.
A timely visit to the doctor will prevent the development of complications.
Treatment includes taking phospholipid and amino acid preparations and vitamins that will help the body recover. In this case, you need to completely eliminate alcoholic drinks, give up fried, smoked, salty and spicy foods. The menu should include potassium-containing foods and fiber. It is possible to use decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs. Pumpkin and plum juice with the addition of honey can restore the functioning of the liver. The main preventive measure for inflammation of the liver parenchyma is its timely and early detection.
Therapeutic and preventive actions will help the liver recover. Not all parenchymal transformations are reversible. With cirrhosis, the damage to soft tissue reaches large sizes, which means that the organ loses the ability to perform its job. Therefore, there is no need to postpone a visit to the doctor when the first symptoms of the disease appear, but it is best to undergo annual examinations, which often reveal the first signs of pathologies in the early stages. The sooner treatment is started, the greater the chance of recovery and recovery.
https://youtu.be/9AGU6Owhf_o
Diet
An important place in the treatment of liver parenchyma is played by a special nutritional system, according to which fried and fatty foods must be completely excluded from the diet. Products containing fiber and potassium are healthy and recommended.
The use of alcoholic beverages and soda is strictly prohibited.
It is recommended to include dietary meats, low-fat dairy products, pureed soups and cereals, sours and homemade jelly in the diet. Decoctions of medicinal herbs that can replace coffee and black tea are useful. Bread should be used stale, soups and cereals can be seasoned with vegetable oil, butter should be used in limited quantities. You should also limit the amount of salt and sugar you use.
You need to take food in small portions, at the same time. You need to have dinner three hours before bedtime.
Effective method of therapy
Dill seeds are used to treat kidney dysfunction. To do this, you need to prepare an infusion in proportions of 1:19. Drink 120 g of the healing remedy several times a day. Thanks to this remedy, the outflow of fluid is accelerated, inflammation and pain are relieved.
Experts recommend consuming more iodine in case of kidney failure. Sea kale contains a large amount of this element, so you need to include it in your diet and prepare salads from it. But before including this product in your diet, you need to consult your doctor.
Prevention
To prevent the development of diffuse changes in the liver parenchyma, it is necessary to completely abstain from alcoholic beverages and control weight. It is important to stick to your diet. A properly formulated diet allows you to provide the body with useful substances and strengthen the immune system, which has a positive effect on overall health.
Toxic and poisonous substances must not be allowed to enter the body. Medicines may be taken after consultation with a doctor, observing the indicated doses and course duration.
Regular examination helps to detect diseases at an early stage, which guarantees a complete recovery.
In some cases, to prevent complications, the patient is prescribed maintenance therapy with hepatoprotectors for life.
Timely diagnosis and properly organized treatment help prevent the progression of liver diseases. The organ is capable of regenerating. Drug therapy, following a diet and giving up bad habits provide positive dynamics in the treatment process with a favorable prognosis,
Functions of parenchyma
The parenchyma is very vulnerable; it is the first to react to any pathological processes in the body. As a result, the parenchyma decreases or increases.
If the changes are not age-related, a full examination should be performed to identify the underlying cause.
The main function of the parenchyma is urine excretion , which occurs in two stages:
- formation of primary urine;
- formation of secondary urine.
The glomerular system of the kidneys absorbs fluid entering the body. This is how primary urine is formed. Then the reabsorption process begins, during which nutrients and some water are returned to the body.
Parenchyma ensures the removal of waste and toxins and maintains a normal volume of fluid in the body.
Reviews
Dear readers, your opinion is very important to us - therefore, we will be glad to hear your feedback about liver parenchyma in the comments, this will also be useful to other users of the site.
Sergey:
I developed jaundice as a result of viral hepatitis. An ultrasound was performed, during which the extent of liver damage was discovered. Treatment was prescribed, and on the 5th day the pain began to decrease. Signs of jaundice disappeared within 14 days. I follow a diet, don’t smoke, don’t drink alcohol.
Denis:
I was worried about pain in the liver area. The pain was accompanied by weakness and nausea. The therapist ordered an ultrasound examination. The specialist discovered slight changes in the liver, which was associated with the viral flu. Vitamin complexes, Essentiale Forte, were prescribed to normalize liver function. The condition quickly improved.
How are changes in the liver parenchyma treated?
The choice of treatment method depends on the underlying disease. They always start with general events:
- It is necessary to make adjustments to the diet. The main enemies of the liver are “fast” carbohydrates, alcohol and animal fats in large quantities.
- It is important for obese people to pay attention to their weight and work on reducing it.
- If you have diabetes, it is important to keep your sugar levels within acceptable limits.
For chronic viral hepatitis, treatment is prescribed by a hepatologist, based on the type of virus, its genotype, stage of the disease, the presence of concomitant pathologies and the presence of cirrhosis. Antiviral therapy is carried out according to individual regimens; today there are modern, highly effective agents.
The liver is a grateful organ that can regenerate itself. However, if it is constantly exposed to unfavorable factors that damage the parenchyma, then its capabilities are inevitably exhausted.
You can contact the hepatologist in the comments. Don't hesitate to ask!
This article was last updated: 07/23/2019
Didn't find what you were looking for?
Try using search
doctor or administrator.
Read the dictionary of terms.
Expert author: Gastroenterologist-hepatologist Ekaterina Kashukh
Characteristics of the kidneys
The human body consists of several metabolic systems, each of which has its own functions and characteristics. One of them is the urinary system, which is responsible for removing waste from the body. It consists of:
- pairs of kidneys;
- urethra;
- pairs of ureters;
- renal arteries;
- Bladder.
The kidneys are a paired organ responsible for filtering mineral salts from the blood and producing urine. The vascular part and parenchyma of the kidneys are the main components of this organ. The vascular part is called the renal pelvis, while the parenchyma consists of two parts, the cortex and the renal medulla . It is in the parenchyma that blood purification and urine formation occur.
The basic unit of the kidneys is the nephrons located in the parenchyma (there are millions of them). Nephrons consist of the renal glomeruli, where the main filtration of electrolytes and salts occurs, as well as the renal tubules, which convey purified blood to the center of the kidneys. Thus, it is obvious that parenchymal diseases can cause serious health problems. In 9 out of 10 cases, end-stage kidney disease requires a kidney transplant, but more often requires dialysis, which is a costly and time-consuming procedure that is burdensome for many patients.
Treatment
If decreased kidney activity and changes in their tissues are detected, it is necessary to find out the cause of this condition and begin timely treatment.
This problem is dealt with by a urologist, depending on various pathologies, he determines treatment methods, if necessary, selecting anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial and other drugs necessary to restore the parenchyma.
In more severe cases, in the presence of stones and neoplasms, including cancerous tumors, they resort to surgical intervention in which the neoplasms are excised, causing minimal harm to the patient.
Kidney diseases are serious illnesses that affect the body as a whole. However, correctly prescribed treatment and the patient’s compliance with all doctor’s instructions will help restore their function and quickly recover.
Reasons for structural changes
https://youtu.be/uNlWoreNf3I
Experts have proven that the most common causes of diffuse changes in kidney tissue are:
- Calcifications. These are kidney stones that form due to poor nutrition, improper metabolism, and other disorders. Such formations cause serious illnesses that can manifest with various symptoms and cause serious complications. The appearance of sand or stones delays the outflow of urine, provokes inflammation or the appearance of renal colic.
- Cyst. One of the common causes of changes is the formation of cysts that occur on both the right and left kidneys. When fluid is retained in the nephrons, a simple or solitary cyst often forms. In simple cases, a thin-walled oval or round formation develops, containing hemorrhagic or serous fluid. The size of such formations can be from 8 to 10 cm, and occasionally large ones can be found, which can contain about 10 liters of liquid. When the cyst is eliminated, the organ is restored and a rapid recovery occurs. Cystic-dysplastic changes provoke the formation of a multilocular cyst, which has the appearance of a multi-chamber formation with clearly defined outlines. The main problem with such formations is that they can become malignant.
- Tumor processes. The formation of a tumor even in one kidney will stop due to serious changes in the structure of the organ. This process can be either benign or malignant. To understand the nature of the formation, you need to undergo the necessary examination.
- The presence of pathologies of an infectious nature (pyelonephritis, pyelitis, etc.). With such ailments, especially in chronic form, the kidneys are most often depleted; prolonged inflammation leads to a decrease in the area of the kidney parenchyma, which significantly affects the functioning of the organ.
- A change in the echogenicity of kidney tissue is a sign of the development of pathologies such as glomerulonephritis, chronic renal failure, nephropathy as a result of diabetes, various inflammations, and disruptions in metabolic processes.
- Chronic kidney disease (nephritis, urolithiasis, etc.)
- Certain diseases of the endocrine system. Ailments such as thyrotoxicosis and disorders associated with the pancreas contribute to the thinning of the kidney parenchyma, followed by its atrophy.
In addition, pathological disorders in the structure of tissues can be caused by age-related changes, hereditary diseases, incorrectly prescribed therapy, the consequences of past illnesses, and in children - congenital anomalies that tend to develop rapidly and therefore pose a serious danger.
Causes of changes in parenchyma
The growth of fibrous (scar) tissue can indicate the presence of serious pathologies. There can be many reasons:
- Alcoholism and obesity cause an increase in liver size. In this case, there is a strong increase in the echogenicity of the tissue. The same picture can be seen in patients with diabetes.
- The presence of parasites can also lead to diffuse transformation.
- With cirrhosis of the liver, multiple lesions of parenchymal areas are detected, and echogenicity also increases.
- The tumor and cyst change the structure of the liver lobes and its size. These are clearly visible on the ultrasound screen.
- Infectious diseases can disrupt the overall pattern of the parenchyma, but this does not have serious consequences. The liver repairs itself.
If pathology is detected, you must contact a physician or hepatologist. The doctor will be required to prescribe an additional examination.
Medicines are not always beneficial. They can also significantly affect the health of this organ.
Prevention of liver diseases
To prevent the development of parenchymal changes in various liver diseases, you must follow simple rules. Such prevention will be useful for the normal functioning of not only the liver, but also other internal organs.
The main recommendations of experts are:
- Eat right. Every day your diet should include lean meats or fish, vegetables, and fruits. Avoid fatty, fried foods. Products with a high fiber content are also useful: cereals, whole grain bread, vegetables.
- Watch your weight. Overeating and, as a result, obesity have a negative effect on the liver. If a person constantly eats a lot, it simply does not have time to break down all the enzymes. However, if you need to lose weight, avoid strict diets, it is better to adhere to the principles of proper nutrition and exercise.
- Don't abuse alcohol. If there are no liver diseases yet, you must adhere to the established permissible alcohol limits. For women – 12 g of ethanol per day, for men – 24 g. If you already have chronic diseases, you must completely give up alcohol.
- Avoid stress. Due to constant stress and adrenaline production, pressure on the liver increases. Try to live a measured life, if necessary, consult a psychotherapist.