Early gestosis
These are manifestations of various kinds of symptoms (nausea, vomiting, salivation) in the first half of pregnancy. They arise due to disorders of all types of metabolism, adaptation of the woman’s body, changes in immunity and brain functioning. In this case, a maximum increase in hCG (pregnancy hormone) is observed. Early gestosis is most severe in multiple pregnancies and hydatidiform moles. Risk factors include:
- Disturbances in the functioning of systems responsible for adaptation of the body (neuroendocrine disorders, high or low blood pressure, rheumatic heart defects).
- Diseases of the liver, kidneys (hepatitis, nephritis, pyelonephritis).
- Diabetes.
- Mental disorders.
- Obesity.
- Infectious diseases.
- Bad habits (alcohol, smoking, drugs).
- Allergies.
- Past diseases of the genital organs.
Prevention of gestosis and toxicosis
Measures to prevent these complications are extremely simple - you need to register with the antenatal clinic on time, tell your obstetrician-gynecologist about chronic diseases, give up bad habits (alcohol, smoking, drug addiction), preferably even at the time of planning the future baby, and especially in moment of pregnancy.
It is also important to follow all the recommendations of your doctor, keep all appearances at the antenatal clinic, and take prescribed tests. The main thing is to understand for yourself that a new life is developing inside you, which wants to be a full-fledged, healthy person. And you will love this life more than your own. Some people just realize this during pregnancy, and others only after childbirth. This is precisely the maternal instinct.
Why, then, destroy your own child in the bud? No normal mother will forgive herself for this later. And with a stone on your heart, seeing how your beloved baby is suffering through your fault, it is extremely difficult to live. Take care of yourself and your future child, besides, our medicine is doing everything for this.
Manifestations of early gestosis
Vomit
Vomiting occurs in approximately 50-80% of all pregnant women. This is a manifestation of a violation of the woman’s body’s adaptation to pregnancy. Vomiting 1-2 times a day without disturbing the general condition of the woman does not apply to gestosis. When vomiting occurs (10-12 times a day), it is manifested by general weakness, low blood pressure, an increase in temperature to 38 C, an increase in heart rate, this is considered a sign of gestosis. Prolonged vomiting is accompanied by loss of water, vitamins, exhaustion, and blood thickening. Such vomiting is observed in 15%.
A mild form of vomiting occurs up to 3-5 times a day (usually on an empty stomach), accompanied by nausea, loss of appetite and normal general condition, blood pressure and urination.
This form goes away on its own in 90% of cases and is easy to treat.
The moderate degree is characterized by vomiting up to 10 times a day, regardless of food intake, as well as nausea, salivation, dehydration, low blood pressure, tachycardia, decreased diuresis (urination) and body weight. There is also adynamia, apathy, and mental lability. 5% of women may experience liver dysfunction.
In severe forms, vomiting occurs up to 20 or more times a day, food is not retained, there is a weak pulse of up to 120 per minute, very low blood pressure (80/40), a woman can lose 3-5 kilograms per week. The woman is exhausted, the skin and mucous membranes of the tongue and lips are dry, the skin and eyes are yellow, there is bad breath, poor sleep, fatigue, loss of appetite.
Salivation
Can occur in all pregnant women. This is a relatively rare type of gestosis. Based on the amount of saliva, mild and severe forms are distinguished, and according to the nature - constant (day and night) and intermittent (it disappears, then it appears). The mild form does not lead to any impairment. Severe ones can cause dehydration, poor health and mental disturbances.
Symptoms in the 3rd trimester
Preeclampsia is accompanied by the development of multiple organ failure, so it is not difficult to determine its symptoms in the later stages. Pathology is manifested by the development of one or more symptoms. The earliest sign is swelling. Edema affects the limbs, the anterior abdominal wall or the entire body.
Another common symptom is a persistent increase in blood pressure. It is associated with impaired microcirculation. This condition manifests itself as fatigue, headaches, and spots before the eyes.
The most severe sign of gestosis in late pregnancy is HELLP syndrome. It is usually detected at 35 weeks. Symptoms increase very quickly:
- severe malaise;
- headache;
- vomit;
- pain in the liver area;
- jaundice;
- Urine tests show high levels of protein.
The outcome is a convulsive attack that turns into a coma.
There are several rare forms of gestosis that have an atypical clinical picture.
- Jaundice. It develops if a woman is sick or has previously had viral hepatitis. The skin and mucous membranes turn yellow, severe itching begins, and bleeding is possible.
- Dermatoses. Typical for women with high allergies. Manifested by dryness, flaking of the skin, severe itching.
- Tetany of pregnancy. Develops with pathology of the endocrine system. Manifested by convulsions due to calcium deficiency.
- Osteomalacia – softening of bone tissue. Caused by a lack of vitamin D.
- Chorea. It is formed due to organic damage to the brain, manifested by involuntary movements and difficulty swallowing.
We recommend further reading Why pregnant women are prescribed a magnesium drip for edema in the 1st, 2nd and 3rd trimester
Atypical forms are difficult to diagnose, which increases the risk of complications.
Early gestosis usually develops in women who are pregnant for the first time. They occur more easily than in multiparous women.
Late gestosis
These are profound disturbances in the functioning of vital organs in the second half of pregnancy, which is manifested by the classic triad of symptoms - increased blood pressure, protein in the urine and edema. Occur more often after 28 weeks of pregnancy.
Preeclampsia
Causes:
- General vasospasm (the intensity of the liver and kidneys decreases, which leads to changes in protein, carbohydrate and fat metabolism, antitoxic function and kidney filtration);
- Changes in rheological characteristics and blood coagulation (thickening, increased coagulability);
- Decreased blood volume;
- Impaired blood circulation in organs and water-salt balance.
Risk factors include:
- Pathologies of extragenital organs (liver, heart, lungs).
- Presence of preeclampsia in a previous pregnancy.
- Age of the pregnant woman (less than 19 and more than 30 years).
- Maternal obesity, anemia, bad habits, unbalanced diet.
- Multiple births, large fetus, its hypotrophy.
Eclampsia
This is a severe form of preeclampsia. It is characterized by the development of a convulsive attack (maybe even several) and loss of consciousness. There is prenatal (75%) and postnatal. Before convulsions, a sharp headache, abdominal pain, vomiting, blurred vision and cerebral circulation may occur. There is also a risk of stroke and paralysis of half the body.
Causes of gestosis in pregnant women
There is no exact explanation for the reasons for the development of late toxicosis, but there are several theories trying to explain what these are and the causes of this pathology. Each of these theories has its supporters, but it is generally accepted that the development of gestosis is facilitated by a number of factors that disrupt the functioning of internal organs.
The following theories are popular:
- Cortico-visceral. It is based on the assumption that the physiological connection between the cortex and subcortex of the brain is disrupted, which leads to pathological changes in the vascular system.
- Endocrine theory. Based on this theory, it is believed that gestosis develops against the background of disruption of the endocrine system. But there is another opinion: such disorders develop already during late toxicosis, and do not provoke it.
- Immunological theory. Preeclampsia occurs due to an inadequate response of the mother's immune system to fetal antigens. The pregnant woman's body tries to reject the developing fetus.
- The genetic theory has a basis: gestosis occurs more often in women, among whose relatives there have already been cases of late toxicosis of pregnancy.
- Placental theory. The theory is based on the fact that pathological changes in the blood vessels occur in the placenta and uterus; they are subject to spasms. As a result, blood flow is disrupted and hypoxia (oxygen starvation) occurs.
None of the theories fully explains how gestosis develops. Most often, several factors are involved in the occurrence of this pathology.
There are also risk factors that increase your chances of developing preeclampsia. These include:
- multiple pregnancy (pregnancy with more than one fetus);
- those who decide to get pregnant over the age of 35;
- or being in early adolescence;
- being pregnant for the first time;
- obese;
- with a history of high blood pressure
- having a history of diabetes;
- with a history of kidney disease.
Nothing can definitively prevent this disorder. Early and consistent prenatal care can help your doctor diagnose the condition more quickly and avoid complications. Having a diagnosis will allow your doctor to provide proper monitoring before delivery.
Pathogenesis of eclampsia
The mechanism of development is not well understood. Now it is considered as the failure of adaptive maternal systems to meet the needs of fetal development. When, under the influence of negative factors (liver diseases, lung diseases, heart defects, obesity, genetic disorders, psycho-emotional stress, infection), a spasm of small vessels occurs in all organs, their function is disrupted and tissue hypoxia (oxygen deficiency) develops. The load on the heart increases, blood volume decreases, the inner lining of blood vessels is injured, which increases blood clotting. As a result, nephropathy and insufficiency of blood flow in the uterus and placenta occur.
Prevention
Women at risk must be identified.
To prevent the formation of gestosis, the following recommendations must be followed:
- sleep at least 8 hours;
- frequent walks in the fresh air;
- reduction of stress factor;
- careful monitoring of the pregnant woman's condition.
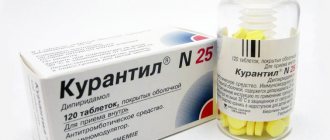
Drug prevention includes taking acetylsalicylic acid from 12 to 36 weeks. The use of this drug is recommended in low doses in women at risk.
Prevention does not completely avoid gestosis. However, it reduces the risk of its formation and facilitates its course. Any woman planning a pregnancy should know about preventive measures.
How is gestosis diagnosed?
Making a diagnosis of early toxicosis is not difficult. A typical clinical picture (vomiting a certain number of times, salivation), the onset of symptoms in the first half of pregnancy, risk factors may be present. In the blood, the level of bilirubin and leukocytes is increased, the level of protein is decreased, the amount of urine excreted per day is present, acetone is present in the urine, the water-electrolyte balance is disturbed - hypokalemia, hypernatremia.
There are some difficulties with late gestosis. It is difficult to make a diagnosis before symptoms appear. It is necessary to pay attention to risk factors and identify early signs (increased blood pressure more than 140/90, edema, protein in the urine more than 1 g/l, weight gain). The main role is given to constant monitoring of pregnant women, in which blood pressure, protein in the urine, body weight are systematically measured and the appearance of edema is observed.
Determining the severity of preeclampsia is very important for treatment. There are 3 degrees:
- Light form. Typical blood pressure is from 130 to 150, there is little protein in the urine (up to 0.3 g/l), swelling is observed only in the lower extremities, a normal number of platelets (a sign of normal blood clotting) and creatinine (an indicator of kidney function).
- Medium shape. Blood pressure is from 150 to 170, protein in the urine can rise to 5 g/l, swelling is already on the face, platelets are below normal, creatinine increases (kidney function is impaired).
- Severe form. Blood pressure of 170 and above, protein more than 5 g/l, swelling throughout the body (especially in the area of the nasal passages, which complicates breathing), headache, stomach ache, in the liver area, in the eyes of the spot, the amount of excreted urine and platelets is greatly reduced ( risk of bleeding), kidney function is disrupted up to kidney failure.
Causes
To this day, the causes of gestosis have not been clearly established, but it is known for certain that the placenta plays the main role in its formation. In case of poor blood supply to the uterus (for example, in the case of narrowing of the uterine arteries) and pathologies directly related to the placenta itself, pressure increases to increase blood flow.
An increase in pressure occurs as a result of narrowing of the blood vessels of the expectant mother, as a result of which the quality of blood supply to organs such as the kidneys and brain deteriorates. As a result, the quality of their functioning decreases.
When edema forms, water escapes from the bloodstream into the tissue, which thickens the blood and increases the likelihood of blood clots. Due to the formation of blood clots, small vessels are blocked and blood flow worsens even more, and due to thick blood, the pressure again increases.
In the early stages of the first trimester
In the early stages of pregnancy, there are several reasons for the formation of gestosis:
- hormonal - there is a destructive effect of hormones, in particular hCG, on a woman’s placenta;
- allergic – the tissues of the fetal egg are considered foreign to the pregnant woman’s body, characterized by strong vomiting throughout the entire 9 months of gestation (in some situations it can end in miscarriage);
- psychogenic – caused by excessive emotionality of the pregnant woman, which provoke disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system.
In the second trimester
The reasons that provoke gestosis during this period include the following:
- toxic - the fetus or placenta releases toxic substances;
- neuroflex – the growing fertilized egg has an irritating effect on endometrial receptors, causing increased activity of the autonomic nervous system.
In the 3rd trimester
During this period, the main cause of gestosis is considered to be immunological - as a result of immunological disorders, the fertilized egg is rejected.
Why are gestosis dangerous?
Early gestosis rarely poses any danger to the mother or fetus. But if vomiting is long-term and cannot be treated, irreversible changes in the body can occur, including mortality. But this happens very rarely. It should be noted that repeated and prolonged vomiting in pregnant women can lead to the threat of miscarriage, preeclampsia, fetal hypoxia, increased blood loss during childbirth and weakness of labor. Also, the threat of miscarriage can arise if salivation is untreatable and the mental state of the pregnant woman is depressed.
Late gestosis poses a high risk for the mother and fetus - renal, adrenal and liver failure develops, fetal development is delayed and fetal death occurs. If eclampsia is left untreated, eclamptic coma develops.
Concept of gestosis
Preeclampsia is a complication
pregnancy, in which there is an increased risk of perinatal death.
This condition leads to complications in the reproductive process, and can also provoke various diseases and even death.
During pregnancy, an exacerbation and manifestation of chronic diseases and hereditary characteristics may occur.
Since the body cannot cope with the load during the development of gestosis in pregnant women,
then this becomes the cause of pathology.
In most cases, toxicosis is diagnosed in women in the later stages. Preeclampsia can be pure or combined.
In the first case, the disease develops in pregnant women who do not have a history of serious illnesses. The second type develops if the body has liver and kidney diseases
, hypertension, chronic diseases.
Treatment of early gestosis
Mild forms are treated at home, while moderate and severe forms must be treated in a hospital. It is necessary to ensure long sleep, a calm environment, proper care, and proper diet. Diet food should be fortified and easily digestible. Take in small portions chilled. If food is not retained, intravenous administration of amino acids, proteins, glucose, and vitamins is prescribed. It is recommended to drink alkaline mineral waters 5-6 times a day. After eliminating vomiting, the diet can be expanded. Be sure to prescribe physical therapy (walking, self-massage of the muscles of the upper half of the body, deep breathing). It is also necessary to conduct psychotherapy, which makes it possible to convince the pregnant woman that vomiting is reversible and the pregnancy will go well. You can use electrosleep, reflexology and acupuncture, acupuncture, herbal medicine, aromatherapy (inhalation of pleasantly smelling substances).
In case of increased salivation, you should rinse your mouth with infusion of chamomile, oak bark, and menthol solution. The skin around the mouth should be smeared with protective creams, and food should be consumed in small portions.
Drug therapy
- Drug treatment is based on the administration of antiemetic drugs. They inhibit the vomiting center in the medulla oblongata. Such substances include chlorpromazine, metoclopramide, etaprazine (does not reduce blood pressure, which has a positive effect on the body during prolonged vomiting), droperidol (also has a sedative effect).
- To eliminate dehydration, glucose solutions and physiological solutions are prescribed.
- To improve uteroplacental circulation and fetal gas exchange, oxygen therapy should be used and drugs that dilate the vessels of the uterus and fetus (potassium orotate, pentoxifylline) should be administered.
- To reduce saliva secretion, atropine sulfate solution is administered intramuscularly.
Every day, your body weight and the amount of fluid you drink and excrete are monitored. In severe cases, protein and amino acid preparations are added. Pour in about 2-2.5 liters. In the most severe cases, hormones (hydrocortisone, ACTH) are administered. If there is a threat of miscarriage, progesterone is administered subcutaneously for 7 days. An indicator of the effectiveness of treatment will be an increase in diuresis, stopping vomiting, improving the patient’s condition and increasing body weight. If there is no effect from therapy (vomiting does not stop, the skin turns yellow, the temperature rises without infection, tachycardia appears, weight loss) termination of pregnancy is indicated.
Symptoms and treatment of gestosis
Knowing how dangerous gestosis is for you and your baby, it is important to be able to recognize the insidious enemy in time.
- Your blood and urine tests, weight and blood pressure are strictly monitored by the attending physician or midwife, from whom obvious swelling cannot be hidden;
- Do not refuse additional tests if a specialist suspects gestosis. Read an article on the topic: What tests are taken during pregnancy?>>>. Among additional studies, you may be offered a blood clotting test, control of the fluid you drink and excrete;
- It is possible to involve a nephrologist and an ophthalmologist in making a diagnosis;
- Treatment of gestosis during pregnancy requires a comprehensive treatment; it is often possible to do without hospitalization.
Nutrition
- Without correcting this point, all treatment will be weakly effective;
- You need to start keeping a close eye on what you eat and even keep a food diary. In it you record every piece that goes into your mouth. Write honestly, as it is;
In order not to miss out on any important products, read the book Nutrition Secrets of an Expectant Mother>>>
This book is not so much about nutrition, but about how, through the use of certain foods, you can eliminate complex conditions during pregnancy, such as:
- nausea;
- haemorrhoids;
- swelling;
- constipation
+ product recommendations to effectively prepare your body for an easy birth.
So, if you suspect gestosis, you need to establish the water-salt balance in the body.
- Mineral water without gas in a volume of at least 2 liters is an excellent option. You can read in detail in the article on the website: Mineral water during pregnancy>>>;
- There is no way to completely give up salt; it will also retain water, but where necessary - in vessels;
- The diet must contain foods rich in protein, amino acids, calcium, potassium, magnesium and other beneficial substances;
- Harmful foods and alcohol are prohibited. Read the article What should you not eat during pregnancy?>>>
Other important components of the treatment of gestosis
- Lifestyle. During the period of development of gestosis, bed or semi-bed rest is recommended, but no one cancels walks in the fresh air. How long can you walk at different times? Read the article Walking during pregnancy>>>;
- Positive attitude. Stress is not the best companion to illness, so it’s time to tune in to a positive mood, surround yourself with beauty and dream of meeting a healthy little one soon;
- Physiotherapy. The main goal of the procedures is relaxation and relaxation. Contrast showers, massage, swimming are suitable. Important article: Massage during pregnancy>>>;
- Medicines. Depending on the reasons that led to the development of gestosis, you may be prescribed medications to normalize the functioning of damaged organs.
Vitamins that affect blood vessels, medications that increase blood circulation in the uterus and placenta, and possibly additional medications to lower blood pressure are prescribed.
Attention! Only with the development of stage 4 of the disease, when there is a threat to life for both mother and child, doctors, after an additional ultrasound, decide on early delivery.
Treatment of late gestosis
The goal of therapy is to restore the functions of vital organs and the fetoplacental system, eliminate symptoms, and prevent the development of a convulsive state. In case of late gestosis, the patient should always be hospitalized.
It is important to adhere to the following provisions:
- Normalization of blood pressure and blood volume.
- Elimination of general vasospasm.
- Improving blood flow in the kidneys.
- Regulation of water-salt balance, metabolism, rheological characteristics of blood (thickness, clotting).
- Prevention of hypoxia and fetal malnutrition, bleeding in the pre- and postpartum period.
- Carrying out a normal birth with adequate anesthesia.
Diet. A pregnant woman should eat about 2900-3500 kcal per day, food should contain a high percentage of protein, a reduced amount of animal fats, cholesterol, and foods that cause thirst. You need to include rest during the day, about 2-3 hours, which improves blood flow in the placenta and kidneys.
Treatment of mild late gestosis
For mild severity, drug treatment is not always prescribed. The consumption of water and salt is not limited. If the pregnancy is up to 37 weeks, observation in a day hospital is possible. Monitor key indicators (pressure, fluid balance, edema, registration of fetal movements). In the case of a stable condition, wait-and-see tactics are used. If at least one moderate sign appears, the woman is hospitalized.
Treatment of moderate late gestosis
For moderate preeclampsia, semi-bed rest, limitation of physical and mental stress, diet, and a complex of vitamins and microelements are prescribed.
Antihypertensive therapy. If the pressure is more than 160, antihypertensive drugs are administered (metoprolol, methyldopa, nifedipine - others are contraindicated). But you need to control your blood pressure because low blood pressure negatively affects the blood flow of the fetus and placenta.
Infusion therapy. The goal is to normalize blood volume, rheological properties and hemodynamics. Saline solutions (Ringer's, 0.9% sodium chloride) and protein preparations are administered.
If there is no effect of therapy for 7-10 days, termination of pregnancy is indicated.
Treatment of severe late gestosis
Severe preeclampsia. The pregnant woman is hospitalized in the intensive care unit, allocated a separate room with round-the-clock monitoring, and a vein is catheterized for long-term infusion therapy.
Strict bed rest is prescribed. The pressure is maintained at 150-160 to prevent cerebral hemorrhage (the drugs are the same as for the moderate form). Magnesium therapy is used by administering magnesium sulfate to maintain the concentration of magnesium in the blood and prevent convulsive conditions. Infusion therapy is under strict supervision.
With this form, if treatment does not have an effect within 24 hours, the pregnant woman is prepared for artificial termination of pregnancy, regardless of the stage of pregnancy. The advantage is given to childbirth through the natural reproductive tract with adequate pain relief. If the genital tract is ready (the cervix is sufficiently mature and preparation has been carried out with the introduction of prostacyclin), delivery is performed through the genital tract. Otherwise, if the cervix is immature, high blood pressure and preeclampsia are progressing, fetal condition is deteriorating, or there is a risk of a convulsive attack, a cesarean section is performed.
Eclampsia is treated directly at the site where the seizures occurred. The pregnant woman is placed on a flat surface on her left side, the upper respiratory tract is emptied, and the contents of the oral cavity are removed. If spontaneous breathing is maintained, oxygen inhalation is performed. Otherwise, artificial ventilation is required. At the same time, the vein is catheterized and therapy with magnesium sulfate is started. After eliminating the seizures, the water-electrolyte balance, metabolism, and blood acidity are normalized with infusion therapy.
Artificial termination of pregnancy is started urgently, regardless of what week the pregnancy is (if possible through the natural reproductive tract, if not - cesarean section).
It is very important to adequately provide medical care to pregnant women with preeclampsia. The help of a psychologist is also important, since stress disorders arise after such complications.
What is gestosis during pregnancy? Classification of gestosis
In modern medicine, it is customary to divide gestosis into “pure” and “combined”.
“Pure” gestosis develops in those pregnant women who do not have any extragenital diseases. Such disorders account for only about 20 - 30% of all gestosis. But such a pathology is always very strange for a healthy female body. This suggests that the pregnant woman actually had chronic diseases, they just proceeded secretly, and she did not know about them (pyelonephritis, vegetative-vascular dystonia, liver disease, cardiovascular disorders).
“Combined” gestosis occurs due to a previously established disease. They often appear in pregnant women who suffer from hypertension, renal failure, various heart defects, adrenal gland diseases, thyrotoxicosis, diabetes mellitus, and bronchial asthma. All these diseases always complicate pregnancy. Therefore, if the expectant mother knows about the presence of the pathologies described above, she needs to very carefully monitor her health and strictly observe appearances at the antenatal clinic.
Preeclampsia is also divided into stages. If measures to stop the initial symptoms are not taken in time, the pathology may progress.
Dropsy of pregnancy
Dropsy in pregnant women is the very first sign of the development of gestosis. With this anomaly, minor swelling develops on the woman’s body (mainly on the legs - feet and lower legs). The reason for this is not a violation of the kidneys, but a change in the water-salt balance in the body due to a violation of mineral metabolism.
This, as a rule, occurs due to the fact that the hormonal system is reconstructed during pregnancy, and active production of aldosterone and antidiuretic hormone begins, which retains excess water in the body. Dropsy is indicated by uneven or excessive weight gain (gain of more than 300 g per week).
Also, with this pathology, swelling is possible on the anterior wall of the abdomen, upper limbs and face. Typically, the accumulation of fluid becomes noticeable towards the end of the day, and in the morning it is not visualized. This happens because during the night, in a horizontal position of the body, excess fluid is evenly distributed in the tissues of the body.
The woman's general condition remains satisfactory. The only thing she may notice is difficulty putting on shoes, as the foot and lower leg increase in volume. Only in 10% of women does this form, without treatment, progress to the next, more dangerous one.
Nephropathy
This syndrome is a disorder of the kidneys. At this stage, there is an increase in edema, protein excretion in the urine and an increase in blood pressure. The development of hypertension is the most dangerous complication, as it contributes to the deterioration of blood supply to the fetus and the risk of cardiovascular critical conditions in the expectant mother.
Pressure not exceeding 135/85 mmHg is considered normal. If it rises above these numbers, then gestational hypertension develops. It is very important to monitor not only the pressure itself in general, but to pay attention specifically to the systolic (first digits) and diastolic (second digits) indicators. Often with nephropathy, the systolic value remains normal, but the diastolic value increases.
There is such an indicator as pulse pressure. This is the difference between systolic and diastolic. For example, your blood pressure is 115/80 mm. Hg Art. We count: 115 – 80 = 35. Therefore, your pulse pressure has a coefficient of 35. Normally, it is from 40 to 50. With our result, you need to consult a doctor.
With low pulse pressure and high diastolic pressure, very poor blood supply to the fetus occurs, which threatens the development of hypoxia, asphyxia and even the death of the unborn baby.
Preeclampsia
This condition is considered a fairly severe manifestation of gestosis. Peripheral edema increases, the feeling of nausea becomes unbearable. Vomiting occurs very often. Also, a pregnant woman is tormented by such symptoms as headache, “spots” or “veils” before the eyes. All this is a consequence of damage to the central nervous system, namely the occipital region of the brain.
Daily diuresis (urine output) decreases to 400 ml and below - this is about one and a half glasses, despite the fact that the patient drinks a lot of liquid. Tachycardia intensifies, blood pressure drops to critical levels. A woman often cannot adequately assess the situation happening around her and practically goes into stupor.
This condition is considered serious and requires emergency medical care, as it is quickly complicated by the next stage - eclampsia. The condition of the fetus depends on the degree of damage to vital structures in the mother’s body, as well as the presence of extragenital diseases and the current state of the placenta.
Laboratory tests for preeclampsia are carried out already when the patient is hospitalized in the hospital. There is a large amount of protein in the urine; blood enzymes indicate serious disorders of hemostasis and metabolism. Blood pressure goes through the roof (systolic rises above 160 mmHg).
The purpose of emergency therapy is to prevent the development of the next final stage - eclampsia, and to prolong (support) the development of pregnancy if it is premature (up to 37 weeks).
Eclampsia
This is the last and most dangerous anomaly in the development of gestosis. At this stage of the pathological process, the woman and fetus are at risk of death. Manifestations of eclampsia, as a rule, begin with convulsions, the strength of which gradually increases. The harbinger of this terrible period is headache and blurred vision.
All this happens because the woman’s blood pressure rises sharply to critical levels, swelling increases, which already spreads to the brain area. As a result, a violation of the integrity of the capillaries and hemorrhage into the brain space is possible.
Prevention of toxicosis
For women who are at risk of preeclampsia, it is very important to plan their pregnancy so that its development occurs in the summer-autumn period. You need to be examined by a doctor once every 2 weeks in the first half of pregnancy and once a week in the second. There should be a calm environment at home and at work; it is important to adhere to the principles of a balanced diet, since during pregnancy the need for vitamins and microelements increases.
An increase in blood pressure by 30-40% of the initial level and body weight, especially after 30 weeks, by more than 400 grams is a risk factor that requires special attention. If at least one symptom of preeclampsia appears, the woman must be urgently hospitalized in the obstetric department.
Attention!
This article is posted for informational purposes only and under no circumstances constitutes scientific material or medical advice and should not serve as a substitute for an in-person consultation with a professional physician.
For diagnostics, diagnosis and treatment, contact qualified doctors! Number of reads: Date of publication: 11/02/2017
Diagnostic measures
With timely registration of a pregnant woman and constant visits to an obstetrician-gynecologist, it is quite difficult not to notice the disease. Patients are advised to regularly undergo clinical
urine
and blood tests. When visiting a gynecologist, an examination is carried out, which makes it possible to timely determine the pathological process.
If there is a suspicion of late gestosis during pregnancy, then it is necessary to regularly weigh the patient. Female representatives are recommended to undergo a urine test, according to which an increase in the amount of protein in the blood is determined. If a pathological process is suspected, it is necessary to examine the fundus of the eye
. It is also recommended to regularly measure blood pressure.
In case of late gestosis, it is recommended to evaluate how much fluid a woman consumes and how much urine is released when emptying the bladder.
A general blood test is necessary. Diagnosis of the pathological condition involves conducting a blood clotting test.
After diagnosis, it is recommended to constantly monitor the condition of the fetus. In this case, ultrasound examination and Doppler sonography are performed.
In late pregnancy, CTG should be performed. The woman is recommended to constantly visit specialists such as a nephrologist, ophthalmologist, and neurologist.
Preeclampsia: what happens in the body?
The basis for the occurrence of gestosis during pregnancy is vascular spasm. As a result, pressure increases, the total volume of blood circulating in the blood vessels decreases, and the nutrition of organs and cells is disrupted. This leads to them not being able to do their job well.
First of all, brain cells, as well as kidneys and liver, suffer from insufficient blood supply. This situation also turns into a disaster for the placenta. It cannot function normally, which threatens the fetus with hypoxia and, accordingly, developmental delay.
Useful video about gestosis
We recommend reading: Are headaches dangerous during pregnancy and how to deal with them?
Gestosis during pregnancy: how to recognize and what to do? — revealing secrets about pregnancy on Pitanie4Zdravie.ru
Pregnancy makes a woman truly beautiful. But during pregnancy, many questions arise that need to be answered. Especially for you, in the “Pregnancy from A to Z” section, we publish interesting and useful articles about pregnancy, so that this wonderful time for you will be as “problem-free” and joyful as possible.
You can also find here the main signs of pregnancy, how the baby’s fetus develops at different stages of pregnancy, understand what is possible and what is not possible at different stages of pregnancy. Learn more about the effect of various foods, vitamins (for example, the effect of folic acid) on pregnancy.
Childbirth
Despite the completed course of therapy, delivery with gestosis always remains an unpredictable and complex process. If treatment is effective, pregnancy is continued until childbirth or until a viable, healthy fetus can be born. Indications for early delivery with gestosis:
- eclampsia;
- preeclampsia;
- moderate gestosis in the absence of effectiveness of treatment within a week;
- rapid deterioration of condition;
- progression of placental insufficiency.
For natural childbirth with gestosis, a number of conditions must be met:
- cephalic presentation of the baby;
- the proportionality of his head and the mother’s pelvis;
- the age of the pregnant woman is up to 30 years;
- cervical maturity.
However, you need to understand that with gestosis, both the mother and the fetus have reduced resistance to stress. At any moment, a woman can suffer greatly from sharply increased blood pressure. Therefore, in such cases, a caesarean section is often performed. Indications for it:
- eclampsia;
- complications of gestosis: retinal detachment, coma, renal failure, retinal detachment, premature placental abruption, cerebral hemorrhage, acute fatty hepatosis, HELLP syndrome (with nephropathy, simultaneous liver damage and hemolytic anemia);
- preeclampsia;
- severe form of gestosis due to pathologies of the cervix;
- three-week persistent gestosis.
In 80% of cases, childbirth with gestosis is complex and requires a lot of experience and professionalism from a team of doctors. They often end in a caesarean section if the situation gets out of control and the life and health of the mother or child are at risk. Young parents must be prepared for this, and no matter how much they would like the baby to be born naturally, doctors know better what is needed for a successful delivery. So it’s better for them to find out in advance why gestosis is dangerous both during pregnancy and after it, in order to be fully prepared.
For your information. Among the causes of modern maternal mortality, gestosis during pregnancy has consistently taken second place in recent years (bleeding is in first place).
Features of childbirth in women with preeclampsia
During the second stage of labor (pushing), an episiotomy is often performed to shorten the duration of this stage.
In the third stage of labor (the period of separation of the placenta), oxytocin is administered to the postpartum woman to prevent bleeding to reduce the risk of massive bleeding. To prevent convulsions during childbirth, epidural anesthesia is indicated for the woman in labor.
Treatment
The treatment plan for gestosis in the second half of pregnancy consists of the following points:
- Organizing the correct regimen for a pregnant woman. Taking into account the severity of the pathological process, the expectant mother is prescribed semi-bed rest or bed rest. For the entire period of bearing a child, a woman should be protected from excessive emotional stress and stress.
- Diet selection. A pregnant woman should eat fortified, varied and light foods. The restriction includes carbohydrate and fatty foods. It is recommended to consume fresh fruits, compotes, juices and fruit drinks daily. You should not limit yourself in fluid intake, even taking into account the development of edema.
- Drug therapy. Drug treatment in this case is aimed at correcting the functioning of internal organs and systems. With the help of drugs, oxygen starvation in the fetus is prevented. A pregnant woman is prescribed vitamin therapy (B vitamins, vitamin E and), medications that simulate uteroplacental circulation, as well as antihypertensive drugs.
- Early birth. This method is used according to strict indications.
At-risk groups
Based on all these theories about the causes of gestosis during pregnancy, doctors identify a risk group that includes women:
- very young (under 18 years old);
- with multiple pregnancy;
- with heredity of gestosis;
- primigravida after 30 years;
- those suffering from systemic lupus erythematosus and other autoimmune diseases;
- those suffering from obesity, diabetes, thyroid pathologies;
- with chronic infections;
- with diseases of the kidneys, liver, gastrointestinal tract;
- with previously recorded arterial hypertension.
In these pregnant women, the risk of developing gestosis is very high, so you need to be constantly on alert and recognize the disease in time by its characteristic symptoms already in the initial stages.
Late form therapy
Preeclampsia itself in the later stages occurs quite rarely, according to statistics, about 8% of all pregnancies.
During the treatment of late gestosis, strict bed rest, prolonged sleep, and the absence of irritants and worries are prescribed. Treatment with sedatives is recommended: motherwort, valerian, sedatives. In addition, it is necessary to follow the correct diet: food should be easily digestible, rich in vitamins, balanced with proteins and carbohydrates. Eating fruits, vegetables, a sufficient amount of fruit drinks and juices. Sometimes it is recommended to eat food directly in bed and chilled.
Contrary to many advice on the Internet, you should not neglect drinking water during severe swelling, since, on the contrary, you need to replenish the volume of the bloodstream.
Drug treatment of preeclampsia
To treat gestosis, drugs of various groups are used - blood pressure reducers, drugs for the treatment of seizures, diuretics, infusion therapy.
It should be remembered that only a gynecologist can select the drug and its dosage. With an excessive decrease in blood pressure in a pregnant woman, blood circulation in the placenta may be impaired, and this can cause deterioration in the condition of the fetus, hypoxia, or even its death.
To prevent and relieve seizures, a woman may be prescribed magnesium sulfate (magnesium). After birth, magnesium administration should continue for 24 hours. Infusion therapy uses intravenous administration of a special saline solution in moderate volumes (about one liter per day). Diuretics are used only for incipient pulmonary edema.
Nephropathy in pregnancy
Nephropathy (kidney damage due to gestosis) is manifested by the presence of three main symptoms - edema, the appearance of protein in the urine, and increased blood pressure. Only two of the three symptoms may occur in different combinations. Typically, nephropathy occurs as a progressive condition with dropsy, the pressure rises above 135/85 against the background of severe edema and changes in urine, and a disturbance in the general condition.
Why is high blood pressure dangerous in a pregnant woman?
High blood pressure is the most obvious and most dangerous sign of gestosis. In this case, the blood pressure numbers themselves will be especially important - an increase in the upper pressure by 30 mmHg or more from normal, and an increase in the lower pressure by 15 mmHg or more. When taking pressure into account, an increase in lower pressure is more dangerous than in the upper one, since lower pressure has a stronger effect on the baby - it reduces blood flow in the placenta and reduces the supply of oxygen to the fetus.
The development of nephropathy can be dangerous for the health of expectant mothers because this condition, without proper treatment, can develop into a state of preeclampsia and eclampsia (severe convulsions with disruption of the functioning of all organs and systems). In addition, the development of nephropathy in pregnant women can disrupt the functioning of vital organs - the liver, heart, brain, since they are all closely interconnected. Among other things, nephropathy can create the preconditions for such serious complications of pregnancy as premature placental abruption (normally located), the development of bleeding, fetal hypoxia and premature birth, and fetal death as a result of acute hypoxia. All these complications arise as a result of sharp fluctuations in blood pressure.
Why is protein in the urine of a pregnant woman dangerous?
The appearance of protein in the urine, which is called proteinuria, is one of the typical signs of gestosis. Moreover, if the amount of protein in the urine gradually increases, this indicates a deterioration in the woman’s condition and requires immediate medical intervention. Simultaneously with the appearance of protein in the urine and an increase in pressure, the volume of urine excreted per day decreases; its amount can decrease to 500 ml or less. The less urine a pregnant woman excretes, the worse the course of the disease and the prognosis for pregnancy will be. Particularly dangerous is long-term nephropathy, which can lead to dangerous complications for the mother and fetus.
Classification
Different countries have their own classification of gestosis, but almost all of them are based on the level of increased blood pressure.
International classification
In 1995, the International Classification of Diseases (the so-called ICD-10) was adopted, according to which gestosis in pregnant women is classified as follows:
- Hypertension (persistent high blood pressure), which previously existed in a woman, complicating pregnancy, delivery, and the postpartum period.
- Pre-existing hypertension, which was accompanied by proteinuria (protein content in the urine).
- Edema and proteinuria during pregnancy, but without hypertension.
- Hypertension during pregnancy, but with slight proteinuria.
- Pregnancy-induced hypertension with significant proteinuria is called moderate preeclampsia.
- The last stage, eclampsia, is severe gestosis with prohibitive levels of high blood pressure both during pregnancy, during childbirth and after them.
Russian classification
According to the Russian classification, there are 4 forms of gestosis, which, under the influence of certain factors, can flow into each other. They are considered as stages of one pathological process.
- Dropsy is an accumulation of fluid in body cavities (edema).
- Nephropathy is a kidney pathology (mild, moderate, severe).
- Preeclampsia.
- Eclampsia.
When diagnosing, according to this classification, two more forms of gestosis are determined:
- clean - a condition that developed when the mother was in full health;
- combined - develops against the background of previously existing diseases in a woman.
Classification of gestosis according to the American Society of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG)
I. Pregnancy-induced hypertension.
- Preeclampsia. Happens:
Easy. This is mild gestosis during pregnancy, which is diagnosed in the absence of signs of the next stage.
Heavy. Symptoms:
- systolic blood pressure over 160 mm Hg. or diastolic blood pressure starts from 110 mm Hg, and these indicators must be recorded twice, with an interval exceeding 6 hours;
- the protein content in the urine is more than 5 g during the day;
- visual disturbances, neurological problems (migraines, confusion or loss of consciousness, vision problems);
- oliguria - a pathology in which the amount of urine does not exceed 400 ml per day;
- pulmonary edema, cyanosis (blue discoloration of the skin).
- Eclampsia is an extreme degree of development of gestosis, threatening the life of the mother and child.
II. Chronic hypertension, not related to pregnancy.
III. Layering of preeclampsia or eclampsia on chronic hypertension (combination of their symptoms).
IV. Transient hypertension is a moderate increase in blood pressure during pregnancy that occurs periodically with normal blood pressure in between.
V. Unclassified hypertension disorders due to unknown etiology, which may manifest themselves in different ways.
NHBPEP classification
In 2000, another classification of gestosis during pregnancy was created. A group from the national educational program on blood pressure worked here.
I. Gestational hypertension.
II. Preeclampsia.
Minimal danger symptoms:
- Blood pressure exceeds 140/90 mm Hg. Art. in the period after 20 weeks;
- proteinuria is over 300 mg per day.
Dangerous symptoms:
- Blood pressure exceeds 160/110 mm Hg. Art.;
- according to tests, serum creatinine is more than 1.2 mg/dl;
- platelet count - more than 100,000/mm3;
- proteinuria - 2.0 g per day;
- according to blood tests, microangiopathic hemolysis (an increase in LDH is diagnosed - lactate dehydrogenase, a special enzyme without which the production of lactic acid and glucose oxidation is impossible), an increase in the enzymes ALT or AST;
- stable headache, brain and visual disturbances;
- prolonged pain in the epigastric region (under the ribs).
III. Eclampsia.
IV. Preeclampsia developed against the background of chronic hypertension.
V. Previously diagnosed chronic hypertension.
Depending on what kind of gestosis in pregnant women was diagnosed by a doctor according to one classification or another, the woman is prescribed a certain course of treatment. At the same time, they try, if possible, to identify the cause of the development of this condition, although this is precisely the main problem.
Origin of name. The term “gestosis” goes back to the Latin word “gestatio”, which means carrying, bearing (i.e. pregnancy).
Causes and risk factors
It is generally accepted that the development of gestosis is caused by the combined effects of various factors: placental, genetic, immunological, hormonal and neurogenic.
The pathology is based on spasm of blood vessels, leading to impaired blood supply to organs and tissues, their hypoxia and ischemia. In addition, the consequences of vascular spasm are:
- decrease in circulating blood volume;
- increased blood pressure;
- increased permeability of the vascular wall;
- leakage of fluid from the vessels into the surrounding tissues with the development of edema;
- increased blood viscosity;
- tendency to form blood clots.
In pregnant women, the brain, liver, placenta, and kidneys are most sensitive to hypoxia. Therefore, it is in these organs that functional and structural disorders occur.
Preeclampsia is based on spasm of blood vessels
Changes in the kidneys are expressed with varying intensity - from minor proteinuria to the formation of acute renal failure. Impaired blood flow in the vessels of the placenta causes intrauterine growth retardation and fetal hypoxia. Focal hemorrhages and necrosis occur in the liver tissues. Impaired blood supply to the brain leads to dystrophic changes in nerve cells, the formation of blood clots in blood vessels, increased intracranial pressure, and the occurrence of small focal or pinpoint hemorrhages.
Factors predisposing to the development of gestosis are:
- chronic somatic diseases of a pregnant woman;
- hereditary predisposition;
- multiple pregnancy;
- Rhesus conflict;
- the age of the pregnant woman is under 18 or over 35 years;
- large fruit.
Consequences
If a woman knows how dangerous gestosis is during pregnancy, she will certainly devote all her efforts to preventing and fighting this disease so that undesirable consequences do not affect either herself or the baby. The most common and irreversible complications include the following pathologies.
For mother
- Disturbances in the functioning of many systems and organs: kidneys, liver, central nervous system, lungs, vision;
- cerebral hemorrhage, vascular thrombosis, cerebral edema;
- coma;
- pulmonary edema;
- heart, kidney or liver failure;
- dehydration of the body;
- acute yellow liver dystrophy is fatal;
- bleeding.
For a child
The main complications of late gestosis for the fetus during pregnancy can be the following:
- premature birth;
- hypoxia and intrauterine death;
- developmental delay.
Later consequences of gestosis for a child already born can be no less dangerous:
- little weight;
- prematurity;
- delayed physical and mental development;
- weak immunity.
Despite the fact that gestosis during pregnancy is being diagnosed more and more often, and its consequences are very dangerous for the life and health of the mother and child, modern medicine makes it possible to avoid complications. In this case, the prevention of the disease at the initial stages, the completed course of treatment, timely diagnosis, and the correct measures taken during delivery are important. If you have been diagnosed with this at some stage, there is no need to panic. Complete submission to doctors and compliance with their recommendations is a guarantee of the safe birth of a new life without pathologies and undesirable consequences.
Diagnostics
An accurate diagnosis of late toxicosis can be established only after extensive use of laboratory and instrumental tests.
Pressure measurements are taken three times every five minutes after changing body position. A positive result means the pressure increases by more than 20 units after each measurement.
Pressure measurements in triplicate quantities.
In each control blood test for coagulation, a decrease in the number of platelets and anticoagulants is noted. The level of lymphocytes steadily decreases, which indicates a serious lack of protective properties of the body or lymphopenia.
An important criterion for gestosis is protein readings; proteinuria toxicosis is confirmed if it is increased to 0.3 grams/l. Edema is taken into account when it persists during night sleep and it rises to the upper part of the body.
If difficulty arises during diagnosis, other informative methods are used:
- daily blood pressure monitoring, electrocardiogram;
- Doppler study;
- assessment of the condition of the fundus;
- all types of urine tests to confirm nephropathy (according to Nechiporenko, bacterial culture, according to Zimnitsky);
- ultrasonography;
- analysis for the production of antibodies to human chorionic gonadotropin.
Preeclampsia in women with hypertension
In pregnant women with arterial hypertension, the diagnosis of gestosis causes some difficulties. The diagnosis is made in the following cases:
- against the background of high blood pressure, protein is detected in a general urine test;
- previously controlled hypertension becomes uncontrolled, blood pressure becomes higher than usual for this woman;
- the appearance of signs of cardiovascular or renal failure, that is, the appearance of edema, severe shortness of breath.
It is worth noting that in women with hypertension the risk of developing complicated preeclampsia is very high.
How is gestosis treated?
Preeclampsia is treated exclusively in a hospital, since this condition is progressive and threatens health and even life. The basis of treatment is the creation of a gentle regime for the woman, restoration of the functioning of all vital organs and the most delicate delivery possible. Only mild edema can be treated in a antenatal clinic under the supervision of an obstetrician-gynecologist.
Treatment requires adherence to a diet with fluid restriction to 1000 ml per day, strict control of salt intake, enriched with proteins and vitamins. Complete rest and taking sedatives, infusion therapy with blood plasma preparations, rheopolyglucin, and saline solution with drugs are required. The volume of incoming fluid is calculated by the doctor. It is necessary to carry out therapy to lower blood pressure with magnesium preparations, dibazole and other drugs, based on the level of pressure and indications. Diuretics, drugs to improve blood circulation, placental blood flow, vitamins, etc. may be prescribed.
The duration of treatment depends on the degree of gestosis and its severity, as well as the condition of the fetus and the mother’s body. Nephropathy is treated in a hospital for at least two weeks, in severe cases up to a month, constantly assessing the condition of the fetus. This may be followed by follow-up treatment in a antenatal clinic, and sometimes women remain in the hospital until the birth. If there is no effect of treatment or there is a threat of preeclampsia, the issue of early caesarean section is decided.