Heat stroke is a condition caused by exposure to high temperatures, which negatively affects the functioning of individual organs and systems of the body. It can occur in people of different ages. However, children, elderly and obese people are more susceptible to it.
Heat stroke - definition
Under optimal conditions, reactions occur in the human body that maintain a constant body temperature. Fluctuations of 0.5-1°C up or down are considered normal.
As a result of a number of reactions in the human body, heat is generated. Its transfer to the external environment through the surface of the body is called physical heat transfer. Heat can be released through the production of sweat, urine, feces and fluid that evaporates during respiratory processes. If more heat is produced than is released into the external environment, body temperature rises.
Which part of the brain is involved in controlling the occurrence of such mechanisms? There are so-called heat and cold receptors. They are sensitive to external temperature changes. Excitation from the receptors travels along pathways to the hypothalamus (a region of the brain). This is where the center responsible for thermoregulation is located. Specific reactions occurring in this center change the ratio of heat transfer and heat generation activities.
Heat stroke develops when thermoregulation mechanisms fail. At first, compensatory mechanisms are activated, but with prolonged exposure to pathological external factors (high ambient temperature), they are depleted. Hyperthermia develops, and the numbers can cross the line at 41-42°C.
Important! Heatstroke is quite severe. Lethal outcome is typical for every third case.
Precautionary measures
If you have recently been exposed to heatstroke, your sensitivity to high temperatures will increase over the next week. Therefore, please pay attention to these precautions and follow them carefully.
Drink more water
The optimal amount of fluid per hour is 2-4 cups of water; sometimes you can drink natural fruit or vegetable juices. This amount is calculated for spending time in the heat, under the sun's rays or while doing physical labor. To sweat effectively, your body needs more moisture than usual. There should be no shortage of it.
Stay indoors during the hottest hours
In summer, the most dangerous time is between 11:00 and 15:00. During these hours, try to avoid physical activity in direct sunlight.
Wear light, light-colored clothing
Clothing should be loose and made of lightweight natural fabric to allow air to circulate around the body.
Wear a hat
A hat or Panama hat will help prevent sunstroke. But a bandana or cap is not the best option for hot days, since the headdress should be light and have a wide brim.
Take cool baths or showers often
This is necessary in order to reduce body temperature.
Don't drink caffeinated drinks or alcohol
This type of drink promotes dehydration and spasms blood vessels. As a result, the body produces less sweat than is needed to cool well.
Causes
Heat stroke occurs when the body is unable to regulate the physical processes of heat exchange. The causes of the pathology may be:
- impaired sweating due to chronic systemic diseases;
- high ambient temperature (for example, working in a hot shop);
- excessive physical activity in high temperatures;
- combination of one of the reasons with the use of alcoholic beverages and drugs;
- high air humidity;
- wearing warm clothes in hot conditions;
- insufficient fluid intake (dehydration);
- diseases of the central nervous system and heart;
- treatment with certain medications;
- a combination of a person’s pathological weight with high temperature outdoors or indoors.
Diagnostics
It is easy to recognize hyperthermia if all the symptoms are present after intense physical activity or heat exposure. The human condition can be confused with an acute infectious disease of the brain and nervous system, but if the factors are present, heat stroke is suspected.
Heat injury causes body temperature to rise.
Methods for diagnosing heat injury include temperature monitoring outside the healthcare setting. If the patient is taken to the hospital on time, he is subjected to a series of laboratory tests - the level of urea, electrolytes and the prothrombin index are determined. Renal-liver tests may be required to assess organ health.
Symptoms
Heat stroke is a condition that is accompanied by an imbalance of water and electrolytes, as well as a change in the course of vital processes. A severe degree is manifested by the development of general intoxication, a change in blood pH to the acidic side, failure of the heart and blood vessels, and the renal apparatus. Some clinical cases may be accompanied by stroke and pulmonary edema.
Symptoms of heat stroke develop depending on the clinical form of the pathological condition. In addition, the symptoms depend on the length of time the victim spent in high temperature conditions, the intensity of the influence of thermal factors, age, and the presence of concomitant diseases of the heart and nervous system.
The following patients are at risk for heat stroke:
- with high blood pressure;
- diseases of the endocrine apparatus;
- allergic conditions;
- liver pathologies;
- anorexia;
- obesity;
- vegetative-vascular syndrome.
Important! Children, elderly people, and women should carefully monitor their well-being when exposed to the sun or in a hot room during pregnancy.
The severity of the condition determines how heat stroke manifests itself. Initially, weakness, drowsiness, and a feeling of fatigue occur. Victims complain of headaches, dizziness, attacks of nausea and vomiting, and excessive sweating.
Later, muscle pain occurs during movement and at rest, ringing in the ears, and symptoms of dehydration. When observing the victim, you may notice the appearance of movement coordination disorders. This stage is characterized by a high temperature and a decrease in the amount of urine produced. How many days the temperature lasts during heatstroke depends on the severity of the pathology and timely provision of assistance.
The nature of breathing changes. Breathing becomes noisy and can be heard from a distance. The pulse quickens, hallucinations and seizures occur. The most severe form of heat stroke is coma.
The following clinical changes occur in the blood and urine of the victim against the background of heat stroke:
- decrease in the number of platelets in the blood;
- decrease in fibrinogen levels;
- high numbers of leukocytes in the blood;
- in the urine - the appearance of casts, leukocytes and protein.
Forms
Stages of heat injury are associated with disturbances in water metabolism and electrolyte levels, as well as changes in cell permeability. The severity depends on the retention of heat in the body. The transition from one form to another during heat stroke occurs when there is a persistent imbalance of thermoregulation in the hypothalamus.
- Overheating and hyperthermia are in the compensated stage for a short period of time. In this case, the body begins to cool itself independently.
- Increased actions on the part of the brain and tissues lead to depletion of resources, and the thermoregulation mechanism fails. The body temperature tends to reach the ambient temperature.
- Decompensation, exhaustion and disruption of the adaptation mechanism occur.
- Severe forms of thermal injury are accompanied by the release of large amounts of toxins into the blood, the acidity of the body increases, and the myocardium undergoes a number of degenerative changes.
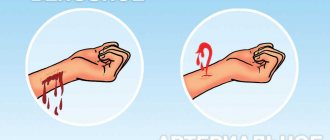
If first aid measures for heatstroke are not performed in time, the risk of pulmonary edema and rupture of blood vessels in the brain increases.
Consequences of heat stroke
First aid for heatstroke should be provided within the first hours after the pathology is diagnosed. In this case, within a few days the patient’s well-being will improve and the symptoms will disappear. Another option may be the appearance of complications of heat (or sunstroke):
- Blood thickening – lack of fluid in the body causes the patient’s blood to become excessively thick. This is fraught with thrombosis, heart attacks, and heart failure.
- Renal failure is a severe pathology that develops as a result of heat stroke. Damage is also provoked by metabolic products that appear under the influence of significant numbers on the thermometer.
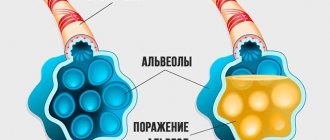
- Acute respiratory failure - appears as a result of changes in the functioning of the respiratory center located in the brain.
- Damage to the central nervous system - manifested by uncontrollable vomiting, loss of consciousness, disorders of speech, hearing and visual functions.
- Shock is a dangerous complication that occurs due to lack of fluid, imbalance of electrolytes and blood supply to internal organs.
Important! First aid for heat stroke is mandatory measures that will allow the patient to quickly recover and prevent the occurrence of the above complications.
Classification of degrees of overheating and thermal shock
The following forms of heat stroke can be distinguished:
- Asphyxial type. In this case, first of all, alarming symptoms from the respiratory system are observed, for example, rapid breathing. In addition, body temperature can rise to 39 degrees.
- Hyperthermic appearance. Signs of sun heatstroke: increased body temperature up to 40 degrees, cramps, dehydration, decreased blood pressure.
- Cerebral form. In this case, disturbances in the central nervous system are observed. Body overheating can reach 40 degrees.
- Gastroenteric type. Manifested by disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, for example, nausea and vomiting. Body temperature rises to 39 degrees.
First aid for heatstroke
First aid for heatstroke (or sunstroke) has the following goal: reducing the victim’s body temperature and restoring the main vital functions of the body. At the first symptoms of pathology, you need to call a medical team, and at this time carry out a number of measures before their arrival.
Eliminate the cause
Emergency care begins with the patient being transferred to the shade if he was under the scorching sun, or to a cool room. If the patient received a heatstroke, for example, in a hot workshop, he must be taken out of the workroom to one where there are coolers or air conditioners.
Peace
The victim should be placed on a couch or bed with the leg end elevated. This improves blood supply to the brain.
Remove clothing
A person needs to be stripped down to his underwear, because any clothing he wears slows down the body’s cooling mechanisms.
Shower and compresses
Cool water procedures are one of the stages of emergency care. If the patient is able to get into the shower, it is necessary to cool the skin with water. This procedure takes 3-5 minutes, but the water temperature should not be less than 19-20°C.
Lack of consciousness and an excessively serious condition will not allow manipulation. For such victims, you can apply a cold compress to the forehead or periodically splash cold water on the face.
Fighting dehydration
The presence of consciousness in the patient is an indication for drinking a large amount of cool liquid, but not more than half a glass at a time (so as not to provoke an attack of vomiting). You can add a little salt to the glass. This will help maintain the balance of electrolytes in the blood.
Fresh air
Difficulty breathing is a sign of the asphyxial form of heatstroke. To ensure access to fresh air, you need to take the victim outside (condition: temperature below 28°C, no direct sunlight) or into a cool room, pointing a fan at the person.
Ammonia
Ammonia vapor has a stimulating effect on the central nervous system, therefore it is effectively used in cases of loss of consciousness.
Resuscitation measures
Respiratory or cardiac arrest is an indication for immediate resuscitation of the victim. It is necessary to start without delay, without waiting for the ambulance team to arrive.
Providing first aid (FAM) for heatstroke prohibits:
- using excessively cold water to cool the body;
- applying cold compresses to the chest and back;
- drinking alcoholic beverages.
Important! In addition to providing assistance, drug treatment of pathology in a hospital is necessary.
How to deal with heat exhaustion
When it comes to only the initial symptoms of overheating, first aid will consist of the following actions:
- Stop physical activity.
- Get out of the sun or move from a stuffy room into the shade, into a draft, or into a room where the air conditioner is running.
- If possible, remove all your clothing.
- Place a towel soaked in cool water on your forehead.
- Drink 1-2 glasses of water, but no less. This way you will eliminate possible dehydration and give your body the necessary amount of moisture to produce the optimal amount of sweat.
- If possible, you can take rehydron or drink an isotonic sports drink, since such a liquid includes electrolytes necessary for metabolism and good functioning of the nervous system. After all, electrolytes can be lost during active sweating.
Heat stroke treatment
Measures to provide medical assistance to the victim are the prerogative of qualified specialists. Prevention of dehydration is based on fluid therapy. The following is administered intravenously:
- saline sodium chloride solution;
- Ringer;
- glucose solution.
The solutions are cooled slightly before infusion, but not below 26°C. To support the functioning of the heart and blood vessels, cardiac glycosides, cardiotonic drugs, solutions that restore blood volume, and other medications are prescribed. The most used are Adrenaline hydrochloride, Mezaton, Refortan.
Measures to prevent cerebral edema include the use of sodium thiopental. This medication not only reduces the need for oxygen in brain cells, but also stops seizures.
Antipyretic drugs from the NPS group will not be effective. The active substances of medications inhibit the production of mediators of the inflammatory response, and in pathologies resulting from exposure to sunlight, the disorders have a different mechanism of occurrence.
Important! Only the doctor selects the treatment regimen. Self-administration of drugs is not allowed.
When does the victim need hospital treatment?
Sometimes full recovery is impossible without hospitalization. This primarily applies to cases when we are dealing with severe forms, as well as when the victim is a person from a high-risk group:
•children;
•pregnant woman;
•elderly person;
•a person with cardiovascular diseases.
In this case, you need to go to the hospital as soon as possible. There, if the need arises, the victim is transferred to the intensive care unit.
Features of the treatment of heat stroke in a child
Every parent should know what to do if a child has a heatstroke. First of all, it is necessary to differentiate the pathological condition in the baby. Heat stroke can occur in an infant even at temperatures acceptable for adults. For example, we are talking about wrapping a child in warm clothes if the temperature does not require this.
Children 3 years old often get hit on the beach. This is facilitated by the aggressive rays of the sun, as well as the inattention of parents. It is important not to let your child go to the beach between 10 am and 4 pm. Another point worth paying attention to is lack of drinking. Children do not always say that they are thirsty, and parents forget to offer them water, juices, and fruit drinks. The result is dehydration under conditions of elevated ambient temperature.
The first manifestations are excessive excitability, moodiness, and tearfulness. Later, on the contrary, motor activity decreases, apathy, drowsiness, and even loss of consciousness occur. Parents complain of the following signs of pathology in their children:
- vomit;
- hyperthermia;
- symptoms of dehydration;
- convulsive attacks.
Important! If no measures are taken and the baby’s body continues to be in the same conditions, respiratory and cardiac arrest, the development of renal failure and cerebral edema, and the appearance of a coma are possible.
You should definitely call a team of qualified specialists. While they arrive, you need to monitor the vital signs of the body (breathing, pulse, reaction of the pupils to light). First aid is provided in the same way as for adults (see above).
Antipyretic drugs, like any other drugs, except the pharmaceutical Regidron (powder for preparing a solution), should not be given to the baby. It is important to change the temperature of the environment in which it is located before the ambulance arrives (not abruptly and not critically!), solder it with water and saline solutions.
Heatstroke and sunstroke: are they different concepts?
First of all, we must say how heatstroke differs from sunstroke. After all, their symptoms are the same, but the causes are different, the duration of treatment is somewhat different.
Heatstroke occurs due to overheating. In this case, processes begin in the body in which heat transfer decreases. This can happen not only due to an increase in temperature in nature, but also in a stuffy room, in a sauna.
A type of heatstroke is sunstroke. It occurs due to overheating in the sun. Subsequently, the blood vessels dilate, and more blood flows to the brain. Then there is pain in the head.
Prevention
It is better to prevent the development of severe pathology than to try to restore health. Preventive measures include the following:
- avoid exposure to the sun in the middle of the day;
- wear a hat, glasses, light clothing made from natural fabrics;
- reduce the level of physical activity while staying in hot conditions;
- drink a lot of water (can be cool, but not cold!);
- stop drinking alcohol;
- give preference to low-calorie foods.
Take care of yourself and be healthy!
How to avoid overheating of the body?
Heatstroke and sunstroke are easier to prevent than to eliminate its consequences.
Overheating of the human body can be minimized if:
- Limit your time in the sun.
- Go to the beach during safe hours.
- During the hot season, drink 2-3 liters of water daily.
- Refrain from consuming coffee, alcoholic and carbonated drinks containing synthetic additives.
- Eat properly. Refuse high-calorie fatty foods, giving preference to vegetables and fruits. In hot weather, the main meal should be moved to dinner.
Consequences
Most often, infants and children under one year of age react to heat stroke with vomiting and diarrhea, and an increase in temperature . If first aid is not provided, the condition may become critical:
- body temperature rises to 41 °C;
- breathing slows down or disappears completely.
In particularly difficult cases, delirium, loss of consciousness, convulsions are observed, and the person may fall into a coma. The longer the body is overheated, the higher the risk of death.
If discomfort occurs during physical activity, this can provoke the development of various complications.
People's shield
How to treat heatstroke at home when doctors have done everything necessary? Using folk remedies. Dilute 6 tsp in 3 liters of water. salt and drink it in small sips throughout the day. Raspberries will help stabilize the temperature. Pour 2 tbsp. l. berries with boiling water and leave for 15 minutes. Drink the infusion like regular tea and repeat the procedure twice with an hour interval. Linden infusion is excellent for refreshing. Brew 2 tbsp. l. dried linden flowers in 250 ml of boiling water for 20 minutes and filter. A glass of this drug a day will be enough. Mix grated cucumber with 5 mint leaves, 50 ml of lemon juice and add a liter of water. This lemonade will quench your thirst and moderate your fever. And if you feel unwell, chew a mint leaf - this technique will bring relief.
Knowing the signs of heatstroke and first aid when it occurs will help you avoid dangerous health consequences. But under no circumstances self-medicate. At the first suspicion of heatstroke, call a doctor immediately.
First aid to the victim
If someone nearby has a heatstroke, it is necessary to call an ambulance as soon as possible. But we must assume that the ambulance will arrive on average no earlier than 10, or even 30 minutes. During this time, the victim may feel worse or even faint.
- The victim is transferred from an area of elevated temperature to a cool place: a well-ventilated room or an open area with a large shady area;
- He is freed from constricting clothing and its parts: the collar or all buttons are unbuttoned, the belt is loosened, shoes are removed;
- Provide a flow of fresh air by fanning the victim using available means. It’s good if you have a fan at hand;
- The victim is offered to drink a large amount of cool water. It can also be used to spray his body parts;
- If possible, it is better to take the patient into a cool shower or cover him with a wet sheet;
- Cold compresses are placed in the following areas: forehead, elbow and knee bends, armpits, heart area:
- For sunburned skin areas, help is provided in the form of cold compresses or special medications. Most often they come in the form of foam.
This is interesting: Thermal burn: first aid
Depending on the patient’s condition, additional measures of medical first aid may be required:
- Stimulation of blood circulation. To do this, the limbs are rubbed with alcohol or vodka, and an improvised cushion is placed under the victim’s legs so that they are higher than the head;
- In case of fainting, ammonia is brought to the patient’s nose;
- In case of loss of consciousness or a poorly palpable pulse, it is necessary to provide resuscitation measures, namely closed cardiac massage and artificial respiration.
Features of hyperthermia in children
There are some features of overheating of the body in children. A febrile reaction is often observed, but the overall temperature varies.
So, if there is overheating and there is a focus of bacterial infection in the body, the body temperature does not rise above 41 degrees. The “central thermostat” is responsible for such features. The hypothalamus is a gland located in the brain. It regulates the process of heat generation and heat transfer.
Fever is a favorable situation. Hyperthermic syndrome in children is a dangerous situation. It develops at temperatures above 41.7 degrees. With nosology, the functionality of the hypothalamus is disrupted, which does not allow the body to rationally balance between the processes of heat formation and sweat production.
Fever is under complete control of the core. Only when the temperature rises above 38.5 do pediatricians recommend starting treatment for the disease. Scientists have not established a reliable connection between increased thermogenesis and infectious diseases. However, in most children with heatstroke and fever that peaks at 38-39 degrees, scientists detect an acute or chronic bacterial infection of a specific organ.
Hyperthermia above 38.4 degrees is never observed from 6 months to 6 years. Only when bacteria join does the temperature increase to 40 degrees.
There are patterns of febrile syndrome when the body overheats:
- 4% of children experience muscle cramps, so the use of Relanium and Sibazon is recommended;
- The likelihood of muscle spasms increases according to the rapid rise in the temperature curve;
- The formation of paralysis is observed in children with congenital anomalies of the osteoarticular system and a lack of calcium in the body.
Children with pathologies of the central nervous system, respiratory diseases, and high hyperthermia develop pathological symptoms associated with the low effectiveness of antipyretic drugs.
Nurofen, recommended by pediatricians, is ineffective in such a situation. The drug is safe, so it can be used for any disease accompanied by fever. However, the drug does not relieve the pathological manifestations of severe heat stroke in a child.
According to clinical studies, the effectiveness of Nurofen for febrile seizures in children increases by 20%. To eliminate convulsive syndrome, anticonvulsants (Sibazon, Relanium, Seduxen) should be used.
After treatment of febrile seizures due to overheating, the patient should be closely monitored to prevent recurrence of seizures.
Scientific experiments have established that the likelihood of pathology increases in the presence of the following signs:
- Hyperthermia in children under 3 months;
- Chronic diseases;
- Hypoxia during childbirth;
- Rigidity of the neck muscles in a child;
- Difficulty breathing due to neurological disorders;
- Perinatal antibiotic therapy;
- Reduced number of leukocytes;
- Meningitis.
In the first years of life, fever above 38 degrees Celsius may occur. Against the background of pathology, the manifestation of clinical symptoms of internal diseases may be observed. Exacerbation of sinusitis, otitis, tonsillitis, colitis can be observed in children under 2 years of age, which is associated with instability of the regulatory system.
Emergency help
What to do if you have heatstroke? If you experience the symptoms described at home or at work, call an ambulance immediately. If the shock hits you on the street, immediately go into the nearest air-conditioned room. Before doctors arrive, a number of important measures should be taken. Remove tight clothing and shoes. Cover yourself with a wet sheet and turn on the fan. But it's best to take a cool shower. To reduce the temperature, apply an ice pack to your forehead or the back of your head. Drink a glass of salted water or iced tea in small sips. When someone close to you needs help, act in the same way. It is recommended to place the patient on a cool floor and raise his legs above his head. If the victim is delirious, apply cotton wool with ammonia to his nose.
Symptoms in adults and children
Observed:
On this topic ▼
Providing first aid for fainting
- skin redness;
- darkening of the eyes;
- dizziness, general weakness;
- rapid breathing;
- the limbs become cold, their skin may acquire a pale bluish tint;
- cold sweat.
In severe cases, vomiting, convulsions and fainting occur; you can read about how to provide first aid for fainting in our article. In children, these symptoms are also accompanied by nosebleeds and high fever (up to 40 degrees). In the article “Emergency care for nosebleeds,” you can find out how to behave in this situation. In addition, a change in the baby's behavior will be a symptom of overheating. He becomes lethargic, apathetic, and tearful.
The signs of sunstroke are similar to heatstroke. Sunburn may occur. Children are much more susceptible to the negative effects of sun and heat. It only takes half an hour for them to get heatstroke or sunburn. You can learn how to provide emergency care for burns by reading our article.
Depending on which symptoms predominate, in medicine there is the following classification of thermoregulation disorders due to overheating:
On this topic ▼
How to call an ambulance or intensive care unit correctly
- Asphyxia (suffocation). Respiratory function is most severely impaired. Due to lack of oxygen, the functioning of the central nervous system slows down.
- Pyretic. Occurs at critically high temperatures. Occurs with convulsions.
- The gastroenteric condition is accompanied by various pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract (vomiting, nausea, abdominal pain).
- Cerebral is accompanied by impaired consciousness.
In case of severe damage, timely and correctly provided assistance for heat and sunstroke can save a person’s life. Be sure to call an ambulance to determine the extent of the person’s condition.
Risk factors
How to prevent heatstroke? The first step is to figure out what causes it. The main reason lies on the surface - it is prolonged overheating of the body, and not necessarily in the sun. A stuffy, enclosed space or hard physical labor also poses a threat. However, there are many other reasons: alcohol and caffeine abuse, side effects of medications, stress and nervous overload. Infants and the elderly are at particular risk. In the first months of life, the body’s thermoregulation system has not yet been adjusted; in old age, it works intermittently. Chronic illnesses seriously increase the risk of heatstroke. Especially if they concern the heart and blood vessels, the endocrine system and overweight.
What everyone needs to know
Hyperthermic syndrome occurs in places where it is hot and stuffy, for example, in offices or stores without air conditioning systems. The same place is a sauna and bathhouse.
The first signs of heat stroke are pale skin, dilated pupils and poor coordination.
Important. The mortality rate from hyperthermia is 30%.
Symptoms
Symptoms of mild to moderate heat stroke:
- tachycardia;
- hard breath;
- increase in body temperature up to 41 ° C;
- tinnitus;
- lack of urination.
People with hypertension and heart disease need to be wary of overheating.
The severe stage manifests itself:
- fainting,
- convulsions
- mental disorders.
People who suffer from cardiovascular disease and hypertension are prone to severe symptoms with hyperthermia. The heat loss can be obtained by staying in stuffy vehicles for a long time.
If you have to use public transport in the summer, be sure to have a bottle of mineral water on hand.
Alcohol increases symptoms and is a complicating factor in providing assistance. Therefore, you should avoid drinking alcohol when visiting baths and saunas.
General principles
It is necessary to help the patient within an hour, otherwise irreversible processes will occur in his body that will lead to disability.
Briefly, the procedure for providing assistance is as follows:
- cool the victim's body;
- drink plenty of water to prevent dehydration;
- call an ambulance.
After providing first aid, all that remains is to wait for the doctor to assess the person’s condition.
Even with a mild degree of overheating, a person needs emergency help. He needs to be taken to the hospital or wait for the medical team to arrive.
Going out fully armed
How to avoid heatstroke? First of all, forget about dark and synthetic tight clothing. Wear exclusively light-colored items made from lightweight, breathable, loose-fitting fabrics. This will help maintain optimal body temperature. A wide-brimmed hat or a scarf in light shades will protect your head. Don't forget to choose good sunglasses. Try to spend less time under the scorching rays from 11 to 17 hours - at this time the sun is especially aggressive. And before you go outside, apply sunscreen to your skin. If you exercise regularly, reduce your exercise at least during the peak heat. And most importantly, make sure that children do not play in the sun, especially without any protection.
Early and late signs of heat stroke in children
Against the background of accelerated biochemical reactions, dehydration of the body occurs, accompanied by excessive loss of fluid. Early signs of fluid loss:
- Thirst;
- Dry mouth;
- Sticky saliva;
- Decreased urination, appearance of yellowish discharge from the urethra.
With moderate hyperthermia, the following signs of the disease appear:
- lacrimation;
- Dry mouth;
- Thirst;
- Brown urine;
- Headaches and dizziness;
- Restless behavior;
- Irritability;
- Muscle cramps;
- Coldness of the extremities;
- Cardiopalmus.
If the above-described signs of the disease appear, the patient must be hospitalized. Correction of violations requires the use of resuscitation equipment. A highly qualified doctor is required to prevent life-threatening complications in children.
In severe stages of the disease, the following symptoms occur:
- Inability to walk;
- Attacks of anger and embarrassment;
- Drowsiness;
- Weak pulse;
- Dry and hot skin;
- Lack of urination;
- Loss of consciousness;
- Increased breathing.
To eliminate complete dehydration of the body, it is necessary to inject saline and detoxifying (eliminate the accumulation of toxins in the blood) solutions. To saturate vital organs with oxygen, an ambulance is required.
Minor dehydration can be treated at home, but if signs of severe intoxication appear, the patient must be immediately hospitalized.
Loss of fluid is especially dangerous for newborns. A rapid rise in temperature, significant loss of water is dangerous, a decrease in the concentration of minerals, vomiting and diarrhea are life-threatening.
Mineral complexes (electrolytes) are natural complexes that are necessary for the occurrence of biochemical reactions in the body. Magnesium, sodium, calcium, potassium are minerals without which normal cellular activity is necessary.
Electrolytes are involved in bone formation, the functioning of the endocrine system, and the gastrointestinal tract. Dehydration can cause the following symptoms of heat stroke:
- Muscle cramps;
- Fainting;
- Increased heart rate;
- Redness of the skin;
- Heavy sweating;
- Hot, dry skin;
- Ulceration.
To prevent the complications described above, first aid should be provided immediately after detecting at least one sign of pathology.
What to do if you have sunstroke?
Sun and heatstroke are the main dangers of summer. Their consequences can be very serious, and in some cases even fatal. That's why it's important to remember safety precautions and know how to provide first aid to an injured person.
What happens in the body when it overheats? In the heat, thermoregulation mechanisms are activated in our body: sweating increases, the blood vessels of the skin and subcutaneous tissue dilate - all this is necessary to increase heat transfer. As a result of these processes, a person’s skin turns red, breathing becomes difficult and the mucous membranes begin to dry out. If such signs appear, you need to go to a cool place, drink water, and, if possible, take a warm shower. If, after the first signs of overheating appear, a person continues to remain in the sun or in a stuffy, hot place, the body continues to rapidly lose fluid, as a result of which its circulation in peripheral tissues increases (sweating), which causes some insufficiency of blood supply to the heart and brain. Therefore, a person may become ill.
Signs of heat or sunstroke:
- Weakness
- Cold sweat
- Pale and dry skin
- Nausea
- Headache
- Rapid breathing
- Accelerated heart rate
- Muscle spasms
- Pupil dilation
- Vomit
- Sudden rise in temperature
- Fainting
- In especially severe cases: delusions and hallucinations
How to help with sunstroke?
First of all, it is necessary to move the victim to the shade or cool room.
“Lay the victim on his back, place a cushion of clothing under his head. Give the victim cold water, strong tea or coffee. Apply cold to the head, as well as to the area of large vessels (these are the lateral surfaces of the neck and armpits). A bottle of water will do, and you can wrap the victim in a wet sheet. If he loses consciousness, lay him on his side and provide him with fresh air. Until the doctors arrive, the victim needs complete rest,” says Leonid Borisenko, deputy director of the disaster medicine center.
The victim's food should contain a lot of vegetables and fruits, especially watery ones, such as cucumbers, tomatoes, watermelons. You should also limit your intake of carbohydrates (cereals, bread, potatoes). Foods high in potassium (dried apricots, prunes, black currants) and fiber (greens, fruits, beans) will be beneficial. You can drink low-fat fermented milk drinks.
What should you not do if you have sunstroke?
- Trying to give drink to an unconscious victim
- Immerse the victim in a cold bath (great stress on the heart)
How to avoid sunstroke?
- Don't stay in the sun for a long time
- Wear a head covering (hat, cap, bandana)
- Prefer clothes made from natural fabrics
- Drink plenty of fluids
- Try not to drink alcoholic beverages
- Prefer light food
- Use sunscreen
- Avoid excessive exercise
Remember:
In the hot season, staying in the sun for a long time means exposing yourself to danger. Children, pregnant women and people who have taken a lot of alcohol are more susceptible to sunstroke. Do not remain indifferent to the victims, provide assistance correctly.
Tatyana Zhilkina
Characteristics of states
Despite the fact that sunstroke and heatstroke are considered to be different critical conditions, their clinical picture is the same. Heat stroke is based on a whole complex of symptoms that arise as a result of disturbances in the thermal balance when interacting with the environment.
At high external temperatures, the body, in order to function normally, is forced to accelerate the process of heat transfer and sweating increases. If no cooling measures are taken, then such measures become insufficient and thermoregulation fails due to overheating.
A stage of depletion of vital resources occurs, and the last attempt to equalize heat exchange is to increase body temperature, and this negatively affects the functioning of internal organs and systems.
Sunstroke occurs as a result of direct exposure to direct sunlight. Overheating causes dilation of the blood vessels in the brain, blood circulation increases and as a result consciousness, speech are impaired, and vision problems arise.
When thermoregulation is disrupted, the most important organs are most affected: the brain, heart and lungs. For this reason, help for heat and sunstroke should be provided immediately, as irreversible disturbances in brain function are possible, which can lead to a stroke.