Features of colonoscopy
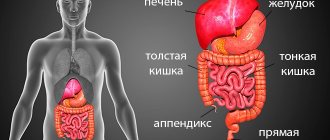
Colonoscopy is a direct visual method that allows you to directly see the inner walls of the colon, identify polyps, tumors and other lesions of this organ.
Examination of the small intestine is difficult, but possible. The procedure is carried out thanks to a camera, which is located at the end of the endoscope tube, about 1.45 m long, with a diameter of 5-7 mm. In this way, it is possible not only to diagnose polyps and neoplasms at an early stage, but also to remove them, avoiding surgical intervention. It is also possible to do a biopsy for diagnostic purposes, cauterize erosions, and administer medications. The manipulation is painful and is performed under anesthesia. The patient, who lies on his side, has an endoscope inserted through the anus. Advantages of the endoscopic method:
- It has the ability to detect the smallest formations of the colon and is distinguished by its efficiency and accuracy.
- The doctor has the opportunity to see the entire internal cavity of the intestine, assess the condition of the walls, while receiving a clear color image.
- During the examination, biopsies and treatment procedures are also possible.
Disadvantages of colonoscopy:
- long preparation of the patient before manipulation;
- the risk of injury and cracks in the intestinal walls;
- the need for anesthesia;
- for children and elderly people, use is limited, only when absolutely necessary;
- inaccessibility of examination of the upper sections;
- risk of complications.
Types of endoscopic method
Virtual (tomographic) colonoscopy is performed using a tomograph and lasts 10 minutes. The diagnosis is made based on the creation of a 3D model of the intestine. The procedure is painless, the contraindications are similar to colonoscopy, but the method is not used during pregnancy.
Capsule endoscopy is indicated for examining the small intestine using a special capsule with a video camera, which moves through the gastrointestinal tract and transmits information to a special medium. It is recommended to conduct the study on an empty stomach.
Balloon enteroscopy is performed for therapeutic and diagnostic purposes. The endoscope is inserted through the anus or mouth. It is performed under general anesthesia. Using this method, a biopsy is also performed, foreign bodies are removed, and tumors are removed.
Rectosigmoidoscopy is used to diagnose pathologies of the sigmoid colon and rectum.
Ultrasound diagnostic results
On the monitor during the examination, you can see and record the size, shape of the organ, the thickness of the tract walls, and the presence of pathological formations several millimeters in size.
How does pathology manifest itself on ultrasound diagnostics:
- There is normally no fluid in the abdominal cavity. The accumulation of fluid appears as an anechoic area. The presence of fluid indicates peritonitis, internal bleeding, inflammatory processes, and tumors. Based on the location of the liquid, one can judge the reasons for its appearance;
- intestinal obstruction manifests itself as increased visualization of intestinal loops filled with gas or liquid. The reason for this condition is the closure of the lumen by a foreign body or tumor;
- appendicitis is manifested by thickening of the appendix, accumulation of gases in the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract, and a small amount of fluid in the abdominal cavity;
- tumors and neoplasms are characterized by an increase in the thickness of the intestinal wall due to hypoechoic areas of round or irregular shape. Ultrasound shows the size of the tumor, the degree and depth of the lesion, and invasion into neighboring organs;
- adhesions are high-density strands, often combined with deformation of nearby sections of the tract.
The conclusion is drawn up by the ultrasound doctor and given to the patient. The document contains a detailed description of the state of the gastrointestinal tract and all pathological changes and neoplasms. The information allows the attending physician to make the correct diagnosis.
Ultrasound of the intestines, features
Ultrasound is based on the use of ultrasonic waves that penetrate tissue, after which they are reflected and captured by a sensor and sent for processing to a computer. Here the information is displayed and interpreted by the doctor. Previously, proctology rarely resorted to this type of diagnosis. It was not informative enough due to the presence of gas accumulations. Modern technologies make it possible to more fully use the capabilities of ultrasound. It is recommended to do the procedure on an empty stomach.
Ultrasound examination can be carried out using two methods:
- Transabdominal through the anterior abdominal wall.
- Intracavitary examination of the rectum using a rectal probe. The procedure is safe and painless.
Often these methods are combined with each other to obtain more reliable information.
Ultrasound of the rectum
It is recommended to do it on an empty stomach. A rectal probe is inserted into the rectum through the anus. The study reveals even minor pathological changes. The advantage of this method is the ability to conduct research without prior preparation or an enema. The research is carried out in stages:
- First, the empty intestine is examined.
- A catheter is then placed in the rectum, a small amount of contrast is injected, and an ultrasound is performed.
- The intestines are examined again after the fluid has been removed.
- The obtained data is compared and analyzed.
Ultrasound has a number of advantages compared to colonoscopy:
- this is a gentle method with no damage or microtrauma;
- the possibility of diagnosis in the early stages of pathology;
- intestinal motility is assessed;
- no contraindications for children;
- availability of examination of all parts of the intestine.
Is there an alternative?
There are alternative ways to examine the condition of the large intestine, which in some cases can replace colonoscopy. They do not cause significant discomfort and are quite accessible; only the degree of information content differs.
In most cases, magnetic resonance imaging is an additional examination method: with its help it is impossible to obtain complete information about the internal state of the mucosa.
In terms of comfort, MRI wins, does not require additional preparation and does not cause discomfort
They usually check with a tomograph:
- mid intestine;
- pelvic area;
- terminal parts of the colon.
CT scan
CT scans provide detailed images of the intestines using X-rays. In some ways, this is a better alternative to a colonoscopy: the final image is quite detailed and clear. According to the results, computed tomography is the most approximate research method.
During the examination, the patient simply lies on a special table, and the tomograph platform rotates around the body. The detectors of the device “catch” X-rays passing through the tissues of the body. The resulting sections are processed by a computer station, resulting in a detailed image of the organs.
Irrigoscopy
Irrigoscopy also refers to x-ray research methods that use a contrast agent. Most often, specialists use barium sulfate, which is introduced into the body through the rectum. You can evaluate the elasticity of the walls, the functions of the folds, the condition of the mucosa and the functional indicators of the organ parts.
Preparation for the procedure includes diet and bowel cleansing. During the examination, a special device similar to an enema is inserted into the colon. Using this device, the intestine is filled with contrast, after which the first overview image is taken. The patient must change position several times to obtain a series of targeted and overview images.
Anoscopy
Anoscopy is an instrumental examination method, thanks to which it is possible to evaluate a certain part of the intestinal surface - a maximum of 15 centimeters. An anoscope, a smooth hollow tube, is inserted into the intestine. The lumen is filled with a removable rod, through which the study is carried out.
Anoscopy is a good substitute and is prescribed not only for diagnosing the condition of the mucous membrane: using the device, you can take tissues or smears for analysis, administer medications, or perform minimally invasive surgical procedures, which are also performed during colonoscopy.
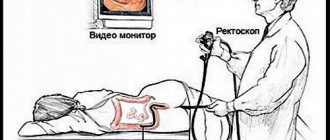
Sigmoidoscopy
Using sigmoidoscopy, a visual inspection of the surface of the lower part of the large intestine is performed. A special device is used for this - a hollow metal tube equipped with an air supply system and a lighting system.
The sigmoidoscope is inserted into the rectum in the same way as a colonoscope.
In addition to examination, sigmoidoscopy allows you to perform a number of invasive manipulations - cauterize tumors, take tissue, get rid of polyps or stop minor bleeding. The procedure has the same contraindications as colonoscopy. In addition, preparation is required, including diet and bowel cleansing.
Capsule endoscopy
Capsule endoscopy is similar to colonoscopy, but the data is obtained not through a probe, but from a special miniature capsule. It is equipped with a video camera and a transmitter that allows it to receive signals in real time. The method allows you to examine not only the distal and upper parts of the intestinal tract, but also the ileum and jejunum.
The day before the examination, the patient is advised to refuse hard-to-digest foods, only semi-liquid foods are allowed, and it is advisable to cleanse the intestines through an enema or special medications.
The study lasts from 6 to 12 hours
A device is attached to the patient that detects and records the signals transmitted by the capsule. It must be swallowed with a small amount of water. Afterwards, you can return to any usual activities: the examination can be carried out without the supervision of a specialist.
The capsule is eliminated from the body on its own; the doctor only needs to give the recording device. Within a few hours, the received data will be deciphered and a diagnosis will be made. The main disadvantage of the procedure is that it is not carried out in all clinics and in most cases is paid.
Indications for bowel studies
Ultrasound is performed to identify:
- tumors;
- intestinal obstruction;
- inflammation and space-occupying formations of the rectum;
- degree of spread of pathology;
- thickening of the walls of the small intestine;
- causes of constipation, bleeding in the stool, positive Gregersen reaction to occult blood.
Colonoscopy has the following purposes:
- Preventive examination to detect neoplasms at an early stage in people who are over 50 years old and have a hereditary predisposition to colon cancer. It is recommended to carry out every 7-10 years.
- Diagnosis of chronic constipation, abdominal pain, anal bleeding, diarrhea.
- Therapeutic measures, including cauterization of erosions, removal of polyps, and administration of medications.
- Prescribing an examination to determine the cause of constant weakness, malaise, decreased appetite, and unexplained weight loss.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of research methods?
As for the examination procedure itself, ultrasound diagnostics is certainly easier for the patient to tolerate. It is painless and takes no more than 10-15 minutes. Colonoscopic examination is usually done without anesthesia, so it is accompanied by unpleasant pain, a feeling of “fullness,” and the urge to defecate.
In addition, ultrasound has no contraindications, while colonoscopy cannot be done in certain pathological conditions, including: bleeding, diverticulitis (hernia-like formations), hernias, etc. However, the advantage of endoscopic examination is that in addition to diagnosis, this method is therapeutically significant . It is possible to simultaneously search for pathological foci and correct them: removal of polyps, coagulation of damaged vessels of the intestinal wall, elimination of volvulus. If a pathological focus is detected, material can be immediately taken (biopsy) for subsequent histological analysis.
Preparation for the procedure
Before endoscopy, a diet is prescribed for five days before the procedure. Foods with minimal fiber content are recommended. You can eat white bread, pasta, rice, eggs, lean meat, vegetables and fruits without skin. Two days before the procedure, eat only soft foods. And in 24 hours you can only take liquid food, take a lot of liquid.
Take laxatives in two doses: 12 hours before the procedure and 6 hours before it. Castor oil and magnesium sulfate are used. To better cleanse the intestines, the patient is offered an enema. There are more modern osmotic laxatives that effectively cleanse the intestines without the use of an enema. It is not recommended to take food or liquids 2 hours before a colonoscopy.
Important! Carrying out a colon cleansing procedure is mandatory. Otherwise, feces will interfere with examination and making a correct diagnosis. In addition, the manipulation will become more painful.
Preparation for an ultrasound is the same as for a colonoscopy. The only difference is the shorter preparatory period, which lasts 3 days.
Preparatory activities
First of all, adults should take care of the location of the baby’s colonoscopy. The pediatric version of the procedure requires special care and caution from medical specialists. Therefore, it is necessary to choose only a highly qualified endoscopist and a reputable clinic.
The effectiveness of a rectal examination in both adults and children depends 95% on the proper level of preparation. Parents should take the preparatory stage as responsibly as possible. If a small patient goes to the examination insufficiently prepared, the doctor has the right to postpone the colonoscopy to another day, since the data will be distorted and the procedure will lose its meaning.
The preparation algorithm includes: dietary intake, regulation of psychological mood, use of laxatives or enemas.
You should start preparing your child no later than three days before the planned procedure. First of all, you need to adjust your diet. The diet involves the following changes described in the table.
| It is forbidden | Can |
| Fresh baked goods | Stewed or steamed vegetables |
| Fresh vegetables, raw | Boiled poultry, fish, veal |
| Berries and fruits with small seeds | Yogurt |
| Nuts | Clarified fruit juices |
| Dishes made from peas and beans | Low-fat broths and soups |
| Factory canned food | White bread croutons without aromatic additives |
| Mushrooms | |
| Milk and milk derivatives (cottage cheese, curd desserts) | |
| Fatty fish and meats | |
| Sausages |
Drinking carbonated drinks is strictly prohibited. Also, it is necessary to limit the consumption of sweets, chocolate, cakes and other sweets. The diet should not contain foods that increase the formation of gases in the intestines. On the eve of the examination, dinner should not be heavy. In the evening you should take a laxative. Adults are most often prescribed Fortrans; for children, this medicine is indicated only from the age of 14.
Duphalac or Microlax are more suitable for young patients. The latter can be used already from infancy. Children should not be given harsh sena-based laxatives. The medicine should be prescribed by a pediatrician, taking into account age, body weight, and individual characteristics of drug tolerance. An alternative to a laxative is a rectal cleansing enema.
In this case, the first enema is done in the evening, the second in the morning (on the day of the examination). The volume of liquid should be 15-20 ml of water per kilogram of weight for children under one year of age, and 30 ml for a child from one to three years of age. As for the psychological state, parents must clearly explain the need for the procedure, reassure the child, talk about anesthesia, and ensure a stable emotional environment in the family.
Comparison of contraindications
Contraindications for colonoscopy:
- intestinal perforation;
- inflammation of the abdominal cavity;
- ischemic colitis (fulminant form);
- acute s/s and respiratory failure;
- myocardial infarction in the acute stage;
- children and old age.
Contraindications are minimal for ultrasound:
- The presence of extensive inflammatory lesions of the skin, burns, dermatological diseases that interfere with the examination of the sensor.
- Transrectal ultrasound is not recommended after rectal surgery, removal of hemorrhoids, or in the presence of fissures and fistulas of the anus. Inserting the sensor in such cases becomes difficult.
- In most cases, refusal of this method is associated with reduced information content of the study in a given situation, and not with a risk to health.
Anesthesia
The psychological characteristics of the child’s body determine the need to put the child into medicated sleep or anesthesia immediately before the study.
A small patient, due to overexcitement associated with fear of an unknown procedure, may become hysterical, begin to break free, and unintentionally injure himself while performing diagnostic procedures. Therefore, before a colonoscopy, the baby must be given anesthesia through intravenous administration of a potent drug.
Propofol injections are usually used for sedation. The use of mask anesthesia is undesirable due to the need to administer muscle relaxants, which reduce intestinal motility and thus distort the picture during the study.
Due to the fact that the diagnostic procedure is performed in conjunction with anesthesia, all manipulations are performed in a specially equipped room (possibly in intensive care or resuscitation wards).
As prescribed by the doctor, the evening before the colonoscopy, the child is given a sedative tablet or syrup to reduce anxiety. This approach helps the baby get enough sleep and prepares him for a more comfortable experience of the next day’s procedures.
Which procedure is better?
Due to the complexity and pain of endoscopic examination, it is advisable to begin the study with ultrasound. Colonoscopy is best used when a tumor is suspected or to clarify the diagnosis. However, the choice of colonoscopy or ultrasound is ultimately decided by the doctor, who can recommend both methods of examination to obtain complete information about the condition of the intestines. These methods do not exclude, but complement each other.
But there are criteria related to the individual characteristics of the body, certain diseases, and the patient’s condition, which confront doctors with the choice of conducting one or another study. Therefore, the most important thing is to choose a professional specialist in a well-equipped clinic, clarify the diagnosis in a timely manner and receive qualified assistance. As they say in Latin, “Bene diagnoscitur, bene curatur” (“Well diagnosed, well treated”). Unfortunately, not all clinics are equipped with modern equipment. Patients sometimes have to go to paid institutions.
Important! Early detection of formations in the intestine and their timely removal are important criteria for the prevention of intestinal cancer.
Anamnesis
Initially, the doctor should familiarize himself with the medical history.
Taking a medical history is the basis for diagnosis. To begin to put forward versions of a possible pathology, the doctor must become familiar with the symptoms and other factors that may indicate a particular pathology. Anamnesis may include collecting information about the following facts:
- presence of taste in the mouth and its character;
- possible painful sensations and information about them;
- data on appetite, thirst;
- fatigue, drowsiness;
- analysis of other symptoms;
- information about intestinal diseases of close relatives;
- chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract of which the patient is aware;
- other diseases, etc.