Today, magnetic resonance imaging methods have become widely used to diagnose serious diseases such as gastritis, ulcers or tumors. MRI for the stomach is performed only on the recommendation of a doctor and in accordance with the indications.
MRI of the stomach and intestines will allow you to accurately and quickly diagnose pathology. However, its widespread use is limited only by the high cost factor, so the method is not affordable for everyone. In this article we will look in detail at what this procedure is, and in which cases it is necessary, and in which cases you can do without it.
Brief Definition
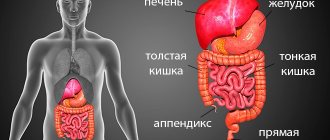
MRI of the stomach is a modern non-invasive diagnostic method that allows you to carefully familiarize yourself with the structure, structure and size of the organs of the digestive system. This research method is carried out thanks to special impulses, which, bypassing the abdominal wall, are reflected from the internal organs. Next, the radio waves undergo careful computer processing and display images with a high degree of detail on special monitors.
Some situations require the introduction of a special contrast agent into the patient’s body, which allows coloring less visible areas of organs; therefore, before such a procedure, you need to find out in advance whether a person is allergic to the components of the contrast solution or not.
Sometimes, instead of an MRI, a person is prescribed an alternative research method - computed tomography, which has a number of positive qualities, including:
- Very low radiation level.
- The presence of a doctor nearby who, as necessary, calms the patient and explains to him the essence of the manipulations taking place.
- There is no need to place a person in a hardware tunnel, etc.
However, CT does not allow the specialist to see the overall picture of the state of the gastrointestinal tract; in this regard, this diagnosis is significantly inferior to its “big sister” - MRI, which is more popular among the population.
How is it going?
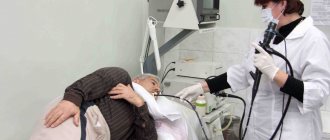
Abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting and other symptoms of gastric diseases require a visit to a doctor who will conduct the necessary diagnostics and make an accurate diagnosis. If necessary, the doctor may prescribe a computed tomography (CT) scan for the patient. Before the procedure, the patient is given a contrast agent, which must be drunk in three doses. The first part of the contrast is drunk and after 30 minutes the next one is drunk, after 60 minutes - the remaining portion of the substance.
When the contrast agent has been drunk, the patient is changed into clothes specially designed for CT scanning and placed on the table. Lying in a horizontal position, the patient receives the remaining amount of contrast agent through a dropper. CT scanning is performed in a special tunnel with a diameter of 75 cm. The tomograph tunnel is illuminated and ventilated. The diagnosis is painless and lasts half an hour. After the examination, an image of the organ being examined is displayed on the screen in 3 projections.
https://youtu.be/9lWctu151ms
What does the study show?
Since the procedure is classified as expensive, it is performed, as a rule, on patients who have previously undergone another type of examination of the abdominal organ, but have not received reliable and clear results. Using MRI, you can clarify a previously stated diagnosis or make a new one based on the data obtained.
Thus, a qualified doctor, having studied the resulting image, is able to identify:
- size, location and nature of metastases;
- features of the formation of one or another pathology in the stomach;
- the main reasons for the manifestation of a dangerous process;
- the presence of any foreign objects;
- general condition of the lymph nodes located near the intestines and stomach;
- focus of the inflammatory process provoked by gastritis or peptic ulcer;
- bleeding of the stomach walls, etc.
Preparation, conduct and consequences of a stomach x-ray with barium
The study itself is carried out on a tomograph. To begin, the patient lies down on a sliding table.
The doctor securely fixes the arms, legs and head. This is all done in order to be able to exclude any movement of the patient that could distort the results of the tomography.
To control breathing, a belt is fastened to the chest of the subject. Using ear plugs or earplugs will help minimize the sound load.
Disadvantages and advantages
The undoubted advantages of the procedure include, first of all, a clear result, which allows specialists to make the correct diagnosis and begin timely treatment of the identified disease. Also, tomography does not cause any pain in the patient during the immediate examination.
However, it is worth keeping in mind that the contrast solution introduced into the body at the end of the study can cause minor but extremely unpleasant side effects: nausea, dizziness, etc. Among the few disadvantages, one can identify the high cost, as well as the impossibility of performing the procedure if a person has pacemaker and other types of metal implants.
Before an MRI, you should remove jewelry, belts with metal buckles, and hair clips.
List of indications and contraindications
A procedure associated with a detailed examination of the stomach, under special circumstances, is indicated for people who are suspected of having: formations of a benign or malignant nature, metastases that have spread from other organs, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, for example, diaphragmatic hernia, gastritis or stomach ulcers. The list continues with the presence of a complex form of helminthic infestation, abnormal structure of an abdominal organ, perforation or malignancy of a peptic ulcer.
The study can also monitor the effectiveness of treatment methods developed to combat stomach cancer. The procedure, despite its relative safety and painlessness, is not carried out in every case. Sometimes the health condition of the subject is a serious reason for refusing to undergo a radiation procedure.
Gastric biopsy - what is it?
The category of contraindications includes:
- Lactation period (breastfeeding) and gestation (pregnancy).
- Severe form of liver failure.
- Presence of a previously implanted heart valve.
- An image on the patient’s body of decorative tattoos made with dyes containing various metallic inclusions.
- The presence in the human body of ferromagnetic metals in the form of bullets, fragmentation elements, vascular clips, pacemakers, bone fixators, plates and wires inserted in fractures.
In addition to the main prohibitions, there are also relative contraindications: heart failure with complications, claustrophobia (pathological fear of closed spaces), mental abnormalities accompanied by uncontrolled movements of the patient, extremely serious condition of the patient.
For people who exhibit such ailments, MRI is prescribed only when absolutely necessary to further minimize dangerous consequences. Medical personnel take the necessary measures to reduce various risks to the patient’s life to zero.
MRI or gastroscopy?
Very often, people with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract ask their attending physicians the question: what is the difference between tomography of the stomach and gastroscopy? Indeed, it will be difficult for a person who does not understand medical terminology to distinguish the two types of diagnostics of the digestive system from each other.
In order to understand the difference between biological concepts, you need to carefully read the educational table, in which procedures are correlated and compared in various categories:
| Characteristic | Magnetic resonance imaging | Gastroscopy (EGD) | |
| Painful sensations | None | Minor. Sometimes there is a spasm or gag reflex when inserting a fibrogastroscope | |
| Accuracy of studying the condition of the mucous membrane | Low | Maximum: this research method allows you to assess the condition of the mucous membrane lining part of the gastrointestinal tract | |
| Duration | 20–40 minutes | Typical diagnostics last approximately 2–5 minutes | |
| Possibility of parallel treatment | No | With the help of an improved gastroscope, the doctor can carry out therapeutic measures in parallel with diagnosis. In such a case, the patient is given anesthesia | |
Which of the presented types of diagnostics is necessary for a particular person is decided only by the attending physician.
FGDS
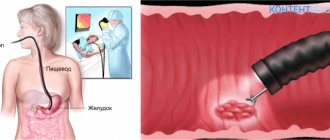
Fibrogastroduadenoscopy is quite well known and loved by doctors for its information content and effectiveness. The procedure consists of extending an endoscope, which is a flexible tube made of a special optical fiber, through the pharyngeal opening and esophagus to the area being examined. The equipment has a microcamera that will broadcast an image of the internal state on the screen.
The actions taken will differ from the well-known FGS in the presence of the possibility of examining not only the stomach, but also the intestines.
Preparation for the study is quite standard; the following actions are prohibited within 8 hours:
- Smoking, as nicotine has an irritating effect on the mucous membranes.
- Eat fatty and spicy foods.
- Eat chocolate, nuts and seeds, the last meal should be light.
- Wear tight and tight clothing.
This technique is quite painful and unpleasant , especially for those people who have a strong gag reflex, therefore, to neutralize this, medical workers usually numb the throat of the person being examined with lidocaine.
Where can I get an MRI?
The examination should be carried out in appropriate conditions on the territory of clinics, hospitals and centers specializing in diagnostics of this level. Reputation plays an important role when searching for a worthy institution. If a person who is about to undergo a tomography has the opportunity to check the relevant reviews and comments about a particular center, he should not shy away from this method of identifying a worthy medical institution: this can save health and life.
If the information received about the hospital in question seems very ambiguous and suspicious, it is better to refuse to visit it and find a more worthy option
Cost of the procedure
In the vast majority of regions of the Russian Federation, the price for an MRI of the stomach ranges from 2.5 to 5–7 thousand. However, medical institutions that use ultra-precise professional equipment can indicate a cost of 10–24 thousand rubles.
Doctors strongly discourage patients from saving on their health: conscious consent to diagnostics using an old-generation device with poor quality resolution in some special cases is fraught with serious consequences.
Patient reviews
When diagnosing problems in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, many patients are recommended by doctors to undergo an MRI to clarify the clinical picture. Reviews about the procedure are very positive, and here are some eloquent examples:
Marina, 34 years old: “I had an MRI for gastritis, they discovered a tendency to ulcers. I didn't even have to swallow the tube. The doctor selected drug therapy, and after that the number of attacks decreased noticeably. Now there are still no ulcers, I’m just maintaining my general condition with chronic gastritis.”
Svetlana, 37 years old: “I had an MRI done when I suspected a malignant tumor, but in the end it turned out that the tumors on ultrasound were just polyps. A year ago they were safely removed, the operation was carried out using MRI without any health complications.”
Karina, 45 years old: “I had an MRI of the stomach several times, after each procedure an unpleasant feeling of nausea appears. There is nothing left, since the method is truly informative and has allowed me to control my ulcer for many years.”
So, conducting an MRI of the stomach is an appropriate appointment, which not only confirms the diagnosis, but also identifies diseases hidden for the patient at an early stage of the formation of the pathological process.