The gastrointestinal tract is a kind of laboratory, the proper functioning of which determines the saturation of the entire body with substances useful and necessary for life. When a failure occurs, most vital processes are disrupted. Gastroenterological problems plague many people these days.
There are many reasons for the development of such diseases: frequent stress, unhealthy diet, serious psychological disorders and polluted environment. But as a rule, patients are in no hurry to seek help from gastroenterologists. When this does happen, during a comprehensive examination the patient may be prescribed an esophagogastroduodenoscopy.
The essence of esophagogastroduodenoscopy
The study can be either planned, recommended in advance by a doctor, or emergency. It is performed using a fiberscope - a flexible probe with an attached small lamp and video camera.
The main advantage of endoscopy over conventional x-ray examination, which was common earlier, is the ability to several times more accurately identify inflammatory processes in the mucous membranes, developing or already scarring ulcers.
If the preparation of endoscopy is prescribed due to suspected cancer of the stomach or esophagus, during the procedure the specialist may also perform a biopsy - tissue sampling for subsequent analysis. The biopsy does not cause additional discomfort to the patient.
Also during the procedure, the doctor has the opportunity to remove polyps, accidentally swallowed small objects, blood clots after bleeding, etc. This makes it possible to exclude abdominal surgery.
Preparation
Before going to the endoscopy room for manipulation, you need to understand how to prepare for EGD. It all starts with a conversation with your gastroenterologist, during which various questions that may concern the patient or doctor should be clarified. The patient must tune in psychologically to the procedure, so he has the right to find out in detail what will happen to his body during the diagnostic process, what he will feel how long it will take and what informational value such an examination has.
It is the patient's responsibility to provide the physician with his or her medical history, as well as any chronic illnesses and any history of hypersensitivity, as this may affect the use of medications during the study. Diseases that are potentially dangerous for esophagogastroduodenoscopy must be corrected. As a rule, special attention is paid to the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. Diseases of these organs can lead to serious complications.
Eliminate diseases of the upper respiratory tract (acute respiratory infections, nasopharyngitis, tracheitis) so that nothing impedes the advancement of the fiberscope and does not cause further complications.
Direct preparation is as follows. The patient must adhere to a special diet. Two days before endoscopy, you should exclude foods that can injure the mucous membrane (spicy foods, seeds, nuts), and give preference to gentle, easily digestible foods. You will also have to give up alcoholic drinks. The last meal should take place 12 hours before the scheduled procedure.
Take medications recommended by a gastroenterologist. Espumisan is most often prescribed. This is necessary to reduce gas formation and remove them from the gastrointestinal tract. This technique will not only reduce discomfort during the procedure, but also shorten the examination time. Particular attention should be paid to clothing. It is better to give preference to those wardrobe items that are fastened with buttons rather than pulled over the neck. Clothes should be comfortable and not brand name.
Refusal of perfume. Even if the patient does not suffer from allergies, you should think about medical personnel or other patients who will also do the endoscopic examination. You should not smoke before the diagnosis. Nicotine strengthens the gag reflex and increases the amount of mucus in the stomach, which makes examination difficult.
Modern medicine strives to eliminate pain, so local or general anesthesia is widely used during endoscopy.
Indications for EGDS
The study is performed to determine the nature of such symptoms:
- loss of appetite;
- unexplained weight loss;
- chest pain;
- pain in the upper stomach;
- a feeling of acidity or bitterness in the mouth;
- belching;
- chronic heartburn;
- quick feeling of fullness in the stomach;
- bad breath not associated with poor dental health;
- causeless vomiting;
- diarrhea with black contents;
- problems swallowing food;
- disturbances in the passage of food through the esophagus;
- regurgitation of ingested food;
- chronic cough;
- chronic intestinal diseases.
What You Can Find
With the help of an examination, you can detect a considerable number of diseases at an early stage and cure them in a timely manner. It's worth checking out the short list:
- Foreign bodies. When examining the gastrointestinal tract, no enlarged organ sizes are observed. The mucous membranes themselves change; their size and appearance will depend on how many foreign bodies get inside and what their shape is. As a result of the research, it was discovered that most of the objects were found in the pyloric part. There may not be any obvious signs; they begin to appear only when the foreign object is in the stomach for a long time. Characteristic signs are: nausea during the day, complicated bowel movements, frequent belching and profuse vomiting.
Contraindications for carrying out
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy is prohibited in the following situations:
- serious condition of the patient;
- myocardial infarction;
- post-infarction state;
- infectious and acute surgical diseases;
- manifestations of atherosclerosis;
- abnormal narrowing of the esophagus;
- heart failure;
- hemophilia;
- varicose veins of the esophagus;
- mental disorders.
The procedure is performed only by specially trained endoscopists who have been trained in gastroscopy.
Decoding the results
As soon as the procedure is completed, all data will be entered by the doctor into the appropriate protocol.
Thanks to this study, gastritis, erosion and other gastrointestinal diseases can be detected in a timely manner.
Norm
If there are no diseases, then the esophagus is freely passable, its mucous membrane is painted a pale pink color. The next stage of the examination is the cardia, namely the part where the esophagus passes into the stomach. Under normal conditions, it closes.
The mucous membranes also have a pale pink color; no ulcerative or tumor formations were found. The folds straighten out immediately.
When examining the contents, mucus in small quantities and characteristic transparency are considered normal.
Deviations from the norm
If the patient has gastritis, then upon examination the red and swollen mucous membrane is immediately noticeable. A common occurrence is hemorrhage and some mucus.
With an ulcer, the doctor will see a cone-shaped crater, the bottom and edges of which are painted bright red or even bluish. Hemorrhages are characterized by a brown color.
If the patient is bleeding, there will be a lot of dark red liquid in the stomach.
When diagnosing duodenogastric reflux, the liquid will be greenish in color.
With this procedure, cancer can be detected early. When stomach cancer is detected, the mucous membrane is smoothed and has a grayish-white color. Polyps appear as well-defined tumors that have a wide base.
How to prepare for EGD of the stomach
You cannot begin research without special preparation. Incorrect preparation or lack thereof can lead to the fact that the results of the procedure will be incorrect and the doctor will not be able to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment.
The main condition for esophagogastroduodenoscopy is the absence of food mass in the stomach and duodenum. That is why the patient must refuse to eat at least 9-12 hours before the procedure.
If the procedure is scheduled for the morning (or the first half of the day), dinner the day before should take place no later than 20-00. It is advisable to eat only light, quickly digestible foods. Boiled egg whites, slimy porridge with water, and chicken broth cooked on the breast work well.
You should avoid salty, sweet, fatty, pickled, spicy foods, baked goods, fast food, flour, citrus fruits, fresh apples, etc. It is unacceptable to drink alcohol and smoke.
In the morning before undergoing the procedure, the patient is strictly prohibited from:
- There is;
- drink;
- chew gum;
- smoke;
- brush your teeth.
On your doctor's recommendation, after waking up, you can drink a cup of still mineral or regular boiled water.
If esophagogastroduodenoscopy is scheduled for the afternoon (although this is extremely rare), the patient is allowed a small light breakfast no later than eight o'clock in the morning. It is best to discuss the menu with the doctor who is specifically treating you.
Also, before endoscopy, the use of various medications that prevent blood clotting is unacceptable. This applies not only to oral drugs, but also to those administered intramuscularly, intravenously, subcutaneously, etc.
What is the difference in the abbreviation
Many patients do not understand the difference between these methods. The methods for carrying them out are similar. However, there are some differences that can be found out while parsing the abbreviation.
- FGDS is a fibrogastroduodenoscopy, which includes visualization of the duodenum and stomach.
- EGDS is an esophagogastroduodenoscopy that allows you to examine the upper parts of the gastrointestinal tract. That is, visualization occurs not only of the duodenum, stomach, but also of the esophagus.
From the decoding of the abbreviation it is clear that the difference lies in indicating which area needs to be examined. In addition, there is also the concept of “videogastroscopy”. During this diagnosis, a video recording is made during the procedure.
How is EGDS performed?
The research methodology itself is as follows:
- To ensure the effectiveness of the procedure and reduce discomfort, the patient’s throat is treated with a local anesthetic spray. Subsequently, for greater relaxation, the patient may be given an additional anesthetic intravenously;
- The subject lies down on the couch on his left side. He clamps the mouthpiece in his teeth to prevent uncontrolled teeth clenching during the examination;
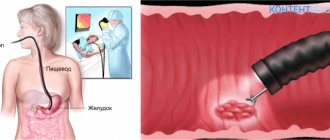
- The doctor carefully inserts the fiberscope into the esophagus, then into the stomach and duodenum. Air is introduced through the device in order to straighten the lumen of the organs and thereby facilitate examination;
- The specialist alternately examines the mucous membrane of the esophagus, then the stomach and duodenum.
During the examination, the patient feels the urge to vomit, salivation increases, and belching may occur. Preparation for endoscopy is also important in order to avoid vomiting during the procedure.
To reduce discomfort during the examination, the patient is advised to take deep breaths and exhales.
The duration of this procedure is only 1-3 minutes.
An incorrectly performed EGD procedure can lead to complications. However, this happens quite rarely. Possible complications include mechanical injuries to the mucous membrane of the stomach and/or esophagus.
Complications from the respiratory and cardiovascular systems are also possible. The risk group includes elderly people, as well as patients with pulmonary pathology, heart failure or stenosis.
If there was food in the patient’s stomach before esophagogastroduodenoscopy, during the procedure it can enter the respiratory tract, and this, in turn, can lead to asphyxia or subsequent pneumonia.
After the examination, the person feels pain or a burning sensation in the larynx. Less commonly, patients experience pain in the stomach area. As a rule, these unpleasant symptoms disappear on their own a day after the study.
The patient can drink and eat food after a few hours, but it should be as gentle as possible.
Can it be done under anesthesia?
There are no obvious indications for this, but in a number of clinics general anesthesia is still practiced. In most cases, medications are given - Motilium or Cerucal, which help cope with the gag reflex. The use of these drugs is advisable only in cases of increased gag reflex.
So that the patient can prepare psychologically, it is appropriate to start taking tincture of valerian or motherwort a few days before the procedure. You can also use other sedatives, but it is worth remembering that without prior consultation with a doctor, you can only use herbal remedies, although they also have a number of contraindications.
Most specialists do not use anesthesia, as it has many contraindications.
Alternative means are used, namely lidocaine anesthesia.
Essence of the method
Endoscopy is performed using a gastroscope. A gastroscope is a device consisting of an elastic tube with a complex optical system and a visualization device. The tube is sequentially inserted into the pharynx, esophagus, stomach and the initial part of the small intestine. Thanks to fiber optics and digital equipment, the doctor can see structural changes in the mucous membrane of the digestive tract and evaluate its functional features.
Information. The abbreviations FEGDS and EGDS are synonyms. The term fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy (FEGDS) emphasizes the important role of fiber optics in the operation of the device (from the Latin fibra - fiber).
You can learn about the operating features of modern gastroscopes from the video.
When using special equipment, additional diagnostics become possible: microscopy of the mucosa after taking biopsy material and intragastric pH-metry - determining the level of acidity of gastric juice.
General information
Gastroscopy is an examination of the stomach from the inside using a gastroscope. This device is a complex optical device whose sensor is attached to the end of a flexible tube. It is introduced through the esophagus into the cavity of the stomach and allows you to visualize its inner lining with all pathological changes. Using a gastroscope, you can also monitor the motor activity of the stomach and the coherence of all its departments.
Peculiarities. Special devices are attached to the gastroscope, which help carry out pH measurements, taking pieces of mucous membrane for biopsy, coagulation of a bleeding vessel, and low-traumatic removal of small benign tumors.
Gastroscopy is prescribed for almost any disease of the upper digestive tract or if its presence is suspected. Often this procedure becomes an alternative to surgery.
Diseases detected by endoscopy
Most often, inflammatory changes in the mucous membrane of the stomach (gastritis), esophagus (esophagitis), duodenum (duodenitis), erosions and ulcers, polyps, cancer, foreign bodies, narrowing or insufficiency of the sphincters are detected. As a rule, all findings require histological confirmation. For this purpose, a tissue biopsy is taken and the cellular composition is examined.
Based on the results of the study, the doctor prescribes treatment
Complications
Patients need to be aware that the procedure is quite invasive and may be accompanied by complications. The most dangerous are perforation of the wall of a hollow organ: the esophagus, intestines or stomach and bleeding when the mucous membrane is injured.
Dangerous consequences of gastroscopy include:
- bleeding after a biopsy (sometimes when varicose veins are damaged);
- perforation of the organ mucosa;
- development of aspiration pneumonia (inhalation of vomit during examination);
- increased blood pressure.