Causes
Gastroenterologists distinguish two types of pathology in which the outflow of bile is disrupted. Intrahepatic cholestasis syndrome develops due to the negative effects of alcohol on the body. And also common causes of this type of bile stagnation are viral infections: hepatitis, papilloma and others. Chronic diseases that disrupt the structure of liver cells and bile ducts also lead to bile stagnation.
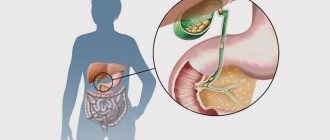
Extrahepatic disruption of bile outflow is the result of a mechanical obstruction that interferes with normal circulation. This happens with the following pathologies:
- cholelithiasis;
- stenosing pancreatitis;
- biliary dyskinesia;
- duodenal ulcer;
- neoplasms in the pancreas and abdominal organs;
- functional failures in the valve system of the biliary tract.
Gastroenterologists insist that if you feel the first symptoms of bile stagnation, you should immediately consult a doctor. After all, without timely treatment, pathology in just a few months can lead to a serious condition - cirrhosis of the liver.
https://youtu.be/R2fqZdjdVw8
Without physical education - nowhere
“Movement is life” - this slogan is also relevant for those who suffer from disorders of the gallbladder, ducts or liver. Exercises for congestion in the gallbladder help normalize the motility of the liver-gallbladder system. A set of exercises should be prescribed by a physical therapy teacher in accordance with the established diagnosis. But the main complex of physical activity contains the following exercises:
- walking in place for 2-3 minutes;
- breathing exercise aimed at activating the abdominal muscles - inhale, drawing in the stomach - hold your breath - exhale, sticking out the stomach (repeat 7-10 times);
- basic stance - legs shoulder-width apart, feet straight, arms down;
- forward bends: raise your arms up, stretching out as high as possible, lower your arms, tilting your body as low as possible;
- rising on your toes, raise your arms up from the sides, turning your palms up, too, then, standing on your full foot, lower your hands, turning your palms down;
- put your hands on your belt, tilt your body forward, then return to the starting position and lean back;
- placing your hands on your belt, perform shallow squats;
- rotate the body while maintaining the maximum amplitude of tilts;
- bend forward and down, trying to reach the opposite foot with the palm of your hand;
- rotation of the body to the right and left, placing hands on the belt, with the maximum possible amplitude of rotation;
- The treatment complex ends with an exercise familiar from childhood - stretch, raising your arms up, and smoothly lower your arms down.
Each exercise should be performed at least 5-7 times. If possible, such exercises aimed at working the abdominal muscles, and therefore activating the work of the internal organs, can be performed lying down - raising and lowering the legs, turning the legs and body, bending over, swinging the legs.
It is important to remember that all physical therapy exercises for a disease such as congestion in the gallbladder should be recommended by a specialist only after examination and diagnosis, in which exacerbations of the disease due to increased physical activity are excluded.
Disturbances in the functioning of internal organs, including the activity of the gallbladder, lead not only to painful sensations, but also to disruption of the usual rhythm of human life. Therefore, it is best to prevent gallbladder congestion than to waste time and effort on examinations and then on treatment.
What is the danger of bile stagnation
Bile plays an important role in the digestion process. It promotes the breakdown and digestion of fats received from food, activates pancreatic enzymes, reduces the acidity level of gastric juice, without it fat-soluble vitamins are not absorbed.
When the flow of bile into the duodenum is disrupted, excess cholesterol is retained in the body, provoking the development of atherosclerosis. Failure of glycogen synthesis from glucose becomes a prerequisite for the appearance of diabetes and other metabolic disorders.
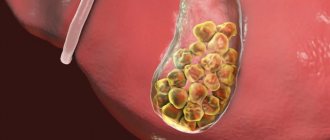
Stagnation of bile in the gallbladder causes inflammation of this organ, often triggering the formation of sand and stones. If cholestasis is not treated in time, it will provoke other pathologies:
- dyspepsia associated with insufficient breakdown and digestion of food;
- cholecystitis, turning into cirrhosis of the liver - due to the development of bacterial microflora;
- osteoporosis and vitamin deficiency due to insufficient absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D).
Prolonged stagnation of bile leads to an increase in the level of bilirubin and its re-entry into the blood. The resulting bilirubinemia causes intoxication in the body.
General information about cholestasis in dogs
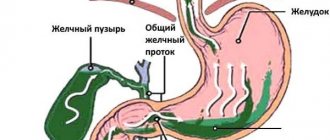
Cholestasis, also called bile duct obstruction, prevents the proper movement of fluid from the liver gland to the gallbladder, as well as to the intestines.
Bile is an important tool of the body that allows the digestion of complex substances in the stomach and helps eliminate substances that are harmful to the body.
Bile acid comes into contact with harmful substances and combines with it, forming special, inseparable compounds that are eliminated in the future.
With compressed, compressed, plugged bile ducts, fluid secretion remains the same, but the movement of acid is hampered or stops altogether, which provokes stagnation.
Gradually, the flow of bile into the gastrointestinal tract stops, and the overflowing acid from the ducts enters the blood, this is caused by pressure and leakage of fluid.
A condition is formed - cholemia, which is extremely dangerous, because it can provoke nervousness, seizures, even death.
When cholestasis persists for 2 or more days, ultrastructural deformations occur; at this stage they are reversible.
After a while, the advanced phase of the development of the disease begins, which is characterized by the appearance of histological changes: the capillaries of the bile ducts increase, a blood clot may appear in the canals, and villi that serve for the movement of acid are eliminated on the canalicular membrane.
Source: https://RealPet.ru/zdorovie/xolestaz-u-sobak.html
Symptoms of stagnation
Cholestatic syndrome is always accompanied by manifestations characteristic of impaired liver function. The main symptom that immediately makes you think about the problem is discomfort in the right hypochondrium. When pressed, the liver feels thick and painful. In parallel with this, skin itching occurs. The shade of urine changes - it becomes darker in color, as well as feces, which, on the contrary, becomes lighter in color.
It is possible to determine that the outflow of bile is disrupted by other signs:
- frequently recurring attacks of nausea, belching and vomiting;
- yellowing of the skin, outer membranes of the eyes (in severe cases);
- unpleasant odor from the mouth.
When the gallbladder spasms, bile is thrown into the upper parts of the digestive tract. This leads to attacks of heartburn and bitterness in the mouth. To prevent bile from the stomach from disturbing digestion, doctors recommend refraining from heavy dinners.
Most people who experience cholestasis syndrome complain of lack of appetite, dry mouth, and bitter belching. If the skin condition suddenly worsens - dandruff, allergic rashes or small subcutaneous rashes appear, this sign should also be a reason to pay attention to the functioning of the liver and biliary system.
Medications
Medicines used in the treatment of cholestasis and similar problems associated with impaired bile circulation can be divided according to the scope of their work:
- choleretic drugs for bile stagnation are used only in cases where the outflow of liver secretions is not impaired. These are medications such as “Allohol”, “Hofitol”, “Kholagol”, “Odeston”. They have different active components, but work to enhance the liver’s production of secretions and activate its circulation;
- hepatoprotectors that normalize the general condition of the liver and, as a result, improve bile production. Substances such as ademetionine, arginine glutamate, betaine, thioctic acid and some others can work in this group of drugs. Only a specialist can decide which drug to prescribe in each specific case.
If the flow of bile is disrupted due to stones, or a change in the physical shape of the gallbladder, surgical intervention is most often prescribed to eliminate the cause of obstruction of the bile ducts. Preoperative preparation and the postoperative period also include a complex of medications that ensure the most positive outcome of such treatment.
Preparations for the treatment of bile stagnation can work on both synthetic and natural substances, the latter being of both plant and animal origin. These can also be derivatives of amino acids, essential phospholipids. One of these substances is ursodeoxycholic acid. It is the primary bile acid produced in the human body and takes an active part in the processes of immunomodulation, bile formation and bile circulation, and has hypocholesterolemic, hepatoprotective, cholelitholytic effects. Preparations containing this substance - Ursofalk, Grinterol, Ursodez - are prescribed for use only by a doctor!
Stagnation of bile during pregnancy
Intrahepatic bile stagnation often occurs in pregnant women. This phenomenon is caused by compression of organs by the growing fetus. But more often the problem arises against the background of hormonal changes occurring in the body of the expectant mother.
An important factor that can cause cholestasis is heredity.
Doctors have noticed that congestion in pregnant women appears more often in the third trimester and when a woman is carrying a baby in the cold season. The most striking symptom is severe itching of the skin. It spreads to the inner surface of the palms, feet, face, and neck. A woman's condition usually returns to normal a few days after birth.
In severe forms of cholestasis during pregnancy, classic signs of bile stagnation occur: darkening of the urine, yellow discoloration of the skin and whites of the eyes. This condition threatens the onset of premature birth, as well as severe postpartum bleeding. There is a danger to the baby's life.
Complications
If signs of cholestasis appear in a child or adult, it is necessary to contact a medical institution to identify the cause and treat the pathological process. Otherwise, many serious pathologies develop in the patient’s body. Due to improper or late treatment, the patient may develop the following complications:
- bleeding;
- the appearance of stones in the gallbladder and its ducts;
- liver failure;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- encephalopathy, as a consequence of the effect of excess bile on the brain.
Pediatric cholestasis
No one is immune from the occurrence of bile stagnation, including children. Cholestasis in children can be congenital when there are no bile ducts in the liver. This form of the disease is the most severe and requires urgent surgery. Stenosis of the papilla of Vater, which causes a problem in children, is treated surgically. Sometimes congestion occurs due to the accumulation of roundworms in the bile duct or the bending of this organ.
Without proper treatment, bile stagnation in a child very quickly develops into more severe pathologies, so it is important to know the symptoms indicating a problem:
- skin itching;
- yellow tint to the body and sclera;
- xanthomas - slightly raised yellow formations above the skin, soft to the touch;
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- lack of appetite, nausea.
Common causes of pathology, recommendations for their prevention
But still, cholestasis is more often a consequence of various liver diseases. This disease is especially typical for miniature varieties of Schnauzers and Collies. No gender predisposition was identified. It is believed that middle-aged and older dogs are especially likely to suffer from blocked bile ducts. However, this is quite natural, since it is at this age that pets are often found to have stones and sand in the gallbladder (causes of blockage).
In carnivorous and omnivorous animals, which includes dogs, opisthorchid is a common cause of liver problems. This is a trematode that parasitizes directly in the bile ducts. When there are a lot of parasites, they plug the lumen of the ducts, cause inflammatory and degenerative phenomena in them, which leads to the impossibility of the outflow of secretions. The result is still the same - intrahepatic cholestasis in dogs, complicated by additional “feeding” of the body with worm toxins.
So if your dog constantly accompanies you on forays into nature, into the forest or to the river, treat him with anthelmintic drugs at least once a quarter! Of course, you should first consult with your veterinarian about their specific type, dosage and frequency of use.
By the way, dedicated to the owners of hunting dogs... When a dog is bitten by a tick, or when it drinks from forest puddles, there is a high risk of developing blood parasitic diseases and leptospirosis. They do not directly affect the liver, but the indirect effect is extremely severe - gigantic volumes of toxins appear in the blood, which contribute to the development of hepatitis and hepatosis. The liver tissue “shrinks” and becomes rougher, this leads to pinching and blocking of the bile ducts.
Indirectly, we talked about another common cause of pathology in dogs – stones. They are often found in those animals whose owners... love and care for their pet, including a large amount of fresh meat and offal in its diet. Remember that after five to six years, dogs do not need large amounts of protein. Moreover, such a diet is very harmful for them and leads to numerous problems with the liver and kidneys! For example, it causes the accumulation of stones and sand.
As your dog ages, he needs to include more vegetables and some cereals in his diet. Beef and other varieties of red meat (if you have the opportunity to give them) should be completely abandoned, switching your pet to chicken and low-fat offal . It is useful to feed your pet fish oil or boiled sea fish of medium fat content. This will protect him from the development of liver diseases and will have a beneficial effect on the general health of the animal.
A very serious and not always identified cause of cholestasis is liver cancer . Again, in dogs, this type of cancer is very often related to nutrition. Only this time - with poor quality food. When a dog is dumped into a bowl with the “dubious” contents of the refrigerator and given moldy bread, his liver takes a severe blow. If such “feeding” is carried out regularly, the development of severe pathologies will not take long.
This also includes cases of cholestasis in small decorative dogs, whose owners (and more often, mistresses) pamper their pets in every possible way, sometimes bringing them to the state of “bunches on their paws.” Obesity is dangerous not only for the cardiovascular system, but also for the liver, which receives an excessive load. In well-fed dogs, stones can appear as early as three or four years of age, which is not observed in “standard” cases.
abdominal trauma can lead to a similar outcome . If a dog falls from a great height, is run over by a cyclist, if a dog is hit by a car or kicked, the liver, as a large and voluminous organ, is often damaged. Such injuries do not always lead to its rupture - connective tissue adhesions , compacting the parenchyma and pinching the bile ducts. They lead to cholestasis.
Fortunately for veterinarians, many causes of pathology are quite easy to identify. However, this does not mean that the disease can be treated carelessly. If left untreated, not only cholemia is possible, but even rupture of the gallbladder. This is almost 100% death from severe peritonitis.
Diagnosis of bile stagnation
If a problem such as a congestive gallbladder occurs, you should seek help from a physician or gastroenterologist. The specialist will prescribe an examination that will determine the cause of poor health.
First of all, the doctor interviews and examines the patient. Palpation allows you to assess the degree of liver enlargement and pain associated with the fact that bile cannot exit normally. After this, laboratory tests are prescribed. The standard diagnostic list includes the following:
- blood tests - general, for antibodies to helminths, biochemistry (bilirubin, cholesterol, bile acids, others);
- stool analysis (to identify worms);
- urine test for urobilin.
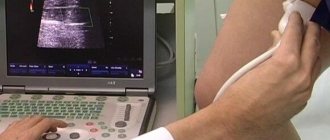
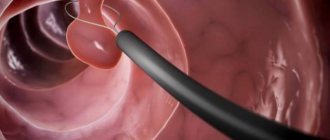
Ultrasound examination helps to identify the causes of bile stagnation. Sometimes a biopsy of liver tissue, cholanography, or esophagogastroduodenoscopy is necessary. Computer or magnetic resonance imaging can also be used.
General information
Cholestasis, or bile duct obstruction , interferes with the normal passage of bile from the liver to the gallbladder and intestines. Bile helps digestion and also removes harmful substances from the body (by binding with them, bile acids form insoluble compounds). If the bile ducts are plugged or compressed, the secretion can no longer exit into the lumen of the digestive tract, but begins to enter the blood (leaking there under pressure). Cholemia is an extremely serious condition, fraught with nervous attacks and death.
Oddly enough, the pathology is often associated with another ailment - inflammation of the pancreas, that is, pancreatitis . In fact, everything is simple - with pancreatitis, the exit parts of the ducts in the duodenum can become plugged, which indirectly affects the liver.
Treatment of bile stagnation
When the outflow of bile is impaired, therapy is selected by a specialist. He focuses on the symptoms of the disease and the causes that provoked it. Taking pharmacological agents recommended by a doctor and following recommendations regarding diet give a good therapeutic effect and help remove bile from the body. But sometimes doctors have to resort to surgical methods.
Treatment with medications
The basis of drug therapy for cholestasis without severe obstruction (narrowing of the ducts) is almost always the prescription of drugs containing ursodeoxycholic acid.
This substance is also present in the human body’s own bile. Its function is to neutralize toxic bile acids, as well as reduce the amount of synthesized cholesterol and prevent its absorption when it enters the intestines. Taking drugs such as Ursofalk, Ursosan, Holacid stimulates the production of bile, while simultaneously preventing the formation of dense clots and promoting the dissolution of existing stones.
Stagnation of bile in the gallbladder should be treated with means based on ursodeoxycholic acid for a long time - from several months to a year and a half.
The dose of medication that should be taken to expel a stone or effectively remove bile is calculated by the doctor individually, based on the patient’s weight. Do not use drugs from this group if signs of cholestasis appear due to the following pathologies:
- biliary dyskinesia;
- severe functional failure of internal organs;
- acute cholangitis and cholecystitis;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- the presence of calcium formations in the gallbladder.
It is imperative to prescribe medications that prevent the accumulation and stimulate the removal of bile from the body. All of them contain plant components that have a beneficial effect on the liver and have a minimum of side effects. The most effective medications are:
- Allohol;
- Chophytol;
- Holiver.
Herbal infusions, which can be purchased at any pharmacy as prescribed by a doctor, help improve the flow of bile, and at the same time remove bad cholesterol. Drink a herbal remedy - collection No. 2 or 3 course, the duration of which is determined by the attending physician, 2-3 times a day 30-40 minutes before meals.
Homeopathy is also very effective in treating conditions such as bile stagnation. Experts recommend Galsten tablets and drops or Hepar compositum injection solution. They contain many components of plant and biological origin, but the base is spotted milk thistle, which contains a complex: various flavonoids, vitamin K, necessary for blood clotting, as well as linoleic acid.
Surgery
Depending on the origin of the pathology in which bile begins to stagnate, doctors have to use various surgical methods to normalize the patient’s condition:
- minimally invasive removal of dense clots from the gallbladder and ducts (laparoscopy);
- excision of a tumor that has become an obstacle to the outflow of bile;
- installation of special dilators - stents in the ducts;
- dilation (balloon) expansion of the ducts when they narrow.
Surgical interventions on the sphincters are also carried out to get rid of bile stagnation and establish normal functioning of the digestive organs. And in the case of congenital pathology - biliary atresia, in which there are no ducts, an operation is necessary to create bile ducts or a liver transplant in the first months after the birth of the baby.
Traditional methods of treatment
Gastroenterologists, when prescribing medications, usually recommend not giving up the use of folk remedies to normalize the outflow of bile. Of the many known ones, it is worth focusing on a few of the most accessible and effective ones.
A good effect is observed if you take a mixture of equal parts of carrot juice, sweet apples, and beets for a month and a half. You need to drink this tasty and healthy remedy 1-1.5 hours after meals three times a day.
30-40 minutes before eating, it is useful to drink a glass of slightly warm water with a tablespoon of lemon juice or apple cider vinegar with a teaspoon of honey added to the solution. This drink not only makes bile flow more actively, but also strengthens blood vessels.
Experts consider fresh, unsalted lard to be one of the healthiest foods for a healthy liver. If you eat a piece (the size of half a matchbox) with a clove of garlic every day on an empty stomach, the biliary system will be adjusted to work effectively, and the toxins accumulated in it will be removed from the liver.
It must be remembered that any traditional method of treatment will give a positive result only if it is used in combination with drugs prescribed by a specialist.
Diet therapy
Whatever treatment for bile stagnation is carried out, it does not have the desired effect, if the patient does not adhere to the diet recommended by the doctor, attacks will occur again.
To avoid worsening the condition, a therapeutic diet No. 5 is prescribed. It implies a complete exclusion from the diet of rich meat and fish broths, fatty meats, and fried foods. You also need to forget about canned food and marinades, semi-finished products, and fresh baked goods.
The list of recommended products includes the following:
- fresh fruits and vegetables;
- lean meat, poultry, fish - boiled, stewed, steamed or baked;
- legumes
- nuts, pumpkin seeds, flax;
- vegetable oils - olive, pumpkin, sesame, rapeseed and flaxseed.
If you are prone to bile stagnation, it is important not to take long breaks between meals. It is better to eat throughout the day, keeping an interval of 2-3 hours, in small portions. Only in this case will bile be regularly excreted into the duodenum.
About the gallbladder
All elements of the human body must perform a single, coordinated job. We remember some of them at least sometimes - the heart, stomach, organs of the reproductive system, for example. And we think about some parts of a single system very, very rarely, only when they make themselves felt. Stagnation in the gallbladder is exactly the reason when a person thinks about the health of this unnoticed worker.
The gallbladder itself is a hollow organ, somewhat reminiscent of a bag - its elongated shape helps it “hide” under the liver. But despite its inconspicuousness and small size, the functionality of the gallbladder is very important for the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, and therefore for the entire body as a whole. The work of the organ is to collect, store and periodically release into the small intestine a secretion produced by the liver - bile. The quality of the digestive process, which means the body’s absorption of all the necessary components supplied with food, largely depends on the proper functioning of the gallbladder. Diseases of the organ, for example, cholestasis of the gallbladder, cause many health problems, ranging from painful sensations to lifelong use of special medications for the quality process of food digestion.
Why does intrahepatic and extrahepatic cholestasis develop?
The disease can occur for a number of reasons. Depending on the specific diseases against which bile failure may develop, cholestasis can be extrahepatic or intrahepatic.
The causes of extrahepatic cholestasis will be formations in the form of stones. Stones formed in the biliary system strictly affect the condition of the liver in the form of improper outflow of bile, improper or slow release of this fluid into the internal environment.
Alcohol becomes the most common enemy among patients. Alcohol abuse can lead to liver damage and a disorder of bile secretion such as cholestasis.
Other causes of cholestasis:
- Infection of the circulatory system;
- Side effects of medications;
- Liver cancer;
- Rejection reaction after transplantation;
- Ingestion of parasitic worms;
- Liver poisoning (intoxication);
- Tuberculosis.
The course of cholestasis can be either acute or chronic. In acute cases, all symptoms arise unexpectedly. Chronic cholestasis manifests itself gradually, step by step.
During the course of cholestasis, it is impossible to say with certainty that the manifestation of jaundice will be one hundred percent. There may not be any yellow skin color at all. It all depends on the causes of the disease.
Cholestasis mainly occurs due to the reasons described; metabolic disorders during pregnancy and heart failure should not be ruled out.
Manifestations of cholelithiasis in humans
Often this disease is asymptomatic in the early stages. What is undesirable for the sick person. The indicator does not mean that all patients will not complain about anything.
One of the most obvious signs of the presence of the disease will be the yellowness of the skin and the inside of the eye sockets. Patients may feel colic, also called biliary colic.
The manifestation of colic is reflected in the right upper abdomen. The localization of pain can be different and is determined depending on the age of the patient and the stage of progression of the disease.
Gastric symptoms that cannot be hidden will be signs of cholelithiasis progression: belching, heartburn, nausea, bloating.
General malaise, increased body temperature, lightened stools and loss of appetite play more than one role in the symptoms of the disease.