The reflex act of vomiting arose in the process of human evolution and is always preceded by nausea. Both nausea and vomiting are subcortical reflexes, therefore, they cannot be suppressed by willpower, and the human consciousness cannot control them. The main purpose of vomiting is to cleanse the body of toxins, poisons, and chemical compounds that have entered it from the outside or are produced by its own tissues and organs.
Vomiting is the release of stomach contents through the esophagus and oral cavity. It manifests itself in attacks that are caused by contractions of the abdominal muscles. Vomiting is accompanied by pain in the stomach, and the person becomes covered in sticky cold sweat. When vomiting, the larynx and soft palate rise, and the epiglottis descends, which protects the airways from vomit entering them.
The vomiting center, located in one of the ventricles of the brain, is responsible for the occurrence of this complex reflex. It is excited by an increase in intracranial pressure, exposure to impulses from the labyrinth of the inner ear, from mental stimuli, chemical reactions excited by the ingress of poisons, toxins, drugs into the blood, as well as by irritation of individual receptors in various parts of the body. The most sensitive receptors are located on the back wall of the pharynx; the peritoneum, mesenteric vessels, and bile ducts are also equipped with them.
Causes of nausea and vomiting:
Pathologies and damage to various parts of the central nervous system;
Food, drug, alcohol intoxication;
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
Very severe pain of any origin.
Vomiting is not a specific symptom, but assessing its characteristics in combination with other manifestations and studying vomit can greatly facilitate the diagnosis of diseases.
What disease may constant vomiting indicate?
There are various groups of diseases that occur with constant vomiting. Depending on the nature of its occurrence and characteristics, the disease is diagnosed:
Central vomiting – meningitis, migraine, hypertensive crisis, encephalitis, glaucoma, brain tumors and abscess, damage to the inner ear;
Psychogenic vomiting – hysterical neurosis, anorexia, attacks of cyclic vomiting in children;
Hematogenous-toxic vomiting - uremia, acetonemic vomiting in diabetes mellitus, porphyria, carbon monoxide poisoning, alcohol, drugs, cytostatics, radiocontrast agents, exposure to viral and bacterial toxins in infectious lesions;
Visceral vomiting – pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract (gastritis, peptic ulcer, duodenitis), diseases of the biliary and urinary tracts, acute appendicitis, pyloric stenosis, atony and gastric paresis;
Vomiting with a putrid odor – stomach cancer;
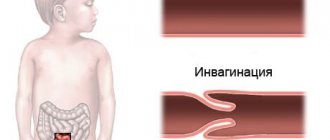
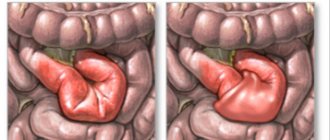
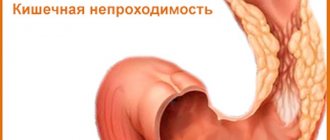
Vomiting with a fecal odor – intestinal obstruction;
Vomiting with bile – complications after surgery on the stomach, biliary colic, narrowing of the duodenum;
Vomiting with undigested food - gastric achylia, achalasia of the esophagus.
To clarify the diagnosis, a bacteriological, chemical, cytological study of vomit is carried out, the relationship of vomiting with food intake is studied (morning, early, late, fasting, night and cyclic vomiting).
Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
With this disease, a tumor develops in the pancreas, which produces large amounts of gastrin, a natural stimulator of gastric secretion.
With its increased amount, the content of hydrochloric acid also increases. The mechanism of vomiting is the same as during the development of gastric ulcer. Vomiting cannot be controlled with antiemetic drugs and requires surgical intervention. In addition to diseases of the digestive tract, vomiting can also occur with diseases of other organs. Most often it occurs with traumatic brain injuries (repeated several times and does not bring visible relief), severe cerebral strokes. Sour vomiting may indicate a decrease in stomach tone and excessive overeating (such vomiting is considered physiological and does not require the intervention of qualified specialists).
Why might there be water vomiting?
This type of vomiting is extremely rare, except for artificially induced vomiting during gastric lavage.
Causes of water vomiting in children:
Pathologies of the ear, nose and throat.
All these reasons are due to large amounts of mucus entering the stomach. It flows from the nasal and oral cavities through the throat and esophagus into the stomach. Irritation of its mucous membrane causes vomiting. The consequence of this is vomiting of water without impurities.
In the absence of visible causes of the disease, this symptom manifests itself due to excessive dry air, exposure to air in frosty weather, and also due to an allergic reaction. In this case, the release of a large volume of mucus is the body’s protective reaction to the negative influence of the environment. Then everything happens according to the algorithm described above - the mucus irritates the gastric mucosa, where it enters in excess quantities.
It is not difficult to eliminate this symptom in children; you need to create optimal living conditions and cure the pathology of the ENT organs.
If vomiting water is diagnosed in an adult, this may be due to long breaks between meals. Gastric juice is secreted reflexively, and the longer the interval between meals, the more juice is formed in the stomach. If a large amount of juice causes vomiting, it may seem like you are vomiting water. Visually, these liquids are almost indistinguishable from each other.
For various reasons, a person does not feel that he is hungry, however, the body needs food. This condition leads to excessive production of stomach acid and vomiting that looks like water.
Causes of nausea and vomiting with gastritis
Nausea with gastritis begins as a result of nerve endings that are located in the affected part of the gastrointestinal mucosa.
Due to this, the nerve transmits a certain signal, which provokes the need to cleanse the stomach.
Thus, the patient feels sick and after a while vomits. This process allows the mucous membrane to recover faster and better, and will also allow some time for the cells to rest, which are occupied by the secretion of gastric juice.
With gastritis with increased production of gastric juice, respectively, with increased acidity, nausea appears as a need to empty the stomach due to a large amount of acid.
Separately, it is necessary to say about pregnant women with gastritis. In the early stages of pregnancy, nausea appears as a result of significant changes in the body and hormonal levels.
Already at the end of the second trimester and the entire third trimester, gastritis becomes acute, after which women feel sick as a result of an enlarged uterus.
Due to its size, the uterus puts pressure on the stomach and solar plexus, causing severe attacks of nausea.
In addition to nausea, gastritis causes vomiting, heartburn and other unpleasant symptoms. Many people are interested in why they vomit with gastritis.
The reasons for this are the stimulation of the vomiting center and in women, a similar condition appears more often than in the male half of the population.
If there is gastritis, then nausea, and later vomiting, can make the patient feel better. Due to this, patients often induce vomiting artificially to alleviate the condition.
If nausea, sour belching and a taste in the mouth appear with gastritis, then this symptom indicates increased acidity in the stomach.
If nausea appears after eating or a short time after a meal, then this condition indicates acute gastritis.
Nausea in the morning
Quite often, with gastritis, patients experience attacks of nausea in the morning. As a rule, the phenomenon is typical for pregnant women during toxicosis.
At this time, the use of pills and other medications is prohibited, so for relief you can eat one sour apple and a few rye bread crackers.
To prevent attacks of nausea in the morning, it is better to leave the window open all night so that air can enter the room.
Morning sickness can be stopped if you use folk remedies; parsley and ginger root are very effective in combating this.
Can there be black vomit and is it dangerous?
Black vomiting may be a sign of a serious pathology or have a physiological cause. Some foods turn vomiting black: chocolate, berries with dark pulp, etc. Knowing about their consumption on the eve of vomiting, you can only focus on relieving this unpleasant symptom.
Diseases that cause bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract:
Neoplasms of any etiology (tumors, polyps);
Trauma to the mucous membrane of the stomach or intestines;
Ulcerative lesions of the stomach or small intestine;
Side effects of drugs that can cause damage to the stomach or intestines (Indomethacin, Aspirin, Ibuprofen, drugs, steroid hormones);
Vomiting due to peptic ulcer
A stomach ulcer can be localized in any part of the stomach. Its development is due to two interdependent mechanisms. The first of them is protective, under the influence of negative factors (hot food, large pieces, exposure to Helicobacter) provokes a decrease in the synthesis of protective mucus that envelops the surface of the gastric mucosa. The second mechanism, an increase in acidity, depends on the same factors that lead to a decrease in protective properties. As a result, there is an increase in the acidity of gastric juice due to increased secretion of hydrochloric acid.
The so-called irritable stomach syndrome develops, which leads to stimulation of autonomic nerve fibers, irritation of the vomiting center, transmission of nerve impulses to the diaphragm and abdominal muscles and subsequently to vomiting. A characteristic feature of vomiting in peptic ulcers is sour contents, and vomiting itself does not bring relief. It appears almost immediately after eating (up to 10 minutes).
What disease can cause a temperature of 38 and vomiting?
Diseases in which there is a combination of vomiting and high fever:
Acute respiratory viral infection;
In the vast majority of cases, these symptoms are observed precisely during gastrointestinal infections. Children may react by vomiting to a rapid increase in temperature during any inflammatory process.
The initial manifestations of an intestinal infection and a viral disease are very similar: in both cases, hyperthermia, redness of the throat, and vomiting are observed. Specific symptoms appear a little later.
Strong smell of feces due to intestinal diseases
If a person feels well, but periodically notices that the excrement has a foul odor, it is necessary to examine the intestines to rule out diseases. First, you should take a stool test for helminths (including scraping for enterobiasis) and a coprogram. These studies will make it possible to determine the chemical composition of feces, detect signs of an inflammatory process and identify possible disorders in the digestive processes (for example, during inflammatory processes, an increased amount of detritus is detected in the feces).
After receiving the results of laboratory diagnostics, the doctor will make a preliminary diagnosis and prescribe additional examination, if there are indications for this. Secondary diagnostics may include hardware and instrumental methods, for example, colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, ultrasound or irrigoscopy. In some cases, a consultation and examination by a proctologist may be required to make an accurate diagnosis.
Intestinal inflammation (colitis and enteritis)
The human intestine consists of two sections: the large and small intestine. The small intestine is located immediately after the stomach, and its inflammation is called enteritis. Inflammation of the epithelial lining of the large intestine is called colitis and occurs in every fourth patient with diseases of the digestive system. Foul-smelling feces in an adult are characteristic mainly of chronic colitis, since acute forms of the pathology occur with severe symptoms, and their clinical picture is similar to the symptoms of intestinal infections.
Chronic inflammation of the small or large intestine can occur for several reasons, including food and drug allergies, dietary errors, alcohol abuse, and smoking. Tumors in the intestines can also provoke an inflammatory process, so preventive endoscopic diagnosis is indicated for all people, regardless of their health, at least once a year.
Signs of chronic colitis or enteritis are:
- painful intestinal spasms accompanied by bloating and flatulence;
- bloating and pressure in the central or lower abdomen;
- nausea (rarely vomiting);
- unpleasant, pungent odor from excrement;
- bowel disorders.
Treatment of both pathologies involves a therapeutic diet (table No. 4 according to Pevzner), physiotherapy, and massage. Drug correction may consist of symptomatic drugs (carminatives based on simethicone, antispasmodics, antidiarrheal or laxative drugs), antibiotics. Also, patients are necessarily prescribed drugs that accelerate the healing of damaged mucous membranes ( Methyluracil
»).
Important!
If the inflammation occurs as a result of circulatory disorders in the intestinal vessels, the patient is additionally prescribed medications to prevent thrombosis (antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants).
Intestinal candidiasis
Fungi of the genus Candida are opportunistic microorganisms, that is, they are normally present in the human microflora, but in small quantities, which does not allow the development of a fungal infection. If the body's protective functions are weakened, Candida begins to actively multiply and secrete toxins that cause acute intoxication and poison the intestines.
It is almost impossible to detect intestinal candidiasis without laboratory diagnostics, since there are usually no specific symptoms for this disease. The main manifestations of intestinal thrush are associated with changes in bowel movements and the appearance of stool. The patient may be bothered by frequent false urges to have a bowel movement, pain of varying intensity in the lower abdomen, and stool disorders. Feces with candidiasis become foul-smelling, it may contain white particles similar to cottage cheese, as well as a small amount of grayish mucus. Other symptoms of the disease include:
- lack of appetite that occurs against the background of moderate nausea (in rare cases, single vomiting is possible as signs of intoxication of the body);
- itching in the anal ring during bowel movements;
- rumbling in the stomach;
- intestinal cramps;
- flatulence;
- flatulence syndrome (“explosive” release of large amounts of odorous gases).
Treatment of candidiasis is carried out with the help of antifungal drugs (in oral dosage form). Their list is given in the table below.
Antimycotics for the treatment of intestinal thrush in adults
| Name of medicine | Image | Application regimen and dosage |
| 1 tablet 4 times a day for 7 days. Additionally, apply “Pimafucin” in the form of a cream to the anal area 1-2 times a day | ||
| 400-800 mg per day for 1-2 weeks | ||
| 1 tablet 3-4 times a day for 7-10 days |
To speed up the colonization of the intestinal mucous membranes with beneficial microflora and restore digestion, the use of prebiotics is indicated. During the period of treatment, you should limit your consumption of sugar, fatty foods, and foods that promote fermentation and decay.
Can antibiotics cause vomiting?
Antibiotic drugs have a large number of side effects, and vomiting occurs when using these drugs along with other symptoms.
Causes of vomiting while taking antibiotics:
Vomiting is a side effect of a specific drug;
There is incompatibility of the antibiotic with concomitantly taken medications from other pharmacological groups;
Dietary disturbances or alcohol consumption occurred during antibiotic therapy.
The occurrence of vomiting directly depends on the form in which the drug is taken. Antibiotics in tablet form are more likely to cause vomiting than the same drugs given in injection form. You should not refuse a particular medication if oral use causes vomiting. It is worth trying intravenous or intramuscular administration. Adjusting the dosage to reduce the volume or frequency of taking the medication will reduce the risk of this unpleasant side effect, but at the same time the effectiveness of the treatment may suffer.
Antibiotics that may cause vomiting:
Ciprofloxacin (Tsiprobay, Tsiprinol, Tsiprolet);
In the process of evolution, humanity developed reflexes and reactions. One of the not very pleasant ones is dyspeptic disorders of various kinds. Usually these states arise together, complementing each other.
Vomiting and nausea are reflexes that cannot be suppressed or controlled consciously. They are necessary to cleanse the body of toxins and harmful substances. Appearing once, they become a consequence of poisoning or a side effect of taking medications. When it occurs regularly, nausea, accompanied by the eruption of stomach contents, often indicates pathologies of the digestive tract.
The smell of feces has changed: possible reasons
If a person eats right, but the stool has become foul-smelling, the cause may be disturbances in the functioning of the body that arise from internal pathologies or exposure to external factors.
Microflora disturbance
A condition in which the balance of beneficial and opportunistic microorganisms in the intestines is disturbed is called dysbiosis. Opportunistic pathogens are bacteria that are normally present in the human body in small quantities, but are in a latent state and do not cause harm to the body. When unfavorable conditions are created, opportunistic colonies begin to grow rapidly, which leads to intestinal infections, gastroenteritis and infectious intestinal colitis. Beneficial bacteria support normal digestion, take part in the formation of systemic and local immunity and increase the body's resistance to pathogens.
In almost 70% of cases, intestinal dysbiosis develops against the background of antibacterial or antimicrobial therapy, because drugs in this group destroy not only pathogenic but also beneficial bacteria. Pathology can be recognized by the following symptoms:
- changes in the odor and consistency of stool;
- flatulence, a feeling of bloating and distension in the intestines;
- rumbling in the stomach between meals;
- bad breath;
- frequent false urge to defecate.
In some cases, against the background of severe dysbacteriosis, a person may develop a skin rash, acne, and pimples. The smell of feces becomes fetid due to the prevailing pathogenic flora and their waste products.
To treat dysbiosis, a diet containing a large amount of fermented milk products (they contain lactobacilli necessary for the immune system) and plant fiber (cereals, vegetables, fruits) is prescribed. Drug treatment consists of taking bifid drugs (“ Bifidumbacterin
", "
Narine
", "
Normobact
", "
Lactofiltrum
").
Food allergies
Allergies to certain foods can also cause human feces to suddenly develop a strong odor. The most popular food allergens are:
- honey and bee products;
- cow's milk (allergy is caused mainly by milk proteins - lactoglobulins);
- Fish and seafood;
- citruses;
- chocolate and products with added butter or cocoa beans.
Food allergies can manifest themselves in different ways. The most typical skin manifestations are itching, rashes, dryness and flaking. Symptoms from the gastrointestinal tract are also possible: dyspepsia, pain in the abdominal area, diarrhea, flatulence. In clinically severe forms of food allergy, systemic signs of allergy are added: lacrimation, runny nose, sneezing, laryngospasm.
Allergy treatment is a long process. The initial stage is a comprehensive diagnosis, which includes immunological tests and tests to identify the allergen. Symptomatic therapy is carried out using histamine blockers ( Claritin
", "
Suprastin
", "
Tavegil
", "
Loratadine
"). Full recovery requires cleansing the intestines of waste and toxins, as well as special therapy, which consists of introducing microdoses of the allergen under the skin. This method allows you to develop stable immunity, as a result of which the body ceases to recognize the allergen as a foreign agent.
Enzyme deficiency
Enzymopathy is a pathology in which the production of digestive enzymes necessary for the absorption and breakdown of certain products is partially or completely stopped. It can be congenital or occur as a result of various disorders in the functioning of internal organs. One of the forms of fermentopathy in adults is lactase deficiency - a lack of the enzyme responsible for the absorption of milk sugar. Symptoms of lactase deficiency in patients over 18 years of age may include abdominal pain, foamy or watery stools with a strong, foul odor, and weight loss associated with poor absorption of milk protein.
All signs of pathology appear mainly after consuming fermented milk products or products based on whole cow's milk. It should be noted that true lactase deficiency is rarely diagnosed - such patients are forced to adhere to a special diet throughout their lives that excludes dairy products. Temporary lactase deficiency is treated with enzyme preparations (“ Lactazar
», «
Lactase
»).
Causes
Why people vomit cannot be answered immediately. To determine the cause, you need to see a doctor and undergo an examination. Regular nausea accompanies pathologies of the digestive tract such as:
- ulcer;
- gastritis;
- Zollinger-Ellison syndrome;
- stenosis;
- change in the acidity of gastric juice, increased secretion.
Irritation of the stomach walls with acid or food, an acute inflammatory process, back waves and reflux of contents into the esophagus - this is what provokes nausea, which ends with vomiting.
Often the appearance of unpleasant symptoms occurs due to infection. Viruses and bacteria are pathogens that affect the gastrointestinal tract. They enter the body with food, water, are carried with dirty hands, and a few are even transmitted by airborne droplets. With these diseases, a person feels sick and then vomits. After the stomach is empty, temporary relief occurs.
Also, the causes of discomfort may be the following:
- neurological diseases (brain injury and infection, migraine, tumors);
- disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system (hypertension, heart attack, functional failure);
- pathologies of the endocrine system (diabetes, thyrotoxicosis, phenylketonuria);
- psychological (fear, panic attack);
- vestibular (sea sickness).
Vomiting occurs when the contents of the stomach are expelled through the esophagus. It is impossible to stop this process or restrain the urges. The masses may have a sour, unpleasant odor, be accompanied by the release of blood, putrefactive impurities, or be watery. In case of poisoning and gastric pathologies, an eruption of undigested food is observed.
Causes of nausea
With gastritis, during the inflammatory process in the gastric mucosa, swelling and damage to its cells occurs. When the stomach is filled with food, additional irritation of the mucous membrane occurs, which immediately begins to react in response. Nerve endings passing through the entire thickness of the walls of the stomach send impulses to the brain in order to give the body an “instruction” to empty the gastric sac of accumulated food chyme. Thus, the mucous membrane itself tries to protect itself from the factor that has entered into its work and recover more quickly from the inflammation it has suffered.
If gastritis occurs with increased production of gastric juice, then there is a need to remove excess hydrochloric acid. Relieve this condition by vomiting. Nausea is often a precursor to vomiting. As a rule, it brings noticeable relief for gastritis. For this reason, people suffering from stomach diseases, after overeating and feeling unwell, artificially induce vomiting in an attempt to alleviate it, which is extremely undesirable.
It is quite common to experience nausea after eating.
By the nature of nausea and vomiting, you can determine the types of gastritis:
- if you feel sick and vomit immediately after eating, then this is a clear sign of acute gastritis;
- periodic nausea after eating or taking medications indicates the presence of a chronic process in the digestive organs;
- nausea and vomiting with a sour taste, especially in the morning, indicates increased acidity of the stomach.
You should not turn a blind eye to these health problems. Vomiting, although it brings relief, can also dramatically worsen your health. The fact is that all consumed liquid leaves the body with vomit, which can quickly lead to dehydration. Also, when vomiting, food does not have time to be processed in the stomach, which means that nutrients, vitamins and necessary microelements do not enter the blood. The cells of the body do not receive energy to work, which leads to loss of strength and poor health.
Constant vomiting causes loss of energy
Remedies
If a patient regularly vomits stomach acid, he should definitely undergo examination. Depending on the type of pathology, suitable treatment is prescribed. Pharmaceutical products are also used to prevent attacks:
- for motion sickness - AviaMore, Dramamine, acupuncture bracelets;
- neuroleptics and tranquilizers - Phenazepam, Etaperazine, Aminazine;
- dopamine antagonists – Cerucal, Metaclopramide;
- antiemetics - Motilium, Domperidone;
- against poisoning - Smecta, Polysorb.
Causes of vomiting
As we already mentioned in the article, vomit can be of different colors and shades, depending on its contents. But the contents are determined by various causes of this dysfunction of the body.
Let's look at them and find out what causes vomiting:
— poisoning (food, alcohol, medication, drugs); - food allergy to a particular product; - severe overeating; — various infections (typhoid, scarlet fever); — excess of toxic substances in the blood (intoxication); - pregnancy;
- diseases of the abdominal cavity (gastritis, ulcers, stenosis, tumors of the stomach and intestines, renal failure, duodenitis, pancreatitis, appendicitis); - mechanical obstruction of the small intestine; - diseases of the gallbladder and liver (hepatitis, cholelithiasis, cholecystitis, dyskinesia of the gallbladder, blockage of the bile ducts); — cleansing the body of harmful substances (self-defense of the body); — emotional stress (fears, depression, worries); — dysfunction in the nervous system (poor blood circulation in the brain, head injury, meningitis, migraine, brain tumors); - irritation of the vestibular apparatus (sickness, dizziness); — diseases of the cardiovascular system (arterial hypertension, myocardial infarction); - diabetes; - AIDS, cancer.
Diagnostics
Vomiting feces indicates severe pathological damage to the digestive system. Therefore, he is referred to a surgeon for examination. In some cases, the patient’s condition is so unsatisfactory that it is possible to carry out the entire range of diagnostic procedures, which is why they are limited to only basic measures. Standard list of studies for vomiting intestinal contents:
- X-ray examination. A survey X-ray of the abdominal cavity is performed, which can reveal signs that indicate intestinal obstruction. These include: transverse striation of the intestine, Kloiber cups. X-rays with contrast are not used in emergency situations.
- Sonographic examination. Ultrasound examination of the colon can determine the presence of diffuse thickening of the walls and the degree of expansion of the lumen. In addition, ultrasound allows you to assess the contractile activity of intestinal loops and demonstrate characteristic motility. If peritonitis is suspected, ultrasonography is performed to check for the presence of free fluid.
- Blood analysis. In case of pathology, the analysis can detect a decreased level of hemoglobin and an increased level of ESR and leukocytes. With an infectious cause of the onset of pathology, a sharp predominance of neutrophils is noted in the analysis. A biochemical blood test for pathology reveals a violation of the water-electrolyte balance and an increase in urea. The presence of creatine also indicates the development of renal failure.
Blood test - a method for diagnosing fecal vomiting
Symptoms of vomiting
- acute and constant pain in the abdomen; - dry mouth; - dehydration of the body; - heartburn; - intense urination; - headache; - dizziness; - disturbances in mental or functional activity; - general weakness.
Sometimes vomiting may be accompanied by an increase in body temperature.
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience the following symptoms:
- vomit contains blood; - nausea and vomiting began after receiving a head or abdominal injury; - there is a sharp deterioration in health; - there is severe vomiting that does not stop; - with vomiting in older people.
Bowel diseases with vomiting
- Food poisoning: Diarrhea, abdominal cramps, nausea and vomiting may indicate food poisoning. Triggers are toxins that are absorbed through food. Most often these are poisonous bacteria (for example, salmonella or staphylococcus), sometimes toxins of other organisms (for example, mushroom poisons) or chemical poisons (lead, copper, zinc, etc.).
- Other poisonings: Nausea and vomiting may also occur with other poisonings, such as poisoning from drugs, carbon monoxide, or pesticides. If you suspect poisoning, you should immediately call a doctor!
- Alcohol and Nicotine: Alcohol and nicotine are toxins to the body. In mild cases, with small doses, nausea, vomiting and nervousness occur. In case of severe alcohol or nicotine poisoning, convulsions and disturbances of consciousness (sometimes coma) are possible. In such cases, you should consult a doctor immediately!
- Caffeine: Large amounts of caffeine (coffee, caffeinated energy drinks, etc.) can cause nausea, vomiting, nervousness and sweating, as well as problems concentrating.
- Drugs: Drug overdose, as well as unavailability of drugs in the context of existing drug addiction, can cause nausea, vomiting, confusion, increased agitation, coma, and possibly severe anxiety and seizures. Call an emergency doctor immediately!
- Acute abdomen: This is a threatening complex of sudden onset symptoms - severe abdominal pain, abdominal wall tension, as well as autonomic symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, sweating, palpitations and a drop in blood pressure.
- A strangulated hernia: The first signs are sudden severe abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting. The hernia is hard, painful and can no longer be pushed back into the abdominal cavity. You should consult a doctor immediately!
- Peritonitis: develops, for example, with gastric rupture, appendicitis, mechanical intestinal obstruction and acute inflammation of the pancreas. Signs of acute abdominal syndrome appear: nausea, vomiting, rapidly increasing, sharp abdominal pain, acute abdomen, cold sweat and palpitations, often anxiety and fever. Contact your doctor immediately!
- Food intolerances: Nausea and vomiting after eating certain foods may indicate a food intolerance. For example, milk intolerance (lactose intolerance), fructose intolerance, cow's milk intolerance and celiac disease (gluten intolerance). Abdominal pain, diarrhea and/or bloating are common with these conditions.
- Stomach overload: After eating too much or too quickly, the body often reacts with a feeling of fullness, nausea and vomiting.
- Inflammation of the gastric mucosa (gastritis): a characteristic feature is the appearance of nausea after eating, often accompanied by vomiting, belching, as well as pain and/or a feeling of pressure in the stomach.
- Stomach/duodenal ulcer (peptic ulcer): May cause nausea, vomiting, belching, loss of appetite, and pain and/or pressure in the stomach before eating.
- Stomach cancer (gastric carcinoma): manifests itself as an unpleasant odor, abdominal pain, aversion to certain foods (especially meat), nausea, a feeling of fullness, loss of appetite, and weight loss.
- Stomach rupture (gastric perforation): Both stomach ulcers and stomach cancer can cause the stomach wall to tear, resulting in a connection to the open abdominal cavity. Such perforation of the stomach is manifested by sudden pain, which often radiates to the left shoulder. The abdominal wall becomes hard, nausea and vomiting appear.
- Appendicitis: Appendicitis causes nausea, vomiting and rapidly increasing pain that extends from the navel to the lower right side of the abdomen. If you have severe pain or a hard abdomen (acute abdomen), you must call an ambulance! In addition, the patient should not eat or drink!
- Infectious diarrhea (intestinal infections): inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract can be caused by viruses or bacteria (less commonly parasites), which can lead to nausea and vomiting, severe diarrhea, and abdominal pain.
- Intestinal obstruction (ileus): Causes nausea, vomiting, rapidly increasing, sharp abdominal pain and a sharp abdomen. You should call a doctor immediately!
Treatment of vomiting
What to do if you vomit? In most cases, vomiting goes away on its own. But if the cause of vomiting is any infectious or other disease, it may have to be treated with medication.
In any case, if you are vomiting, it is better to consult a doctor, especially if the vomiting does not stop within 48 hours or the vomiting is a consequence of chronic diseases.
1. Place the patient in bed, or on another plane, so that the body assumes a horizontal position. Pay attention to the fact that when vomiting, the patient can turn freely and vomit the capacity of the stomach into some container;
2. If the patient is too weakened, when vomiting, help him turn his head to the side so that he does not choke on the vomit;
3. After vomiting, give the patient slightly warm ordinary water to rinse the mouth. Rinsing the mouth with disinfectants has a particularly beneficial effect, for example: 2% sodium bicarbonate solution or potassium permanganate (potassium permanganate);
4. After vomiting, wipe the patient’s lips and corners of the mouth;
5. If the vomiting is not prolonged, you do not need to take medications, just provide the patient with peace.
6. To stop vomiting, the victim can be given mint drops or a piece of ice, otherwise the following medications.
Antiemetic injections (administered intravenously or intramuscularly): m-anticholinergic blocker (0.1% atropine solution: 0.5-1 ml), antispasmodic (2% no-spa solution: 2 ml).
Diagnosis of fecal vomiting
The doctor conducts an external examination, which reveals that the intestines in the abdominal area are clearly visible - they bulge noticeably. In addition, you can hear the rumbling of the stomach during acute attacks. Also during the examination, the presence of local swelling, which is called Wahl's syndrome, is revealed.
Analyzes
After a diagnostic examination, the doctor should prescribe urine and blood tests for a general analysis.
Instrumental diagnostics
Instrumental diagnostic procedures are also prescribed.
An ultrasound and x-ray examination is required. An ultrasound examination allows you to find out the diameter of the intestinal loops, as well as identify the presence of accumulated free fluid inside the abdominal cavity - these factors confirm the diagnosis.
The department of surgery may perform a repeat X-ray examination to study the passage of barium through the intestines. Barium suspension can be seen during fluoroscopy, making it possible to determine the level of obstruction and assess how the disease progresses. Emergency irrigoscopy (barium enema) allows you to identify the cause of pathology in the colon. In this case, the colon is completely filled, after which its condition is assessed using fluoroscopy.
Colonoscopy - during this procedure, the colon is cleansed, and then an endoscope is inserted into it through the anal entrance, with the help of which the organ is examined from the inside. This method allows you to identify tumors, take a sample for a biopsy and perform intubation at the site of narrowing - this action will relieve the patient from the manifestations of an acute form of intestinal obstruction. Thanks to these procedures, surgery due to cancer will be performed in more comfortable conditions.
If it is very difficult to diagnose the disease, a laparoscopy procedure is performed - an endoscope is inserted through a puncture on the anterior abdominal wall, which allows one to examine the internal organs.
What to do after vomiting?
During the urge and after vomiting, it is advisable for the patient to observe some bed rest so that the body relaxes, diet, and also restore lost fluid.
1. If you vomit, stop eating for several hours to give your stomach a break from working. Eating, incl. Drinking fluids can be started when symptoms stop and the urge to vomit;
2. After vomiting, you need to start by drinking, often, but in small doses. For drinking, it is best to use non-carbonated mineral water, low-fat broth or sweet tea.
3. It is strictly not recommended to consume dairy products, caffeinated products, alcoholic beverages, citrus fruits, as well as medications based on ibuprofen or aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid);
4. Eating can be started 6-8 hours after the last attack of vomiting, as well as when the symptoms of this disorder decrease. You should also eat in small portions. You can start your meal with the following foods: vegetables, lean meat, rice, cereals, bananas, bread;
Avoid eating spicy, fatty and fried foods for 48 hours;
What to do if you vomit?
If nausea and vomiting are accompanied by symptoms of a medical condition that requires treatment, you should consult a doctor.
But what should you do about nausea and vomiting in harmless cases, such as in the car, fever, stomach flu or during pregnancy? In such situations, you can take steps to alleviate the condition:
- you should refrain from eating for at least one day or at least limit the amount;
- drink sweet tea with a small amount of wheat crackers;
- eliminate alcohol, caffeine, raw, fatty foods, and hot spices for a while.
If nausea is accompanied by vomiting, you need to drink plenty of fluids (at least two to three liters per day).
You can purchase special formulations at the pharmacy that will restore lost electrolytes and prevent fluid loss from the body.
- For nausea during pregnancy, it is best to have breakfast in bed in the morning.
- Food should be light.
- Eat small carbohydrate-rich meals throughout the day.
- Avoid spicy and fatty foods, coffee, black tea, and carbonated drinks.
Treatment of vomiting with folk remedies
Mint. An excellent soothing remedy against vomiting is mint or mint tea. To make tea, simply pour boiling water over a teaspoon of mint and cover the container with something to steep the tea. You need to drink tea in small sips. If the mint is allowed to brew for 6 hours, then it can be taken 3 times a day, 1 tbsp. spoon. This tincture will be an excellent post-emetic remedy that restores the mucous membrane and walls of the stomach.
Mint drops. If attacks of nausea with vomiting are caused by stress, then the patient can simply be given 10-15 drops of mint tincture diluted in 1 tbsp. spoon of water, then remove the victim to fresh air.
Dill. Pour 1 teaspoon of dill seeds into a glass of boiling water. Let the product brew, then use it, like mint, in the form of tea.
Maple. Dry the maple leaves well, chop them, then pour 1 tbsp. a spoonful of cooked leaves with a glass of boiling water. Next, keep the broth for 30 minutes in a water bath, but do not bring it to a boil. Then strain the product and let it cool. Take 50 ml 3-4 times a day.
Lemon. Add lemon zest juice to plain water and just drink it.
Melissa. 2 tbsp. Pour a glass of boiling water over spoons of thoroughly dried and crushed lemon balm. Leave the product to sit for 2 hours. Drink 100 ml infusion before meals.
Potato. An excellent sedative and antiemetic is potato juice, which should be taken before meals, half a tablespoon.
Asparagus. To calm the stomach and reduce the urge to vomit, take a remedy from 1 g of asparagus powder (sold in pharmacies) dissolved in a glass of warm water. The product is drunk immediately after stirring.
Pregnancy. For nausea and vomiting in pregnant women, it is recommended to eat split meals. In the morning – crackers and water with lemon juice. Add grated ginger root to your dishes. To calm your nervous and mental systems, drink green tea.
Treatment of nausea with gastritis
Nausea with gastritis can be eliminated only with the help of correct and systematic treatment prescribed by a doctor.
Diet
The leading role in therapy is given to nutrition. You can take table No. 2 as the basis for your diet, which is important to adapt to your own taste preferences. Eating should be enjoyable, otherwise getting rid of nausea will be problematic.
The menu for gastritis during an exacerbation should include:
- porridge with water;
- lean varieties of fish and meat;
- baked apples;
- boiled vegetables.
It is strictly forbidden to consume fried, salted, smoked food, canned food, fast food and alcohol. In order for the pathology to remain in remission, it is recommended to adhere to such a diet constantly.
To receive specific nutritional recommendations based on the stage and type of disease, you should consult a physician or gastroenterologist.
Medicines for nausea
Drug therapy for gastritis can be divided into two categories: the first suppresses nausea, that is, it has a symptomatic effect. The second – protects the mucous membrane of the organ from damage, thereby preventing attacks of nausea.
Anti-nausea drugs that block the vomiting center can be found in pharmacies under the following names:
- Zoloft;
- Metoclopramide;
- Cerucal.
Medicines to protect the gastric mucosa work by forming a protective membrane inside the organ cavity and reducing the acidity of gastric juice:
- Omeprazole;
- Nexium.
As a rule, both groups of drugs are used in therapy.
Traditional methods for nausea
Traditional methods help cope with attacks of nausea in the chronic form of gastritis, when the symptom is mild and not accompanied by vomiting.
- The most famous and effective remedy against nausea is freshly squeezed potato juice, which is drunk on an empty stomach (about 100 ml) for 20 days. The effectiveness of the method is based on reducing the acidity of gastric juice.
- A well-known folk remedy for neutralizing nausea is lemon juice, but it is not recommended to use it if the stomach has high acidity. For gastritis, it is necessary to consume citrus juice not in its pure form, but as part of tea.
- Peppermint tea effectively reduces nausea. The drink can be replaced with regular tea.
Before using any traditional treatment method, you should consult your doctor.