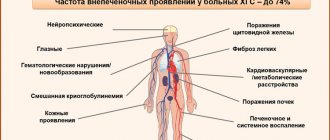
Today, almost every person is at risk of infection with HCV. The disease is rarely characterized by gender characteristics of the clinical picture. Therefore, the signs of hepatitis C in men and women are basically the same. However, sometimes there are certain differences in symptoms that you need to be aware of.
Despite the same transmission routes, similar clinical picture, and completely identical therapy, HCV infection is diagnosed much more often in men. Experts associate such statistics, in particular, with an increased risk of infection during homosexual intercourse (anal sex) without using a condom, inattention to hygiene rules, and a number of other socio-psychological factors.
How does hepatitis C manifest in men? Often information differs from one source to another. This is due to the variability of clinical signs. In some representatives of the stronger sex (especially those who adhere to a healthy lifestyle and diet, without bad habits), the pathology does not make itself felt for many years and is diagnosed by chance during a routine medical examination. In others, the disease manifests itself with clear signs, including jaundice and pain in the liver. It is impossible to predict the course of viral hepatitis C.
How can you get infected with a virus?
Hepatitis C is transmitted parenterally, through the blood. To infect a person, only 0.0001 ml of infected biological fluid is enough. Moreover, the virus does not lose viability for a long time when it dries out, during freezing and at low temperatures.
All objects and instruments that come into contact with contaminated blood are dangerous. This could be medical instruments, nail scissors, tattoo machines. It is possible to become infected with the virus through sexual contact with an infected partner, but this route of transmission is much less common.
In 5% of cases, the virus is transmitted in utero, and only from an infected mother. Contact and household transmission of HCV is very rare: in conditions of complete unsanitary conditions, in drug-dependent families and large prison cells.
More and more hepatologists and infectious disease specialists are inclined to argue that to date, all possible methods of HCV infection have not been studied and that the infection in some cases can be transmitted by blood-sucking insects.
Routes of infection
The incidence of hepatitis B is becoming widespread throughout the world.
According to the latest data, about two billion people on the planet are infected with HbsAg (the main pathogenicity factor): most of them are carriers of the virus, a smaller part (350 million) have clinical manifestations of liver damage. Hepatitis is an anthroponosis: you can only get infected from a sick person or a virus carrier. The mechanism of transmission of HBV is parenteral, associated with the content of viral particles in all biological fluids - blood, semen, vaginal secretions and, to a lesser extent, in saliva and urine.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wsxxRBJkNE0
There are three main routes of transmission:
- parenteral – for medical and cosmetic operations accompanied by a violation of the integrity of the integumentary tissues (provision of dental services, injections, blood transfusions, manicures, etc.);
- sexual – with unprotected sex;
- household - with the general use of individual hygiene items (razors, washcloths, bath accessories, manicure instruments).
Note! There is a high risk of transmission of the virus through close contacts. In families where a virus carrier permanently resides, infection of loved ones usually occurs within several years.
Greater chances of becoming infected with hepatitis B are associated with:
- high contagiousness (infectivity) of the virus for humans - even a minimal amount of the pathogen can cause an infectious process in the body;
- stability of the virus in the environment - biological material containing viral particles is able to retain its pathogenicity for 5-7 days (even after complete drying).
Transmission of the pathogen is possible in several ways:
- direct contact with the blood;
- from an infected mother to the fetus through the placental barrier;
- during sexual intercourse.
Infected men who do not use barrier contraception infect women through seminal fluid. Women's vaginal secretions contain viruses in concentrations at which infection is possible.
The virus easily adapts to the external environment and remains active in dried blood components and wound exudate for a week. It remains on a toothbrush, razor, towel. When another person gets into the wound, infection occurs. Drug addicts transmit the virus through contaminated needles.
The risk of infection remains if the skin is accidentally damaged by a used syringe. Clandestine tattooing with raw instruments is common among young people. In the last decade, the disease has been diagnosed in patients aged 20 to 50 years, the majority are men. This is associated with their increased incidence of injuries in urban environments and at work.
Vaccines have been developed for hepatitis B. After a course of injections, antibodies are produced in the blood. If there is a high risk of infection or contact with a virus carrier, it is better to get vaccinated. After the first dose, 90% develop immunity within a week. To consolidate the result, a second injection is given after a set time interval.
When vaccination is contraindicated, it is necessary:
- use only individual personal hygiene items;
- choose licensed dental and medical centers;
- visit salons providing services related to skin damage with caution; the client has the right to check how instruments are disinfected;
- reduce the risk of casual sex;
- periodically undergo testing for the presence of hepatitis B antigens;
- give up bad habits that lead to loss of self-control.
The virus carrier undertakes to take precautions towards others in order to protect them as much as possible.
If you follow the doctor's recommendations, complete recovery from the virus occurs within 3-6 months. Failure to follow a diet and alcohol consumption aggravate the course of the disease. It becomes protracted or chronic.
Hepatic encephalopathy is a dangerous complication of the disease that occurs against the background of the development of cirrhosis. In 10% of cases, the cause of necrotic degeneration of the liver is hepatitis.
With prolonged illness, cancer cells develop. Hepatitis B is dangerous, even if it occurs in a latent form, without symptoms. The chronic form threatens relapses. With lightning-fast flow, death is possible.
Hepatitis can only be contracted from a sick person. The virus is released into the environment with feces, contaminates water, and settles on food and household items. Therefore, there are 3 transmission routes:
- Water. Hepatitis A is transmitted through water contaminated with the virus. This is the main route of infection and is characterized by outbreaks. You can get sick if you drink unboiled water, brush your teeth with it, swim in pools, natural reservoirs, wash dishes, and food without further heat treatment.
- Food. Infection occurs when a person shares dishes with a sick person, eats the same food, does not wash fruits and vegetables well, or eats them raw.
- Contact. The infected person touches objects through which the virus is transmitted to others. Therefore, infection is provoked by direct contact with the patient, the use of shared towels, toothbrushes, and lack of disinfection of toilets.
Infection is possible at home and in public places - in cafes, canteens, toilets. The risk of getting sick increases when sewage breaks into the water supply. More often, infection occurs in the summer, when the consumption of fresh fruits and vegetables increases. They must be washed with warm water - boiled or purified. Theoretically, there is also a transmissible route of transmission, through the bite of a person by a louse, mosquito, or tick. However, such cases are not documented.
Through contact with an infected person, the virus can easily enter the body, although the first symptoms in men appear after a few weeks. This is why prevention is so important:
- compliance with the rules of personal hygiene - wash your hands after using the toilet, after going outside, using soap, preferably antibacterial;
- wash vegetables and fruits before eating;
- If there is a sick person at home, clean the toilet and dishes with disinfectants.
When going to a region where the incidence is high, you need to pay special attention to the prevention of hepatitis:
- It is advisable not to travel to remote areas and villages, where the likelihood of water and food becoming infected increases;
- do not eat raw vegetables, fruits, shellfish if there is a suspicion of non-compliance with storage conditions and sanitary standards;
- cook your own food.
To be sure to avoid infection, you should get vaccinated. Hepatitis vaccines are safe and suitable for children aged 2 years and older and adult men and women.
In case of a sewer break or direct contact with the patient, the disease can be prevented by administering immunoglobulin. If you do this within 15 days, the body will fight the virus on its own. In regions with unfavorable sanitary conditions, immunoglobulin injections are also given in autumn and winter, which provides short-term protection.
The first signs of viral hepatitis C in men
The first signs of hepatitis C in men appear in laboratory tests. Specific symptoms of a viral disease, which in most cases are mild, force you to undergo a diagnostic examination. But if you are especially attentive to your own health, you will certainly notice what changes are occurring in the functioning of almost all internal organs. This is manifested by chronic fatigue, weakness, and decreased tolerance to previously habitual physical activity.
External manifestations
External signs of hepatitis C in men, especially in the initial stage, may be absent. This fact explains the large number of transitions from acute to chronic forms of the disease. The disease does not make itself felt in the early stages, which entails a lack of treatment.
The very first sign of hepatitis C is darkening of the urine. At first, only morning urine acquires a dark color, reminiscent of beer, then the dark shade remains almost unchanged throughout the day.
After 1–3 days, stool becomes lighter, which indicates the progression of the pathological process. The stool may be almost white, despite eating the day before. And last but not least, jaundice appears - the most striking external sign of infection. It can only cover the part of the eye sclera hidden by the lower eyelid, then the sign of the disease goes unnoticed. In more severe cases, the eyes and the whole body, especially the palms and feet, turn yellow. On the Internet you can find enough photos of patients who have been diagnosed with acute viral hepatitis C, with a typical appearance.
Laboratory indicators
Chronic hepatitis C can be verified by laboratory tests.
The list of nonspecific and specific markers of infection is presented in the table below:
| Laboratory indicator | Description |
| Liver test data | |
| Total bilirubin | Increases due to the connected. Characteristic of the icteric form of acute or chronic hepatitis C |
| Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) | An increase in enzyme concentration indicates necrosis of hepatocytes, which speaks in favor of infection |
| Alanine aminotransferase (AlAt) | With HCV, this figure exceeds the norm by 10 or more times |
| Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) | Just like other liver enzymes, it increases when the organ is damaged by viral etiology |
| Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) Glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH), Sorbitol dehydrogenase (SDH) | Normally present in the bloodstream in small (often undetectable) quantities. Identification of these biologically active substances indicates the active course of the pathology and the presence of complications |
| Biochemical blood test indicators | |
| Total protein, protein fractions | The analysis is carried out during a general examination of the patient and for differential diagnosis with autoimmune hepatitis |
| Glucose, amylase | Routine examination, part of the overall diagnostic process |
| HCV specific markers | |
| Anti-HCV (ELISA) | Determination of total antibodies, analysis is performed at the initial stages of diagnosis. Determines infection without reference to the activity of the pathological process. The specificity of the study reaches 90%. However, there is a possibility of false-positive and false-negative results due to the physiological characteristics of the patient, the presence of concomitant diseases (HIV, autoimmune pathologies, etc.) |
| Differentiated anti-HCV | The level of IgG and IgM is assessed, which allows the doctor to establish the approximate timing of infection and determine the form of pathology (acute, chronic, exacerbation of chronic hepatitis C) |
| Qualitative PCR | Determination of virus RNA in blood. It is highly sensitive (up to 98%), detects infection before ELISA |
| Quantitative PCR + genotyping | It is carried out with a positive result of other tests and a confirmed diagnosis of hepatitis C. Demonstrates the viral load, that is, the severity of the infection, identifies the specific genotype and subtype of the virus |
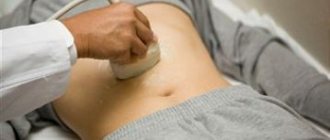
Ultrasound and other diagnostic examinations
In addition to laboratory tests, hardware methods are actively used to detect liver dysfunction and the degree of damage to liver tissue.
Ultrasound of the abdominal organs. On ultrasound examination, the signs of chronic viral hepatitis C are as follows:
- the structure of the liver tissue is homogeneous, or hepatolienal syndrome is present;
- the parenchyma density is often uneven, with areas of increased echogenicity and granularity;
- an increase in the size of the lymph nodes in the area of the portal vein;
- changes in the vascular pattern of not only the liver, but also the spleen.
As the liver tissue is destroyed, portal hypertension occurs. Its ultrasound signs are somewhat different and look like this:
- the presence of portosystemic collaterals (the sign has maximum diagnostic value, because its appearance 100% indicates the presence of portal hypertension);
- increase in the size of the spleen;
- the appearance of ascitic fluid in the abdominal cavity;
- increased diameter of the portal and splenic veins;
- the reaction of the superior mesenteric vein to the phases of the respiratory act is not visualized;
- slowing down the speed of blood passage through the hepatopetal blood flow;
- the internal lumen of the portal and splenic veins exceeds the norm, etc.
FGDS (fibrogastroduodenoscopy). The examination is performed using an endoscope. It looks like a flexible centimeter tube, one end of which is equipped with an eyepiece, the opposite end with a light source. During FGDS in patients with advanced stages of HCV, varicose veins of the esophagus and stomach are recorded. With mechanical injury, they can bleed, even to the point of bleeding.
X-ray signs characteristic of CT (computed tomography). In acute hepatitis C, the X-ray picture is insignificant and does not provide sufficient diagnostic benefit.
Chronic hepatitis C manifests itself:
- uniform enlargement of the organ: the liver shadow is large and intense;
- the lower hepatic angle is widened, somewhat rounded;
- the lower contour has a flat shape;
- the enlarged right lobe of the liver displaces the diaphragm upward, and downward - the right kidney, pyloric section of the stomach, duodenal bulb, hepatic flexure of the colon;
- the enlarged left hepatic lobe displaces the body of the stomach posteriorly to the left;
- splenomegaly.
Histological picture of hepatobiopsy (a fragment of liver tissue). The biopsy obtained by liver biopsy is subjected to histological analysis.
With HCV, the histological picture is not pathognomonic, but the following histological signs are observed:
- a pronounced tendency to form accumulations of lymphoid elements and the formation of follicles in the portal tracts;
- non-purulent cholangitis;
- areas of steatosis (fatty degeneration of hepatocytes);
- stepped and/or bridging necrosis;
- proliferation of hepatic satellite cells of the liver and bile canaliculus epithelium;
- spread of fibrosis with active formation of septa, etc.
In chronic hepatitis, regardless of the genesis of the disease, expansion of the portal tracts is recorded. This occurs due to the proliferation of fibrous tissue due to lymphoid-mononuclear infiltration.
The PCR method is used to determine HCV RNA in hepatobiopsy material.
Elastography. Carry out using the Fibroscan device. This technique has a number of advantages: non-invasiveness, speed of obtaining results. The method of conducting it resembles an ultrasound examination. Necessary for identifying and assessing the severity of fibrosis. Less informative than liver puncture biopsy.
Features of the manifestation of pathology at different stages of the disease
There are no significant differences in symptoms between women and men.
In the clinical picture of the pathological process, doctors distinguish several successive stages - the incubation period, the pre-icteric stage, the icteric stage, and the period of convalescence.
The duration of the incubation period is, depending on the situation and the state of the body, from one month to six months. This period is characterized by the absence of any sign of infection.
The preicteric stage is accompanied by the appearance of signs of the development of asthenoneurotic syndrome, characterized by causeless fatigue, sleep disturbance and headaches. During this period of progression of the disease, there are no external manifestations of the presence of infection in the body. When palpating, the formation of compactions is revealed. The patient has a high probability of experiencing pain in the area of the right hypochondrium. Symptoms accompany progressive pathology for 1-2 weeks.
The icteric period is characterized by a change in the color of the skin throughout the body, and yellowing of the sclera of the eyes is also observed during this period. The duration of the process is several days, and the stage itself lasts from several days to one month.
The convalescence stage is characterized by the appearance of pain in the area of the right hypochondrium, in the area where the liver is located. At the same time, the patient’s condition improves, and signs of jaundice disappear.
A characteristic symptom of the development of the disease in the male body is the appearance of signs of gynecomastia - an increase in the size of the mammary glands.
In addition to gynecomastia, there is a decrease in libido and erectile dysfunction; in some cases, pain can radiate to the right shoulder in the form of shooting.
The presence of bad habits has a negative impact on the course of the pathology, for example, regular consumption of alcoholic beverages leads to complications as the pathological process progresses.
The first signs of the development of a pathological process in the body are the appearance of:
- nausea;
- decreased appetite;
- pain in the area of the liver;
- weakness and lethargy;
- change in color of stool and urine.
As a result of impaired liver function, intoxication of the whole body develops, which leads to an increase in body temperature and the appearance of muscle pain.
How to detect HCV at an early stage
Only regular specific tests 1-2 times a year will help to identify the body’s contact with HCV in the early stages. The enzyme immunoassay method will confirm or deny the presence of antibodies in the body, which are produced when the virus appears in the blood.
In accordance with the protocols of the World Health Organization, which are followed by both domestic and foreign specialists, the initial diagnosis of HCV is carried out using a serological test (ELISA).
But when decrypting the received data, erroneous results may be obtained, which is due to:
- “serological window” is the name given to the period from the moment of infection to the production of specific immunoglobulins (on average, from 4 to 6 weeks);
- the presence of immunodeficiency conditions (HIV, taking cytostatics, a course of chemotherapy, malignant lesions of the hematopoietic system, etc.);
- autoimmune diseases.
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test for hepatitis C is more specific. Modern test systems are extremely sensitive and are able to detect viral RNA in minimal concentrations. But PCR, which can detect infection 10–14 days after infection, is much more expensive.
Therefore, a qualitative determination of viral RNA (often referred to as HCV RNA) is prescribed when:
- positive ELISA result;
- negative ELISA result, but with a high probability of infection;
- negative ELISA results against the background of increased levels of liver enzymes and symptoms characteristic of hepatitis C.
A positive qualitative PCR analysis is the basis for making a diagnosis, as well as further examination.
The presence of hepatitis C is indicated by data from general clinical blood and urine tests. Pay attention to deviations from the norm in the following indicators:
- increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate, which speaks in favor of an active inflammatory process;
- an increase in the number of leukocytes, which indirectly confirms the presence of pathology in the body;
- change in prothrombin time;
- decreased hemoglobin levels, which is associated with impaired liver function.
HCV can be suspected by a clinical urine test. Bilirubin, which is normally absent, is often detected.
Confirmation of diagnosis and selection of treatment regimen
Laboratory diagnostics includes the following:
- general blood test;
- biochemical study (AST, ALT, bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase);
- coagulation studies: bleeding duration and clotting time;
- albumin determination: hypoalbuminemia is common,
- deviation from the norm will indicate a violation of the hepatic synthesizing function;
- according to indications, nitrogen, creatinine and electrolytes in the blood are examined.
The scope of serological tests for viral hepatitis C is determined by the doctor. But ELISA is mandatory.
Hepatitis C is confirmed in a clinical laboratory, because treatment in men begins only after receiving genotyping results. Blood samples are sent for analysis if the development of the disease is suspected, even if the symptoms are mild.
The duration of the course and treatment regimen directly depend on the HCV genotype. It includes the prescription of direct antiviral medications. To alleviate the patient’s condition, inpatient or outpatient symptomatic therapy is additionally selected.
Features of the chronic form of the virus
The signs of chronic hepatitis C in men largely coincide with the manifestations of cirrhosis and portal hypertension, which we will discuss below.
Indirectly, the chronic course of HCV will be indicated by signs of endocrine system disorder:
- the male mammary gland greatly enlarges and, in rare cases, becomes painful;
- testicles decrease in size;
- Libido decreases, up to the complete disappearance of sexual desire.
These signs can be pronounced or blurred.
How dangerous is the disease for a man?
Disappointing statistics
Hepatitis C in men is a fairly common pathology. According to statistics, approximately 1% of the world's population is infected with HCV. To complicate the situation, this viral liver disease is virtually asymptomatic, and the exact numbers may be much higher.
The chart below shows WHO data on HCV prevalence by region.
Total in the world - about 71 million infected
In general, the symptoms of hepatitis C in men and women are practically not much different. However, there are also important nuances:
- It is believed that the female body copes better with the damaging activity of the virus. Therefore, representatives of the fair sex recover faster from illness.
- In the stronger half of humanity, the symptoms of infection are usually more pronounced, and in general the pathology is more pronounced.
- Complications and their symptoms also develop faster: hepatitis in men often leads to the development of cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Gender matters
Otherwise, hepatitis C in men and women follows approximately the same scenario.
To talk about the prognosis of HCV, let's turn to statistics again.
It is known that out of a hundred patients with this disease:
- 55-85 people will experience chronic infection or asymptomatic carriage;
- 70 will consult a doctor about chronic liver disease;
- 5-20 people will be diagnosed with cirrhosis over the next 20-30 years;
- 1-5 people will die from complications.
To avoid possible negative consequences, it is important to diagnose the disease in time and consult a doctor as early as possible. Since 2012, direct-acting antiviral drugs have been successfully used in practical medicine, which guarantee complete recovery in 97-99% of patients with hepatitis C.
Treatment is expensive, but it allows you to completely defeat the disease
In our review, we looked at such a common and insidious pathology as hepatitis C: symptoms in men, treatment. Paying attention to your health and timely recognition of the signals that the body “sends” will allow you to diagnose the disease at an early stage and prevent the development of serious complications.
A man sick with the virus feels constant weakness, forgetfulness, and patients fall into a state of depression. His performance decreases, his appetite worsens, these symptoms especially manifest themselves during an exacerbation. As a result, during illness a decrease in libido and sexual desire is observed. Some men have thyroid problems, flaking skin, dry mouth and bleeding gums.
According to statistics, the chronic stage of the disease is more common in men than in women. They develop liver cirrhosis more quickly due to the disease.
Signs of complications
Complications of viral hepatitis include cirrhosis and hepatocarcinoma. These pathological conditions have a number of distinctive features that should be discussed in detail.
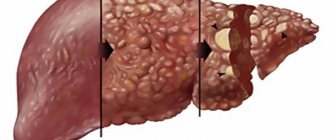
Signs of cirrhosis and portal hypertension. In the early stages of the disease, a moderately enlarged spleen can be palpated. The liver increases in size, also characterized by a deformed surface, compacted consistency, and a pointed edge. At the beginning of cirrhosis, both lobes of the organ are evenly enlarged, later only the left one is enlarged.
The hair on the pubis and armpits becomes thinner, until it disappears completely. When examining the palms, plantar erythema (redness, “liver” palms) is recorded, the fingers take on the appearance of drumsticks. When examining a patient, an experienced hepatologist will pay attention to characteristic skin signs: ecchymoses, spider veins.
The veins on the anterior wall of the abdomen expand and diverge from the umbilical region in winding cords (head of the jellyfish). The tongue takes on a characteristic appearance: its surface is shiny, crimson or bright crimson in color. The same picture of the tongue occurs in alcoholic cirrhosis.
Severe and terminal stages of cirrhosis are characterized by icterus of the sclera, visible mucous membranes, diffuse jaundice of the entire skin. During digital rectal examination, hemorrhoids are palpated.
Signs of HCC (hepatocellular carcinoma). This is a common type of malignant tumor of the liver tissue. The initial stages of the disease may occur without visible signs. Splenomegaly, ascites, and jaundice may indirectly indicate HCC. But these manifestations are also characteristic of cirrhotic liver decay.
In an advanced situation, palpation reveals a neoplasm and/or a dense, tuberous surface of the liver in the upper part of the abdominal cavity. On auscultation, the murmur of the hepatic artery is heard above the tumor. Variceal or acute intraperitoneal bleeding is another sign of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Changes in laboratory tests are nonspecific. The hemogram reveals thrombocytopenia, less often - an increase in ESR, and in an advanced stage - all the signs of anemia. Biochemical tests show hypoalbuminemia (low protein), hyperbilirubinemia (high bilirubin), coagulopathy (blood clotting disorder), increased levels of alpha fetoprotein, alkaline phosphatase, and electrolyte imbalance.
Diagnostics
The following tests are performed for hepatitis A:
- examination of blood and urine for bilirubin - the causative agent of hepatitis disrupts its metabolism, so there is more of it;
- ALT, AST - due to a violation of the enzymatic activity of the liver, the activity of transaminases increases, this indicator is used to judge the severity of the process;
- A general blood test reveals a decrease in ESR, leukopenia (if the case is severe, thrombocytopenia), an increase in ESR plus leukocytosis indicate possible complications.
A decrease in protein levels in the blood due to albumin, cholesterol, and prothrombin is also established. To clarify the diagnosis, the titer of immunoglobulin M, which increases with jaundice, and immunoglobulin G, which increases with recovery, are examined. PCR diagnostics are the most informative.
Early detection of hepatitis B in men reduces the risk of complications and the disease becoming chronic. When the liver is damaged, the indicators of general and biochemical blood tests change. When the protein content is reduced, the concentration of indirect bilirubin is increased, testing for virus carriage is carried out.
Treatment of hepatitis B in men
There are no drugs that can destroy the pathogen yet. New generation antiviral drugs reduce the risk of concomitant infections. Treatment for men and women includes:
- removal of intoxication associated with a decrease in the secretory functions of the parenchyma, deterioration of metabolism;
- stimulation of the body's protective properties;
- elimination of obvious symptoms;
- increasing the level of protein in the blood (it binds excess bilirubin and accelerates its utilization);
- vitaminization of the body;
- normalization of water-alkaline balance.
When hepatitis B becomes complicated, intensified therapy is given to improve the prognosis for recovery. It is important to adhere to therapeutic diet No. 5. It is necessary to eat a balanced diet, eliminating foods that burden the liver:
- fatty meats and fish;
- smoked and preserved foods;
- fried food;
- alcohol in any form;
- carbonated drinks;
- sweets;
- baked goods.
It is important to divide the diet into 5-6 parts. It is useful to lead a healthy lifestyle, moderate physical and psycho-emotional stress.
Treatment and prognosis
Before starting treatment for HCV, each patient should be informed that today there are different treatment regimens for the disease.
Foreign drugs that destroy the virus are very expensive. But there are no less effective generics on the pharmaceutical market. In addition, medications are prescribed to combat complications associated with serious liver problems, including the development of liver failure.
There are simply no traditional medicine recipes that can help kill the virus. But such therapy provides additional assistance in the fight against ascites, edema, and heart failure. Such techniques are very effective and are aimed at improving the quality of life of the infected patient. That's the only reason why you shouldn't give them up.
If the disease was detected in advanced stages, when the liver tissue is significantly destroyed, then in addition to specific treatment, patients receive symptomatic therapy and strictly follow dietary recommendations. The criterion for recovery is the absence of the virus in the body for six months after the end of treatment.
The prognosis for patients who managed to identify and treat the virus early, and later avoid re-infection, is quite favorable. The life expectancy of such people does not differ from the life span of a healthy person.
Otherwise, predictive data will depend on the following indicators:
- HCV genotype;
- effectiveness of treatment;
- immunity status;
- the initial health of the liver and the body as a whole.
The patient's lifestyle plays a big role. The fewer factors that negatively affect the liver, the more optimistic the prognosis. Many people can suffer from hepatitis C for two to three decades, while others die within just a few years of infection.
What tests need to be taken?
A correct diagnosis can only be made after a complete diagnosis. The main test required for signs of hepatitis is an enzyme-linked immunosorbent blood test. It allows you to identify the virus itself and the extent of infection, whether a person is exclusively a carrier of the virus or is sick himself. This test is not cheap, but it is extremely important in identifying liver disease.
A PCR test may also be required; this type of diagnosis allows you to literally identify the virus and its amount in the body. The level of viral load allows us to predict the outcome of the disease in each individual case.
In addition to ELISA and PCR, liver ultrasound and other studies may be prescribed to help establish the extent of damage caused to the human body by the virus and its complications.
What is prevention?
It is believed that proper awareness of a person, as well as compliance with all norms of behavior, is the best prevention of the disease. If a patient is infected and knows about it, then he has the power not to spread the virus and not infect other people. To do this, it is enough to cover cuts, scratches, and wounds with a bandage in a timely manner, to prevent sexual contacts not protected by a condom, and to strictly observe personal hygiene measures.
If a person does not want to allow infection, then preventive measures come down to other measures: do not come into contact with the blood and other biological fluids of strangers, do not use the services of semi-legal or illegal medical clinics.
After the occurrence of a potentially dangerous event (injury with a non-sterile instrument, blood transfusion, unprotected sexual intercourse), you should definitely visit a hepatologist and undergo a series of laboratory tests.
The basic preventive measures for hepatitis C are simple, therefore a vigilant, serious attitude towards your own and others’ health is an important value that can reduce the risk of infection.
Alcoholic hepatitis
More often than viral forms of the disease, alcoholic hepatitis occurs in men, as they often tend to abuse alcohol. This disease is a pathological change in liver tissue, which is characterized by inflammatory processes, fatty degeneration, and fibrosis. Alcoholic hepatitis occurs due to the toxic effect on the liver of alcohol metabolites that accumulate in its cells, the disease progresses to cirrhosis of the liver.
The severity of alcoholic hepatitis depends on the amount of alcohol drunk, the regularity of libations, and how long a person drinks during his life. In men, daily consumption of only 50-80 g of alcohol can lead to pathology associated with alcohol consumption, if this is done regularly - for 3-5 years or more. Treatment for alcoholic hepatitis is aimed at complete abstinence from alcohol. A special diet is prescribed that provides healthy and high-calorie nutrition that normalizes liver function.
The liver is a vital hematopoietic organ. Like the condition of other organs and systems of his body, a man must monitor the health of his liver and regularly visit a doctor for preventive examinations in order to detect the disease in time and begin treatment.