The first signs of a diseased liver
Early symptoms of a diseased liver rarely indicate damage to the organ. More often, the first signs of the disease are associated with the fact that the liver cells cannot cope with cleaning the blood of toxins and chronic intoxication appears. Men make the following complaints:
- decreased ability to work;
- increased irritability;
- sleep disorder (problems falling asleep, daytime sleepiness);
- indigestion (diarrhea or constipation, stomach discomfort, nausea);
- rapid weight gain or loss (caused by metabolic disorders);
- phlebeurysm;
- frequent colds (intoxication reduces immunity).
Men often ignore the first signs of liver pathology, trying to relieve discomfort by taking “stomach” medications or sleeping pills. For a short time, medications alleviate the condition, and then the state of health worsens again and symptoms of liver damage develop.
The problem of asymptomatic liver diseases
If the initial signs of liver disease are accompanied by non-typical symptoms (varicose veins, sleep problems, frequent colds), then when you consult a doctor and conduct an examination, it is possible to identify liver pathology.
In most men, the disease continues for a long time in a subclinical (asymptomatic) form. This is due to the fact that there are no nerve endings in the organ and the patient feels only moderate discomfort when the liver cells work under increased load. Clinical signs appear when serious problems with the liver have arisen and the disease has entered the decompensation stage.
The subclinical course of the disease is sometimes detected by chance during routine examinations. But the absence of characteristic symptoms leads to the fact that a man, feeling healthy, postpones undergoing additional examination and does not receive treatment. As a result, severe functional disorders develop in the organ.
Prevention
Proper nutrition, weight control, giving up bad habits, maintaining a sleep and rest schedule, taking medications only as prescribed by a doctor - all this will help avoid the development of liver problems.
Hepatitis is often transmitted sexually; monogamous relationships and condoms will help prevent infection; if you are sexually active, tests should be done every six months. When working in hazardous industries, use protective equipment and follow safety regulations.
The best prevention of liver disease is proper nutrition and a healthy lifestyle.
The liver is an important organ in the human body; it performs more than 500 functions; when the gland is destroyed, its functionality decreases, which can cause disability and death. In treatment, hepatoprotectors are used based on plant and animal ingredients, phospholipids, amino acids, which promote organ regeneration. Following simple rules of prevention and proper nutrition will help avoid the occurrence of liver pathologies.
Features of symptoms
Belonging to the stronger sex has almost no effect on how liver disease manifests itself: the signs of pathology are similar for men and women. Symptoms depend on the nature of the damage to hepatocytes (liver cells) and the cause that provoked the disease.
Alcoholism
Disturbances in the organ develop slowly. If a man regularly abuses alcohol, after 10 or more years the following symptoms will appear:
- yellowness of the sclera and skin;
- nausea and heartburn;
- diarrhea;
- heaviness under the ribs on the right;
- psychical deviations;
- decreased appetite;
- increased fatigue.
With alcoholism in a man, the synthesis of sex hormones is disrupted and the following is noted:
- testicular atrophy;
- erectile dysfunction or impotence;
- decreased sex drive.
Stones
The formation of stones causes stagnation of bile or an excess of fatty foods in the diet. There are no nerve endings in the organ, and when liver stones form, symptoms do not appear immediately.
In approximately 10% of men, stone formation is asymptomatic, and pathology is detected during ultrasound of the organ.
If the stones do not interfere with the flow of bile, then a couple of hours after eating the man will experience the following symptoms:
- heaviness or moderate pain in the hypochondrium on the right;
- nausea or bad taste in the mouth;
- flatulence.
When a blockage of the bile duct occurs, the symptoms develop acutely. The man begins to vomit, and the acute pain under the ribs on the right becomes unbearable. Yellowing of the skin and sclera may appear.
Obesity (fatty hepatosis)
With this disease, hepatocytes are gradually replaced by adipose tissue. Symptoms of fatty liver appear in a man when most of the liver cells are replaced by fat and the organ cannot fully perform its functions. In men it is noted:
- feeling of heaviness under the ribs on the right;
- digestive disorders;
- yellowing of the dermis and skin rashes;
- intoxication (weakness, sleep problems, headaches).
The organ is greatly enlarged in size and extends beyond the edge of the lower costal arch.
Hepatitis
An inflammatory process in the liver parenchyma caused by a virus.
Symptoms of inflammation depend on the nature of the viral pathogen. Botkin's disease (hepatitis A) is acute and is accompanied by characteristic symptoms:
- yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes;
- discoloration of stool and darkening of urine;
- pain in the hypochondrium on the right;
- fever;
- nausea;
- lack of appetite;
- weakness.
On palpation, the liver is moderately enlarged.
Hepatitis B, C and D are less acute. Most patients have a latent (hidden) course of the disease, when there are no external signs of inflammation. Men experience only moderate discomfort in the right side and minor digestive problems. Asymptomatic viral liver damage is detected only when donating blood for hepatitis.
Parasitic infestations
The cause of liver dysfunction may be helminthic infestations. The following parasites “like” to penetrate the hepatic ducts:
What symptoms appear during a parasitic infection depend on the location of the parasite’s attachment and the nature of the liver dysfunction. Most male patients experience moderate heaviness under the ribs and signs of intoxication.
Cirrhosis
The pathology is accompanied by the death of liver cells and the replacement of dead tissues with connective tissue structures. The onset of the pathological process is accompanied by symptoms that are not characteristic of liver damage:
- asthenia (weakness, decreased performance);
- dyspepsia;
- weight loss;
- mood swings and sleep problems.
Gradually, the number of destroyed hepatocytes reaches a critical level, and the liver cannot do the job of purifying the blood and ensuring complete digestion. At this stage of the disease, a man develops characteristic clinical symptoms:
- jaundice (excess bilirubin in the blood);
- hepatomegaly (the liver becomes enlarged due to the proliferation of fibrous nodes);
- enlarged spleen;
- anemia.
The first symptoms of liver damage are mild and the deterioration in health cannot always be associated with a malfunction of the organ. A man should pay close attention to his health and have his liver examined if signs of fatigue do not disappear after rest or there is a sudden change in weight.
Hepatic coma
Hepatic coma is another name for hepatargia. Three stages of development are known
- precomatous period - during this period, the development of anorexia (lack of appetite or complete aversion to food), attacks of nausea, the liver decreases in size, yellowness of the skin and eye sclera;
- threatening coma - mental abnormalities are detected, the speed of thinking is significantly reduced, a false sense of euphoria, sudden mood swings, depression;
- coma - sudden mood swings: from excitement to complete depression, possible loss of consciousness. The patient's face becomes thin and the limbs become cold. A sweetish liver odor emanates from the skin.
https://youtu.be/dIFhg4i9QDg
Treatment
Before selecting therapy, the doctor examines the man, asks what symptoms appeared with liver disease, and selects treatment taking into account the data obtained.
The main treatment is aimed at maintaining liver function and restoring hepatocytes:
- to reduce the food load on the liver, a gentle diet is selected for the man;
- hepatoprotectors will help restore damaged tissue;
- taking choleretic drugs will eliminate bile stagnation;
- Antiviral drugs will help with hepatitis.
In addition to treating the liver, complex therapy is selected to eliminate concomitant symptoms. Patients are prescribed medications to improve the functioning of the pancreas, intestines, or gallbladder.
Treatment of liver inflammation
For viral hepatitis, treatment at home is impossible. Inflammation of toxic or autoimmune origin in mild forms is treated on an outpatient basis. For severe lesions, bed rest and treatment in a hospital are indicated. During therapy, complex measures are used: medications that eliminate the harmful factor, drugs to restore liver cells, as well as a special diet.
Diet and lifestyle
The liver is part of the digestive system, so diet affects its condition and the course of recovery. A diet for liver inflammation includes avoiding alcohol, spicy foods, marinades and sauces, fatty and fried foods, as well as coffee and other energy drinks.
All you can eat are low-fat soups, cereals, and some fruits and vegetables. Drinks allowed are weak tea, vegetable and fruit juices, and still mineral water. If you have chronic inflammation of the liver, you will need to stick to this diet for the rest of your life. If the inflammation is acute, it will be possible to return to your favorite junk food only a few months after complete recovery.
Physical activity is contraindicated during illness and rehabilitation. During the recovery process, you will need to perform special gymnastics under the supervision of a specialist, but this is the only permitted type of exercise.
Drug therapy
When treating hepatitis, doctors prescribe:
- Drugs to eliminate the cause of inflammation. These are antiviral, antiparasitic agents, and for toxic lesions - antidotes and sorbents.
- Hepatoprotectors – Phosphogliv, Essentiale, Heptral. These medications protect liver cells from toxic effects and accelerate the elimination of harmful substances.
- B vitamins. In severe cases, they are prescribed in the form of droppers, and in mild forms of inflammation, you can take tablets.
You cannot exceed the dosage of the drug and replace it with analogues yourself, because drugs have side effects and contraindications. After selecting a therapeutic regimen, you must continue to take medications until complete recovery.
Traditional and other alternative methods
There is no effective way to relieve liver inflammation at home. Among the folk methods, the use of decoctions of artichoke and milk thistle roots has a mild effect. To prepare them, you will need to pour a tablespoon of raw material with a glass of boiling water and let it brew for half an hour. Take half a glass of decoction before meals. To better cleanse the liver, you can drink 100 ml of carrot or pumpkin juice before each meal.
These methods do not replace full treatment. To eliminate the risk of side effects from such measures, you should consult your doctor before using them.
Causes of liver disease in men
Men are more likely to drink alcohol, smoke and take drugs than women.
Therefore, liver dysfunction develops much faster in them. A likely cause of liver disease in men is long-term use of medications, especially if the doctor’s recommendations and prescriptions are not followed.
It is possible that the symptoms of the disease are completely harmless. The liver can be damaged if a man does not regularly follow a balanced diet or consumes processed foods. If there is a lack of nutrients, mechanisms that accumulate fats and carbohydrates are immediately launched, which provokes weight gain and destruction of gland cells.
Predisposing factors also include hepatitis virus, fat metabolism disorders, diabetes mellitus, and a sedentary lifestyle. The risk of developing liver disease increases with:
- work associated with harmful toxic substances;
- living in regions that are unfavorable from an environmental point of view;
- blood diseases, tuberculosis.
Pathologies of the filtering organ are inherited and occur when infected with parasites that destroy the liver. It happens that your own immune system accepts liver cells as foreign agents and tries to get rid of them.
How do liver diseases manifest in men?
Liver dysfunction does not appear for a long time, since specific symptoms appear when the pathological condition worsens and concomitant diseases develop.
The reason for this is the absence of nerve endings in the liver that transmit pain signals to the brain. Soreness becomes the result of involvement of other organs in the pathological process.
Symptoms of liver disease in men often go unaddressed even after their health worsens; some men are in no hurry to see a doctor for consultation and treatment. It happens that alarm bells are not associated with the liver at all.
Among the symptoms indicating problems with the operation of the filter organ, the following signs should be highlighted:
- excessive fatigue;
- indigestion;
- drowsiness or insomnia.
This also includes frequent cases of acute respiratory viral infections, a specific color of the skin - excessive pallor or jaundice. The consequence of hormonal imbalance in liver diseases is weight gain and obesity.
Gastrointestinal symptoms
The first signs of liver disease in men are problems with the digestive system. The patient begins to experience attacks of nausea and vomiting; the man may notice a connection between the symptoms and the consumption of spicy foods and fatty fried meat.
The liver simply cannot cope with its functions and does not fully process toxic substances that come with food. A similar picture is observed after drinking alcoholic drinks; general intoxication increases in the body.
Liver diseases are manifested by diarrhea, flatulence, a yellow or white coating may appear on the tongue, and a change in color to purple is not excluded. A specific symptom is the so-called liver odor from the mouth.
You can suspect a problem based on the following symptoms:
- lack of appetite;
- change in liver size;
- attacks of heartburn.
In the morning, there is a feeling of heaviness in the epigastric region, discomfort increases during the day, and an unpleasant taste in the oral cavity occurs. By palpation and even visually, the doctor will determine an increase in the abdominal cavity on the right side.
Liver signs on the skin
Liver signs and yellowing of the skin are not observed in all cases of liver damage in men.
Among the symptoms, skin itching most often appears; due to constant subcutaneous hemorrhages, the patient is diagnosed with spider veins.
Liver diseases provoke increased pigmentation:
The skin around the thumb and little finger on the upper and lower extremities turns red, and the man notices brown spots near the roots of the hair. The skin becomes cold and sticky to the touch, it is difficult for the patient to warm up, and the skin does not warm up even after intense physical activity.
Specific symptoms
A sign of a diseased liver in men is sexual dysfunction, due to the active production of female hormones. As a result of estrogen secretion, there is a decrease in libido, an increase in breast size, and testicular atrophy. In especially severe cases, a man faces impotence.
The patient's figure changes, fat deposits appear on the hips and abdomen, female-type hair growth occurs, and hair stops growing on the face. Some liver diseases have a detrimental effect on bone structures, a man experiences increased pain in the bones, bone deformities occur, and the frequency of fractures increases.
Blood clotting problems
Due to impaired absorption of vitamin K, the production of blood inhibitors decreases. The symptom makes itself felt by bleeding:
In addition, slight bleeding is observed when brushing teeth.
Nervous system symptoms
A man’s character can change dramatically, causeless irritability and apathy appear, and he loses interest in life. Against the background of nervous disorders, addiction to drinking alcoholic beverages and smoking occurs. Bad habits only aggravate the situation and aggravate the medical history. In severe cases of pathology, sleep is disturbed, convulsions, hand tremors, and symptoms of intoxication appear.
Cirrhosis of the liver
There are 4 stages of development of liver cirrhosis:
- initial stage - the patient’s liver cells begin to die. A person gets tired quickly, concentration is impaired, and appetite decreases. Without treatment, the patient's condition worsens every day;
- the second stage - the death of functional liver tissue occurs, which is replaced by connective tissue. As the disease progresses, tissues of a large area of the organ are replaced. In many patients, accumulation of fluid in the peritoneum is recorded; upon examination, you can notice a protrusion of the abdomen on the right side;
- stage of decompensation - the development of concomitant diseases occurs: hepatic coma, thrombosis, sepsis. In some cases, bleeding from the anus was recorded. There is a high probability of death;
- terminal stage - the person is in a coma. The size of the liver decreases, while the volume of the spleen increases. This is the last stage of liver cirrhosis, causing leukopenia and anemia. Brain cells die. A person dies without waking up from a coma.
What liver diseases are diagnosed in men more often than others?
Cirrhosis of the liver
Liver cirrhosis is a chronic disease characterized by the proliferation of the connective tissue of the organ.
The pathological condition is fraught with circulatory disorders in the filtering organ and the death of hepatocytes. The disease is deadly, it becomes the result of chronic alcoholism. A prerequisite for cirrhosis can be hepatitis of any etiology or a parasitic infection. Symptoms of cirrhosis are: a feeling of fullness, bloating of the abdominal veins, varicose veins of the stomach, liver, and esophagus. Any bleeding, even minor, can result in the death of a man. The disease is characterized by hormonal changes, jaundice, and intoxication.
Cirrhosis can be:
Primary biliary cirrhosis develops for no apparent reason and appears as a consequence of genetic immune failures. Alcoholic cirrhosis is the result of long-term consumption of alcoholic beverages. Congestive cirrhosis is the death of hepatocytes associated with cell hypoxia. Doctors call bleeding, renal failure, hepatic coma, sepsis, peritonitis, and collar vein thrombosis complications of the pathology.
Liver cancer
Liver cancer is a very serious disease. Among all oncological pathologies, cancer of the filtering organ ranks seventh in mortality. Prerequisites for the development of the disease in men may be a long course of hepatitis B, C, cirrhosis, and alcohol abuse.
Liver cancer gives symptoms:
- cachexia;
- sudden weight loss;
- anorexia;
- general weakness in the body;
- phlebeurysm;
- venous bleeding.
On the skin side, an earthy or yellow tint of the epidermis appears, spider veins, intense itching, a feeling of heaviness in the pit of the stomach, an increase in the size of the mammary glands, and dull pain.
Hepatitis
The inflammatory process in the liver associated with infection with viruses is called hepatitis.
The most common types of disease are hepatitis A (Botkin's disease), B, C, D. Hepatitis A is transmitted through food and contaminated water.
The pathology proceeds rapidly and does not become chronicled. Hepatitis B is transmitted through blood, for example, by doing:
- medical operations;
- trim manicure;
- tattoo session.
The disease is often contracted through unprotected sexual intercourse. Hepatitis B is severe; men almost always develop a chronic form of the disease.
Hepatitis C is a very insidious disease; it very often develops without symptoms and is always detected in a chronic form. A complication of this form of the inflammatory process is hepatitis D. Other forms of the disease are poorly understood. Signs of liver inflammation in men occur differently. Complications include: liver cancer, cirrhosis, weakened immunity, hemangiomas.
Cysts
Cystic neoplasms cause specific symptoms only when they reach large sizes. Signs of a health problem will include attacks of nausea, heartburn, bloating, increased sweating, and pain under the right rib. With the parasitic etiology of cysts, urticaria symptoms appear throughout the body.
Types of cysts: parasitic (associated with tapeworm infection), non-parasitic, hepatolenticular (copper metabolism disorder). Diseases affect not only the liver, but also the brain. Cysts do not form in old age; they are more common in children and adolescents.
Primary amyloidosis
Primary amyloidosis is a genetic pathology provoked by infectious processes.
In a man with the disease, the concentration of protein in the urine increases, the size of the spleen and liver increases, and sclerosing cholangitis develops, an inflammatory process in the bile ducts, accompanied by their narrowing.
Symptoms of a diseased liver in men and primary amyloidosis are: increased body temperature, discomfort in the right hypochondrium. Complications may include infectious diseases of the genitourinary system, the formation of cysts and tumors.
Steatosis
Steatosis is a disease associated with the accumulation of large amounts of fat in hepatocytes. Predisposing factors may be:
- heredity;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- poor nutrition.
All causes initially provoke obesity, then type 2 diabetes mellitus, protein deficiency and other diseases of the digestive system. Only after the acquisition of all the listed disorders does steatosis develop.
The disease is characterized by an increase in the size of the liver. In medicine, there is a special type of disease that develops only in alcoholics. Lack of treatment threatens cirrhosis, bleeding, and the development of oncological processes.
Classification and types of diseases
Once in the body, the virus multiplies quickly, primarily affecting the liver.
Liver pathologies are divided into primary, which develop in its tissues, vessels, bile ducts, and secondary, which are a consequence of other diseases. The first group includes such types of liver diseases as:
- hepatitis;
- hepatic vein thrombosis;
- cirrhosis;
- cholangiohepatitis.
Secondary diseases are caused by oncological processes in the pancreas, catarrh of the gallbladder, biliary dyskinesia, parasitic infestations, diseases of the vascular, nervous and endocrine systems, and infections of the gastrointestinal tract. Another type of classification divides diseases into three groups: parenchymal, hepatobiliary and vascular.
Liver hepatitis
This is an acute or chronic inflammation of an organ, accompanied by a lack of blood supply. The pathology is provoked by viruses, medications, alcohol addiction and cholestasis. Hepatitis A is considered the least dangerous; infection occurs through contaminated food or dirty hands. Viruses B and C enter the body through the blood. These forms have a severe course, are treated in a hospital setting and lead to complications, including cirrhosis and cancer.
Cirrhosis of the liver
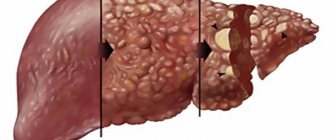
In the final stages of the disease, all cells of the organ are affected.
Irreversible parenchymal damage. Connective tissue forms in place of the dead cells of the affected liver. Statistics provide figures according to which 40 million people die from this disease every year in the world. It occurs in several stages. In the first case, the condition is compensated, there are no symptoms. In the second, the first specific symptoms appear, the subcompensated state can be normalized and the process can be reversed. At the third stage, general intoxication of the body develops due to organ failure. As a rule, it ends with internal bleeding, portal vein thrombosis, coma and death.
Liver cyst
Focal formation in the parenchyma, filled with fluid. Women taking hormonal contraceptives are more likely to be affected by this disease. Symptomatically manifests itself only when the cyst is large or when there is multiple damage to the organ. It can be treated conservatively if the diameter is no more than 3 cm and surgically with partial or complete resection of the organ with its further transplantation. It has a favorable prognosis if treatment is started on time. Otherwise, complications may develop: rupture, suppuration, bleeding of the tumor, peritonitis.
Liver hepatosis
They include the names of diseases that are manifested by dystrophic changes in parenchymal structures. There are acute and chronic, which are most often associated with alcohol abuse. The mechanism of development will be different depending on the provoking factor: from metabolic disorders and intrahepatic cholestasis to severe cell cytolysis.
What is cholangitis?
The disease occurs against the background of an inflammatory process.
The disease with this name is accompanied by inflammation of the internal or external bile ducts. The most common cause is stagnation of bile caused by stones, helminthic infestations, and pancreatic cancer. It can be acute or chronic with frequent relapses. Treatment of the disease is aimed primarily at eliminating the provoking factor. The affected liver can be successfully treated with timely diagnosis.
Liver failure
The deviation causes serious consequences resulting from massive disturbances in the structure and functional activity of the liver. Accompanied by intoxication, disorders of the central nervous system and metabolic processes. There are three stages of development: compensated, subcompensated and terminal, ending in coma. Therapy is aimed at eliminating the symptoms of intoxication.
Liver cancer
The degeneration of cells into a malignant neoplasm has an unfavorable prognosis.
Malignant cancer of a human organ that leads to death. If the neoplasm is formed from parenchyma cells, it is called hepatocellular carcinoma, if from the epithelium of the bile ducts, it is diagnosed as cholangiocarcinoma. The tumor can be localized or diffuse, engulfing the entire organ. Surgical interventions are indicated for local form and absence of damage to other organs.
List of other liver diseases
- Hemochromatosis.
- Budd-Chiari disease.
- Amyloidosis.
- Hyperplasia.
- Hepatomegaly.
How to deal with liver diseases?
A man must understand that he will not be able to cope with liver diseases without revising his eating habits. Doctors prescribe gentle nutrition that relieves stress on the digestive organ. During the period of therapy, spicy, fried, salty foods are excluded from the diet; caffeine and alcohol are prohibited. The most effective diet will be dietary table No. 5 according to Pevzner.
To help the male body cope with the disease faster, hepatoprotectors are recommended. This can be ursodeoxycholic acid, preparations based on the milk thistle plant, substances of animal origin, tablets containing essential phospholipids.
If the liver has not been treated for a long time, it is in a neglected state, and it is quite difficult to restore its adequate functioning. In such cases, we can only talk about inhibiting the disease.
The liver is a vital gland located in the abdominal cavity. According to medical research, representatives of the stronger sex suffer from problems associated with this organ more often than women. That is why you need to know how to recognize liver pathology in time by signs characteristic of men in order to avoid possible complications.
Causes of development of diseases of the liver gland
In this article we will understand how the liver hurts. Symptoms in men and how to treat this disease can only be helped by a doctor after an examination. Like other vital organs in the human body, this gland is located in the central region of the body. The liver occupies almost the entire right section below the diaphragm. Patients with problems with this gland complain of unpleasant sensations in the right hypochondrium with possible irradiation to the epigastric region.
Many people are interested in why and how the liver hurts? Symptoms in men with this pathology can be different. There are many reasons for the development of liver diseases, which are most often encountered by males. This may be due to the fact that they are more prone to smoking and drinking alcohol excessively than women. And these bad habits are known to lead to the destruction of liver cells.
In addition, hepatitis virus, lipid metabolism disorders and diabetes mellitus are common causes of liver diseases. The functioning of this gland is also negatively affected by factors such as:
- Long-term exposure to toxic substances.
- Long-term use of certain medications.
- Dangerous parasites that destroy the liver.
- Heredity. In this case, the immune system mistakes hepatocytes for foreign cells, so it tries to get rid of them.
- Blood diseases and tuberculosis.
It also happens that the causes of symptoms of a diseased gland are completely harmless. If you do not adhere to a regular, balanced diet, it will become a serious stress for the whole body, including the liver. With a deficiency of certain nutrients, mechanisms that accumulate carbohydrates and fats begin to turn on, which first leads to weight gain and then to the destruction of the liver gland.
Does diet affect the risk of developing liver disease?
There is such a thing as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (fatty liver, steatosis, “fatty” liver). The main reason for the development of the disease is the accumulation of triglycerides and other fats in liver cells - hepatocytes. In this case, changes occur in the organ that are similar to those with alcoholic liver damage. As a rule, this is a problem for people who are overweight.
The prevalence of the disease in Western countries is 20-40%, which is primarily associated with physical inactivity and dietary habits: consumption of high-calorie foods and fast carbohydrates. In recent years, Russia has come close to similar indicators. Unfortunately, fatty liver disease occurs even among children.
It is important to remember that patients with fatty liver in the presence of certain criteria, or so-called predictors, are in a group with a high risk of disease progression, that is, transition to the next stage - steatohepatitis with fibrosis. These predictors include: obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and the presence of arterial hypertension. By the way, the high incidence of fatty liver and these factors, which are known to be components of metabolic syndrome (MS), has led to the conclusion that fatty liver itself is a component of it.
Lifestyle changes such as weight loss through a balanced diet and exercise are critical to the successful treatment of these patients.
The nature of pain in diseases of the organ
Unpleasant sensations due to liver pathology can be different. As its size increases and the capsule overstretches, slight aching pain appears in the hypochondrium on the right side, as well as distension and unpleasant heaviness. They indicate the development of a sluggish pathological process in the body of toxic or other origin. Patients with such ailments cannot accurately indicate the pain point.
Diseases of the extrahepatic bile ducts and gallbladder are characterized by strong pinpoint pain in the area of this organ.
When there is a pronounced purulent, traumatic, inflammatory process or destruction of the bile ducts, intense discomfort appears. In this case, many people are interested in how the liver hurts? Symptoms in men with such problems are as follows: severe pain in the hypochondrium on the right side, vomiting and darkening of urine.
If pain does not occur in the hepatic gland, it means that we are most likely talking about indolent pathologies of the organ. Such diseases go undetected for a long time, they are detected only at the stage of cirrhosis or liver failure.
Symptoms
Modern means of self-defense are an impressive list of items that differ in their operating principles. The most popular are those that do not require a license or permission to purchase and use. In the online store Tesakov.com, you can buy self-defense products without a license.
The main symptoms of liver disease include:
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- indigestion;
- jaundice;
- skin itching;
- changes in the size and shape of the abdomen;
- fever.
Pain
The typical localization of pain in liver pathology is the right hypochondrium.
Chronic diseases are characterized by prolonged aching or dull pain, sometimes described by patients as a feeling of heaviness or fullness.
In acute processes, the pain is intense, occurs suddenly, often for no apparent reason, and is paroxysmal or increasing in nature.
Many liver diseases are characterized by irradiation of pain into the upper right sections of the chest, right shoulder, collarbone, under the right shoulder blade, and into the interscapular space. This distribution of pain is explained by the common innervation of the liver capsule and some parts of the chest.
Dyspepsia
Among dyspeptic complaints, patients note:
- bitterness in the mouth and bitter belching;
- nausea;
- decreased appetite;
- vomiting;
- rumbling and bloating;
- constipation or diarrhea.
These symptoms result from a disruption in the formation and secretion of bile, which is necessary for the digestion of fats. Another cause of dyspepsia is the accumulation of various toxins in the body due to a decrease in the neutralizing function of the liver.
Fever
A high temperature is usually a marker of active inflammation in the liver, gallbladder or ducts. Febrile fever is accompanied by diseases such as acute cholecystitis, cholangitis, hepatitis, active cirrhosis, and liver abscess. Low-grade fever is observed in chronic diseases, hepatic colic, and liver cancer.
Itchy skin
Severe painful skin itching usually accompanies jaundice, but sometimes appears long before it and serves as a harbinger of serious liver diseases. The cause of itching is bile acids, which, due to impaired bile excretion, accumulate in the blood and irritate the nerve endings of the skin. The itching is constant, persistent, does not stop day or night, disrupts sleep and significantly worsens the quality of life of patients. In some cases, scratches on the skin become infected.
Jaundice
Jaundice is of utmost diagnostic importance for liver diseases; its appearance is associated with an excess content of bile pigments in the blood. Pathology of the liver and biliary tract is characterized by 2 types of jaundice:
- parenchymal (liver);
- mechanical (subhepatic).
Parenchymal jaundice is caused by damage to liver cells. It usually develops gradually, over a long period of time, so that the patient himself does not notice its appearance. First of all, the sclera, soft palate, and underside of the tongue turn yellow, a little later - the palms and soles of the feet, and only then the whole skin turns yellow. The color of the skin with hepatic jaundice is saffron yellow or orange.
Obstructive jaundice is a consequence of blockage of the common bile duct by a stone or tumor. It appears suddenly and grows very quickly, the skin color ranges from greenish-yellow to dark olive. Subhepatic jaundice is accompanied by severe skin itching.
In some diseases, jaundice is always present, only its intensity changes.
Skin change
Other typical skin manifestations include pinpoint hemorrhagic rashes, multiple bruises, and cholesterol deposits in the form of yellow plaques on the hands, elbows, feet (xanthoma), and on the eyelids (xanthelasma).
With long-term liver diseases, a characteristic change in the palms is observed - palmar erythema. There is a symmetrical redness of the skin in the area of the eminence of the thumb and little finger; when pressed, the skin turns pale and then returns to its previous color. Palmar erythema does not manifest itself as subjective symptoms.
Along with changes in the palms, spider veins . They are localized exclusively on the upper half of the body, face, neck, and have the appearance of pulsating nodules rising above the skin level with thin capillaries diverging from it.
The tongue becomes smooth, shiny, bright red.
There is an enlargement of the mammary glands (gynecomastia), and hair growth on the abdomen, chest and face stops.
Abdominal enlargement
An increase in abdominal volume may be due to hepatomegaly, flatulence and ascites.
Almost all diffuse liver diseases are accompanied by an increase in its size. With portal hypertension, the spleen enlarges simultaneously with the liver.
In malnourished patients, there is a pronounced asymmetry of the abdomen with a noticeable bulging of the enlarged liver. The cause of flatulence is difficulty in digestion.
With portal hypertension, fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity (ascites), its volume can reach several liters. With ascites, the abdomen looks saggy and the navel protrudes. In a horizontal position, the belly resembles that of a frog - it is spread out, bulging out at the sides.
Mental disorders
In many chronic liver diseases, severe asthenia is observed: weakness, apathy, and decreased ability to work.
How does the liver hurt: symptoms in men
Treatment for damage to this organ should not be delayed under any circumstances. Early symptoms of liver diseases developing in males include:
- Gaining extra pounds due to metabolic disorders.
- Changeable behavior - constant quarrels, unreasonable anger and increased irritability.
- Frequent colds associated with disruption of various organs. Bacteria quickly multiply and penetrate the blood, and the liver gland cannot remove toxins. As a result, immunity decreases, so a person begins to catch colds more often.
- Low pressure.
Structure and functions of the organ
The liver is located in the right hypochondrium and has a mass of about 1500 g. The organ consists of the right and left lobes. The right one, in turn, is also divided into 2 lobes: caudate and quadrate. In general, it is customary to conditionally divide the organ into 8 segments, each of which has its own supply of blood, nerves and bile outflow.
Venous and capillary blood is supplied to the organ, and there are 3 stages of this process:
- blood supply to the lobules;
- blood circulation inside them;
- outflow of blood.
The main functions of the liver include:
- Production of hormones and enzymes necessary for the digestion and absorption of food.
- Storing a blood supply that is used in case of significant blood loss.
- Production of bile and bilirubin.
- Accumulation and storage of vitamins and microelements necessary for the body: metals, folic acid, nicotinic acid, vitamins A, B, C, D, E.
- Accumulation and storage of glycogen reserves, which the body may need during high energy expenditures.
- Gluconeogenesis is the conversion of fatty acids, amino acids, lactic acid, glycerol into glucose, which can provide the body's energy needs.
- Neutralization of poisons, toxins, allergens, waste, which can be converted into less dangerous and easier to remove compounds.
- Neutralization of excess hormones, vitamins, metabolic products.
Basic liver functions
In the fetus, which is still in the womb under the protection of the placenta, the detoxification function of the liver is not so pronounced, but the organ is involved in hematopoiesis.
Other symptoms of a diseased liver
Disturbances in the functioning of this organ are often recognized by characteristic signs. Everyone should know how the liver hurts. Symptoms in men, how to treat and eliminate them correctly, will only be described and helped by a specialist after an examination. With this illness, heartburn, a strong smell of sweat, itching in some areas of the skin, constant thirst and hunger, vomiting, bitterness in the mouth, nausea, hair loss from the eyebrows and head may occur.
Moreover, with liver disease, slight yellowing of the sclera of the eyes and skin, acne, the appearance of spider veins, and dark urine are possible. In a serious condition, a person’s breath begins to smell like raw liver.
Symptoms of liver damage
The primary manifestations of changes in liver function are almost unnoticeable and can be attributed to ordinary malaise or weakened immunity. Overweight appears, the frequency of infectious diseases increases, varicose veins occur, and pressure drops begin.
In men, the signs of the disease have their own characteristics. The fact is that, for example, alcohol greatly affects the synthesis of male hormones (testosterone, androgen), which are gradually converted into female estrogens. Because of this, the male body begins to change, namely the following manifestations occur:
- male impotence (impotence);
- testicular atrophy;
- breast enlargement, it becomes like a woman’s;
- the type of hair growth changes. Bald spots and large bald patches appear on the head;
- libido disappears.
For reference! Due to changes in hormonal levels, the production of parathyroid hormone, which is actively involved in the regulation of calcium metabolism, occurs. As a result, a man may experience bone deformities, bone pain, and fractures.
Other obvious symptoms include:
- yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes;
Yellow whites of eyes
Tense ascites in a patient with liver cirrhosis and chronic hepatitis B
Among the nonspecific symptoms that do not always appear are:
- extreme thirst or hunger;
- acne on the skin;
- decreased visual acuity;
- worsening sleep;
- increased heart rate;
- hair loss;
- the appearance of convulsions, tremors of the limbs;
- change in consciousness;
- irritability;
- development of diabetes mellitus.
Table. Characteristics of pain in liver damage
| Type of pain | What does it indicate? |
Organ destruction due to hormonal imbalance
You need to be aware of liver pain. Symptoms in men depend on the type of disease, the presence of concomitant pathologies, as well as the individual characteristics of the body. Sometimes hormonal changes, which are especially noticeable in chronic alcoholics, lead to damage to this gland.
In men with similar changes, female hormones appear in the blood. Feminization occurs in most patients from excessive drinking. In other cases, hormonal changes appear due to viral cirrhosis.
Remember that every person should definitely know how the liver hurts. Symptoms in men, recognized in time, will help detect the disease and begin adequate treatment on time. After all, chronic pathologies of the liver gland in representatives of the stronger sex often lead to the development of diabetes.
Skin reaction to a diseased liver
The skin reacts to all pathological processes in the body, and ailments of this organ are no exception. With liver diseases, the skin turns yellow. A rash in the form of boils or pustules may also appear in men, since the gland ceases to normally produce immunoglobulins. In the event that papules and spots appear on the body, we are talking about detoxification of the organ. But when the rash is hemorrhagic, the synthetic function of the liver has most likely decreased.
When the shade of the skin changes, the amount of bilirubin in the blood increases. It is jaundice that most often indicates the development of hepatitis or cirrhosis of the liver.
What other changes are happening?
When collecting an anamnesis of the disease, the doctor pays attention to the frequency of causeless bleeding. The reason for their development can be brushing teeth, minor injuries, hemorrhoids, and even regular menstruation.
Some note blood in the stool, signaling internal gastrointestinal bleeding.
The presence in the body of harmful toxic substances that are not neutralized by a diseased liver cannot but cause general body intoxication.
With hepatitis of infectious etiology, immune disorders develop, as a result of which a person becomes susceptible to disease.
A typical manifestation of intoxication is a sharp increase in body temperature, especially if the liver inflammation is purulent in nature.
Moreover, if the liver is inflamed, the patient loses appetite, complains of weakness, pain in the limbs, periodic chills, sudden weight loss and weight loss.
The symptoms described are not typical only for liver inflammation. They are also present in a number of other diseases. The doctor’s job is to carry out differential diagnosis and determine the true pathogenesis of the process.
Inflammatory phenomena in the liver prevent the normal destruction of bilirubin, a toxic substance that is formed when red blood cells are destroyed. This affects the coloration of the mucous membranes, skin, and sclera yellow. It is thanks to the liver that during its normal functioning, bilirubin is neutralized. When the process of their destruction is disrupted, the coloring becomes visible.
Gland problems due to alcohol
With long-term consumption of alcohol-containing drinks, a person develops various ailments. As a rule, symptoms of a diseased liver begin to appear only after 10 years. Usually in such cases, doctors discover alcoholic hepatitis, cirrhosis and fatty degeneration in drinkers.
The development of such diseases is diagnosed in most cases in the stronger sex than in women, since men drink alcohol more often. But in women, such pathologies develop faster, even if they drink much less alcoholic beverages. This is due to the gender specificity of alcohol removal from a woman’s body.
Liver diseases occur almost imperceptibly with such addiction, so it is important to undergo examinations on time and know how the liver hurts. Symptoms in men after drinking alcohol are as follows:
- Heartburn and constant nausea.
- Yellowness of the skin.
- Mental disorder.
- Weakness.
- The appearance of severe discomfort in the hypochondrium.
- Loss of appetite.
Diagnostic measures
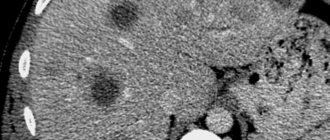
When your liver begins to hurt, you need to consult a doctor to determine the exact cause of these unpleasant sensations. The doctor will make a diagnosis based on an examination of the patient, instrumental diagnostics and blood test results. If a diseased liver is suspected, the patient will have to undergo non-invasive examinations - MRI, ultrasound and CT.
In addition, laparoscopy, immunological tests, biopsy, blood tests, genetic studies, and puncture of focal lesions are prescribed. It is on the basis of the examination results that the specialist selects the appropriate therapy.
Diagnostics
Initially, the doctor will be able to assess the degree of liver enlargement and make a preliminary diagnosis after examination, taking an anamnesis, and palpating the area of the right hypochondrium and abdomen. To identify the cause of the pathology, an additional comprehensive examination is prescribed.
Diagnostic methods:
- general analysis of urine and blood;
- coprogram;
- biochemical blood test to determine the level of liver enzymes;
- hepatitis test;
- tumor marker test;
- biopsy, diagnostic laparoscopy;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- MRI, CT.
Liver biopsy is one of the most reliable diagnostic methods for identifying the disease.
Important!
The appearance of a sweetish, fishy odor from the mouth is a reason to immediately consult a doctor; the symptom indicates rapidly developing liver failure.
How to treat the disease
How the liver hurts, symptoms in men and treatment of any pathologies of this organ depends on the degree of its damage, the diagnosis and the presence of other diseases. When toxic hepatitis is detected in a patient, various procedures are carried out to remove harmful substances from the body. They also resort to techniques that help eliminate the symptoms of intoxication. The patient will still have to change his diet.
People who know how the liver hurts have a greater chance of recovery. Symptoms in men are quickly relieved by medication. Complex therapy of liver pathologies involves taking antibacterial, antiviral and other medications. In advanced cases, surgical intervention is often resorted to. During the operation, doctors excise the affected areas of the liver.
Representatives of the stronger sex should definitely be aware of liver pain. Symptoms in men, reviews and causes will help detect the disease at an early stage. To avoid problems with the gland, it is recommended:
- Avoid smoked, spicy and highly salted foods. They should be replaced with porridge, lean meat and vegetables.
- Stop drinking alcoholic beverages.
- Get rid of bad habits.
- Constantly undergo medical examinations.
- Do not neglect personal hygiene.
If symptoms of liver damage occur, you should immediately see a doctor. Remember that timely treatment will help prevent negative life-threatening consequences.