A rectal biopsy is a method for examining the condition of the mucous membrane, which helps to identify a number of diseases that have a latent form. The procedure involves inserting an endoscope into the rectum, which helps to visually examine the condition of the mucous membrane. Under video surveillance control, a particular section of the intestine is taken, which is subsequently examined under a microscope. Histological examination has a number of advantages, the main of which is the identification of serious pathologies at an early stage.
The essence of the technique
A biopsy involves taking part of the biomaterial from the surface of the inner wall of the rectum and examining this sample for the presence of modified cells. It is extremely difficult to visually assess what is happening in the rectum and why certain symptoms appear. A biopsy allows more accurate results, which makes it possible to correctly diagnose, select treatment and make a prognosis.
Manipulation is carried out in two ways:
- Targeted biopsy - performed under endoscopic control, allows you to take a section of mucosal tissue from a specific place in the intestine.
- Blind aspiration biopsy involves taking biomaterial without video surveillance.
A rectal biopsy involves taking part of the biomaterial.
After the sample is obtained, it is sent to the laboratory, where thin sections are prepared and applied to glass. They are then examined under a microscope, which makes it possible to correctly establish a diagnosis.
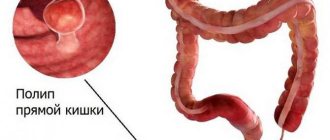
What is a "polyp"?
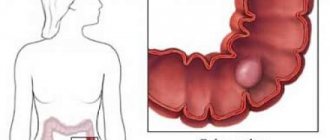
Polyps are growths of the inner layer of the colon wall that protrude into the intestinal lumen. There are two types of polyps based on their shape: pedunculated (they are usually small, with a smooth surface, reminiscent of a mushroom) and broad-based (flat and larger, creeping, soft, “villous”), their sizes can vary from a few millimeters to centimeters . Polyps, as a rule, do not bother the patient until a certain time and are accidentally discovered during an endoscopic (colonoscopy/rectosigmoidoscopy) or X-ray (irrigoscopy) examination of the intestine. In some cases, large polyps can cause discomfort, pain in the anus and abdominal area, stool disturbances, which can also be signs of other diseases (hemorrhoids, anal fissure, inflammatory bowel disease and others). In cases where the polyp is located in the lower intestine (rectum or sigmoid colon), the polyps may appear as a streak of blood and/or mucus on the surface of the stool.
There are inflammatory polyps (appearing at the site of inflammation), hyperplastic (the result of excessive growth of normal tissue) and neoplastic (with the presence of atypical cells). Most polyps are benign formations, but in some cases they can degenerate into cancer. This transformation is more typical for villous glandular polyps.
Indications for the procedure
Rectal biopsy is indicated:
- The presence of a tumor process in the rectum, which is accompanied by severe symptoms.
- Chronic inflammatory process of the rectum, which is indicated by smear studies.
- Autoimmune diseases that can provoke the development of inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Severe symptoms indicating possible pathologies: frequent constipation, diarrhea for no reason, the appearance of blood after bowel movements, painful straining, etc.
- The presence of fistula tracts in the intestines.
- Genetic predisposition to colon cancer.
- Detection of intestinal pathologies using ultrasound, which is necessary for differential diagnosis.
The procedure is shown as the main diagnostic method and differential, allowing to exclude inappropriate ones from the general list of diseases. For people over 60 years of age, rectal biopsy is indicated as a preventive measure for malignant neoplasms.
Why is a biopsy necessary?
A biopsy is necessary to rule out cancer or other malignancy. Also, biopsy and histological examination provide significant assistance in clarifying the diagnosis. Often, biopsies are performed at certain intervals for precancerous lesions, as an observation. For example, for cervical erosion, annual screening is indicated, and it is also indicated for certain types of intestinal polyps.
The importance of biopsy and histological examination to confirm the diagnosis is invaluable. For example, if colon polyps are identified during fibrocolonoscopy, a biopsy can answer a number of questions, including the following:
- type of polyp (adenomatous, villous, hyperplastic);
- the degree of differentiation of the polyp and the presence of malignancy of the intestinal polyp (i.e. the presence of malignant degeneration).
This information is important from the point of view of treatment and observation tactics, the need for urgent removal of the polyp, and the frequency of observation.
In recent years, with the advent of video colonoscopy and examination of the mucous membrane with multiple magnification and in the i-scan mode, it has become possible to detect the early stages of intestinal cancer that occurs without obvious changes in the intestinal mucosa. In this case, a biopsy of the intestinal mucosa followed by histological examination is of decisive diagnostic importance. Detailed cases of early colorectal cancers have not been previously diagnosed.
A biopsy of the mucous membrane has diagnostic value in ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease, as well as in identifying precancerous intestinal diseases.
During mammography, a detected mass formation indicates the possibility of developing breast cancer. For diagnosis, a puncture biopsy is performed.
In the presence of chronic hepatitis, a biopsy can provide information about the structure of the liver and the developing cirrhosis of the liver.
Features of preparation
To obtain the most reliable results and make the procedure less painful, preliminary preparation is required, which consists of following these rules:
- Adhere to a strict diet a week before the proposed test, eliminating fatty, spicy and salty foods, as well as any foods that can negatively affect the digestion process.
- The patient should refrain from eating 24 hours before the biopsy. You are allowed to drink only clean water without gas.
- A day before the test date, it is necessary to take special medications that help remove excess gases and bloating from the intestines, and also stimulate the gentle excretion of feces.
- Immediately before the procedure, in the first hours after waking up, it is important to cleanse the intestines as much as possible from feces. Cleansing enemas help with this. They are placed until the withdrawn liquid becomes as clean as possible.
24 hours before the rectal biopsy, you are allowed to drink only water.
The doctor informs the patient in advance about the need and features of preparation. Most patients, due to the inconvenience of enema, prefer to use special medications that have a laxative and cleansing effect. They remove the contents of the intestines no worse than a conventional enema, without causing discomfort.
How to prepare?
Preparation for the procedure is similar to that carried out before hemorrhoid surgery. If contents remain in the intestines, the study will be inaccurate.
Currently, new methods of intestinal cleansing are being carried out, which include the use of Fortrans. The product gives an effect much better than several enemas and does not cause any discomfort. It is done the day before the procedure.
When preparing the day before the test, you should avoid heavy and fatty foods and alcohol in your diet.
Only the attending specialist can recommend the best option for cleansing the intestines, as well as tell you what kind of nutrition before the biopsy will be best.
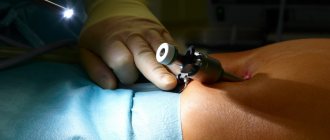
Technique for performing rectal biopsy
The biopsy is performed as follows:
- The patient, who has been mentally and physically prepared for the procedure, is asked to lie on his left side with his legs tucked under his chest. Take a deep breath, then exhale slowly.
- The doctor lubricates the colonoscope and the anal area with a special lubricant containing an analgesic to reduce pain.
- The device is slowly inserted through the sphincter. It is important that the patient is as relaxed as possible. Otherwise, any manipulation will be accompanied by pain.
- The doctor examines the dilated rectum for damage, tumors, and bleeding. Using special forceps, a piece of the mucous membrane is taken from the most suspicious places.
- The test sample is placed in formaldehyde and then sent to the laboratory.
- The colonoscope is carefully removed from the rectum, the patient is allowed to lie down for a few minutes, after which he can get up and get dressed.
The resulting samples are crushed and applied to glass, which are then examined under a microscope.
Possible complications
Increased bleeding and the presence of ulcers on the rectal mucosa increases the risk of biopsy injury. If the doctor detects bleeding after collecting the sample, coagulation may be used.
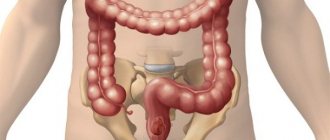
Microcracks in the anus are common companions for patients who have undergone colonoscopy. This can be avoided by the abundance of lubricant used, as well as maximum relaxation of the sphincter during insertion of the device into the rectum.
Microcracks of the anus - possible complications after rectal biopsy
If after the diagnostic procedure the patient’s condition rapidly deteriorates and new unpleasant symptoms appear, then you should immediately consult a doctor. If it is necessary to examine not only the rectum, but also deeper parts of the large intestine, the procedure is performed under local or general anesthesia.
For children, a rectal biopsy is performed by inserting a pediatric colonoscope, the diameter of which is several times smaller. The procedure is painful, so it is recommended to perform it exclusively under general anesthesia.
Colon biopsy
The structure of the large intestine allows you to completely examine it with an endoscopic probe and take a biopsy of material for further research. To do this, a sigmoidoscopy is performed, during which it is possible to examine the rectum and sigmoid colon, as well as take a tissue sample or remove a polyp. The biopsy collected during the process is sent for histological analysis.
Before fibrocolonoscopy, irrigoscopy is usually prescribed. This procedure involves an x-ray examination of the colon with retrograde injection of a radiopaque contrast agent into it. This manipulation allows you to present the overall picture and see the state of the intestinal lumen, which will help prevent damage when the probe is inserted.
Colonoscopy with biopsy can also be performed in children. For this, a special children's fiberscope is used, under the preliminary administration of sedatives, and at an early age a short anesthesia can be used for the duration of the procedure - 30-40 minutes.
The result of a colon biopsy helps confirm or refute the malignant nature of the neoplasm. Histological studies help the doctor decide on the scope of further surgical intervention or refuse it altogether.
Contraindications
Rectal biopsy is contraindicated in the following cases:
- Recent surgery in the rectal area.
- Infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract in acute form (exacerbation of chronic ones). First, drug therapy is prescribed to suppress severe symptoms, after which a biopsy is prescribed.
- Mental illnesses in which it is impossible to establish contact between the doctor and the patient due to inappropriate behavior.
The procedure lasts on average 10-15 minutes. If you follow all the doctor’s recommendations, it will be painless and without the development of dangerous complications. If the duration of the manipulation is longer, you can discuss with the doctor in advance the choice of appropriate anesthesia.
Symptoms and consequences of the disease
Often there are no symptoms. In most cases, the disease is discovered during screening or examination for another pathology. People who have an increased risk of developing this pathology are recommended to undergo regular screening tests.
The most common symptom is intestinal bleeding. They can manifest themselves in different ways. Sometimes the stool is streaked with blood, and sometimes it takes on a dark, tarry appearance (melena). May cause abdominal pain, constipation or diarrhea.
Manifestations of the pathology are nonspecific and can occur in a number of other diseases. So, an admixture of blood in the stool is a possible sign of hemorrhoids and rectal fissures.
You need to see a doctor and get examined if you are bothered by the following symptoms:
- Constipation or diarrhea that persists for a long time.
- Blood in the stool.
- Stomach ache.
Interpretation of results
From the moment the analysis is submitted to the laboratory until the first results are received, on average, 10-14 days pass. The glasses are studied by pathologists who record the results of the study, on the basis of which a conclusion can be drawn about the possible pathology, its type and progression, as well as the probable causes.
Histological examination reveals the presence of atypical areas, which may be precursors of oncological tumors, autoimmune diseases, benign tumors, ulcers and perforation areas. After receiving a transcript of the glasses, you must contact the attending physician who gave the referral for the study to agree on the final diagnosis and draw up a treatment plan.
If the biopsy has controversial results, it is repeated, using several samples from different parts of the mucous membrane. In combination with other research methods, it is possible to obtain the most accurate diagnosis.