Opisthorchiasis is a common helminthic disease that can cause a lot of inconvenience and without proper treatment leads to serious consequences for the body. The causative agent of opisthorchiasis is flatworms, which are localized in the liver, stomach and other vital organs. Find out how opisthorchiasis is transmitted and whether the disease can be transmitted from person to person, which will allow you to protect yourself from becoming infected with opisthorchiasis.
What is opisthorchiasis and the reasons for its occurrence
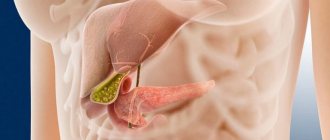
This disease, also called Vinogradov's disease, is a very dangerous parasitic disease. The pancreas and liver are primarily affected. Vinogradov's disease is one of the most difficult to treat parasitic diseases. This is what a parasite (cat fluke) looks like, which enters our body and begins to multiply, laying opisthorchiasis eggs (worms).
As statistics show, if a person moves to an area where opisthorchiasis is detected with high frequency, then within a year the probability of infection is about 16-17%, and if he lives there for more than five years - about 75%.
If we talk about statistics for the European part of the world and Russia, then we can say that in Russia, especially in Siberia, 70-75% of the population suffers from Vinogradov’s disease. In Belarus this figure is 3-5%. In Ukraine and Kazakhstan, 8-10% in each country. The Baltic countries and Western Europe show 2-5% of infections in each country.
Read about other parasitic diseases: echinococcosis, ascariasis and giardiasis.
As we already said in the introduction, the main cause of Vinogradov’s disease is opisthorchia. These parasites live in fish, but you can get infected both from fish that has undergone insufficient thermal treatment, and from our beloved pets - cats who eat raw fish, and then we play with them, hug, kiss, etc.
The incubation period for the parasite is approximately 2-4 weeks. It first settles in the duodenum, then moves to the gallbladder, and the liver becomes infected. Opisthorchia (eggs) begin to live and develop in the body and release toxins. These toxins irritate both the gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract) and the epithelium, lining of the bile ducts, and in addition, they specifically affect the human body so that it gives an allergic type response, that is, several lesions at once.
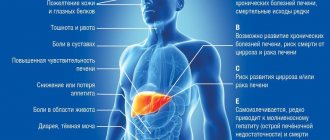
The sooner therapy is started, the faster opisthorchiasis can be destroyed. The consequences depend on how long the parasite “lived” in the body. The end result may be jaundice - this is already a clear clinical picture. The manifestations of this disease are similar to hepatitis.
Opisthorchiasis is not transmitted from person to person only if somehow the waste of one person gets inside the healthy body of another.
In this video, the doctor will clearly show how a person can become infected with opisthorchiasis.
https://youtu.be/b4ukPOnH-Yw
How helminths are transmitted and infect people
As mentioned above, the larvae prefer river and lake fish, in which they are able to live for an extended period of time. That is why the main infection of a person with opisthorchiasis occurs through the consumption of low-quality fish infected with parasites. The greatest risk of infection is observed when eating fish from the carp family. At the same time, it must be said that this parasite can be observed in any river fish. That is why it is not recommended to eat raw and insufficiently thermally processed fish. Remember that this parasite retains its vitality even when the fish is temporarily frozen and treated at high temperatures. We talked about which fish you can get opisthorchiasis from and how to properly process fish without the risk of infection in a separate article.
In recent years, cases of opisthorchiasis infection have increased significantly. This can be explained not only by the expansion of the epidemiological zone, but also by changing gastronomic preferences. In recent years, oriental cuisine has become very popular, which involves eating a variety of raw and semi-raw seafood. So, for example, the well-known sushi to all of us is made from rice from raw fish. If, according to classical technology in Japan, this dish is prepared from seafood and salmon, then in our country we increasingly use raw lake and river fish. As a result, such a dish poses a great danger, since the fish may contain eggs of opisthorchiasis and other worms.
Symptoms and types
There are two types of illness, depending on the duration and intensity of infection, and the symptoms are divided according to the same principle. So, there is acute and chronic opisthorchiasis. The acute form of the disease does not manifest itself in everyone and can be asymptomatic, especially among the indigenous peoples of the North, the level of damage among whom reaches almost 100%.
But still, for the majority, the disease manifests itself as follows:
- fever;
- breaking of joints and muscles;
- hives;
- a little later pain appears on the right under the ribs;
- pain attacks in the solar plexus area;
- liver enlargement;
- nausea, sometimes vomiting;
- temporary increase in temperature.
Among those infected, there are sometimes those who experience an allergic reaction to the parasites in the form of bronchitis.
The acute form of Vinogradov's disease often lasts 1-3 weeks, and then the patient gets better and the disease becomes chronic.
The chronic form can manifest itself with the same symptoms as cholecystitis and hepatitis. On the right side there is persistent pain, reminiscent of biliary colic, radiating up the chest.
At this stage, opisthorchiasis already affects the nervous system, so the patient begins to complain of rapid fatigue, lack of sleep, high irritability, increased sweating, trembling of the eyelids, hands and tongue. Because neurological symptoms become too obvious, the disease is often misdiagnosed.
In addition, as with the acute form of the disease, allergic reactions may occur in the form of urticaria, itching, and bronchitis.
A very unpleasant feature of Vinogradov’s disease is that at an early stage it does not have its own special symptoms. As a rule, body aches, fatigue and fever are perceived as a common cold. However, after one month, when opisthorchises “get used to” and begin the process of laying eggs, eggs can often be found in the patient’s feces.
Depending on the damage to the body systems, several more types of Vinogradov’s disease are distinguished:
- Hepatocholangitis type There is an increased temperature, the liver and spleen are enlarged and this is noticeable. Dull, aching pain in the abdominal area, which sometimes resembles contractions. Frequent vomiting and nausea. In a blood test, you can see increased bilirubin levels.
- Typhoid-like appearance A clearly defined allergy is observed, in addition, the body temperature is increased and chills appear. In addition, patients complain of constant pain in muscles, joints and heart. A rash appears on the skin, coughing, nausea and vomiting appear.
- Gastroenterocolitic type Characterized by lack of appetite and loose stools. The disease causes the development of gastritis, ulcers, and colitis.
- Respiratory tract damage All symptoms of this type of disease are similar to those of bronchitis and pneumonia. Chest pain, coughing, nasal discharge and asthma attacks occur.
If not diagnosed and treated in time, this can lead to very serious consequences. At the first suspicion of opisthorchiasis, immediately contact a specialist who will prescribe the therapy you need.
Manifestation in children
In general, the symptoms in children are not very different from the symptoms of the disease in adults.
After the incubation period ends and opisthorchis begins to multiply, children become drowsy and their temperature rises, often up to 38 degrees. In children, the mild form of Vinogradov's disease is distinguished by the fact that all symptoms disappear after a week. The disease now proceeds latently and gradually becomes chronic. The worsening of the disease may take months, or even years, to appear.
With moderate severity, children's temperature rises to an average of 39-40 degrees, chills appear, suffocation due to the action of toxins on the lungs produced by parasites, redness appears on the skin, as with urticaria.
In addition to a very high temperature, the severe degree is characterized by yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes, lack of sleep, and pain attacks under the ribs on the right.
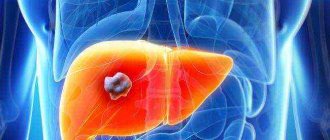
A moderate and severe disease without timely and appropriate treatment can lead to serious damage to the gastrointestinal tract and malignant tumors.
How to avoid getting infected with opisthorchiasis
To eliminate the possibility of infection with this helminthic infestation, it is enough to follow a number of simple rules, namely, properly prepare infected fish.
In this case, we are talking about heat treatment of a diseased food product through exposure to low or high temperatures. It is necessary to freeze fish only after preliminary preparation, gutting and cutting into small pieces. This stage is intended for uniform freezing, since otherwise there is a possibility of maintaining the viability of metacercariae localized in the unfrozen parts of the fish.
The rules for freezing are as follows:
- When exposed to a temperature of -24 degrees, O. fileneus larvae lose viability on the 5th day;
- When exposed to temperatures of -30 degrees, the parasite larvae die after 8-10 hours;
- When the temperature drops to -40 degrees, the death of the cat fluke metacercariae occurs within 3-4 hours;
With heat treatment everything is simpler. Moreover, high temperatures are most effective in eliminating parasites:
- Cooking contaminated food in boiling water for 30 minutes destroys all larvae. Small fish can be cooked without first cutting into slices, but must be gutted;
- Infected fish should be fried for 20-30 minutes. During the frying process, you should monitor the uniformity of the temperature effect;
- Baking fish in the oven also helps to destroy parasitic larvae. The optimal cooking time is an hour or more;
One type of parasite, a typical trematode, causes opisthorchiasis, which causes damage to the liver and pancreas tissue. According to the latest data, about 21 million people in the world are carriers of this disease. Moreover, more than 60% live in Russia. In this article we will look at how you can become infected with opisthorchiasis, what symptoms appear and the main methods of treating the disease.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing Vinogradov's disease in the first stages is almost impossible, because opisthorchiasis eggs are found in feces and bile only a month and a half after infection. That is why the final diagnosis - opisthorchiasis - is confirmed one and a half months after the onset of the disease when cat fluke eggs are found in the waste.
Before this, diagnostics are carried out by doing x-rays, ultrasound, CT (computed tomography), etc., as well as conducting laboratory tests of urine and blood.
If a patient is suspected of having opisthorchiasis, the specialist draws up a medical history in order to have a complete picture. For example, it finds out whether the patient has been to places where the infection was spreading, or whether he ate raw or undercooked fish. The infection can enter the body even if you cut fish, and then began to cut other products with the same knife without first treating it, so it is very important to have different boards for meat, fish, bread and vegetables, the same goes for knives.
Brief information about the life cycle of the cat fluke
The cat fluke is a biohelminth; therefore, it is characterized by an indirect development path, that is, with the participation of intermediate carriers, which are various living organisms.
For each stage of development, a specific living organism is provided. It is important to understand the dependence of parasites on the environment and the immune reactions of the host. In other words, in an unsuitable environment, the egg or larva of the parasite dies
The final host of the cat fluke can be either a person or various carnivorous (piscivorous) animals (dogs, ferrets, foxes, cats, etc.).
The eggs of the cat fluke enter the external environment with the feces of the carrier, in the process of natural defecation. In an arid environment, they do not retain the ability to live for long, but once in a fresh body of water they can survive for about a year.
The first intermediate carrier is a freshwater mollusk belonging to the genus Codiella. It ingests O.felineus eggs during feeding and subsequently cercariae are formed from the eggs in the body of the mollusk. The cercarium floats freely in the water space, leaving the body of the first intermediate carrier.
The next intermediate carriers are fish from the carp family. When the necessary carrier is found, the cercariae penetrates its body through independent penetration into the body. In the fish body, the larva is localized in the subcutaneous tissue and muscles, where it again undergoes metamorphosis and is transformed into a metacercaria, forming a round cyst with the larva inside.
How is opisthorchiasis transmitted? Next, we will consider the main methods of infection with this helminthic infestation.
Drug treatment
If you suspect Vinogradov's disease, you need to go to a general practitioner, a gastroenterologist, but it is best to go straight to an infectious disease specialist. Therapy for Vinogradov’s disease must be carried out in combination, in three stages, following a strict diet, which we will talk about a little later, but now about the stages of therapy:
- Preparatory At this time, choleretic, anti-inflammatory, antiallergic, and painkillers are prescribed. Thanks to all these drugs, the functioning of liver cells improves, inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract and biliary tract is relieved, the intestines are cleansed and the body is detoxified. The quality of treatment at the next stage depends on how well the first stage of therapy is carried out.
- The treatment itself involves treating the parasites with a special medication - biltricide (praziquantel). This is the most effective broad-spectrum antiparasitic drug. Self-administration is prohibited! Treatment is carried out strictly in a hospital under the supervision of a doctor, since this drug is very toxic.
Biltricide has a very toxic effect on internal organs, especially on liver cells and pancreatic cells, causes intoxication and, as a result, nausea, vomiting, headaches, abdominal pain, diarrhea mixed with blood, disruption of the normal functioning of the liver, kidneys, allergies, dizziness and various neurological disorders. You can use this drug only 1-3 times in your life! With further doses, the liver will be irreparably destroyed. In the hospital, when this drug is prescribed, therapy is prescribed in parallel to relieve signs of intoxication.
- Recovery stage After antiparasitic therapy, many dead parasites accumulate in the bile ducts and bladder; in order to remove them, a good outflow of bile is needed, so choleretic medications are prescribed. In addition, additional bowel cleansing is recommended throughout this stage, so laxatives are prescribed if necessary. To restore and support the body after such stress, various vitamins and dietary supplements with strengthening effects are prescribed.
How does the infection process occur?
Diseases are transmitted from a sick person or an infected animal through parasite eggs that are released in feces into the environment. When helminth eggs enter a lake or river, they continue their life cycle by settling in freshwater snails. Over time, cercariae emerge from the eggs, after which the parasites reach the second intermediate host - fish, and then settle in the human body.
The route of infection with opisthorchiasis covers a fairly long period. In the body of fish, the larvae gradually develop and have special suckers. After entering the human body, the parasites attach to the mucous membranes of internal organs using those same suction cups. Due to the influence of parasites, the walls of organs are mechanically damaged, which, in turn, leads to bacterial infection. And in some cases, opisthorchiasis provokes an allergic reaction on the human body.
After only 4 weeks of development in the human body, helminths mature completely and begin the reproduction process. Female opisthorchiasis are capable of producing about 800 eggs per day, which accumulate in the human body, thereby causing stagnation of bile fluid and changes in the biochemical composition of urine.
Treatment at home
We all understand that Vinogradov’s disease is a serious illness and it is absolutely not worth considering traditional treatment as an alternative. This type of therapy can be used to support the body. You should definitely consult with your doctor and find out whether this or that remedy can be used and whether it is compatible with the medications prescribed by him, so as not to harm your body even more.
We offer you several recipes that are recommended for Vinogradov’s disease:
Recipe No. 1 – infusion of aspen bark
- Collect young aspen bark and chop it.
- Take 20 grams and pour 2 tablespoons of boiling water over it, leave in a thermos overnight (or you can boil the infusion for 25 minutes).
- Strain and take 3-4 times a day 30 minutes before meals.
- Course 2-3 weeks.
Recipe No. 2 – St. John's wort infusion
- Pour 10 grams of dried St. John's wort herb into 1 tablespoon of boiling water.
- Leave for 30 minutes.
- Express through cheesecloth.
- Drink 1 tbsp. l. 4-6 times a day.
Recipe No. 3 – infusion of calendula flowers
- Take one tablespoon of crushed dry calendula flowers.
- Fill them with 200 ml of boiling water.
- Leave to sit for 30 minutes.
- Strain and drink 1 tbsp before meals. l.
- Course - 1 month.
Instead of calendula flowers in recipe No. 3, you can use herbs such as wormwood, immortelle flowers, blueberries, chaga growths (mushroom), plantain leaves. All these herbs have a choleretic and enveloping effect, which is very necessary after undergoing drug treatment.
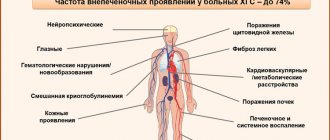
Symptoms of opisthorchiasis infection
People infected with helminths have several characteristic symptoms of the disease:
- regular abdominal pain;
- nausea or vomiting;
- the liver and spleen increase in size;
- irritability;
- insomnia;
- increased body temperature;
- skin rashes;
- poor appetite;
- metabolism or diarrhea;
- constant weakness;
- cough or shortness of breath.
Quite often, infectious opisthorchiasis is confused with regular flu and people start taking pills on their own, but over time the patient’s condition only worsens. Only a doctor can confirm the suspected diagnosis after examining the patient, so if you notice at least a few similar symptoms, do not waste time and contact a specialist.
Diet
As with any other disease of the liver or biliary tract, with Vinogradov’s disease it is necessary to follow a certain diet to help the body recover faster and not strain the liver unnecessarily.
You need to consume 2200 – 2500 kcal per day. The amount of carbohydrates, proteins and fats must be balanced; the patient’s body should receive 300-350 grams of carbohydrates and 80-90 grams of proteins and fats per day.
You need to eat food at a moderate temperature - not too cold, not too hot. It is allowed to bake or boil food, but under no circumstances fry it. Meals should be fractional, that is, 5-6 times a day in small portions. Perhaps these are all the basic principles of our diet, now about which foods are allowed to be consumed and which should be limited or completely removed from the diet.
| ALLOWED | FORBIDDEN |
| Compotes from dried fruits, juices (tomato juice without salt is especially recommended), jelly, rosehip decoction, weak green tea, coffee is also weak, but it is better to limit its intake | Alcohol, soda, cocoa, strong coffee |
| Dairy and vegetarian soups | Mushrooms, meat, fatty fish and soups based on them |
| Lean fish and meat | Caviar, lard |
| Non-acidic and unsweetened berries and fruits | Sour and sweet fruits |
| All low fat fermented milk products | Mustard, pepper, radish, sorrel, horseradish, green onions, spinach |
| Crumbly porridges, except semolina | Very cold or very hot food |
| Honey is ok, but should be limited. | Sweets from the store, cakes, ice cream, freshly baked bread and buns |
| Eggs no more than 1 per day (in the form of an egg white omelet) | Fried or hard-boiled eggs |
| All greens and vegetables except potatoes | Smoked meats, pickles, marinades, canned food |
The diet must be followed throughout the entire therapy process. All additional dietary recommendations can be given by your attending physician, taking into account the characteristics of your body. By following the diet and prescribed treatment, re-infection can be avoided.
Life cycle of a parasite
The fluke is a translucent worm of small size - up to 1.5 cm. Adult parasites are shaped like cucumber seeds. The natural reservoir of infection is piscivorous mammals. The fluke's life cycle begins when contaminated animal feces enter a body of water.
The next intermediate host is fish of the carp family. Fluke larvae floating in the water are attached under the scales. In muscle fibers they develop to the stage of metacercariae and form a dense shell around themselves - a cyst. The cysts are a few millimeters in size and are practically invisible to humans. Fish containing helminth cysts appear healthy in appearance.
The final host of the parasite is animals or people who eat fish. After ingestion, the larvae migrate from the intestine to the ducts of the gallbladder or pancreas, where they attach to the mucous membrane using special suckers and develop into adults.
The fluke can live in the host’s body for about 45 years, that is, almost its entire life. These worms are hermaphrodites and fertilize themselves. The adult parasite is highly fecund, producing an average of 900 eggs per day.
In the human body, the number of worms does not increase, but at the site of infection, new parasites can enter the body along with food. The more fish eaten, the more helminths accumulate in the body. The most acute cases of the disease are recorded in families of fishermen, when the number of opisthorchids in the body of patients reaches several thousand.
Acute course of the disease
Opisthorchiasis can develop into an acute form of the disease, in such cases the following appears:
- fever;
- hives on the body;
- aching sensations in joints and muscles;
- bloating, stool disorders;
- heat.
Opisthorchiasis of a chronic nature can be accompanied by the appearance of a wide variety of symptoms, but the most obvious sign of the presence of helminths is stagnation of bile in the body.
Prevention of opisthorchiasis - precautions
Measures to prevent opisthorchiasis are simple:
- To prevent opisthorchiasis, you should not eat raw or undisinfected fish.;
- To prevent opisthorchiasis, it is necessary to strictly follow the rules of heat treatment of fish - fry the fish in a sheet form for at least 20 minutes in a well-heated frying pan in boiling fat. The same time is required for frying fish cutlets. Cook the fish for at least 15 minutes from the moment the water boils, after cutting it into pieces. Salt in a warm solution at a temperature not lower than 15°C for at least two weeks, with a salt consumption of 270-290 g per kilogram of fish. Dry the fish (25 cm in size) for at least 3 weeks after 2-3 days of salting at the rate of 12-14% salt to the weight of the fish. Opisthorchids die when fish are frozen at -40°C for 7 hours, at -35°C for 14 hours, at -28°C for 32 hours;
- To prevent opisthorchiasis, it is necessary to thoroughly treat kitchen utensils after cutting fish.;
- To prevent opisthorchiasis, you must wash your hands thoroughly after cutting and preparing fish..
Strict adherence to preventive measures will protect you and your loved ones from infection and the need for treatment for opisthorchiasis.
Diagnosis of opisthorchiasis
In the early stages, diagnosis of the disease is ineffective due to the fact that eggs in stool can only be detected for 4-6 weeks. Therefore, the diagnosis is made on the basis of a survey of the subject according to the following parameters: being in an epidemic area, eating dried, raw, low-salt food.
Due to the high concentration of globular proteins of the JgM class, the following diagnostic methods are distinguished:
- The indirect hemagglutination reaction is effective in 85% of cases of detecting antibodies and antigens.
- Radio-electronic diagnostics are effective in 92% of cases. The conclusion is confirmed only after one and a half months when worm eggs are detected. In the chronic phase of the development of the disease, the following methods are used: parasitological, which is based on the analysis of feces or gastric juice. The following methods are considered effective methods for coprooscopic diagnosis: ether-formalin sedimentation of eggs, ether-acetic sedimentation and Kato smear.
Diagnosis and prevention of opisthorchiasis includes the following activities:
- Therapeutic and preventive: constant monitoring of cured patients.
- Sanitary and epidemiological: protection against the entry of feces into water bodies; adherence to fish processing technologies.
Epidemiology of helminth
You need to know that the final hosts are considered to be: humans, predatory animals, in whose feces the parasite eggs are found. The main source of infection is unprocessed, lightly salted or lightly dried fish products that contain cat fluke. The main period of infection with worms is considered to be summer and autumn.
Worms, penetrating the human pancreas and living there for several weeks until puberty, lay eggs. The pathogenesis of helminths is manifested as follows: a source of toxic and allergic reactions in the host’s body; damage the biliary system; disrupt the secretion and activity of the gallbladder, stomach and duodenum, and in isolated cases cause liver cancer.
Prevention of opisthorchiasis - precautions
Measures to prevent opisthorchiasis are simple:
Strict adherence to preventive measures will protect you and your loved ones from infection and the need for treatment for opisthorchiasis.