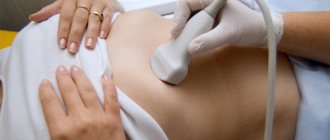
Liver elastography is the latest diagnostic method, which evaluates tissue elasticity; this study allows you to accurately determine the stage of development of organ fibrosis. Sometimes doctors call this method of diagnosis virtual palpation, because with the help of an ultrasound sensor it is possible to “palp” the organs of the human body.
Understanding Elastometry
Liver elastometry is a modern non-invasive (non-traumatic) method for identifying the stage of the fibrotic process in elastic hepatocytes.
Elastometry is carried out using the Fibroscan device, which is why the procedure is often called fibroscanning. This study is similar to ultrasound, but elastometry does not use a sound wave, but rather determines the speed of the pulse.
With its help, you can detect any changes in the structure of the gland.
Elastometry is performed to prevent various gland diseases. This is important, since many liver pathologies have a hidden course, so it is necessary to monitor the condition of the body.
If standard ultrasound diagnostics allows you to evaluate only the density of tissues, then fibroelastometry will help determine how strongly they resist the electromagnetic vibrations that the device emits. In this way, it is possible to identify areas of the organ whose density is reduced.
Fibroscanning is used to achieve the following goals:
- Assessing the degree of damage to the gland.
- Selecting a patient treatment regimen.
- Monitoring the course of the disease (progression or regression of fibrosis).
- Making a prognosis for the disease.
Using elastometry, it is possible to identify the disease in the early stages, when conservative treatment is still possible without serious complications.
Pros and cons of elastometry
According to doctors, liver fibroscanning has the following advantages:
- The study is carried out on an outpatient basis.
- The patient does not feel pain, so there is no need for anesthetics.
- Fibroscanning is a non-invasive study during which the integrity of the skin is not compromised, so the patient does not need rehabilitation.
- Does not cause adverse reactions or complications.
- The patient receives the result immediately after diagnosis.
- Makes it possible to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and, if necessary, adjust it.
- Using elastometry, you can examine the entire area of an organ.
- Fiber scanning guarantees an accurate result; with repeated diagnostics, the result may differ by 3.2%.
- This is a simple examination that does not require special preparation and takes little time (5–10 minutes).
- Can be used for liver diseases in late stages (except ascites).
Elastometry is often compared to biopsy. According to doctors, the first study is much safer and more informative than the second. During a biopsy, only a separate area of the organ is examined, while fiber scanning allows one to examine the entire volume of tissue. With a biopsy, there is a risk of infection as well as bleeding. In addition, this procedure is carried out in a hospital setting, and it requires a highly qualified doctor.
Despite the advantages, this study has disadvantages:
- Using elastometry, it is impossible to assess necrotic lesions of gland tissue.
- In some cases, it is difficult for a specialist to differentiate between the early stage of fibrosis and its absence.
- Results may be distorted in some patients.
But in general, fibroscanning is much more informative than a biopsy. It helps the specialist get his bearings, prescribe additional examinations, and draw up an effective treatment regimen. In addition, it is important that elastometry does not cause pain or complications.
The essence of technology
Elastography is a safe alternative to liver biopsy. During such an examination, a fragment of tissue is removed from the organ using a special needle - a biopsy specimen, which is examined under a microscope. A biopsy is associated with risks, primarily injury to the organ. The procedure has a number of contraindications. In addition, it is accompanied by psychological and physical discomfort for the patient.
Using non-traumatic sonoelastography, you can scan the organ with the latest Fibroscan device. Within a few minutes, it allows you to fully examine the organ and determine the degree of development of fibrosis in the patient. In this case, such an indicator as the elasticity of the liver is analyzed. It is measured in Pa and kPa.
All measurements are carried out at points, which makes it possible to examine most of the organ. Biological liver tissues are characterized by uneven elasticity coefficient. Thus, the reflected sound wave will have a different length, which is recorded by special equipment.
Progress of the study
In order for the diagnostic results to be reliable, preliminary preparation for fibroscanning (elastometry) of the liver is required:
- The last meal should be planned 2 - 3 hours before the procedure.
- 2–3 days before elastometry, it is recommended to avoid foods that cause flatulence: milk, legumes, tomatoes, rye bread, soda, sweets.
- If the patient is undergoing drug treatment as prescribed by a doctor, the drug is taken according to the prescribed regimen.
- Before the examination, you should remove any piercings from the navel area or a belt with a metal buckle, as they may distort the results.
The procedure is carried out on an empty stomach. The patient lies on his back, places his right hand under the back of his head and raises it above his head. The specialist applies the gel to the right hypochondrium and places a sensor on it, which emits short sound pulses towards the liver.
The patient feels a slight vibration or slight tingling during the scan.
The scanner reads the sound waves that the iron reflects and also calculates their speed. The device independently processes the elastometry results. The session lasts no longer than 10 minutes.
Immediately after the procedure, the patient can go about his business.
https://youtu.be/dlrPis5P7mo
Preparation
Preparation for the procedure is important, because its results will depend on it. Eating is prohibited 8 hours before the procedure. It is important to take the results of your biochemical blood test with you. It should contain data on the level of enzymes such as ALT, AST, GGT, bilirubin. Before the liver elastography procedure, drinking alcoholic beverages is strictly prohibited. You should not smoke for several hours before the examination.
The day before, it is prohibited to consume foods that cause increased gas formation. The presence of gases in the intestines significantly changes the results of the study, and the diagnosis may be inaccurate. It is forbidden to consume all foods that can cause heartburn or provoke increased acid formation.
You should avoid using:
- all legumes;
- milk;
- kefir and fermented baked milk;
- cheese;
- cabbage;
- apples;
- grapes;
- pears;
- of bread.
No other special preparations are required.
Decoding indicators
During diagnosis, a fibroscan shows information about the density of liver tissue. Density is measured in kilopascals (kPa). The lower this value, the healthier the iron.
Note. With fibrotic changes, the density of the organ increases. As a result, the sound waves emitted by the sensor overcome strong resistance. For this reason, with advanced fibrosis, fibroscan readings will be high.
The result is deciphered using the Metavir scale:
- F0 – does not exceed 6.2 kPa, there are no signs of pathological changes.
- F1 – from 6.2 to 8.3 kPa, the initial stage of fibrosis.
- F2 – from 8.3 to 10.8 kPa, moderate fibrotic changes.
- F3 – from 10.8 to 14 kPa, pronounced fibrosis.
- F4 – from 14 and more. This indicator indicates liver cirrhosis, when almost all hepatocytes are replaced by connective tissue fibers.
Contraindications
In some cases, elastometry is contraindicated:
- Pregnancy. The effect of electromagnetic waves on a child has not yet been fully studied, so doctors do not recommend fiber scanning to avoid complications.
- Children under 18 years of age. The procedure is prohibited, as it is difficult to predict the child’s reaction.
- Ascites (abdominal dropsy). Free fluid in the abdominal space can distort diagnostic results. For this reason, elastometry is not recommended for hepatitis and cirrhosis, since ascites is often detected in patients.
- Presence of a pacemaker. Electromagnetic radiation can disrupt the settings of a precision device.
- In case of severe obesity, the study is also not recommended.
Elastometry can be performed in the presence of inflammatory processes, allergies, circulatory disorders, vascular diseases, etc.
Differences between elastography and elastometry
Liver elastography and liver elastometry are essentially similar procedures that are performed on the same device. Fibroelastometry allows you to quantify the density of liver tissue (the ratio of normal cells to fibrotic changes).
Many patients are interested in the question of what elastography is. This is the most informative method for identifying the degree of fibrosis. The study is performed in 2 modes, during which the specialist observes an ultrasound image of the area of interest and color mapping to assess tissue density.
There are 2 types of elastography:
- Dynamic (shear wave method). This is a “blind” fibroscanning method, which allows you to determine the problem area, as well as assess the degree of fibrosis.
- Static or compression. This liver examination is performed in real time. During the procedure, the specialist uses a combination of ultrasound radiation and virtual palpation of the affected area (light pressure with a sensor on the organ being examined). As a result, he receives the value of the density of the affected tissues, which are highlighted in a certain color (soft tissues are blue, and dense ones are red).
Using elastography, you can determine the phase of chronic pathology, the severity of inflammation, and the level of tissue scarring.
Indirect elastometry of the liver helps to track the dynamics of fibrosis development. If it is necessary to identify the disease, additional diagnostics will be needed.
Thus, elastometry differs only slightly from elastography.
https://youtu.be/370TKGY9rl4
Indications for liver fibroscanning
We recommend liver analysis using Fibroscan:
- to detect liver cirrhosis, including alcoholic;
- if viral or autoimmune hepatitis is suspected;
- with cytomegalovirus, cholecystitis;
- for obesity and Gilbert's syndrome;
- in case of hereditary hepatosis;
- with obstructive jaundice caused by unknown causes;
- if the concentration of bilirubin in the blood is exceeded, the content of liver enzymes is increased, blood clotting is impaired;
- when a plexus of venous vessels appears on the surface of the abdomen, and the spleen is enlarged - signs of portal hypertension.
An indication for examination is any disease that is accompanied by liver fibrosis. For people over 40 years old, doctors recommend elastometry for preventive purposes.