Liver flukes
Worms in the human liver most often belong to the class of tapeworms. One of their representatives, the liver fluke, is often found. The life activity of this type of parasitic worms is also dangerous due to the development of complex pathological processes. Parasitic liver diseases, which develop as a result of the activity of the fluke, lead to the fact that liver functions begin to be impaired. The main reason for the appearance of these parasites is the consumption of raw fish and meat.
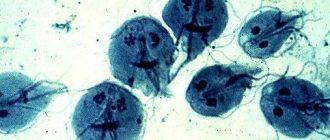
Giardia
These protozoa cause the development of giardiasis, a parasitic disease that leads to functional and organic disorders, inflammatory processes, and the addition of bacterial infections.
Roundworms
When talking about what parasites live in the human liver, we must not forget about roundworms. These helminths can cause diseases, which subsequently lead to the patient developing microabscesses and micronecrosis of liver tissue.
Schistosoma
These parasites can be considered one of the most dangerous organisms leading a parasitic lifestyle. Their activity can lead to the development of deadly diseases such as hepatitis and cirrhosis.
Echinococcus
Cleansing the liver from parasites may also be necessary if echinococci are detected by specialists. The vital activity of these organisms can lead to the development of processes that may require surgical intervention. The main parasitic liver diseases caused by echinococci are tissue atrophy or echinococcal cyst. Also, their vital activity leads to progressive circulatory disorders and compression of the bile ducts.
As already mentioned, symptoms indicating the presence of helminths and protozoan parasitic organisms can be very similar to the clinical picture of other diseases. Therefore, doctors use a variety of diagnostic methods to detect the presence of foreign organisms in the liver. These include:
- microscopic analysis of duodenal contents and bile;
- tests for the presence of antibodies;
- enzyme immunoassays;
- implementation of PCR to detect the DNA of parasitic organisms;
- endoscopy;
- radiography, etc.
Using the above types of diagnostics, helminths and protozoa can be identified, after which appropriate therapy will be prescribed.
96-well microplate used for ELISA
What parasites infect the liver?
Parasites enter the body mainly through the oral route through dirty hands and poorly processed food. People living in regions with developed agriculture are at risk. The initial stage of invasion is often asymptomatic, which makes early diagnosis difficult. Parasites in the human liver multiply quickly, absorbing useful and fortified products of liver cells. The liverworm adapts to changing living conditions and is resistant to many medications. Helminths living in the liver:
- Schistosoma. The worm inhabits the blood vessels.
- Roundworms. The cause of necrosis of the hepatic epithelium, leading to abscesses and inflammation.
- Giardia is a worm that attacks the liver. Giardiasis is characterized by severe symptoms.
- Amoebas. They disrupt systemic blood flow and promote the formation of blood clots.
- Echinococcus. Invasion is accompanied by expansion of the parenchyma, which provokes compression of blood vessels and bile ducts. The affected liver decreases in size.
https://youtu.be/j6QXtO4vc9c
Schistosomes
Schistosomiasis is distinguished by an acute onset and a chronic course, the cause is blood flukes, trematodes of the genus Shistosoma, which parasitize the liver. Schistosomes penetrate organs using spines and attach to the walls of the organ using a suction cup. The life cycle requires an intermediate host - a freshwater mollusk, the final host - humans and some warm-blooded animals. Life activity and mating occur in the venous blood.
Unilocular echinococcus
The larval form of the tapeworm Echinococcus leads to the development of pathology - echinococcosis. Cattle, sheep and pigs are carriers of Finnish. The excrement of sick animals contaminates feed supplies of agricultural livestock and fresh water bodies. Once in the human stomach, the larvae of echinococcus are spread throughout the body through the bloodstream. The liver, lungs and brain suffer. The inner surface of the worm is covered with heads from which tape forms of the parasite develop. Echinococcus larvae are resistant to temperature changes, but sensitive to humidity.
Giardia in the liver
Giardia is a single-celled parasite whose life activity occurs in the liver and intestines. In the intestines, helminths form cysts, with the help of which reproduction occurs; in this form, the parasite survives unfavorable living conditions. In the host’s body, the vital activity of the cyst begins after it is released from the shell. Signs of pathology are an acute onset with indigestion and pain in the right hypochondrium.
Alveolar echinococcus
The introduction of alveococcus tapeworm eggs into the body leads to the progression of the disease - alveococcosis. Once in the gastrointestinal tract, the larvae are freed from the shell and, penetrating the bloodstream, disperse throughout the internal organs. Most of the eggworms in humans settle in the liver, they germinate into other tissues and spread to neighboring organs. As a result of pressure on internal membranes, it leads to degeneration and atrophy of organs. Mature larvae are released into the environment and soil with feces.
Ascariasis
A parasitic liver infection, ascariasis, develops with the introduction of a round helminth, ascaris. The larvae live in the soil for 10 years or longer. Development begins only in the human body. Orally, the eggs penetrate the intestines and there, invading the walls, reach the bloodstream and move to the liver. Cause various types of dysfunction. The disease is easy to treat; self-treatment often occurs, since sexually mature individuals die within a year. The simultaneous death of a large number of roundworms will lead to blockage of blood vessels.
Amoebas and amoebiasis
Amebiasis is a disease of “dirty hands” caused by a single-celled organism - amoeba. Helminth cysts penetrate into the gastrointestinal tract with food. Once in the intestine, under the influence of enzymes, the membrane of the cyst dissolves and 8 mononuclear amoebae appear. Cysts are often resistant to antibiotic therapy. Parasitic liver diseases more often affect adult men than women and children. Large lesions lead to hepatitis and peritonitis.
Types and characteristics of infections
Regardless of what type of parasite is diagnosed, it is important to promptly begin treatment for the infection.
In this way, you can stop the destruction and depletion of the body's resources. The most common diseases are:
- Ascariasis. Once in the body, roundworms also affect the liver, releasing toxic toxic substances, clogging the bile ducts and causing inflammatory processes and microabscesses of the organ. In severe stages of pathology progression, complications are possible in all organs of the gastrointestinal tract and even the nervous system.
- Giardiasis. According to statistics, almost half of the entire current population of the Earth is infected with Giardia. In large quantities, parasites cause disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, blockage of the bile ducts, inflammation, acne and skin rashes.
- Echinococcosis. Most often, the pathology is diagnosed in people who have systematic contact with domestic and wild animals, including through their occupation. When they enter the stomach and blood, echinococcus eggs settle in various internal organs of a person, including the liver. When the disease is active and reaches a severe stage, serious consequences and health complications are possible.
- Amoebiasis. Most often, the infection enters a healthy body due to a lack of hygiene measures. First of all, parasitic protozoan microorganisms settle in the organs of the gastrointestinal tract, and enter the liver from the large intestine. As a result of active reproduction and progression of pathology, amoebic hepatitis and abscess can develop. The phenomenon is accompanied by general malaise and a steady increase in body temperature.
- Opisthorchiasis. The disease is caused by a fluke parasite, which, when it enters the liver, forms abscesses in the tissues. Among the most dangerous complications and consequences of the progression of the pathology are cirrhosis of the liver, heptomegaly, peritonitis, and purulent cholecystitis.
- Schistosomiasis. Entering the host's body through the skin, flukes are localized in the bladder and liver. As a result of extensive damage, blockage of ducts, veins and vessels, as well as surges in blood pressure, are possible.
Parasites enter the human body in various ways. Most often there may be the following reasons for this:
- Failure to comply with basic hygiene rules;
- Drinking raw water;
- Insufficient heat treatment of food products (especially meat products and fish);
- Insufficient hygiene when working in the garden;
- Frequent contact with affected animals;
- Contacts with sick people.
Each type of infection has its own methods of infection and treatment methods.
https://youtu.be/IGjQnsAWqAg
What diagnostics are performed and what tests should I take?
- primary diagnosis is carried out by interviewing the patient to check for symptoms of the lesion;
- fecal matter is visually checked for the presence of oviworms;
- PRC diagnostics makes it possible to determine the causative agent of the disease in biological material;
- endoscopic and fluoroscopic diagnostics confirm the presence of parasites in the liver;
- it is necessary to take a blood test for antigens and antibodies to helminths to find out which parasite caused the deviations;
- take plasma and stool tests for serological testing.
Symptoms and how to identify parasites in the human liver?
It is quite difficult to identify parasites in the liver at an early stage, since the onset of the disease is characterized by the absence of symptoms, which leads to a late visit to the doctor. Parasitic liver lesions cause bad breath and a foul taste. Helminthic diseases are accompanied by loss of appetite, a permanent feeling of hunger and skin rashes. The main symptoms of parasites in the liver:
- a sharp decrease in body weight, up to dystrophy;
- nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and dehydration;
- disturbance of mineral metabolism;
- fever, with an increase in temperature to 37-39 degrees and above;
- rashes on the skin: acne, seborrhea, age spots;
- nervous excitability and sleep disturbances;
- pain when inhaling on the right side;
- change in liver size;
- yellowness of the skin and sclera;
- hair loss and brittle nail plate.
Treatment of parasitic disease
Each type of parasite manifests itself differently during active reproduction. However, in the first stages of infection progression there may be virtually no signs of pain.
However, as they progress, parasitic organisms adapt to existence in the intestines and liver and begin to move throughout the body, penetrating other human organs and systems.
In the first stages, the following symptoms of parasites in the liver may be observed:
- Weakness and fatigue, general malaise;
- The appearance of acne on the skin of the body;
- Changes in the activity of sebum production;
- The appearance of dryness and flaking of the skin;
- Hair loss;
- Swelling;
- Fragility of the nail plates;
- Deterioration of complexion.
In severe advanced stages, the following may also be observed:
- Change in stool, persistent diarrhea;
- Nervousness and irritability, sleep disturbance, nightmares;
- Increased appetite;
- Pain in the abdomen and right hypochondrium;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Hyperthermia;
- Enlarged liver (detected by hardware diagnostics);
- Detection of a dense node when pressed, pain during palpation;
- Heartburn;
- Jaundice of the skin and sclera;
- The appearance of a rash;
- Loss of body weight;
- Bad breath.
Parasites in the human liver come in a wide variety. What parasites live in the liver? This organ is mainly affected by amoebas, roundworms, lamblia, alveolar, unilocular echinococcus, and schistosomes.
Amoebas are able to penetrate from the intestinal region into the human liver. They are sent to the liver region through the lymph nodes and venous vessels, where they end up penetrating through the intestinal walls.
Amoebas, being active in all tissues and healthy cells of the organ, can provoke the development of thrombosis and disruptions in cellular nutrition. During the life of parasitic forms, secreted toxins penetrate into the liver tissue, which cause necrosis. When several necroses merge, an amoebic abscess develops.
Schistosomes
These parasites attack the hepatic blood vessels. And parasitic larvae are localized, grow and develop in the tissues of the organ. Infection of the body with schistosome threatens a person with the development of hepatitis or cirrhosis of the liver.
Giardia
Giardia actively multiplies in the liver area, causing:
- addition of a foreign infection;
- severe inflammatory processes;
- hepatocyte dystrophy;
- active production of leukocytes.
It is worth noting that Giardia in this organ feels quite good, but cleansing the liver of parasites at an unadvanced stage proceeds quickly and practically does not cause any complications.
Roundworms
This type of parasitic form belongs to round helminths. Localized in the liver tissues, roundworms cause microabscesses and micronecrosis. Accompanied by the development of purulent inflammation in the tissues. When an organ is affected by adults, people may notice the development of hepatitis, and cholangitis may also be diagnosed.
Alveolar echinococcus attacks healthy cellular structures and tissues of the organ. Usually there is an active spread of metastases to nearby organs, for example, the lungs. Such metastases can also affect the central nervous system.
As the bladder develops, it increases significantly in size, which increases the risk of developing atrophy of the liver tissue, squeezing blood vessels, and deteriorating the functioning of the bile ducts.
How to check yourself for parasites? The presence of worms in the human liver can be judged by the following symptoms:
- the appearance of seborrhea;
- spread of acne;
- manifestation of freckles and age spots;
- formation of early wrinkles and bald spots;
- the appearance of layering and brittleness of the nail plates;
- engorgement of the epidermis;
- spread of papillomas;
- formation of cracks in the skin.
Parasitic liver diseases in the early stages of their development have scanty symptoms, and in some cases they are completely absent. The difficulty in determining pathology lies in the fact that many symptoms are a sign of other diseases.
Symptoms of liver parasites begin to actively appear when the worms have reached their maturity.
Damage by amoebas manifests itself:
- leukocytosis;
- weight loss;
- the appearance of pain in the liver, which can radiate to the shoulder area;
- the presence of prolonged fevers.
Other parasites can be identified by the following signs:
- nervousness;
- sleep disturbances, insomnia or wakefulness between 2 and 3 am, since it is at this time that the liver is activated;
- regular feeling of hunger;
- presence of unpleasant odor from the oral cavity;
- presence of an unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- the appearance of acne;
- development of migraine;
- diabetes.
At least one identified symptom from the list above is a good reason to consult a doctor.
So, how to remove parasites from the liver? When diagnosing, the first thing the patient should do is calm down, since cleansing the liver from parasites with timely consultation with a doctor occurs effectively and quickly. This is due to the fact that the liver is an organ that can fully recover in a fairly short period of time.
It is generally accepted to treat parasites with medications on a synthetic or natural basis. However, in some cases, the disease may recede even with the use of traditional recipes.
Doctors recommend their patients to use medications in order to get rid of parasites as soon as possible. However, it is worth considering that such antiparasitic drugs have a very extensive list of side effects. The main one is intoxication, which occurs as a result of the massive death of helminths and the disintegration of their bodies in the human body. Intoxication can impair kidney and liver function, and can also negatively affect the circulatory and central nervous systems.
To eliminate intoxication, as well as improve the effectiveness of drugs against parasites in the liver, doctors recommend additionally drinking probiotics and sorbents. By removing toxins, these medications help strengthen the patient's immune system, reduce the risk of side effects from anthelmintic drugs, and actively remove dead parasitic individuals and their larvae.
There are many signs that your liver is not functioning properly. Let's look at the main points that are worth paying attention to:
- rapid weight loss, since the parasites take almost all the nutrients from the patient’s liver, the body does not have time to replenish the losses;
- constant headaches, which intensify at night and in the evening, as worms constantly release harmful substances, intoxication of the body occurs;
- there is a lack of calcium, if there are parasites in the liver, then the patient will definitely have hair loss, crumble nails, teeth, and bone fractures may occur under light loads;
- a large number of freckles and age spots will appear on the body, which is associated with metabolic disorders;
- the skin will become rougher, small cracks will begin to appear, which may be joined by secondary infections;
- severe pain in the liver area, resulting from the destruction of cells and tissues of the organ by parasites;
- nervousness and irritability that appear unexpectedly to everyone around you is the effect of parasites on the central nervous system. There is also constant fatigue, the patient constantly wants to sleep;
- poor or, on the contrary, very good appetite, but at the same time, naturally, the person does not gain weight, since all nutrients are absorbed by parasites;
- allergic reactions, most often of a skin nature, such as rashes and itching;
- bad breath caused by intoxication of the body;
- Possible itching near the anus.
If a person has discovered several of the above symptoms at once, it is highly likely that the body is affected by worms and needs treatment. Naturally, such symptoms are not always caused by liver parasites and the cause of various abnormalities in the body’s functioning may be more common intestinal helminths. In any case, the risk of helminthic infestation is high and it is recommended to consult a doctor for a more detailed diagnosis.
How to get rid of worms?
The first signs of helminth detection require serious monitoring. It is necessary to get rid of parasites in the liver in order to quickly reduce the negative effects. A special medicine removes parasites in a few days, although the process of getting rid of some worms takes a long period. Cleansing the liver with pharmaceuticals has a detrimental effect on the functioning of internal systems. The treatment complex should include the intake of probiotics and enterosorbents that reduce the toxicological effects on the body. The choice and dosage depends on the degree of damage and the helminth that caused the disease. You can take medications only after prescription by a doctor. Treatment for worms looks like this:
- preparatory actions that prepare the body to get rid of parasites;
- taking anthelmintic drugs;
- procedures for restoring the functioning of the organ.
Deworming tablets
- broad-spectrum drugs are used when schistosomes and echinococcus are detected: Prazaquantel, Mebendazole, Allendazole;
- for ascariasis, Pirintel and Levamisole are prescribed; the drug Piperazine treats helminthiasis in children of the first year of life and in pregnant women;
- Giardia and amebiasis are treated with antimicrobial and antiprotozoal agents - “Trichopol”, “Fazizhin”, “Hiniophone”;
- to reduce the toxic effects associated with the death of helminths, sorbents are prescribed - “Smecta”, “Sorbex”, “Enterosgel”, “Activated carbon”;
- against dysbiosis, complexes of beneficial bacteria are prescribed - “Linex”, “Biogaia”, “Bifidum”, “Lactobacterin”;
- You can restore liver function using liver medications - Karsil, Gepabene, Silymarin.
Folk remedies for worms
You can cleanse the liver of parasites using traditional medicine recipes. Most often, pumpkin seeds, onions, pine nuts and garlic are used for such purposes. To remove parasites from the liver, a medicinal herb is used - wormwood or tansy. Folk remedies for parasites in the liver have virtually no contraindications and do not have a toxicological effect on humans. But it is dangerous to be treated without consulting a specialist.
https://youtu.be/eg-YLyf2b9E
Medicinal herbs
Previously, when there was a suspicion of helminthic infestation in the liver and bile ducts, medicinal herbs were recommended - tansy, yarrow, St. John's wort flowers, immortelle and chamomile. To prepare a cleansing infusion, take a tablespoon of dried herb in half a liter of boiling water and leave for 12 hours. This amount of tincture will be enough for 4 days if you take 100 ml every morning. Drink on an empty stomach for 12 days. Repeat twice with an interval of 3 days. Prevention is carried out once a year.
How to remove parasites using onions?
If a blood test for parasites confirms that helminths live in the liver, traditional medicine suggests using an onion tincture recipe. A large chopped onion is steamed in a liter of boiling water and kept in a thermos for 12 hours. Before use, it is filtered and taken in the morning on an empty stomach. Therapy lasts 10 days and is performed daily. For prevention, repeat once every six months.
Parasites in the human liver can be eliminated with folk remedies, but subject to careful adherence to the instructions.
Treatment with other methods
- Parasitic liver disease is also treated with clove seasoning, which is crushed in a coffee grinder and taken in an amount equal to a match head in the morning and evening.
- The alcohol tincture is infused on the partitions of the walnut shell for a week, taken on an empty stomach, one teaspoon at a time.
- The most famous method is pumpkin seeds. One-time dose - 300 grams of ground seeds, filled with water, with a teaspoon of honey.
Treatment methods
Therapy for helminths in the liver is usually carried out in several stages:
- Elimination of intoxication, removal of waste products of parasitic organisms, restoration of liver functions. At this stage, a special therapeutic diet is prescribed that blocks the growth and reproduction of parasites. Therapy is also carried out with sorbents, antiallergic and choleretic medications.
- Cleansing the liver of parasites by direct action. At this stage, anthelmintic drugs are prescribed.
- Restoration of the human body’s immunity, preventive measures against relapse of infection.
For each type of infection, a specific set of anthelmintic medications is prescribed:
- For giardiasis: Furazolidone, Trichopolum, Tinidazole;
- For amebiasis: Metronidazole, Delagil, Ornidazole;
- For ascariasis: Pyrantel, Levamisole, Piperazine;
- For schistosomiasis: Praziquantel, Albendazole;
- For opisthorchiasis: Mebendazole.
Medicines for liver parasites are selected on an individual basis. Sorbent preparations are of particular importance throughout the entire treatment period. In this case, the following are most often used: Smecta, Polysorb, Enterosgel, Nemozol, Vormin and activated carbon.
In advanced stages, surgery may be indicated to remove abscesses, cysts and other neoplasms resulting from the activity of parasitic organisms.
During pregnancy and lactation, elimination of worms in the liver is carried out in a gentle manner according to a special scheme. Traditional medicine recipes are often used for this.
Preventive measures
- wash your hands thoroughly before eating and after using the toilet;
- Do not touch mucous membranes with dirty hands during the day;
- process consumed products;
- do not buy meat that has not undergone sanitary inspection;
- before cooking, check the meat for the presence of finn;
- It is better to store raw foods, especially meat and eggs, separately;
- do not swim in unfamiliar fresh water bodies;
- do not drink raw water.
https://youtu.be/b4ukPOnH-Yw
The main reason why liver parasites enter the organ is non-compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards. Owners of cats and dogs are at risk. Such animals are carriers of the disease. A pet can easily become infected with parasites, despite receiving antihelminthic medications. Recolonization of helminths occurs quickly after cure. Remember that all traditional treatment methods require consultation with a doctor.
Routes of infection
Worms and other parasites can enter the human body in several ways. There are two types of parasitic lesions: primary - the liver is immediately affected, secondary - first they live in other internal organs. The main routes of infection are:
- Ground contact. The eggs of some types of parasites can live in the ground for a long time. You can become infected with them if you do not wash berries, vegetables and fruits, hands and feet well after working with the soil.
- From person to person. Household items can become a source of infection, especially if the room is not thoroughly cleaned and surfaces are not cleaned. For example, if someone in a group is a carrier of pinworms, then most likely they can be found in someone else. They can even be transmitted through a handshake.
- From pets. No matter how carefully your pets are cared for, they are still carriers of various parasites. Adults or eggs can enter the human body through contact with fur, saliva, or feces. You can also become infected after an insect bite.
- Infected water. Unfortunately, some people do not have access to clean water. Some people collect it in their own wells, others use public ones. Experts advise everyone to check the quality of the water they drink by contacting the appropriate services.
- Improperly processed food. This applies to undercooked meat, especially kebabs, fish, and other products that have not undergone sufficient heat treatment.