Causes
If the results of an ultrasound show that the area of the reproductive organ is enlarged, this may indicate the presence of certain disturbances in the functioning of the body.
The uterus, like any other organ, has its own proportions (sizes); it must be located in a certain area (some deviations from the normal value are allowed). If the uterus is enlarged in size, this may be a sign of pathology (disease, tumor, etc.)
But there are cases when expansion occurs for other, non-pathological reasons; it appears:
- During menstruation (clearly visible on ultrasound, provided that bleeding is heavy).
- During menopause (occurs against the background of hormonal changes in the body).
- During pregnancy (do not forget that the expansion of the uterine cavity may indicate the onset of pregnancy).
The uterus increases in volume and dilates after an operation called a caesarean section.
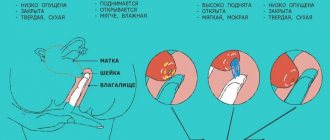
Cervix during pregnancy
The task of the cervix during this period is to protect the fetus from infection and prevent miscarriage or premature birth.
Soon after conception, the following changes occur in her:
- The pink surface of the canal acquires a bluish tint due to the increased pattern of blood vessels. This is facilitated by intensive blood circulation in the uterus.
- The mucous membrane becomes softer. This also occurs due to increased blood circulation and mucus production.
- The cervix drops lower, and the lumen of the canal narrows and is tightly “sealed” with a plug.
Based on these changes, a gynecologist can visually determine pregnancy a few weeks after conception.
As the fetus develops in the womb, the length of the cervix gradually decreases. It is very important that it corresponds to the duration of pregnancy, since a too short cervix can threaten miscarriage or premature birth.
In the third trimester, the cervix becomes shorter, softer, and closer to childbirth it begins to open slightly. The mucus plug may go away within a few weeks of labor.
How to determine whether the uterine cavity is dilated?
Dilatation of the cervix or the uterus itself is diagnosed through several studies. As part of a preventive or diagnostic examination, the following may be prescribed:
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- Ultrasound of the ovaries;
- Ultrasound of the uterus and fallopian tubes;
- CT organ.
Uterus on ultrasound
Using an ultrasound, it is easy to determine whether there are problems with the reproductive organ or whether the cause of enlargement is the monthly menstruation period. But not only ultrasound is prescribed to patients; if indicated, the gynecologist can prescribe a CT scan of the organ.
Enlargement of the reproductive organ should not be considered a pathology, since there are a number of reasons that have no connection with diseases, but are a consequence of the natural state of the woman’s body.
But dilation of the uterine cavity can be asymptomatic; signs of the disease appear only when the phenomenon has a certain connection with the pathology and is diagnosed against its background.
What to do if dilation is visible on ultrasound:
- Contact a gynecologist.
- Carry out a number of additional diagnostic procedures.
- Do an ultrasound on another day of the cycle.
All this will help confirm or refute the accuracy of the diagnosis and identify the pathology that caused this phenomenon.
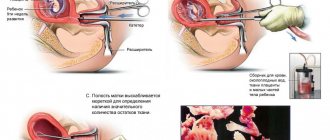
Progress of the curettage procedure
The operation is performed in an operating room on a gynecological chair. The process is painful, therefore it is carried out under mandatory anesthesia (general or local - according to the indications or desire of the patient).
Stages of gynecological cleansing of the uterus
- Treat the external genitalia with an antiseptic (Lugol's solution).
- The location of the cervix is identified using a gynecological speculum.
- The cervix is fixed with forceps to prevent its displacement (the organ is suspended by ligaments).
- Dilation of the cervix: a dilator is inserted into the vagina to gain open access. The purpose of Hegar dilators is to enlarge the cervical canal so that the working curette can penetrate the uterine cavity. If necessary, several dilators of different sizes are used, which are introduced sequentially one after another until a channel of the required size is obtained. This stage is omitted if curettage is done immediately after childbirth (at this time the cervix is dilated enough for the procedure).
- Hysteroscopy of the uterus is performed. A 5 mm tube with optical fiber is inserted through the vagina into the cervical canal and further into the uterine cavity. With its help, the localization of pathological formations is determined, visual control is carried out during the operation itself, and the result of the work is assessed after the end of the main procedure.
- The cervical canal is scraped out (the smallest curette is used for this).
- The uterine cavity is cleaned step by step: first the area of the front wall, then the back and lastly the sides. If there are formations beyond the control of the curette, additional instruments are introduced into the uterine cavity, with the help of which, under the control of a hysteroscope, an operation is performed to extract the contents of the uterine cavity.
- Material is collected for histological analysis.
You should know! Histological analysis is the study of tissues for their structural organization, identifying the presence/absence of pathological changes.
Recovery period
If the elective procedure is successfully completed, full recovery takes 4-5 weeks. In the first 14-15 days it is recommended:
- stop using suppositories, vaginal tampons, douching and other effects inside the vagina;
- abstain from sexual intercourse;
- limit physical activity and work in an inclined position;
- avoid temperature changes (visits to baths, saunas, hypothermia, etc.);
- Avoid taking baths and swimming in pools and ponds.
Attention! The first days after surgery, it is especially important to follow all the rules of intimate hygiene.
On the first day after the intervention, the discharge of blood clots may be observed; normally, the discharge may continue for several more days. Normally, minor discharge can last up to 10 days. To prevent cervical spasms and the appearance of hematometra ( accumulation of blood in the uterine cavity), antispasmodic drugs should be taken (selected individually by a gynecologist).
Possible complications
- inflammatory processes of the uterine cavity;
- hematometra (accumulation of blood in the uterine cavity);
- damage to the basal germ layer of the endometrium (almost impossible to correct and can cause infertility);
- perforation of the uterine wall (an extremely rare occurrence; possible only in case of obvious negligence of the doctor or inappropriate behavior of the patient);
- cervical rupture.
When performing separate curettage using hysteroscopy, the likelihood of complications is minimized.
Causes of an enlarged uterine cavity
There are several factors that can lead to the development of expansion:
- Myoma is a benign formation that forms in the muscle layer of the uterus. The tumor is prone to rapid growth, it increases in size rapidly and leads to certain consequences. Myoma rarely develops into a malignant formation. But with a tendency to grow rapidly, the tumor compresses the blood vessels, leading to the development of certain complications. A woman with fibroids may experience some difficulty conceiving.
- Endometriosis or adenomyosis are 2 diseases, when diagnosed, there is an expansion, an increase in the volume of the reproductive organ.
- An ovarian cyst is an unruptured follicle that has turned into a cyst filled with fluid. The appearance of a cystic formation leads to certain consequences. The formation may burst or rupture, resulting in bleeding.
- Cancer. An oncological disease develops latently and does not make itself felt until a certain time, but a doctor can suspect the presence of oncology in a patient based on the results of an ultrasound, which showed the presence of pathology.
The causes of the pathological phenomenon are different, but we should not forget that this phenomenon is not always associated with pathology, it can also be completely natural.
Structure and physiological changes of the uterus
The pelvic cavity is where the uterus is located. It is located in the lower part of the abdominal region. What does the uterus look like? Normally, it looks like an inverted pear. This is a cavity organ, the wall of which consists mainly of muscle tissue up to 3 cm thick. In front of it is the bladder. The posterior part is in contact with the anterior surface of the rectum.
The pelvic and uterine axis are in the same plane, which is considered normal. In addition, it may be slightly inconsistent. This is also not a pathology and does not require action.
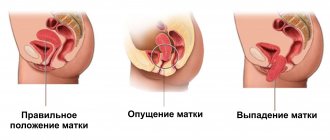
The location of the uterus is influenced by the ligaments located on the sides and performing the function of holding it in the required position. Pathology is considered to be a strong deviation of the organ from the pelvic axis. It can descend, fall out, be located behind the rectum, or bend.
The weight of the uterus in a nulliparous woman does not exceed 50 grams. After the birth of a child, it increases one and a half to two times, reaching 100 g. In addition, the size of the organ matters. Its length in women who do not have children is approximately 7 cm and its width is 4 cm. During pregnancy, the uterus stretches. After childbirth, it shrinks, but it no longer decreases to its previous size. The longitudinal and transverse dimensions increase by 2-3 cm.
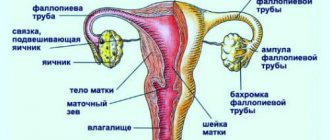
The uterus consists of the fundus, body and cervix. The fundus is the area located above the conventional line passing through the fallopian tubes. The body of the organ in a triangular section starts from the fundus and continues to the uterine constriction.
The cervix is a continuation of the previous part and makes up the entire rest of the uterus. It opens into the vagina and consists of three parts - anterior, posterior and a section located above the vagina. The latter, in women who do not have children, resembles a cut cone, and in those who have given birth, it is cylindrical in shape.
Many of our readers actively use a new method based on natural ingredients, which was discovered by Natalya Shukshina, to TREAT UTERINE FIBROIDS. It contains only natural ingredients, herbs and extracts - no hormones or chemicals. To get rid of uterine fibroids you need to eat every morning on an empty stomach...
The inside of the neck is covered by a layer of epithelium. The part that is visible in the vaginal cavity is covered by stratified squamous epithelium, which is not prone to keratinization. The remaining segment is lined with glandular epithelial cells.
The place of transition from one type to another is of important clinical significance. Dysplasia often occurs in this area, which, if left untreated, can turn into a cancerous tumor.
The frontal section of the organ is similar to a triangle. Its acute angle is directed downwards. A fallopian tube opens into the uterus on each side. The base of the triangle passes into the cervical canal, preventing the release of mucus produced by the glandular epithelium. This secretion has antiseptic properties and kills bacteria heading into the abdominal cavity. The cervical canal has two openings. One protrudes into the uterus, the second into the vaginal cavity.
The cervical canal is round or resembles a transverse slit. The place where the body meets the neck is called the isthmus. Here, a woman's uterus often ruptures during the birthing process.
The uterine wall has three layers: the outer layer is the serous membrane, the middle layer is the muscle fibers that form the basis of the organ, and the inner layer is the mucous membrane. In addition, the parametrium is distinguished - this is fatty tissue that is located in front and on the side of the uterus, in the space between the sheets of the largest ligament. It contains vessels that provide nutrition to the organ.
Contractility is influenced by sex hormones. It is the muscle layer that ensures the birth of a child. The internal pharynx and isthmus also play a certain role in this process.
The mucous layer (endometrium) is covered with epithelial cells. It is smooth and divided into two sublayers. The surface sublayer has a variable thickness. Before menstruation, it is rejected, which is accompanied by bleeding.
The surface layer is also important for gestation. The fertilized egg is attached to it. The basal sublayer is like the base of the mucous layer. Its function is to ensure the restoration of the surface epithelium. It contains tubular glands that reach the muscle fibers.
The serosa is the outer covering layer of a woman's uterus. It lines the muscles of the bottom and body outside. On the sides it passes to other organs.
It forms a vesicouterine cavity near the bladder. The connection with it is carried out through fiber. At the back, the peritoneum passes onto the vagina and rectum, forming the rectouterine cavity. It is closed by serous folds, which consist of connective tissue cells. They also contain some smooth muscle fibers.
Review from our reader Svetlana Afanasyeva
I recently read an article that talks about Father George’s Monastic Collection for the treatment and prevention of fibroids. With the help of this collection you can FOREVER get rid of fibroids and problems like women at home.
I’m not used to trusting any information, but I decided to check and ordered a bag. I noticed changes literally within a week: the constant pain in the lower abdomen that had tormented me before receded, and after 3 weeks disappeared completely. Uterine bleeding has stopped. Try it too, and if anyone is interested, below is the link to the article.
How much can the uterus expand?
An ultrasound of the uterus and appendages will help to see the size of the organ and determine the presence of abnormalities and pathologies.
If the uterine cavity is not dilated, then this should be considered normal, but there are a number of certain indicators that are considered normal.
Interpretation of ultrasound, table of indicators:
| Dimensions of the uterus according to ultrasound results: | Normal indicator: | Patient characteristics: |
| The indicator should not be: | more than 30 mm and less than 50 mm. | This rule applies to those women who have never had children. |
| The indicator does not exceed: | 90 mm. | In the event that a woman has previously given birth. |
The appearance of a tumor in the area of the reproductive organ leads to an increase in its volume by several tens of mm.
The size of the organ, its indicators, the presence or absence of changes in the structure, etc. are noted in the results of diagnostic studies.
The structure of the uterus. Where is a woman's uterus located?
The uterus is pear-shaped, with its narrow part facing downwards. The mature uterus of a nulliparous woman weighs about 50 g and is 7-8 cm in length and 4-5 cm in width. The walls of the uterus are quite dense, and their thickness can reach 3 cm.
The uterus of women who have given birth is somewhat larger - the weight of the organ can increase up to 100 g, and the size of the uterus is 2-3 cm larger than the above.
The internal reproductive organs have only autonomic innervation. This means that the movements of the uterus are not subject to volitional efforts, but are carried out under the influence of neuro-vegetative changes. The body of the uterus has mainly sympathetic innervation, and the cervix has predominantly parasympathetic innervation.
The peculiarity of the autonomic innervation of the internal genital organs is that it occurs through the plexuses. The uterus receives innervation from the uterovaginal plexus, the ovary from the ovarian plexus, and the fallopian tubes from the ovarian and uterovaginal plexuses.
But this knowledge is especially important for the fair sex, since women’s health depends on the correct location and condition of this organ.
Therefore, it is useful for girls from adolescence to be interested in its structure and location. After all, it is quite possible that such information will help avoid serious problems in the future.
Signs of expansion
There are specific symptoms that may indicate problems with the reproductive organ.
Most often, patients complain of:
- Pain in the lower abdomen.
- Unpleasant sensations during sexual intercourse.
- Sensation of a foreign body in the lower pelvis.
- Abdominal bloating, an increase in its volume (can be regarded as a sign of fibroids or cancer).
- Headaches of varying intensity.
- Monthly uterine bleeding that is profuse.
- Lumbar pain.
- Various dizziness.
- Acyclic bloody discharge.
The appearance of unpleasant sensations in the lower abdomen, back, or even in the perineum may indicate the presence of pathology. If such symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor, since there is a high risk of developing enlargement or other pathologies of the uterus.
An increase in the volume of the mammary glands, their engorgement, as well as a sharp decrease in blood pressure levels indicate that certain problems have arisen with the level of hormones, as a result of which an expansion of the uterine cavity has appeared.
What are the dangers of an enlarged uterine cavity?
According to ultrasound, the expansion may not lead to problems of a different nature, but if the phenomenon is related to pathological processes, various diseases and tumors. Then the complications will have a direct connection with the underlying disease that led to the appearance of the expansion.
Complications include:
- problems with conception;
- heavy and painful menstruation;
- hormonal imbalances of various types;
- cystic formations in the ovarian area;
- endometriosis;
- cancer.
Complications arise only under unfavorable conditions. In most cases, a woman has to endure discomfort associated with sexual intercourse or menstrual bleeding. More serious complications occur less frequently.
The most severe is the formation of a cancerous tumor in the pelvic organs. The tumor can metastasize and lead to death; long-term treatment will help get rid of it.
Diagnostics
In order to find out where a woman’s uterus is located and determine its parameters, you should visit an ultrasound diagnostic specialist and a gynecologist.
Examination of the uterine body is carried out in different ways. Every woman knows what a gynecological examination is. Using a special mirror, the gynecologist examines the condition of the external pharynx and palpates the body and bottom of the organ through the vagina and abdomen.
During ultrasound diagnostics, it is necessary to study where the uterus is located. In each individual case, its location may deviate slightly from the norm. A pelvic examination is carried out using a vaginal and transabdominal sensor. To perform an ultrasound through the abdomen, the bladder must be full to increase echogenicity. This is how virgins and pregnant women are examined. But during pregnancy, a vaginal sensor is also used, since it allows you to more accurately determine where the embryo is located and how it is attached, and also allows you to determine the parameters of the cervix.
Treatment of an enlarged uterine cavity
The therapy has a number of features and helps to cope with the disease even before various complications appear.
Before prescribing treatment, the doctor carries out:
- A thorough medical history is taken and the patient is interviewed.
- Prescribes an ultrasound of the pelvic organs (examination of the uterus and appendages).
- Colposcopy (examination helps at an early stage of development, it will detect small areas of expansion).
- X-ray examination (helps to examine the area of the fallopian tubes and uterus).
- Laparoscopy (a person makes punctures in the abdominal wall to carry out diagnostic procedures).
After carrying out the necessary diagnostic procedures, the doctor may prescribe:
- oral contraceptives (combined-spectrum drugs combining estrogen and gestagen);
- antispasmodic or anti-inflammatory drugs of non-steroidal origin (Ibuprofen, Nosha);
- histogenic drugs (hormonal in nature).
Treatment is prescribed by the doctor; if necessary, he can supplement the list of medications with various means.
- If taking medications does not bring the desired effect, then doctors decide to perform surgery.
- Surgical procedures are different; women are prescribed:
- The operation is performed laparoscopically, through punctures in the abdominal wall.
- The expansion is removed using a laser beam, the doctor acts on the tissue, removing excess using a laser.
Abdominal surgery is less commonly performed because it is associated with various risks and has a long recovery period.