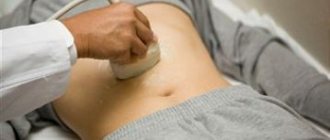
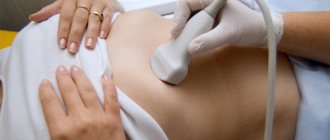
One of the most important human organs is the gallbladder, the function of which is to accumulate and then release bile in as much volume as necessary. Usually this organ is located above the liver and looks like a funnel. If the shape is changed, then experts call this phenomenon constriction of the gallbladder. This disease is not life-threatening for the patient, but if this is not eliminated, then the appearance of unpleasant symptoms is guaranteed.
Tightening of the gallbladder sometimes leads to stagnation of bile in the human body.
What is gallbladder constriction?
Many patients who are diagnosed ask the question - what is a constriction?
Deformation changes that develop in the gallbladder, which has the appearance of an oval, cause a bend or inflection that tightens the gallbladder. The constriction usually occurs in the body, bottom or neck of the problem organ.
Constriction of the gallbladder sometimes leads to the fact that the human body experiences stagnation of bile, which is necessary to properly absorb fatty foods and fat-soluble vitamin-mineral complex in the gastrointestinal tract. With an excessive amount of these substances, an inflammatory process and cholelithiasis begin to develop, as a result of which the bile duct closes.
In order to cope with these problems, you should determine the reasons for the formation of the constriction.
Traditional methods of treatment
For better health and normal gallbladder function, medicinal herbs are used. Pharmacies have a choleretic collection intended for this purpose. It is sold in the form of tea bags. One package should be filled with 200 ml of boiled water, then left for 5 minutes and drunk warm, 1/3 cup 3 times a day. The course should last from 7 days to 3 months.
It is recommended to drink a choleretic preparation, which can be purchased at a pharmacy.
Let's consider other treatment methods:
Types of gallbladder constriction
In modern medicine, gallbladder constriction is divided into two types. The illness happens:
- congenital;
- acquired.
Constriction of the gallbladder is divided into two types: congenital and acquired.
The congenital variety is formed due to the fact that the gallbladder is bent during the intrauterine development of the fetus. In the first year of life, the organ acquires an irregular shape due to the fact that the walls of the gallbladder lengthen. This usually happens at the moment when the baby begins to be transferred from breast milk to another form of nutrition. If such a deformation develops, then the gallbladder is deformed by a constriction, which does not in any way affect the functioning of the digestive system. Typically, this phenomenon does not cause any discomfort and can only be detected by chance, so corrective measures are not required.
Acquired inflection of the gallbladder region can be caused by infectious inflammatory processes developing in the gastrointestinal tract. A stone may form in the cervical area, which then blocks the bile duct and causes severe pain. Such phenomena can be triggered by a number of factors:
- improper diet;
- obesity;
- development of acute or chronic inflammatory process in the area of the gallbladder;
- after a long stay in a sitting position;
- after lifting heavy objects;
- internal organs drop down for some reason (experts call this manifestation visceroptosis);
- the presence of bad habits can also provoke this disease.
The presence of a double bend in the neck often leads to the aggravation of symptomatic signs of various diseases developing in the gastrointestinal tract. Such a disease can lead to muscle rupture, and as a result may be the factor that leads to acute peritonitis.
https://youtu.be/PSMsUwlWPn8
Treatment of congenital pathology
In cases where the congenital anomaly does not cause discomfort to the patient, no treatment is required. If such a pathology causes concern, then the same therapy is necessary that is prescribed for acquired constriction.
How to cure a child from gallbladder constriction
The famous pediatrician Komarovsky believes that therapy for such pathologies should be carried out individually. In this case, it is necessary to influence not the pathology itself, but those factors that contribute to its appearance.
Since in most cases this pathology appears due to errors in nutrition and poor lifestyle, parents should obtain information from their pediatrician about their child’s diet, daily routine and other points.
Dr. Komarovsky recommends adhering to the following recommendations:
- You should not allow your child to overeat; the best option is portion feeding;
- the child should eat only when he has an appetite;
- You should not allow your child to eat a lot of fatty foods and sweets;
- Do not give your child spicy or salty foods;
- In order for the baby to have a good appetite, he must actively walk and play;
- He must drink the required amount of clean water per day.
Komarovsky claims that bending, constriction of the gallbladder and dyskinesia do not pose a danger to the child, which means that drug therapy is not required. The child will grow, and the shape of his gallbladder will also change. Therefore, the problem may resolve itself.
Drug therapy may be prescribed for a child with hypomotor dyskinesia to stimulate motor skills and thus get rid of uncomfortable symptoms. Most often, choleretic drugs made from plants are prescribed, for example, “Hofitol”, “Flamin”, “Allohol”, “Holosas”.
Choleretic herbal remedies
For hypermotor dyskinesia, antispasmodics are required to help relax the gallbladder and relieve pain.
For complex treatment, medications to improve liver function and vitamins may be prescribed.
If the disease was caused by bacteria or helminths, antibiotics and antiparasitic drugs are prescribed.
If we talk about homeopathic remedies that are recommended for diseases of the gallbladder, Dr. Komarovsky calls them ineffective, but at the same time emphasizes that they will not cause harm.
Of the auxiliary methods of treating dyskinesia, Komarovsky prescribes physical therapy and physiotherapy. All this increases blood supply to the biliary tract, increases the activity of muscle tissue in the liver area, promotes the outflow of bile, which helps restore the functioning of the gallbladder.
Symptoms and signs of constriction
Usually people live with such a pathology without knowing about its existence, since there are no symptomatic signs of the disease. Therefore, most often, a constriction can be detected accidentally as a result of an ultrasound examination of the gastrointestinal tract.
With the development of bile stagnation or an inflammatory process developing in the gastrointestinal tract, the pathology appears suddenly in the form of a number of disturbing phenomena for the patient:
The disease is often indicated by the presence of pain in the area of the right hypochondrium
- one of the main signs of the disease may be nausea, which often leads to vomiting;
- the presence of a bitter taste in the patient’s mouth is disturbing;
- Constipation may occur or, conversely, acute diarrhea;
- the disease is often indicated by the presence of pain in the area of the right hypochondrium;
- the patient feels heaviness in the stomach;
- there is a loss of appetite.
Constriction of the gallbladder that develops in a child is almost no different from a similar disease in adults. Typically, such manifestations of pathology begin to worry after poisoning or various intoxications. They often lead to the patient developing other symptoms:
- breathing quickens;
- the heart begins to beat strongly;
- drooling begins to occur excessively;
- lacrimation appears.
Together with stretching, that is, if the organ is stretched and painful, the pathology leads to damage to the tissue of the gastrointestinal system. This is usually typical for young patients.
In the pathology of the gallbladder, symptoms in adults are expressed in varying degrees of varying intensity and radiate to various parts of the body: to the area of the scapula, sternum, spine, and clavicle.
Other gastrointestinal disorders may also be the main symptoms. There is bloating and dysfunction of the circulatory system. This means that cracks form in the tissues of the gallbladder, through which bile flows into the intestines. If such symptoms bother you for a long time and treatment is not carried out, then treatment will then be carried out only with the help of surgical intervention.
With long-term pathology, mechanical jaundice sometimes appears, and weight loss is also observed. The small intestine stops breaking down and absorbing fats.
Complications
In adults, such deformation can provoke a number of complications and cause unpleasant consequences.
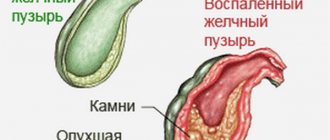
With anatomical changes in the organ and its constriction, the outflow of bile is disrupted. As a result, most of it accumulates at the bottom, forming a chemical compound that eventually turns into stones.
A person may experience serious disruptions in digestion. At the same time, it should be noted that by eating fats, the body does not have the opportunity to break them down. As a result, the person begins to gain weight and becomes obese.
Also, poor fat breakdown affects blood vessels and vision. The skin may become dull and even take on a yellowish tint. Jaundice develops in the body.
Other pathological complications:
- Stone formation in the ducts closes the passage for bile.
- Long-term negative impact on the walls of the bladder eventually causes perforations. This is already fraught with the development of peritonitis and death.
- If bile enters the gallbladder from the liver, but cannot exit into the intestines due to constriction or blockage of the lumens, a rupture may occur. As a result, all the contents disperse throughout the body, poisoning the blood and other organs. This also threatens death for the patient.
Modern medicine can boast of its achievements. Removal of the gallbladder is performed using laparoscopy. This allows you to effectively carry out all the work within a short time.
If symptoms of intoxication appear, you should contact a specialist immediately. This will allow you to diagnose the problem in time, identify the threat and eliminate it.
Diagnostics
Dysfunction of a deformed organ can only be detected by chance. To determine the nature of the disease, it is necessary to conduct several studies that help determine the method of treatment.
Diagnosis of constriction is carried out using:
Ultrasound allows you to evaluate not only the shape of the gallbladder cavity, but also determine why the constriction occurred
- ultrasound examination. Ultrasound allows you to evaluate not only the shape of the gallbladder cavity, but also determine why the constriction occurred, what functional state the organ is in, and also measure the thickness of its walls;
- computed tomography, which is the most modern device that more fully and accurately determines the shape and structure of the pathological zone;
- cholangiographic examination, as a result of which the nature of the biliary tract is determined. The contrast agent required for the study is administered through the oral cavity or skin, directly into a vein, or using an endoscope, which is inserted into up to a third of the problem area.
Examining the condition of organs using ultrasound is considered a more accessible method. Other methods are used only when more accurate data is needed to make a diagnosis.
Causes
The disease is both acquired and congenital in nature. As a child's body grows during puberty, dramatic changes occur in the arrangement of organs in some individuals. This is fraught with the appearance of deforming changes in the abdominal organs. Adverse pathophysiological changes can affect both the gallbladder and other vital organs of the digestive system - stomach, intestines, pancreas, spleen, liver.
When the gallbladder is deformed, constriction, bending or twisting of the neck, including other anomalies, may occur. The reasons directly depend on whether it is an acquired pathology or a congenital one.
Congenital
It is believed that the main formation of fetal organs occurs before the 12th week of gestation. If the mother’s body has been subjected to adverse or teratogenic effects, then disturbances and mutations occur in the anlage of organs. This is fraught with the occurrence of congenital anomalies in the fetus.
Factors contributing to the appearance of bending of internal organs in the fetus:
- Infectious, chronic diseases in the expectant mother.
- Alcohol abuse.
- Smoking during pregnancy.
- Use of teratogenic drugs.
- Emotional stress, stress.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Some complications during pregnancy.
- Difficult and protracted labor.
- Physical overload in unprepared mothers.
- Bad ecology.
- Severe health problems in a woman in labor.
To minimize the risk of abnormalities in the fetus, it is necessary to plan your pregnancy in advance. It is recommended to undergo screenings and genetic tests.
Purchased
Acquired deformity of the gallbladder in a child is rare, but can occur in the following situations:
- Inflammation of the biliary tract.
- Stress.
- Curvature due to obesity.
- Rarely eating large portions of food.
- Hyperactivity.
- Hypovitaminosis, lack of minerals and trace elements can deform the gallbladder.
- Overstrain of the abdominal muscles.
- Pathological changes in the abdominal organs that cannot be treated.
- Malignant or benign tumors in the cavity of the gallbladder.
- Presence of stones in the gallbladder.
- Gallbladder hyperplasia.
- Weakness of the diaphragm.
- History of pericholecystitis.
- Lifting heavy weights with an unprepared body, axial loads.
It is important to carry out timely preventive diagnostics of the child’s health in order to identify deformation of the gallbladder without obvious deterioration in the form of complications.
Treatment of gallbladder constriction
In the absence of pathological symptoms, experts do not recommend treating this disease. If the patient is bothered by various symptoms, then he should go to a special medical institution. After the examination, the doctor will decide what to do with the constriction. In each specific case, the decision is made individually. Therapy methods come in a wide variety. To eliminate symptoms, the patient must change his lifestyle. After the examination, if the disease cannot be eliminated using medications, then conservative therapeutic actions are prescribed, as well as sometimes surgical intervention to eliminate biliary pathology.
The pathological picture in the gallbladder can sometimes change if you change your taste preferences:
- eating the daily norm of food in small portions in 5-6 doses;
- refusal of fried, fatty and spicy foods, as well as smoked meats and marinades;
- Soda and alcoholic drinks should be removed from the diet;
- it is necessary not to eat raisins, dried apricots, grapes;
- food must be boiled, stewed or steamed.
If the patient’s well-being has not changed, then the problem is eliminated with drugs with choleretic properties in the form of Alohol or Chophytol, antispasmodic drugs (No-shpa) or medicinal herbal preparations.
If taking medications does not improve the clinical picture, and the person continues to feel unwell, then surgical intervention is prescribed - cholecystectomy.
Methods of treating pathology
Laparoscopy procedure
You can radically get rid of the constriction only through surgery, completely removing the organ (cholecystectomy).
Drug therapy is necessary to get rid of uncomfortable symptoms and eliminate relapses, but the pathology can only be completely eliminated through surgery. Surgery is prescribed only if there is no result from traditional treatment, there are several constrictions, stones have formed, or the disease is severe. Surgery can be performed using 2 methods: open surgery or laparoscopy.
The first method is classic, it is used in the presence of large stones and severe inflammation. The incision is made in the abdominal cavity. The recovery period is difficult and takes up to 3 months. Complications are possible.
Laparoscopy is a modern technique performed through small punctures in the peritoneal cavity. The patient can be free within 24 hours. The risk of inflammation and side effects is minimal. A few days are enough for rehabilitation.
At the same time, one cannot ignore the risks and discomfort of patients. Because of this, it is not advisable to remove the organ surgically if there is no inflammation. In such a situation, there is a chance to use only traditional therapy and traditional methods of treatment.
Treatment of pathology in the traditional way means the use of medications that are necessary to relieve inflammation and reduce congestion:
- Choleretics are drugs that increase the production and secretion of bile.
- Cholekinetics are drugs that increase the passage of bile into the duodenum.
- Anti-inflammatory medications are necessary to reduce inflammation that may occur due to bladder constriction.
Choleretic drugs
It is possible to use folk remedies in parallel in the form of herbal decoctions that provide a choleretic effect.
Features of therapy
For traditional treatment of acquired constrictions in adult patients, medication is required:
- painkillers (“Nurofen”, “Ibuprofen”) and antispasmodics (“Drotaverine”, “No-shpa”);
- choleretic drugs (“Flamin”, “Gepabene”, “Hofitol”), but provided that there are no stones in the organ;
- if there are stones in the lumen of the gallbladder, hepatoprotectors (Ursosan, Ursohol) are prescribed that can protect the liver, dissolve stones, and normalize the excretion of bile;
- To relieve inflammation, antibiotics are prescribed (Cefolasporin, Ampiox), and after them probiotics (Bifiform, Linex).
Probiotics to relieve inflammation
Therapy with the prescription of medications is supplemented with physiotherapy. If the patient suffers from colic or spasms, they are relieved using ultrasound or electrophoresis.
Removal of stagnant bile from the bladder and ducts is done using a mineral water tube. This procedure, like exercise therapy, promotes the proper functioning of the organ.
For complex therapy, traditional medicine methods are recommended - for example, drinking decoctions of plants that have a choleretic effect (dandelion inflorescences, corn silk, immortelle, yellow gentian).
Raw pumpkin seeds and its juice, and pollen can help relieve congestion in the gallbladder.
To eliminate inflammation, use anti-inflammatory herbal decoctions based on chamomile, calendula, St. John's wort and nettle. Some of these herbs help the flow of bile.
Diet is an integral part of treatment. Experts advise eating small portions. The dishes must be warm.
Salted, smoked, fatty and fried foods, marinated foods, as well as bone broths and semi-finished products are prohibited.
It is prohibited to consume chocolate, sweets, high-fat dairy products, sour apples, and coffee. Fatty meats and fish, beans and mushrooms can cause harm.
In some situations, children may show signs of congenital constriction. They need to be put on a diet. On the advice of specialists, you can give your child various remedies.
If necessary, use painkillers and choleretic agents, as well as antispasmodics in small doses, if they have no contraindications for children.
Treatment of biliary constriction in a child
When biliary constriction develops in a child's gallbladder, choleretic drugs are used according to age standards
Typically, children are susceptible to congenital pathological processes, so they do not need to be treated, since the symptoms do not appear clearly. When biliary constriction develops in the gallbladder, choleretic drugs are used according to age standards. Cholecystectomy examination is rarely performed at this age. The most effective method of eliminating the disease is the technique developed by Komarovsky. Currently, this method is becoming increasingly widespread, as it is the safest and most effective for treating young patients.
Symptoms of tissue compaction
The thickening of the gallbladder wall does not appear externally. Therefore, if this process is suspected, it is necessary to undergo an examination, in particular an ultrasound. Manifestations of the disease are not always expressed, but only during the period of exacerbation of inflammation of the organ. In this case, symptoms such as nausea, a feeling of bitterness in the mouth, pain in the right abdomen, and general weakness are noted. During remission, these signs are absent. However, after eating fatty and difficult-to-digest foods, the discomfort occurs again.
Nausea and bitterness in the mouth during an exacerbation are not always associated with food. Patients often complain of discomfort in the morning, before bedtime. After eating, the symptoms intensify. Vomiting of bile is sometimes observed.
Diet for gallbladder constriction
Having a special diet is important to carry out along with treatment of the disease. In addition to avoiding unhealthy foods, you should consume all kinds of cereals, vegetable broths, fermented milk drinks, and cottage cheese. Constriction of the gallbladder requires a balanced diet and plenty of fluids. It is important not to overeat during meals.
The diet for constriction of the gallbladder in children and adults should include taking decoctions and special infusions. They help prevent the onset of cholecystitis. The use of such folk remedies becomes possible after consultation with a doctor.
Gallbladder constriction is one of the ailments that can be caused by a number of factors. Usually this disease does not cause any concern to a person. If you experience severe discomfort, you should go to the hospital to prevent other dangerous pathologies.
Prevention
As preventive measures, you must follow several simple rules:
- lead a healthy and moderately active lifestyle;
- avoid emotional and physical stress;
- take medications only as prescribed by a clinician;
- eat properly and balanced;
- promptly treat pathologies that can lead to the development of the underlying disease. To do this, you need to undergo a full medical examination several times a year.
The prognosis of gallbladder constriction will depend on the factors causing the disease.
This article was checked and edited by Candidate of Medical Sciences, toxicologist Stanislav Radchenko.
Features of pathology in children
In children, the congenital form of the disease is more often diagnosed. Since it does not have specific symptoms, it does not require special treatment.
The basic rule for preventing complications is following a diet, taking vitamins, bed rest, doing physical exercises and breathing exercises.
When biliary constriction develops, choleretic drugs Gepabene and Odeston are prescribed. To reduce pain, you can offer the antispasmodic No-shpu.
Sometimes physiotherapy in the form of electrophoresis and ultrasound is prescribed.
An acute course can begin after poisoning with the development of intoxication. Symptoms in a child differ from the manifestations of pathology in an adult: they include shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, drooling, and lacrimation.