Liver oncology is a serious pathology, against the background of which death can occur in a matter of time - within a few months from the moment of formation of a neoplasm of a low-quality nature.
With early diagnosis and adequate therapy, a person’s life expectancy can be significantly increased, and in some situations, primary cancer can be completely cured. The earlier the disease is detected, the better the prognosis.
The causes, symptoms and treatment of liver cancer - chemotherapy, surgical techniques, radiation exposure - will be discussed further.
Classification
According to ICD 10, the pathology is assigned code C22 “Malignant neoplasm of the liver and intrahepatic bile ducts.”
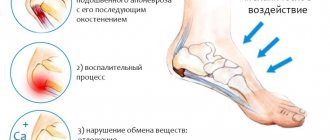
In medicine, liver cancer is classified according to different criteria. Distribution into types helps determine the nature of the disease, the degree of malignancy, prognoses for successful recovery, and life expectancy. Considering the nature of the origin of the pathology, cancer can be:
- Primary. It is a liver tumor that has begun to form and grow directly in the organ. The main causes of development are cirrhosis, chronic inflammation, and abuse of bad habits. Secondary. It occurs as a result of the spread of metastases throughout the body from other foci affected by cancer - the large intestine, lungs, mammary glands, ovaries, stomach, pancreas.
I distinguish tumors by the type of forming cells.
Taking into account the specifics of the cells that make up the tumor, the following types of tumors are distinguished:
- Epithelial. These include the following forms: cholangiocellular;
- hepatocellular;
- hepatocholangiocellular.
- carcinosarcoma;
Types of liver cancer
The medical classification presents two types of liver cancer, which differ in etiological factors.
Primary cancer - tumor cells grow in their own liver tissues. In 75-80% of pictures, the transformation process occurs from fully functional cells (hepatocellular carcinoma), from immature structures (hepatoblastoma), blood vessels feeding the liver tissue (angiosarcoma), from tissues of the bile ducts (cholangiocarcinoma).
In the general statistics of liver cancer tumors, the share of primary tumors is about 3%. The most common provoking factors include long-term cirrhosis, hepatitis of viral origin, and parasite infection.
The metastatic (secondary oncology) type is formed due to the growth of metastases in the liver tissues from malignant tumors that are localized in other organs or systems. This type of disease is most often diagnosed.
Main reasons for development
Until now, the root causes of the development of cancer have not been precisely established. The pathogenesis of the disease consists of a pathological failure at the cellular level, as a result of which a mutation occurs, the process of cell division becomes uncontrollable, and a malignant tumor develops. However, taking into account the genesis of the development of the disease, a number of provoking factors have been identified that, to one degree or another, can provoke liver cancer:
- Infection and chronic course of viral hepatitis. The pathogen is capable of mutating, changing the structure and process of division of liver cells.
- Cirrhosis. In advanced cases, functional liver tissues are gradually replaced by connective tissues, which disrupts the normal functioning of the organ.
- Increased content of iron elements in the body.
- Systemic pathologies, for example, diabetes, HIV.
- Helminthiasis.
- Sexually transmitted diseases that disrupt the structure of organ tissue.
- Uncontrolled use of steroid drugs that promote muscle growth in people involved in sports.
A common cause of cancer is the abuse of bad habits, in particular, this includes alcoholism and smoking. This dangerous disease is rarely diagnosed in children. In this case, the predisposing factors for the development of pathology are heredity and genetic predisposition, and the use of toxic drugs or drugs by a woman during pregnancy.
General characteristics of pathologies
There are several types of diseases of this organ. Neoplasms in the liver are a group of ailments that are benign or malignant. Tumors can be formed from parenchyma, bile ducts or blood vessels. The presence of the disease is indicated by the following symptoms:
- Feeling nauseous.
- Loss of appetite.
- Significant weight loss.
- Increase in organ size.
- Yellow tint to the skin and whites of the eyes.
- Accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal area.
Today there are many ways to diagnose liver tumors. After the specialist manages to establish the type of pathology, he will be able to make a decision about therapy. Treatment for patients with such diseases usually includes surgery. It involves removing damaged areas of the organ.
Risk factors
The tendency to bad habits accelerates the development of pathologies.
Liver cancer most often occurs in individuals belonging to the following categories:
- Male gender. Men take less care of their health, more often abuse bad habits, ignore the symptoms of pathology and are in no hurry to visit a doctor.
- Uncontrolled use of steroids. Hormones that increase muscle mass contribute to liver dysfunction, which increases the risk of developing cancer.
- Diabetes mellitus, cirrhosis. If a patient is not adequately treated for these diseases, he has a high chance of developing cancer.
Malignant liver tumors
Malignant liver tumors are characterized by uncontrolled growth and the possibility of damage to other organs.
Symptoms
Symptoms of malignant liver tumors are often vague and do not appear until the cancer reaches advanced stages.
These include:
- unexplained weight loss;
- loss of appetite;
- feeling extremely full after eating, although the amount of food consumed may be small;
- nausea and vomiting;
- abdominal pain, its increase in size;
- jaundice (yellowish color of the skin and sclera);
- skin itching;
- severe fatigue and severe weakness;
- swelling in the legs;
- increased body temperature;
- enlarged veins on the anterior abdominal wall;
- slight occurrence of hemorrhages or bleeding.
Some liver tumors produce hormones that affect other organs.
These hormones can cause:
- Increased calcium levels in the blood, which manifests as nausea, confusion, constipation, weakness, or muscle problems.
- Low blood sugar levels, which causes fatigue and loss of consciousness.
- Enlargement of the mammary glands and reduction of the testicles in men.
- An increase in the number of red blood cells in the blood, which can cause redness of the skin, especially on the face.
If you have these signs of a liver tumor, you should consult a doctor. Most often, they can be caused by more common diseases, such as infection. However, it is better to undergo an examination and establish the correct diagnosis.
Causes
Secondary liver cancer is metastasis of malignant neoplasms of other organs to the liver, so its causes depend on the location of the primary tumor.
The exact cause of primary cancer is unknown, but in most cases its development is associated with damage to the liver and the accumulation of scar tissue in the liver (cirrhosis).
Cirrhosis can have a number of different causes, including:
- Drinking alcohol in large quantities for many years.
- Chronic viral hepatitis B or.
- Hemochromatosis is a genetic disease in which iron levels gradually increase in the body over many years.
- Primary biliary cirrhosis is a chronic liver disease in which the bile ducts of the liver are damaged.
It is also believed that obesity and an unhealthy diet may increase the risk of developing liver tumors, as they lead to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
In addition, the following factors play a role in the development of liver cancer::
- Anabolic steroids – often used by athletes. These male hormones, when taken regularly over a long period of time, can increase the risk of developing a malignant tumor in the liver.
- Weakened immunity – people with this problem develop liver cancer 5 times more often than healthy people.
- Aflatoxins are substances produced by fungi that can be found on moldy wheat, corn, nuts, and soybeans.
- Diabetes mellitus – Patients with this disease, especially those who drink a lot of alcohol or have hepatitis, have a higher risk of developing liver cancer.
- Smoking – Patients with hepatitis C have a higher risk of developing liver cancer if they smoke.
- Heredity – people who have close relatives with liver cancer are at risk.
- L-carnitine deficiency - scientific studies have shown that a lack of this substance increases the risk of malignant tumors on the liver.
- Gender – liver cancer develops more often in men. A number of scientists believe that this is not due to gender, but to lifestyle characteristics - men smoke more and abuse alcohol.
Diagnostics
People at increased risk of developing liver cancer should be screened for liver cancer every 6 months. Treatment of malignant liver tumors in the later stages of the disease is much more difficult than in the early stages.
Since the symptoms of this disease are not obvious or non-existent in the early stages, the only way to make a correct diagnosis in time is through screening.
Diagnostic tests for liver cancer risk include:
- Blood test for alpha-fetoprotein. This is a protein that is produced in liver tumors and can be found in the blood.
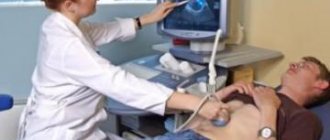
- Ultrasound is an examination method that allows you to create an image of the liver and identify abnormalities in it.
If these methods indicate the possibility of a tumor in the liver, further examination is carried out to confirm the diagnosis.:
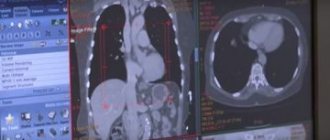
- Computer or magnetic resonance imaging.
- Liver biopsy - a small piece of tissue is taken from the organ, which is then examined in the laboratory. Read more about elastometry as an alternative to liver biopsy →
- Laparoscopy - a small incision is made in the abdominal wall under anesthesia, after which a flexible instrument with a camera is inserted into the abdominal cavity to study the liver.
Based on determining the size of the tumor and its penetration into other organs, the stage of liver cancer is determined:
- Stage 0 – the tumor is less than 2 cm in diameter, and the patient feels healthy and has no liver dysfunction.
- Stage A - one tumor measuring up to 5 cm in diameter, three or fewer tumors less than 3 cm in diameter in a patient who feels well and whose liver function is not impaired.
- Stage B – multiple tumors are present in the liver, but the person feels well, liver function is not impaired.
- Stage C – regardless of the size and number of tumors, the person feels unsatisfactory, the organ does not function properly. At this stage, liver cancer begins to penetrate the main blood vessels of the organ, nearby lymph nodes or other parts of the body.
- Stage D – The liver has lost most of its functional abilities, and the patient develops symptoms of severe liver failure.
Treatment
Treatment for malignant liver tumors depends on the stage of the disease and may include surgery and drug therapy. For the treatment of liver cancer, it is useful to create multidisciplinary teams of doctors who together develop an individual treatment plan for each patient.
If liver cancer is stage 0 or A, complete cure is possible. Once the disease has reached stage B or C, cure is usually not possible. However, chemotherapy can slow the progression of the disease, relieve symptoms, and prolong life by months or years.
If a liver tumor reaches stage D at the time of diagnosis, it is usually too late and it is impossible to slow the progression of the disease. In such cases, liver tumor treatment focuses on relieving the symptoms of the disease.
The main treatment options for liver cancer are:
- Surgical resection . During surgery, cancer cells can be removed, provided that the damage to the liver is minimal and they are contained in a small part of the liver. Since the liver has the ability to regenerate itself, a fairly large part of it can be removed without seriously affecting the patient's health. However, such operations are not performed on all patients with liver cancer; the choice is made taking into account the stage of the disease and an assessment of the severity of liver cirrhosis.
- Liver transplantation . In this operation, the patient's cancerous liver is removed and replaced with a healthy donor organ. Liver transplantation is only performed on patients with stage 0 or A cancer.
- Microwave or radiofrequency ablation . This treatment method is an alternative to surgery in the early stages of liver cancer. It heats cancer cells using radiofrequency or microwave waves generated by small electrodes.
- Chemotherapy . Chemotherapy uses powerful drugs to kill cancer cells and slow the progression of the disease. This treatment can prolong the lives of patients with stage B and C liver cancer, but it cannot cure them completely. In stage D, chemotherapy is not used.
- Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization . During the procedure, a chemical is injected into the artery supplying the tumor, blocking its lumen. This helps slow down the growth of cancer.
- Targeted therapy . During treatment, sorafenib is used, which is prescribed in the last stages of liver cancer. This drug can slightly prolong the life of patients.
- Symptomatic therapy . The goal of treatment for advanced liver cancer is to relieve pain and other symptoms of the disease.
Prevention
To reduce the risk of developing liver cancer, the likelihood of cirrhosis should be reduced.
To do this you should:
- maintain a healthy weight;
- do not abuse alcohol;
- be careful with chemicals.
To reduce the risk of contracting hepatitis B virus, you need to be vaccinated against this disease.
To prevent hepatitis C infection, you should:
- know about its presence or absence in a sexual partner;
- do not use intravenous drugs;
- do piercings and tattoos only in safe conditions.
The same tips are also suitable for preventing infection with any diseases transmitted through contact with blood.
Forecast
The prognosis for liver cancer depends on many factors, such as the size of the tumor, the number of tumors, the presence of metastases in other organs, the condition of the surrounding liver tissue, and the general health of the patient.
The 5-year survival rate for all stages of liver cancer is 15%. One reason for this low rate is that many patients with liver cancer also have other diseases, such as cirrhosis.
If the tumor has not spread beyond the liver, the 5-year survival rate is 28%. If the cancer has spread to nearby organs, this figure drops to 7%. After the appearance of distant metastases, life time decreases to 2 years.
What symptoms are you worried about?
Primary cancer
Signs of primary liver cancer in men and women are nonspecific, so it is rarely possible to diagnose the problem at the initial stage. The manifestation of the disease begins to worry when the malignant nodules have reached large sizes, due to which the organ has ceased to function normally. A person should be alert to the following pathological changes in health:
- chronic fatigue;
- feeling of heaviness in the stomach;
- deterioration or complete loss of appetite;
- rapid weight loss;
- increase in body temperature;
- nausea, vomiting;
- yellowness of the skin;
- itching, which indicates an increase in the content of bile acid in the blood.
Secondary cancer
Poor liver function allows toxins to spread throughout the body.
This type of cancer is much more common. The main sources of pathology are malignant tumors localized in other organs. Clinical signs of a secondary form of liver cancer appear as follows:
- The patient's condition is rapidly deteriorating.
- Intoxication develops, as a result of which the person constantly feels sick, vomits, and symptoms of dehydration are also observed.
- Ascites and fever develop, and the skin acquires a lemon-yellow tint.
If complications progress, symptoms of liver cancer in women and men are:
- obstructive jaundice;
- dilation of the subcutaneous vessels of the abdominal cavity;
- intragastric bleeding;
- splenomegaly;
- ascites.
Treatment of liver cancer in Israeli, German and Moscow oncology centers
The question of which country is best to remove cancerous tumors worries all cancer patients. According to many oncologists, liver cancer patients who prefer foreign clinics have a higher chance of prolonging life. This indicator is influenced by the experience and professionalism of the oncologists and hepatologists receiving them.
Also important are:
- prompt diagnosis of liver cancer, allowing timely and adequate treatment of the disease to begin;
- use of modern equipment and innovative therapeutic techniques;
- availability of effective antitumor drugs in foreign clinics.
In Russia, the situation with therapeutic measures to destroy liver cancer can be called almost deplorable. The main problems of Russian oncology are the impossibility of timely detection of the disease, a significant lack of highly qualified specialists, the technical lag of medical institutions and the lack of necessary medicines. But recently, this deplorable situation has begun to change for the better, and several clinics have appeared in the capital, successfully carrying out many therapeutic measures to eliminate cancer foci in the liver parenchyma.
Therapeutic techniques and advantages of Israeli clinics
In this country, the latest gentle techniques are used to rid a person of a malignant neoplasm in the liver parenchyma. They are often a better alternative to surgery to resect liver tumors. The best oncology centers providing treatment for liver cancer in Israel are Assuta MC, Hadassah MC, Top Ichilov, Tel Aviv CLINIC.
To save the patient from a dangerous illness, they use the following methods that effectively cure liver cancer:
- Radiation surgery using the innovative IMRT method. It is based on the use of linear accelerators belonging to the latest generation. Removal of liver cancer using this technique is carried out without affecting healthy tissue.
- Radioembolization SIRT. A new technique that allows internal contact irradiation of malignant lesions that have affected the hepatic parenchyma.
- Embolization. The procedure involves introducing microgranules into the blood vessels supplying the neoplasm, blocking blood flow.
- Arterial chemotherapy. For liver cancer, only this method of administering potent drugs can be quite effective. That is why in Israeli clinics they try to prescribe infusion chemistry in the initial stages of the disease, after the first negative manifestation of liver cancer has been identified.
The methods used in Israeli cancer centers show very high effectiveness, which, together with the professionalism of leading oncologists, puts this country in first place in ridding people of liver cancer.
German clinics specializing in the treatment of liver cancer
Therapeutic measures that make it possible to quickly and without any special consequences or complications remove an oncological tumor from the liver tissue, as well as prevent the development of secondary malignant foci, are carried out in many oncological centers in this country. The most popular are the Charité MC, Asklepios (Academic Hospitals of the University of Hamburg), and the Bremen Mitte Cancer Center.
It is in these medical institutions that patients are given a real chance to stop the growth of the tumor and make liver cancer recede.
The fight against this pathology in German clinics involves the use of excellent diagnostic equipment and innovative therapeutic techniques, allowing world-famous oncologists to help even terminally ill people.
Treatment of liver cancer in Germany has the following features:
- If a cancer patient is diagnosed with primary hepatocellular liver cancer, the operation offered by German oncologists is completely organ-sparing. It consists of removing one liver segment, which, given the great regenerative capacity of this organ and the high professionalism of specialists, allows the operated person to recover very quickly.
- In the last, inoperable stages of cancer, German clinics conduct contact radiation therapy and intra-arterial chemistry, which have long proven their high effectiveness.
For treatment in cancer centers in Germany, not only adult patients are accepted, but also children, and for children diagnosed with liver cancer, all conditions are provided to help fight the disease - family wards, a children's creativity center and a psychological assistance department.
The best oncology centers in Moscow
Russian cancer centers have one thing in common – their catastrophic shortage. There are only 25 of them in the capital. The most promising for patients with this disease are the Medical Rehabilitation Center (Treatment and Rehabilitation Center of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation), Clinic K+31, Clinical Hospital on Yauza and Moscow Research Institute named after. P. A. Herzen. The main therapeutic method in them is surgical treatment of liver cancer. Most operations are performed using the resection method. Transplantation of a secretory organ in Russia is still performed very rarely. Alternative methods for destroying liver tumors include cryoablation, radiofrequency ablation and proton therapy. Prices for liver cancer treatment in Moscow, as well as in Israel or Germany, are directly dependent on the chosen technique.
Stages: classification
Early diagnosis and treatment will help prevent relapse.
Liver cancer has 4 stages of development:
- At stage 1, the cancer has just formed and has not yet had time to spread beyond the epithelium. There are no characteristic symptoms, the organ functions normally, pain or other pathological manifestations do not bother you. If the problem is diagnosed at this stage and antitumor treatment of the liver is successful, cancer recurrence is extremely rare.
- At stage 2, the patient begins to be bothered by the first signs, as the tumor increases in size, affecting the deeper layers of the organ and blood vessels. After eating food, aching pain may occur in the right hypochondrium, and symptoms also worsen after physical activity.
- With the progression of grade 3, the hepatic and portal veins are involved in the pathological process, the malignant nodes become large in size and are easy to identify by palpation. In addition, oncological damage to neighboring tissues and organs is observed, and metastases also spread to the lymph nodes.
- At stage 4, the tumor affects most of the liver, with active spread of metastases through the circulatory and lymphatic systems. And also the disintegration of a malignant neoplasm is observed, accompanied by internal bleeding and intoxication. In this case, tumor removal is contraindicated; the patient is provided with palliative care.
Clinical manifestations
At the stage of tumor initiation, there are no clinical manifestations. And this often leads to the disease being diagnosed at stages 3-4, which greatly complicates the treatment process. Against the background of gland cancer, specific and nonspecific symptoms appear.
First signs
The liver filters blood in the body, helps digest food, and neutralize toxic components. A growing tumor or metastases impair functionality, which leads to the appearance of certain symptoms.
At an early stage, nonspecific symptoms are determined - nausea, vomiting, diarrhea/constipation, sleep disturbance, heaviness in the right side. And specific ones - moderate hepatomegaly - enlarged liver, portal hypertension (not always).
Sometimes the body temperature rises and a febrile state is observed. These manifestations are caused by the state of the immune system, which begins to fight malignant cells.
Late symptoms
Late signs appear when the disease progresses, the tumor grows, and metastases are found in neighboring and/or distant organs.
Symptoms:
- Constant pain in the liver area, epigastrium, which tends to radiate to different parts of the body.
- Sharp weight loss, anorexia.
- Drowsiness and fatigue increase, dizziness appears, which ends in fainting.
- Bitterness in the mouth due to glandular cancer.
- Central nervous system disorders, apathy, depressive syndrome.
- Swelling of the limbs, which is caused by a disorder of proper blood circulation.
- Ascites - free fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity.
- Internal bleeding, benefits in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Significant increase in liver size due to tumor growth.
The clinical picture is usually pronounced, causing a lot of anxiety to a person, complemented by symptoms that are associated with a disorder of the functionality of the digestive system, CVS.
Features of the manifestation of secondary oncology
Metastases are detected in the liver due to malignant damage to neighboring organs. Most often with pancreatic cancer. Symptoms from the liver are usually overlapped by a more pronounced clinical picture of the primary lesion. As it progresses, clinical manifestations increase and new symptoms appear.
How is diagnosis carried out?
The study will determine with high accuracy the degree of damage to the organ.
To ensure that liver cancer treatment is as effective as possible, the following modern diagnostic methods are prescribed:
- Ultrasound. Shows the location of the nodules, size and degree of development.
- CT or MRI with contrast. Determines the extent of damage to organs and neighboring structures.
- Biopsy. Samples of the affected tissue are taken, which are then examined in the laboratory.
- Biochemistry. It will show an increase in AFP, ALT and AST, cholesterol.
- Macrodrug of liver cancer. The section allows you to determine the shape and type of cancer, the stage of the lesion.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of hepatic carcinoma includes a whole range of studies:
- Primary laboratory blood test: in case of cancer, ESR increases significantly. But it is impossible to make a diagnosis based on this indicator alone, because the erythrocyte sedimentation rate also increases with infections, acute inflammatory processes, indolent diseases, and even menstruation in women.
- Blood test for alpha-fetoprotein: the disease is manifested by an increased level of this protein.
- Ultrasound: one of the most accessible diagnostic methods, which will reflect changes in the size and structure of the organ, but may not detect a small tumor.
- MRI and CT: the exact size, location, type of tumor, and its structure are determined (with the introduction of contrast). Usually prescribed to clarify and correct the diagnosis.
- Biopsy: a tissue sample is taken through a puncture followed by histology to determine the nature of the tumor.
Also, if necessary, the doctor may prescribe a study of blood vessels with contrast, an x-ray of the organ and bones to identify metastases.
What treatment is prescribed?
Medicines
It is possible to treat the problem with conservative methods only in the very initial stage of development, when the tumor is small in size and spreads no deeper than the epithelial layer. The drug Nexavar has proven itself to be effective, as it blocks tumor reproduction and growth. Nexavar is a unique new generation drug that inhibits the tumor process without causing negative side effects.
The drug “Refnot” has positive reviews from doctors, which also has an antitumor effect, having a direct cytostatic and cytotoxic effect on malignant cells. The medicine stimulates the production of antibodies that destroy malignant neoplasms.
Chemotherapy
A healthy diet helps the body recover faster.
The chemotherapy procedure involves the administration of chemical drugs through the hepatic artery that specifically destroy the tumor. The drugs used for chemotherapy are characterized by increased toxicity, so during the course of therapy the patient experiences nausea, vomiting, and hair loss. A special diet will help alleviate the condition during chemotherapy. The menu should consist of healthy foods rich in vitamins, micro- and macroelements. Food should not contain cholesterol, preservatives, or food additives.
Folk remedies
Liver cancer cannot be cured with unconventional methods, but with their help it will be possible to alleviate the condition and reduce unpleasant symptoms. To prepare such remedies, medicinal herbs are used, on the basis of which infusions, tinctures and decoctions are prepared. Useful folk remedies for liver cancer are:
- Antitumor medicine with celandine. Pour celandine in the amount of 1 tbsp. l. 250 ml boiling water, leave for 30 minutes. Take the prepared infusion ½ glass in the morning and evening before meals.
- Oat decoction. Pour 100 g of grains into a glass of boiling water. Cook over low heat for 20 minutes. Separate the oats from the liquid and take the prepared decoction 3-4 times a day.
- Herbal tincture. The herbs chamomile, St. John's wort, and yarrow are mixed in equal proportions. The raw materials are placed in a glass container and filled with vodka in a ratio of 1:3. Infuse the product for 30 days, take 20 drops. Every time before the main meal.
- Tincture with dead bees. Pour 100 g of dead water and 300 ml of vodka. Infuse the product for a month, shaking occasionally. Strain the finished tincture, take ¼ cup in the morning and evening.
What causes the disease?
Today, experts cannot accurately answer the question of why tumors of this organ occur. However, doctors name the following as factors that can provoke a pathological process:
- Regular use of medications containing hormones.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Taking drugs.
- Smoking.
- Abuse of drinks containing ethanol.
- Parasitic infestations (schistosomiasis, opisthorchiasis).
- Metabolic disorders associated with a lack of thyroid hormones or diabetes mellitus.
- The formation of polyps in the large intestine.
- Infection with hepatitis viruses types B and C.
- Long-term effects on the body of harmful chemical compounds.
- Consumption of products containing poisonous molds.
- Excess animal lipids in the diet.
- Infectious pathologies of a chronic nature.
Cirrhosis, a disease that occurs as a result of prolonged and uncontrolled drinking of alcohol, is one of the most common causes of the development of liver tumors. Damage to organ tissue and changes in its structure lead to mutations in cells. In 80-85% of patients suffering from this pathology, malignant lesions occur.
How long do they live: forecast
Timely treatment is the key to a positive outcome of the disease.
Liver cancer is a dangerous pathology with a high mortality rate, and the prognosis for recovery depends on the stage of development and type of tumor. At the first stage, if diagnosis and treatment are carried out in a timely manner, the chances of recovery are as high as possible. Further, the likelihood of dying from cancer increases: at stage 4, a person dies within 1-2 months after diagnosis.
Classification of liver tumors
Liver tumors can be divided into benign and malignant.
All malignant liver tumors, in turn, are divided into two main groups:
- Primary liver cancer, in which a tumor appears in the organ itself.
- Secondary liver cancer, in which the cancer spreads to the liver (metastasizes) from other organs - for example, a tumor of the sigmoid colon with metastases to the liver.
Classification of primary malignant liver :
- Hepatocellular (hepatocellular) carcinoma.
- Cholangiocarcinoma.
- Angiosarcoma.
- Hepatoblastoma.
Classification of benign tumors in the liver:
- Hepatocellular adenoma.
- Focal nodular hyperplasia.
- Hemangiomas.
- Lipomas.
Prevention
Liver cancer cannot be infected, but if there is a predisposition, its active progression can be provoked.
To prevent relapse of the pathology, the patient is required to strictly adhere to preventive measures. First of all, it is important to constantly monitor your condition, undergo medical examinations and routine drug treatment. It is important to follow a diet, give up bad habits, follow all the doctor’s advice and recommendations, and not self-medicate.
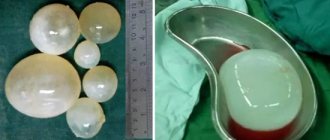
Adenomas
Tumors of this type are round in shape and grayish or dark red in color. The volume of these neoplasms on the human liver can be either small or quite large. Adenomas are usually located in the parenchymal region or under the capsule of the organ. The structure of the tumors is spongy and cavernous. Neoplasms are formed from the network of blood vessels in the liver. Adenomas are divided into two groups:
- Cavernoma.
- Cavernous hemangioma.
Many experts classify such neoplasms not as tumors, but as vascular anomalies that form before birth.
Symptoms
The symptoms of liver carcinoma are quite varied. In general, it resembles a number of symptoms that can accompany most diseases of this organ. Experts note the following changes in the human body:
- general deterioration in health, which consists of rapid weight loss, loss of appetite, constant fatigue and fatigue;
- gastrointestinal disorders in the form of diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, increased gas formation;
- manifestation of pain in the abdominal area, starting on the right under the ribs during physical activity and continuing as the disease progresses, even in a calm state;
- increase in body temperature up to 38 degrees Celsius due to intoxication of the body;
- the skin becomes yellow as well as the sclera of the eyes, because bile products enter the bloodstream and travel throughout the body;
- ascites, that is, an increase in the abdomen due to the fact that the liver itself changes in size;
- internal or nasal bleeding.
If these symptoms occur, you should immediately seek help from a doctor and undergo an appropriate specialized examination at a medical institution.
Diagnostics and therapy
If the development of this pathology is suspected, the specialist prescribes the following measures to the patient:
- CT scan.
- Assessment of the condition of the organ using ultrasound.
- Study of liver vessels.
- Laparoscopy and tissue biopsy.
Focal benign tumors in the liver can transform into cancer and lead to complications. Given these circumstances, the main treatment tactic is surgery to remove them.
The extent of the procedure is determined by the location of the tumor and its size. For example, with a large tumor in the right lobe of the liver, resection of this part of the organ is performed. In some cases, operations are performed using a laparoscope. For cysts, excision and drainage (open or endoscopic) are recommended.
Other methods of treating neoplasms include:
- Immunotherapy. This is the injection of medications into the tumor area to prevent its growth.
- Injecting alcohol into the affected tissue. This method is used for small tumor volumes.
- Chemotherapy. Usually several courses of such treatment are carried out.
Traditional treatment
Patients are interested in whether liver cancer can be treated with folk remedies? Many traditional healers are confident that even the 4th stage of cancer can be cured with folk remedies: hemlock, clubmoss, celandine for oral administration.
Hemlock is a poisonous herb, but within the permissible dose it is indicated for liver cancer, it kills cancer cells well and often becomes the only salvation for patients at the 4th stage of cancer. An alcohol tincture is prepared from the herb and gives good results even in advanced cases.
Liver cancer can be completely treated by constantly taking sage decoction, potato juice, kidney tea, and vegetable juices. You can prepare infusions from St. John's wort, lemon balm, mint, and kombucha.
Birch chaga helps well against liver cancer even at the 4th stage. The body is exhausted and weakened. Patients need enhanced nutrition to continue the functioning of important organs. Dishes should be easy to digest, and meals should be split, up to 8 times a day.
To stimulate digestion, it is recommended to take raw plant foods, vegetables, fruits, berries, herbs, sprouted wheat grains, vegetable soups, carrot juice to cleanse liver cells, brown rice, buckwheat and oatmeal, foods containing protein, i.e. meat, fish, poultry, vegetable fats, scrambled eggs, fermented milk products, sauerkraut, herring to improve appetite, pastille, jam and rosehip decoction.
But you need to completely exclude nuts, legumes, fried, fatty foods, coffee, chocolate, alcohol, and processed foods from your diet.
Diagnostics and therapy
If a pathology is suspected, the following medical procedures are performed:
- Examination and assessment of the patient’s external condition.
- Laboratory analyzes of biological material.
- Ultrasonography. A neoplasm in the liver is easy to identify on ultrasound, both benign and malignant.
- Puncture and biopsy of organ tissue.
Competent diagnosis allows not only to identify a tumor, but also to establish at what stage of development the pathology is.
The main method of treating malignant liver tumors is surgery. This method allows the patient to live much longer. This procedure should be performed in a specialized surgical center. If there is a small tumor, the part of the organ in which it is located is removed. If a large tumor is detected, large volumes of the liver are resected, but its function remains intact.
Unfortunately, specialists working in many general medical centers consider patients suffering from this pathology to be incurable. But today this approach is wrong. Thanks to effective therapy methods, about 40% of patients live more than five years.
Etiology
The formation of cancerous liver damage is preceded by some pathology of this organ, against the background of which changes in the structure of cells occur, therefore the cancerous process cannot form on healthy tissues.
The most common causes of liver cancer:
- chronic form of hepatitis, regardless of etiology. However, malignant tumors most often occur in the presence of hepatitis B;
- cirrhosis of the liver - favorable conditions for the formation of cancer are determined by the fact that against the background of such a disease, the process of replacing healthy cells of this organ with denser connective cells occurs;
- cholelithiasis, during which the formation of stones in the bile ducts is observed. The cells surrounding the stones are most prone to mutation;
- diabetes mellitus – the risk of cancer increases due to metabolic disorders;
- hemochromatosis is a condition in which iron accumulates in internal organs;
- syphilis;
- pathological influence of parasites and pathogens, in which case liver tissue is poisoned by their waste products, i.e. toxins.
Causes of liver cancer development
In addition to such reasons, there are several predisposing factors to the formation of such a pathology. These include:
- belonging to the male gender. Clinicians have noted that liver cancer is diagnosed four times more often in men than in women;
- age category over fifty years;
- long-term addiction to such harmful habits as drinking alcoholic beverages and smoking;
- effects on the body of chemical or toxic substances;
- the use of certain medications, namely: anabolic steroids, which change hormonal levels and have a detrimental effect on the liver;
- genetic predisposition - some experts believe that cancer can be inherited.
People whose life history includes at least one of the above factors are at greater risk of developing this type of cancer. For this reason, they are recommended to undergo regular medical examinations, as well as take medications aimed at protecting the liver.
Causes and risk groups
Patients who are carriers of the hepatitis B antigen virus encounter a serious illness in 15% of cases. Patients with hepatitis C are also at risk. Experts believe that viruses that cause liver inflammation inhibit the action of a specific antioncogene, which is responsible for the proper division of cells in the body. People at risk of contracting viral hepatitis should undergo timely vaccination. This will be a stage of prevention and oncological process.
The causes of liver cancer include alcohol abuse. Ethanol has a detrimental effect on the condition of hepatocytes (gland cells), provoking the development of cirrhosis. In the future, signs of cellular atypia may be observed. Liver cancer can also develop against the background of opisthorchiasis infection. This is a pathology characterized by the entry into the human body of flatworms from the class of trematodes.
Infection occurs when eating fish that has undergone insufficient heat treatment. As a result, helminths penetrate the gallbladder and bile ducts, disrupting the outflow of bile. Opisthorchiasis can cause the development of cholangiocarcinoma. The list of causes of liver cancer also includes:
- violation of healthy eating rules (abuse of fatty and fried foods, preservatives);
- influence of industrial toxic substances on the body;
- smoking.
Abuse of foods with food additives will only worsen the situation.
Forecast
In most cases, the prognosis is unfavorable. Whether liver cancer is treated in a particular case can only be answered by the specialist who observes the patient. Statistics show that an operated patient can live up to 3–5 years after surgery. If cases are inoperable, doctors predict no more than 4–5 months, although this period also depends on a number of factors.
The attending physician tells the relatives of a cancer patient, who can no longer be helped, about how they die from liver cancer, suggests what medications can be used to relieve pain, and what can be used to make them feel better. He can also recommend a hospice that helps such patients in the last months of life. It is important to remember that health is difficult to restore, so you need to contact specialists at the first symptoms of a pathological process in order to carry out early diagnosis, select treatment and, if possible, save a life.
Causes
Benign liver tumors are quite rare. In this case, the development of the formation is hidden, asymptomatic, and is often detected by chance during an ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs, which is carried out for other indications.
The causes of benign degeneration of liver tissue have not been fully established. However, there are a number of factors that significantly increase the likelihood of developing pathology. These include:
- bad habits;
- poor nutrition, predominance in the diet of heavy, fatty foods, foods with chemical preservatives, dyes;
- long-term use of hormonal drugs for various endocrine diseases;
- hereditary predisposition (if there are close relatives with this diagnosis, the risk of developing a tumor is 3 times higher);
- unfavorable environmental conditions.
Chronic use of oral contraceptives can cause the development of liver adenoma
Primary malignant neoplasms in the liver can be a consequence of other serious pathologies of the organ or unfavorable external factors. These include:
- hepatitis B and C (increases the risk of developing cancer by 200 times);
- cirrhosis;
- parasitic infestations, including schistosomiasis;
- hemochromatosis;
- colon polyps (benign formations that develop from glandular epithelial tissue);
- syphilis;
- neuroendocrine and metabolic disorders (including diabetes mellitus, obesity);
- alcoholism;
- exposure to highly toxic chemicals (nitrosamines, chlorine-containing pesticides, carbon tetrachloride).
Secondary damage to an organ by metastases occurs 20 times more often than primary degeneration of hepatocytes. This is due to the fact that blood from various organs enters the liver, and along with it, malignant cells are introduced into the organ. For example, with intestinal or pancreatic cancer, the liver is affected by metastases in 70% of cases.
Treatment
Treatment of the disease depends entirely on the nature of the neoplasm. For example, treatment of benign tumors involves:
- withdrawal of hormonal substances, which will lead to spontaneous regression of the disease;
- surgical excision of the tumor - indications for this treatment tactic are: severe manifestation of symptoms, planning pregnancy, danger of rupture, high probability of internal hemorrhage and large volumes of formation.
Treatment for malignant liver tumors includes:
- surgical or cryosurgical excision of the tumor. The extent of resection is determined by the location and size of the tumor. Surgery is performed by segmentectomy, lobectomy, hemihepatectomy and marginal resection;
- chemotherapy;
- radiation therapy;
- healthy organ transplantation.
Types of liver resection
Types of malignant neoplasms
Next, the types of malignant tumors of the gland, features of their location in the organ and histological characteristics are considered.
Hepatocellular carcinoma
This is primary liver cancer, which is the most common among all types of gland cancer. It can occur against the background of cirrhosis, so signs of its development are sometimes mistaken for the progression of cirrhosis. HCC, as the type of tumor is also called, more often affects the male body, which gives reason to think about the place of action of specific hormones in the pathogenesis of cancer.
Cholangiocarcinoma
This type of pathology is diagnosed less frequently compared to other types of gland cancer. The disease occurs as a result of mutation of epithelial cells of the biliary tract. The first symptoms appear quite late, so it is difficult to diagnose liver pathology in the early stages.
Bile duct cystadenocarcinoma
The neoplasm has a cystic structure; its glandular cavities are lined with epithelium, which secretes mucin. It is quite difficult for specialists to distinguish cystadenocarcinoma from a benign tumor during macroscopic diagnosis. There is another similar form - mixed hepatocholangiocellular cancer. This neoplasm combines elements of cystadenocarcinoma and hepatocellular tumor. This type of oncology should not be confused with those tumors that have insufficiently clear cell differentiation.
Hepatoblastoma
The oncological process usually develops in early childhood. This is an embryonic, low-grade type of tumor that occurs more often in boys. Doctors say that risk groups include patients whose relatives have familial colon polyposis and Beckwith Wiedemann syndrome. Hepatoblastoma has 4 histological subtypes.
Hemangiosarcoma
A malignant neoplasm, which is represented by elongated cells lining the spaces between the vessels. It is more common in older men, often against the background of liver cirrhosis. There are known cases of tumor nodules connecting with each other, which is why the process covers most of the gland.
Embryonic sarcoma
It occurs in pediatric patients, but is almost uncommon in people over 17 years of age. It quickly grows into the thickness of the liver and forms extrahepatic metastases.
Undifferentiated cancer
More often diagnosed in pediatric patients. The tumor is considered the most aggressive and quickly forms metastases.
Treatment options
The treatment method is selected taking into account a wide range of factors. The number and nature of neoplasms, stage, growth rate, and localization of pathology are taken into account. No less important aspects are the general physical and psychological condition of the patient, the presence of distant metastases, and concomitant diseases.
It is important to know! The most effective methods of therapy are radiation (radiotherapy), chemotherapy, and surgical treatment.
Chemotherapy
The procedure is aimed at destroying a cancerous tumor by introducing potent toxic substances and stopping the development of the disease. With repeated sessions, the effect of reducing the tumor and causing remission is achieved.
Chemotherapy for liver cancer is rarely used, due to increased toxicity. The use of drugs for the treatment of tumors of other organs often leads to the development of severe liver damage, which is a provoking factor for cancer of this organ.
Radiotherapy
The procedure is aimed at destroying liver cell formations using ionizing radiation. The effectiveness of the method is explained by the fact that cancer cells divide quickly and are extremely sensitive during the division period. Exposure to radiation causes them to decay.
Types of radiotherapy:
- Remote (the radiation source is located at a distance from the organ).
- Radionuclide (a radioactive drug is injected into the blood and penetrates the liver).
- Contact (the radiation source comes into contact with the affected areas of the liver).
The disadvantage of the procedure is that along with the affected cellular structures, healthy tissues are also damaged. As a result, a large number of dead cells enter the blood, which cause severe intoxication. During the recovery period, patients experience many side effects.
Surgical therapy
Provides for resection - an operation in which the affected areas of the organ are removed. Treatment is carried out for small nodes (up to 3 cm), and only if the tumor does not affect large vessels. With large tumors, cancer is considered inoperable, since removal of a large area of tissue provokes failure, which in 10% of cases leads to the death of the patient.
One of the treatment methods is transplantation, which involves the transplantation of a healthy donor organ. After surgery, long-term recovery and supportive drug therapy are necessary, but this method eliminates the risk of recurrence of the disease.
The importance of timely diagnosis
Detecting the disease at an early stage significantly reduces the likelihood of patient death. Timely diagnosis opens up the possibility of using a wide range of procedures to achieve a therapeutic effect. If detected late, irreversible changes occur in the liver, which lead to death.
Attention! Liver cancer is a serious cancer that is incurable in its later stages. The disease leads to failure of a vital organ, spread of metastases and further death.
When early symptoms appear, a comprehensive diagnosis is required, including laboratory and instrumental methods. Treatment is prescribed according to the stage of cancer, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient.
Complication
Unlike oncological pathologies, benign tumors do not pose an immediate threat to the patient’s life. They are characterized by slow growth, rarely transform into cancer and do not lead to significant deterioration of the condition. But this does not mean that a person with such a disease should not consult a specialist.
Neoplasms in the liver that have reached large volumes can cause complications. For example, in patients with hemangioma or adenoma, there is a possibility of disruption of the integrity of the tumor, bleeding into the peritoneum and bile ducts. Large cysts can lead to suppuration and jaundice.
With nodular hyperplasia, ruptures rarely occur, but such complications are not excluded.
Symptoms and signs
Symptoms of liver tumors in the early stages practically do not appear. The compensatory capabilities of the body determine the preservation of the functions of the gland. As they develop, neoplasms disguise themselves as inflammatory diseases of the hepatobiliary system. The patient may experience only general symptoms: malaise, fever, headache. Depending on the quality of the tumor and the speed of its growth, characteristic symptoms also appear over time.
Clinical signs of malignancy
Cancer begins with signs of intoxication. A sick person complains of decreased appetite, irritability, drowsiness, and increased fatigue. As the pathology progresses, pain on the right side, enlarged liver, and splenomegaly appear. Blood tests indicate a decrease in glucose and hemoglobin levels and an increase in the concentration of transaminases and bilirubin.
Compression of the portal vein leads to portal hypertension and the development of ascites. The patient quickly loses weight, while his abdomen becomes greatly enlarged. Veins are clearly visible on the skin of the abdominal wall, and swelling appears on the legs.
Such signs usually indicate the last stages of cancer, except in cases where the tumor is located near large bile ducts. Late symptoms include jaundice, vomiting, diarrhea, bleeding tendency, and exhaustion.
Secondary dysfunctions of other organs (paraneoplasia) occur. The most common skin changes are: pigmentation, dryness, itching. Sometimes, even before a malignant tumor is diagnosed, black keratinizing spots appear in the patient’s armpits, inner thighs or neck. This disease is called papillary skin dystrophy. Other changes include hormonal disturbances and encephalopathy.
Clinical signs of benign formations
Features of the clinical picture of benign tumors are associated with their slow growth. Patients are unaware of the presence of pathology for a long time. Manifestations of the disease become noticeable as the formations increase. A person experiences a feeling of heaviness on the right side, belching, and flatulence.
In rare cases, a growing tumor leads to ascites. For example, a hemangioma can occupy the entire abdominal cavity and completely replace gland tissue. Total destruction of the parenchyma in some types of neoplasms causes liver failure.
Symptoms of hamartoma include loss of appetite, pain, dyspeptic disorders, and breathing problems. With focal nodular hyperplasia, signs of chronic inflammation occur: periodic aching pain and nausea. However, in most cases the disease is asymptomatic.
Liver cleanse
It is important to cleanse the liver after chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Juice therapy is the best way to deal with this. You can drink different juices on an empty stomach:
- carrot-beetroot in a ratio of 13:3;
- carrot-beetroot-apple 7:3:6;
- carrot-beetroot-cucumber 10:3:6;
- carrot-spinach in a ratio of 10:6;
- apple-beetroot 10:3.
There is another recipe from:
- young pine needles (5 tablespoons);
- dry rose hips (2 tablespoons);
- onion peel (2 tablespoons).
Pour the mixture with 0.5 liters of activated water, bring to a boil and cook over low heat for 10 minutes. Place in a warm place overnight. Drink instead of water for no more than 4 months, as the body gets used to it.
It is worth paying attention to such drugs as Karsil, Hepatosan. Liver cleansing should be done under the guidance of your doctor.