What does light-colored stool mean?
The brown color of stool is given by the enzyme bilirubin, secreted by the liver. The coloring of feces is also affected by the gallbladder and pancreas. These three organs must work harmoniously and then an adult will have the usual brown feces.
If an adult’s stool becomes discolored and the stool becomes yellow, sandy, light green, beige, or white, then it is necessary to find out why such changes occurred.
Photo:
The color of a person's stool always indicates their state of health, but a change in stool to light colors is not always a cause for concern.
But acholic (completely discolored) feces in adults indicates serious problems in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, and the reasons for this should be sought immediately. These are often serious illnesses and it is very important to identify them at an early stage.
Causes of yellow stool during poisoning
Due to intoxication caused by bacteria, poisonous plants or chemicals, irritation of the intestinal mucosa occurs.
This leads to the formation of mucus on its surface, which prevents the absorption of excess fluid. The disorder provokes yellow, foamy diarrhea with a foul odor.
As first aid for acute diarrhea and poisoning, it is necessary to:
- Empty the stomach of its contents.
- Eliminate food consumption.
- Take medications that restore and support intestinal microflora.
The stomach can be cleansed by rinsing with warm boiled water. Then take several tablets of activated carbon (at the rate of 1 piece per 10 kg of patient weight).
If a microbial provocateur of intoxication is detected, antibacterial agents are used. The dosage and duration of administration are determined by the doctor.
For preventive purposes, on the advice of a gastroenterologist, in case of recurring diarrhea, you can take Linex, Bificol, Lactobacterin.
An important place in restoring intestinal activity is given to following a gentle diet.
https://youtu.be/5bldA_12z-A
Causes of stool lightening
When an adult’s stool suddenly turns light, questions arise. There are fairly harmless reasons for stool becoming discolored:
- Eating cottage cheese, sour cream, milk and other fermented milk products (fecal matter will be yellow, light yellow or white).
- If the stool is yellow, this may be a consequence of eating melons, bananas, pears and apples, pumpkins and other yellow-orange foods.
- The stool may be light yellow due to the use of antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs.
- If a woman’s stool turns lighter, this is due to taking oral contraceptives.
- Drinking large amounts of alcohol can cause stool to become light, pale, or completely white.
- The rapid speed at which feces move through the intestinal tract means that the feces do not have time to color properly, and then light-colored poop comes out of the adult’s body.
Any of the above reasons for lightening the stool of an adult is not a big cause for concern, especially if such a sign as light or colorless stool is a one-time occurrence. You will only need to worry if pale yellow, sandy, or light green stool bothers an adult for more than a week in a row, and there are additional symptoms of improper functioning of the digestive tract.
Types of feces in children
With various pathologies, there are several types of feces in children, which you need to know about in order to prevent various diseases and unpleasant consequences in time.
- "Hungry" feces The color is black, dark green, dark brown, the smell is unpleasant. Occurs with improper feeding or fasting.
- Acholic feces Whitish-gray color, discolored, clayey. With epidemic hepatitis, biliary atresia.
- Putrefactive. Pasty, dirty gray, with an unpleasant odor. Occurs during protein feeding.
- Soapy. Silvery, shiny, soft, with mucus. When feeding with undiluted cow's milk.
- Fatty feces With a sour odor, whitish, a little mucus. When consuming excess fat.
- Constipation. Gray color, hard consistency, putrid odor.
- Watery yellow stool. When breastfeeding due to a lack of nutrients in mother's milk.
- Pasty, thin stool, yellow in color. It is formed due to excessive feeding of cereals (for example, semolina).
- Feces for dyspepsia. With mucus, coagulated, yellow-green in color. Occurs when there is an eating disorder.
What diseases affect the color of stool?
Lightening of stool in an adult can begin when certain organs of the body are not functioning correctly. This happens in the presence of diseases. An adult’s stool may become lighter in color if:
- Crohn's disease – extensive damage to the intestinal tract, when the functioning of all parts of the intestine is disrupted, which manifests itself in severe disorder.
- Hepatitis of various etiologies - inflammation of the liver does not go away without a trace and the first sign that helps to suspect pathology is light intestinal contents, plus dark urine is added and feces over time do not just lighten or turn white, but become completely discolored.
- Pancreatitis - disturbances in the functioning of the pancreas affect the contents of the intestines, since the first enzymes that enter the intestinal tract are secreted by the pancreas. If they are deficient, serious digestive problems occur and the stool becomes very pale.
- Cholecystitis - the stool becomes mushy and light-colored, and diarrhea is noted. There are other symptoms, but they appear a little later after the discharge of beige or white feces.
- Fermentative dyspepsia - stool has a foul, sourish odor, often the stool is quite liquid and light, sometimes even completely uncolored.
- Oncological diseases of the intestines , liver, pancreas or gall bladder - the poop of an adult quickly turns white, which means that the disease has reached the phase of active development, since the first period is asymptomatic. Whitish or light yellow stool will be accompanied by abdominal pain, since the tumor has already grown in size and can now block the ducts for secreting enzymes or even part of the intestine.
These diseases are dangerous for strong adults, and for an elderly person they can even become fatal. Therefore, if the stool changes to light-colored and other symptoms of pathology begin to appear, you should immediately seek help from a specialist.
If you carry out diagnosis and treatment on your own, you can worsen your situation, so it is better not to do anything at random, but to find out how to treat the disease from an experienced doctor.
Discoloration of stool during pregnancy
During pregnancy, the hormonal levels in the female body change significantly, and the load on all organs increases due to the fact that they ensure the vital functions of not only the woman, but also the child in the womb. Light-colored stools often occur during pregnancy.
And very often this happens as a result of increased load on the pancreas. This situation is often caused by taking multivitamin complexes. And the problem can be solved by timely contacting a doctor who is managing the pregnancy to correct the treatment plan.
But what light-colored feces and yellow urine mean can be understood by understanding that discoloration of feces is caused by a lack of the enzyme bilirubin. The coloring of urine the color of strongly brewed tea indicates that the enzyme does not undergo purification through the kidneys and ends up directly in the urine; it also penetrates into the skin. Very light stool indicates the development of hepatitis.
With such symptoms, a liver disorder is most often suspected. A pregnant woman should consult a doctor who will select the right treatment. Very often this problem is solved after childbirth, since the load on the body as a whole is removed.
Important! During pregnancy, a woman should carefully monitor the consistency and color of stool, as they are a quick indicator of changes in the condition of the mother and child. With a timely response to the signal, doctors will be able to quickly eliminate the problem without consequences.
Associated signs of the disease
No doctor can say for sure what disease caused the stool to become lighter in color in an adult without the presence of additional symptoms and diagnostic procedures.
In diseases of the digestive system, the following may additionally be observed:
- Nausea and subsequent vomiting.
- After diarrhea there may be constipation or vice versa.
- Dehydration.
- Loose stools.
- Increased gas formation.
- Belching.
- Feeling sour in the mouth.
- Malaise.
- Temperature increase.
- Chills.
- Complete lack of appetite.
- Stomach ache.
Such symptoms, together with light-colored feces, require mandatory diagnosis and identification of the causes, as they may indicate the presence of serious diseases. There is no point in delaying a visit to the doctor, because the disease progresses every day.
Symptoms
If, in addition to lightening the stool, you feel unwell and a deterioration in your general condition, you should seek medical advice. Especially if you eat, the malaise does not go away within a day. Symptoms to watch out for:
- persistent increase in temperature;
- stool disorder;
- nausea, vomiting;
- pain in the abdomen, left hypochondrium, girdle pain;
- yellowed sclera of the eyes and skin;
- lack of appetite;
- sudden weight loss;
- dark urine;
- flatulence, abdominal enlargement;
- stool with mucus.
If there are at least two additional signs with light-colored stool, it is necessary to undergo a medical examination to determine the diagnosis. With some problems, for example, with advanced pancreatitis, the count is not days, but hours. Be attentive to symptoms and do not ignore serious ailments.
The relationship between stool color and cause
The concept of “light feces” is very vague, because there are several options for light.
The color of stool in an adult can indicate possible diseases, pathologies or other causes.
Depending on the color of stool, the following reasons are distinguished:
- Light brown – unbalanced diet, rapid peristalsis, love of lactic acid products.
- Light yellow – predominance of fruits in the diet.
- Beige - narrowing of the bile ducts, insufficient production of bilirubin by the liver, hepatitis, cirrhosis.
- White – hepatitis, tumor of the liver or intestines, less often of the gallbladder, fermentative dyspepsia.
- Pale – diabetes and other pancreatic diseases.
- Light green – dysbacteriosis, food toxic infections, acute enterocolitis.
The color of stool and its consistency are important diagnostic signs, so you should not remain silent at a doctor’s appointment, considering this an uncomfortable topic of conversation. It is better to immediately report all disturbing symptoms in order to quickly receive the necessary help in treatment.
Yellow color of feces: what ailments does it usually indicate?
Such changes occur most often when consuming certain foods. Among them:
- apples, carrots, oranges, dried apricots, melon;
- milk and dairy products;
- beans, peas.
Significant changes in the color of stool also provoke:
- inability to digest gluten;
- hormonal disorders;
- stress;
- depression;
- taking certain medications - antibiotics, vitamins, contraceptives.
In order to exclude possible serious diseases, it is advisable to undergo an examination to identify the true causes of changes in the color of stool.
Light yellow stools do not always indicate the presence of any pathological changes in the human body.
Let's look at why stool is light yellow:
- If a person’s diet is dominated by carrots, melon, persimmons and other fruits and vegetables that contain carotene, orange stools may appear;
- if fermentation processes occur in the intestines, they provoke yellow feces;
- For some, this occurs from dairy products;
- if a person eats a large amount of peas;
- with hormonal imbalance it is yellowish;
- stress, anxiety, depression;
- when taking certain pharmacological drugs.
How to fix the problem?
If light-colored feces bother an adult for several days, then you need to find out what is causing this. First of all, you need to change your diet, introduce protein foods, vegetables and give up alcohol. If such actions helped, then you just need to stick to this diet.
If an adult is undergoing treatment with certain medications, you should consult with your doctor about possible side symptoms, one of which may be changes in the color of stool.
If the methods described above for eliminating the unpleasant symptom are not suitable, then you should go to the hospital to diagnose the functioning of the digestive organs, since only pathological conditions remain.
Video
After establishing the cause, the doctor will prescribe a course of treatment, including maintenance therapy (enzymes, painkillers, antibacterial agents) and etiotropic treatment that helps normalize the body’s functioning.
Treatment
After conducting the necessary examination and identifying the causes of the disease, the doctor will prescribe adequate treatment. Typically, therapy is complex and consists of several components.
Drug therapy
The following medications will help normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, improve their functionality and restore the thickness of stool.
Pharmacological agents used to eliminate mushy stools - table
| Pharmacological group | Enterosorbents | Prebiotics | Antisecretory | Drugs to normalize peristalsis | Carminative | Antispasmodics | Antidepressants | Biologically active additives |
| Examples of drugs |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
If the cause of mushy stool is a serious illness, the doctor will prescribe medications to treat the corresponding condition. It is possible that antibiotics, pancreatic enzymes, sedatives and antifungals, and corticosteroids will be needed. In severe cases, hospitalization is necessary.
Drugs used to eliminate mushy stools - photo gallery
Bruskopan will relieve pain
Colofort reduces gas formation in the intestines
Trimedat slows down peristalsis
Linex will quickly restore intestinal microflora
Omez helps restore the gastric mucosa
Fevarin is often used in the treatment of depressive disorders.
Enterosorbents Polyphepan and Polysorb will help normalize stool
Traditional medicine recipes
There are a large number of traditional medicine recipes to alleviate the condition of a patient suffering from frequent bowel movements and pasty stools. The most popular recommendations are:
- Infusion of oak bark. Pour 1 tablespoon of plant material into a glass of boiling water. Leave for 1 hour, then filter. The resulting drink is taken 1–2 tablespoons 3–5 times a day.
- Rice water. A thick broth is prepared from rice grains (preferably crushed) without adding salt, oil or seasonings. The resulting product is taken throughout the day, ¼ cup every 3-4 hours.
- Dried blueberry decoction. One tablespoon of raw material is poured into a glass of hot boiled water, brought to a boil, and boiled for 5 minutes. The resulting drink is filtered and cooled. Take instead of tea several times a day.
- Chamomile tea. For one glass of water, take 1 tablespoon of plant material. The mixture is boiled for 10 minutes, cooled, and filtered. The resulting decoction is drunk as tea before meals 2–4 times a day.
- Decoction of pomegranate peel. The dried peel of the fruit is crushed. Pour 1 teaspoon of raw material into one liter of boiling water and cook in a water bath for 30–40 minutes. Cool, filter and consume 2 teaspoons 3–5 times throughout the day.
To consolidate the effect of the medications used, you can additionally use herbal teas based on medicinal herbs and plants:
- lemon balm;
- St. John's wort;
- mint;
- chamomile;
- bird cherry;
- carrot seeds;
- dill;
- fennel;
- ginger
Folk remedies for eliminating mushy stools - photo gallery
Products based on oak bark have a pronounced antimicrobial effect
Chamomile has disinfectant properties
Blueberries contain vitamin C and other beneficial substances
Pomegranate peel contains many useful substances
Diet
If mushy stool appears, the following foods should be excluded from the diet:
- milk;
- fructose and sugar substitutes;
- legumes;
- carbonated drinks;
- fresh vegetables and fruits;
- herbs and spices;
- coffee;
- fatty foods;
- alcohol;
- baked goods;
- fresh bread;
- mushrooms;
- juices;
- canned food;
- smoked meats.
Foods that need to be excluded from the diet - photo gallery
Eating foods made from legumes can lead to increased gas formation.
Carbonated drinks can cause flatulence
Alcoholic drinks have a negative effect on the liver
Butter confectionery products contain a lot of sugar and yeast
Smoked foods increase the secretion of digestive juices
The following products must be present in the diet:
- stale bread;
- crackers;
- boiled eggs;
- lean meats and fish;
- steamed and boiled dishes;
- compotes and jelly;
- bananas;
- quince;
- persimmon;
- cottage cheese;
- baked apples;
- pureed or slimy porridges;
- cream soup;
- lean broths;
- fresh carrots.
Products recommended for consumption - photo gallery
Rusks are healthier than baked goods
Kissel envelops the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines
Persimmon contains vitamins and fiber
Porridge is a product that is extremely beneficial for the intestines
A hard-boiled egg is good to include in your first meal of the day.
After long-term use of the diet, you should gradually switch to eating foods that were temporarily excluded from the diet. Fresh vegetables, fruits, berries and natural juices must be included in the menu with caution, in small portions.
Which doctor will help?
If there is light-colored stool, an adult can seek advice from a therapist, but it is better to immediately go to a gastroenterologist, since in 80% of cases the problem lies in improper functioning of the digestive tract.
It may not be superfluous to consult an endocrinologist if the problem lies in the pancreas, but you will need to contact him after a diagnosis carried out by a gastroenterologist.
In the worst case scenario, the patient will be referred to an oncologist if a tumor is detected during the examination.
An adult should look for the cause of the appearance of light-colored stool immediately, and not wait until other symptoms begin to appear. Any treatment should be started at an early stage of the disease, then the effect occurs faster and fewer drugs need to be taken. You should always worry about your health and pay attention to even such minor changes as the lightening of stool.
What to do and what treatment to take
If you notice that the stool has an unusual color, but this is the only manifestation, you should adjust your diet and exclude fatty and fried foods, mushrooms, and alcohol. If this produces the desired effect, you should take more care of proper nutrition and the health of the liver and pancreas.
If discolored feces appear along with abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, fever, changes in taste preferences, or weight loss, you should immediately consult a doctor, who will help determine the cause of such manifestations and help get rid of disturbing symptoms.
Diagnostic methods
To determine the exact cause that could provoke the deterioration of the condition, it is necessary to undergo diagnostics. First, the doctor collects all the necessary information about when light-colored stools appeared, accompanying symptoms and other important factors.
After this, a stool test is taken, which allows you to confirm or refute the development of pathology. Laboratory examination of stool can also reveal the presence of helminths or the development of internal bleeding.
A biochemical blood test is also performed. This is necessary to determine the concentration of bilirubin in its composition.
If there is a deficiency of this enzyme, then further examination of the liver and gallbladder is required..
To complete the task, an ultrasound examination is prescribed.
Timely diagnosis and identification of pathological processes at an early stage of development allow timely treatment to begin and prevent the occurrence of more serious complications.
Acholic stool with dark urine
You need to immediately listen to your body if you have unusually light-colored stools, and at the same time your urine has acquired a dark brown tint. The cause of this symptom is most likely to be viral hepatitis.
Regardless of the form and type of pathology, stool always becomes light-colored. Hepatitis in 10% of cases leads to the development of liver cirrhosis. When the disease occurs, the skin and mucous membranes of the eyes become unnaturally yellow. The stool develops a sharp and unpleasant odor, which indicates the progression of the pathology.
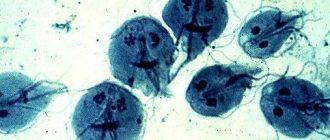
In some cases, viral hepatitis of the chronic type does not appear for several years; it may be hidden, because there are no characteristic signs for it (unreasonable bitterness and dryness in the mouth, loose stools). In such situations, the presence of discolored feces should alert a person. Timely diagnosis is complicated by the fact that the urine darkens both in the early and late stages of the disease.
But not only against the background of viral hepatitis does discolored, gray or pale yellow stool appear, accompanied by darkened urine. In some cases, such symptoms indicate the presence of parasites in the liver that provoke regular inflammation of the organ.