General recommendations
The diet for intestinal obstruction is designed to facilitate its work.
You have to follow this diet very carefully. The attending physician will draw up an individual nutrition plan, and the patient will only have to adhere to the recommendations received.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JUPGlHVoIG8{amp}amp;modestbranding=0{amp}amp;controls=1{amp}amp;rel=0{amp}amp;showinfo=1{amp} amp;enablejsapi=1{amp}amp;origin=
The main cause of intestinal obstruction is various tumors.
After their removal, the intestines cannot cope with the work of digesting and absorbing food for some time, so after surgery on the intestines you have to follow a special diet for some time.
The actual diet for intestinal obstruction begins on the second day after surgery. In the first 24 hours, the intestines should be clean, nothing should enter it.
On the first day, the patient does not eat or drink; his lips are only moistened with water. During this time, postoperative wounds in the intestinal wall will heal at least a little.
On the second day after surgery, you can already drink water. By the end of the second day, instead of water, the patient is given several tablespoons of chicken broth.
Chicken broth is a product with special properties; it is quickly and easily absorbed in the intestines and therefore is definitely included in the diet for intestinal obstruction.
In the first days after surgery, the patient receives basic nutrition by introducing into the blood special solutions that contain substances necessary for the body in the postoperative period.
On the third day after surgery, pureed, steamed dishes made from products containing a minimal amount of toxins can be introduced into the diet.
First of all, it is a slimy porridge of refined rice without milk or sugar.
When 5–7 days have passed after the operation, you can include familiar dishes in your diet, but with strict restrictions on the method of preparation and composition of the products.
This diet should be followed for another 2-3 months.
Principles of diet after intestinal surgery:
- The volume of food eaten at one time should not be more than 100 ml;
- Food is taken every 2.5 hours, a break is taken at night;
- The menu includes a large number of protein products;
- Fermented milk drinks are very useful for postoperative intestinal obstruction, but they must be low-fat so as not to promote the secretion of bile;
- Bread can only be eaten dried, in the form of toast and crackers. Butter dough is strictly prohibited;
- You can eat sweet fruits, except grapes and citrus fruits. Sour fruits are prohibited;
- Vegetables are included in the diet only in boiled and pureed form.
During the diet for intestinal obstruction, the following foods are prohibited:
- all types of cabbage, except mashed boiled broccoli;
- legumes;
- asparagus;
- nuts.
Prohibited foods cause strong fermentation in the intestines. If eaten even 2-3 weeks after surgery, they can cause postoperative sutures to come apart.
The consequences of this will be peritonitis and a new, more severe operation.
Treatment table No. 3
For chronic intestinal diseases, which include chronic obstruction, treatment table No. 3 is prescribed. Diet No. 3 is a special therapeutic diet that spares the large and small intestines.
- The duration of diet No. 3 for intestinal obstruction is determined by the attending physician;
- The menu should be based on products that accelerate peristalsis;
- Products that cause rotting and fermentation in the intestines are prohibited;
- Food should have a daily calorie content of 2500 kcal;
- The daily amount of food is divided into 5-6 meals;
- Drink 1.5 liters of clean water per day;
- Acceptable methods of cooking: baking, boiling, steaming.
Diet No. 3 for intestinal obstruction excludes processed foods, sausages, smoked meat and fish. For meat dishes, choose lean beef and chicken.
Seafood is very useful for intestinal obstruction: shrimp, mussels, octopus, squid.
Seafood is not just a source of quickly digestible protein, but also a way to replenish an organism weakened during a chronic illness with a mass of valuable microelements contained in sea water (and this is practically the entire periodic table).
Eggs are allowed during the diet, but their quantity is limited to two per day. The healthiest way to eat eggs is as a steamed omelet.
Flour products are represented in the diet for intestinal obstruction with stale bread made from 1st and 2nd grade wheat flour.
Biscuits, crackers, including rich, non-yeast confectionery products are acceptable. Any fresh products made from yeast dough are prohibited.
Milk and dairy products occupy a central place in the diet. Fermented milk drinks are quickly absorbed, restore intestinal microflora, and enrich the diet with protein.
They should be included in your diet daily. Cottage cheese of any fat content, kefir, Varenets, fermented baked milk, unsweetened yogurt, sour cream, and soft unsalted cheeses are useful.
Vegetables may be present on the menu in full, with the exception of potatoes and cabbage. Vegetables are used to make casseroles, cooked as a side dish in boiled and stewed form.
Preference is given to zucchini, pumpkin, beets, carrots, and cauliflower.
Some drinks are prohibited: liquid chocolate, coffee, strong black tea (green is welcome), soda and kvass.
Diet for constipation
Chronic intestinal obstruction is often explained by common constipation. In this case, including fiber-rich foods in your diet will help.
Fiber (plant fiber) ensures good intestinal motility.
A lot of fiber is found in the peel of the fruit, seed coats, stems and leaves, so if you are prone to constipation, you should not peel apples, cucumbers and other fruits.
For constipation, be sure to include leafy vegetables in your diet, as they contain the maximum amount of healthy fiber.
The green color of these products indicates their good supply of magnesium. This chemical element is especially useful for intestinal obstruction.
According to the latest European fashion, lunch ends with a salad of green vegetables: broccoli, leafy vegetables.
This rule fits perfectly into a diet for constipation - vegetables rich in fiber and magnesium, eaten at the end of the meal, can speed up the movement of other foods through the intestines.
For those who do not like raw vegetables, you can include porridge with prunes for breakfast in your daily diet.
Anyone who has encountered the problem of poor peristalsis could see how neatly and gently prunes solve this problem.
Just a few prunes a day restore activity to the intestines and help cleanse them.
What drinks should you avoid if you are prone to constipation? First of all, this is strong tea. Thanks to tannins, tea relaxes smooth muscles, which leads to sluggish bowel movements.
Coffee lovers, on the contrary, do not have problems with bowel movements.
An effective recipe for constipation: eat an apple, washed down with strong coffee with milk - the intestines will empty in the next 30 minutes.
Nutrition for intestinal obstruction depends on the causes of this pathology. Only a doctor can decide what can and cannot be eaten during acute and chronic obstruction.
If the cause of obstruction is constipation, then the diet serves not only as nutrition, but also as medicine.
Every patient who is faced with intestinal obstruction tries to find out from the attending physician about what can be eaten after the therapy. Regardless of the reasons that provoked the pathological condition, this category of patients must adhere to general rules when forming a daily diet:
- There should be equal time intervals between meals to ensure a constant supply of food and normal functioning of the digestive tract.
- To prevent exacerbation or new blockage, it is prohibited to transfer. Portions should be kept minimal, approximately 150g.
- From the daily menu it is necessary to exclude foods that can cause increased gas formation and problems with constipation.
In case of partial CI, not accompanied by obturation, patients are prescribed the “Table No. 0 or No. 4” diet. Experts recommend eating grated or pureed food at room temperature. It is advisable to include mucous soups in the menu, which can create a protective membrane on the walls of the organ.
The “Table No. 0” diet for intestinal obstruction requires adherence to strict rules not only in the process of preparing dishes, but also in the selection of products:
- The volume of a single serving should not exceed 100g.
- Breaks between meals can vary from 2 to 3 hours.
- Patients' menus should be enriched with proteins.
- Food must be steamed or boiled.
- The diet may include dried or day-old bread, zero-fat fermented milk products, sweet varieties of berries and fruits.
- Vegetables should be ground or heat treated.
- Patients should completely exclude nuts, legumes, asparagus and cabbage from the menu.
This is due to the fact that they can provoke divergence of postoperative sutures. To prevent unpleasant consequences and repeated surgery, the diet menu must be followed for three months. After this period, patients are prescribed “Table No. 4,” which provides a more extensive diet.
Nutrition for intestinal obstruction, which is not accompanied by complications and intussusception, should be aimed at normalizing bowel movements. The diet for adhesive obstruction, which occurs in a chronic form, has some features:
- The menu should be balanced so that the body receives the necessary microelements.
- The basis of the diet consists of liquid dishes.
- Patients should ensure that food is not too hot or cold.
- Dishes should not stimulate the active production of gastric juice.
- For gastrointestinal diseases, the number of meals is increased to six times a day, with 2-3 hour intervals between them.
- The daily amount of liquid is 1.5-2 liters. Patients are allowed to drink purified water, homemade compotes, jelly and weak teas.
In acute cases
During the period of exacerbation of the disease, patients must exclude from the diet all dishes that can provoke irritation, fermentation and putrefactive processes in the organ.
The daily calorie content of food consumed should not exceed 1850 kcal. Doctors strongly recommend limiting the amount of salt to 6g per day.
Nutrition after surgical treatment
Surgical intervention is aimed at eliminating the factors causing the disease. For this reason, the intestines cannot perform their functions normally. In such cases, for the first few days after medical intervention, it is recommended to adhere to the rules of therapeutic fasting, which involves refusing any food. The only thing patients are allowed to do is drink a little purified water without gas or weak tea.
For several days, the patient is fed through a special tube, thereby bypassing the gastrointestinal tract. Approximately five days after the intervention, nutritional mixtures are introduced. In cases where a person’s condition has stabilized, the doctor decides that the patient can eat independently.
The main diet is started a few days, often a week after the operation. The attending physician decides how long it should take individually for each patient. In most cases, a zero diet is indicated. It is designed in such a way as to remove as much stress as possible from the gastrointestinal tract.
This diet involves the consumption of liquid foods, without adding oil and salt. It is recommended to consume food at room temperature in small portions, approximately every two hours.
When more than a week has passed after surgery, the patient is shown diet table No. 4. Such nutrition implies strict adherence to the rules of preparation and selection of the chemical composition of dishes.
The basic principles of the diet for intestinal obstruction after a surgical procedure are:
- the volume of food consumed at one time should not exceed one hundred grams;
- breaks between consumption of dishes are two or three hours;
- the menu must be enriched with proteins, and dishes must be steamed or boiled;
- The basis of the diet is low-fat dairy and fermented milk products. They are very useful in the postoperative period and do not contribute to the secretion of bile in large quantities;
- It is best to eat yesterday’s bread or slightly dried bread;
- You can eat sweet varieties of fruits and berries in any quantity. Citrus fruits and grapes are prohibited;
- vegetables can be eaten boiled and grated.
Diet for intestinal obstruction: maximum caution
This diet is gradually expanded and over time they switch to diet No. 4B for patients with intestinal diseases in the recovery stage. This diet provides complete nutrition while sparing the intestines. The diet becomes more varied, food is not pureed. But all dishes are also steamed or boiled.
Diet for chronic intestinal obstruction
The main purpose of the diet for chronic intestinal obstruction is the regulation of stool. For this purpose, patients are prescribed moderately mechanically gentle nutrition. And since this diet is permanent, it must be complete, contain a sufficient amount of all the proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, macro- and microelements necessary for the body.
The diet contains easily digestible foods (meat, cottage cheese and others) containing complete proteins. The meat should be ground in the form of meatballs, meat soufflé, meatballs, steamed cutlets, and so on. Fermented milk products, butter, cookies, apples and so on are healthy. It is recommended to remove the skin from apples and eat them in moderation, depending on your tolerance - too much fiber can cause bloating.
Warm food relieves spasm of intestinal smooth muscles well, which promotes the movement of feces through it. It is also necessary to drink a sufficient amount of fluid - this dilutes the stool. For constipation, it is recommended to eat dried fruits (plums, dried apricots, figs) and drink a glass of fresh kefir at night (three-day kefir causes constipation).
It is necessary to exclude hot and salty seasonings, rich meat, fish and mushroom broths, blueberries, strong tea, coffee and cocoa - these products slow down the movement of feces through the intestines. You should not eat foods that contribute to increased gas formation, such as fresh white cabbage, peas, legumes, beets, and so on.
During the period of exacerbation of the disease, mechanical sparing of the intestines should be maximum. It is possible to switch to diets No. 4 or No. 4B, and after the exacerbation passes, the diet is gradually expanded, but the basic principles (mechanical and chemical sparing, the use of easily digestible foods and a rational amount of fiber) remain, as well as frequent split meals .
A diet for chronic intestinal obstruction can prevent exacerbation of the disease, which is the prevention of further deterioration of the patient’s condition.
General dietary recommendations for constipation
Constipation and constipation are different. Different constipation requires different diets.
Only one rule is the same in therapeutic nutrition for constipation of all types: this is to drink as much fluid as possible; you need to drink at least 1.5 liters per day. But you can’t drink everything; drinks shouldn’t be carbonated or sweet.
Fresh kefir is a very controversial product; for a century and a half we have been convinced of the benefits of kefir, but in practice many patients categorically cannot tolerate it. Kefir, like other dairy products, can cause CONSTIPATION and sometimes intestinal irritation with flatulence.
An interesting observation: not a single animal uses sour milk (kefir) in its diet; probably, if fermented milk products were so beneficial for health, then instinct would push our smaller brothers to consume them. But no, kefir is the work of human hands, and it is not a fact that this conquest of civilization is so environmentally friendly for everyone.
Vegetable oils (sunflower, olive) not only soften stool and accelerate peristalsis, but also supply the body with unsaturated fatty acids, vitamins and microelements. If a patient suffering from constipation has a gallbladder in its place, then vegetable oils have a choleretic effect, and bile, as is known, enhances peristalsis of the gastrointestinal tract. After cholecystectomy, vegetable oils have a different effect on intestinal motility.
“Dried fruits, in particular prunes and dried apricots, help relieve constipation.” Some sites recommend eating as much as 200 g per day. But God forbid that a patient with constipation and irritable bowel syndrome with flatulence eat such quantities of dried fruits!
Daily meals for constipation should contain “as much plant fiber as possible.” This not at all harmless phrase wanders from site to site, and until recently was supported by the majority of doctors. But recent large studies have shown that in some patients with constipation, fiber is unsafe:
In patients with a tendency to intestinal paresis and carbohydrate intolerance, excess fiber in the diet can cause exacerbation of colitis and not only increase constipation, but also cause increased flatulence, and even intestinal obstruction. The cut and flaxseed in the daily diet for constipation are recommended by the international organization of gastroenterologists, but also with some reservations.
A very good laxative vegetable is beets. For almost all types of constipation, beets can and should be consumed. Beets rarely cause flatulence and can be recommended for daily nutrition for people suffering from constipation. If there is no gastritis or colitis in the acute stage accompanying constipation, then the diet can be enriched with beetroot juice, which is drunk only settled and diluted!
Cabbage is not just a controversial product, but even, I would say, a bomb for some patients. Yes, obviously there will be no constipation when eating cabbage, but flatulence and abdominal pain occur in every second patient with constipation when eating cabbage (any cruciferous vegetables - cauliflower, broccoli, kohlrabi, and other types). Particularly unpleasant sensations from cabbage can occur in patients with dolichosigma. For them, the unfortunate ones, food lingers longer in the intestinal tube, and if the cabbage is left to rot in it for an additional day, then the poor fellows simply crawl into the wall from pain and bloating. Sauerkraut is better tolerated than raw cabbage. So, be careful with cabbage! In moderate quantities, cabbage will have a laxative effect and cause stool, but with abundant consumption of this product, gas formation in the intestines will increase, which will bring additional inconvenience in the form of flatulence. By the way, sauerkraut is often better tolerated by patients than fresh or boiled-stewed: (scientific information about the dangers of cabbage)
Fresh greens, potatoes, carrots, as well as other vegetables and fruits can be consumed both raw and boiled, taking into account individual tolerance. Eating cereal porridges (oatmeal, buckwheat, millet) will speed up peristalsis and move feces through the intestines faster. Read about colon cleansing with oatmeal
Legumes in the diet of adults with constipation are a source of misunderstandings and disagreements! No legumes if they make you painfully bloated! People born in our cold climate do not have the same enzymes for processing legumes that southerners (Greeks, Italians, Latin Americans) inherit. The “Mediterranean diet” is certainly healthy, but leave legumes to those who tolerate them well from birth.
It is logical that if stool is disrupted, foods that cause constipation should be excluded from the diet. If you have constipation, you should avoid fatty, fried, smoked, chocolate, spicy foods and alcohol. In addition to constipation, excessive consumption of these foods can lead to the development of gallstones and pancreatitis, so even in the absence of problems with stool, it is necessary to minimize the intake of these dishes. Learn 7 basics of mindful eating for constipation, no matter the cause of constipation.
Menu for chronic conditions
What diet should you follow if you have intestinal obstruction: reviews from doctors
Intestinal obstruction is a condition that makes it difficult to naturally eliminate feces through the anus.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=
In case of exacerbation, surgical intervention is required, but if the syndrome is mild, then following a diet and taking medications is often sufficient.
Intestinal obstruction can occur for many reasons:
- The presence of worms, hernias, adhesions, hematomas, gallstones and fecal stones;
- Reduced intestinal lumen;
- For oncological diseases;
- For inflammation, congenital cords of the peritoneum, intestinal obstruction, problems with blood vessels;
- In case of malfunctions of the gastrointestinal tract, Hirschsprung's disease, spasms, paralytic phenomena.
One common sign of an obstruction is the inability to have a bowel movement naturally (constipation), but other symptoms include:
- Sudden weight loss, which occurs due to lack of fluid;
- Increased body temperature;
- Bloating;
- Gas retention;
- Unnatural skin tone;
- Vomiting after eating.
There are also several types of obstruction: adhesive, partial, obstruction of the small or large intestine.
First of all, a person who suspects such a syndrome in himself or his child should consult a doctor. In the future, medications and a therapeutic diet are prescribed for intestinal obstruction, but if the condition is advanced, surgery will be required.
The diet for patients with intestinal obstruction includes the following products:
- Wheat bread crackers;
- Puree porridge on water;
- Minced meat from lean fish or meat;
- Soups with weak broths;
- Lean types of meat and fish;
- Scrambled eggs;
- Butter;
- Fresh low-fat cottage cheese;
- Mashed berries and fruits;
- Vegetable decoctions;
- Rosehip decoction, tea and coffee without adding milk.
Check your body fat %, BMI and other important parameters
Therapeutic dietary nutrition for intestinal obstruction completely excludes flour products, pasta, barley, millet, egg, sausages, fatty meat and fish, salty foods, dairy products (except cottage cheese), dried fruits and vegetables.
If the patient is hospitalized, he is prescribed perinatal nutrition for intestinal obstruction.
What you need to eat to restore normal intestinal patency: diet, menu
Diet rules for intestinal obstruction:
- The patient's menu should consist only of easily digestible dishes;
- Calculation of BZHU should be done as follows: proteins - 80 g, fats - 70 g, carbohydrates - 250 g per day;
- The amount of salt should be limited to 8 g per day, and water to 2 liters;
- The daily calorie intake is 1900 Kcal.
This therapeutic diet for intestinal obstruction in adults is most often prescribed by doctors, and its approximate menu looks like this:
- We have breakfast with porridge on water, pureed cottage cheese and tea;
- For lunch we drink 250 g of rosehip decoction;
- We have lunch with semolina soup, meatballs and blueberry jelly;
- We have an afternoon snack with currant decoction;
- We have dinner with pureed buckwheat porridge, steamed omelet and tea.
If obstruction occurs in childhood, then the following rules must be observed:
- It is necessary to remove all products that cause increased gas formation;
- Dishes must be served pureed;
- It is advisable to prepare dishes from beets, carrots and vegetable oils every day.
Most often, obstruction occurs in the elderly due to various diseases, and here simple principles must be followed:
- Eat only foods that are easily digestible;
- Eliminate salt from your diet and limit sugar.
With this form of the syndrome, you need to plan your menu from the following:
- Low-fat meat broths;
- Fresh kefir;
- Vegetable broths;
- Soft-boiled eggs;
- Chicken breast;
- Butter – limited;
- Cottage cheese, steam omelettes.
If an operation has been performed, then it is necessary to adhere to a diet after acute intestinal obstruction, which includes a limited number of dishes:
- Mucous decoctions;
- Low-fat broths with meat;
- Decoctions, jellies and juices from fruits or berries.
The daily routine and nutrition during intestinal obstruction in this case are regulated by a doctor, but expanding your diet is usually allowed only 1-2 weeks after surgery - it all depends on the recovery process.
We also recommend that you read the article Diet for liver steatosis.
The main results of the diet for adhesive intestinal obstruction are noticeable already 3-4 days after its start, when the patient ceases to be bothered by flatulence and stool normalizes. If you comply with all the doctor’s requirements, then a complete cure is quite possible, but only if the disease is not acute.
Tips to avoid intestinal obstruction:
- Eat right, do not abuse fast food and other foods that cause intestinal clogging, and do not overeat;
- To live an active lifestyle.
Simple prevention of intestinal obstruction can prevent such a problem, because a person’s health mainly depends on what he eats.
“Often, obstruction occurs due to intestinal tumors, and here it is simply necessary to follow a diet. If you continue to eat unhealthy foods, complications are possible: necrosis, ischemia and peritonitis.”
“In most cases, obstruction can be eliminated at the initial stage, and here diet comes to the rescue. If the patient does not comply with it, then even the most powerful medications will not give the maximum effect.”
“Diet is needed for any gastrointestinal disease, and even more so for intestinal obstruction. If it is not followed, the syndrome is much more severe, and it also allows you to avoid surgery.”
If an acute intestinal disease occurs, the diet should be aimed at minimizing the likelihood of fermentation and putrefactive phenomena in the digestive tract.
Food that irritates the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal canal is prohibited. Calorie intake per day should not exceed two thousand. The amount of salt should not exceed 6 grams per day.
The menu for such a pathological process should consist of:
- crackers based on white bread;
- vegetable drinks;
- low fat cottage cheese;
- small amount of butter;
- boiled porridge on water;
- soft-boiled eggs or omelet;
- low-fat soups;
- drinks based on rose hips and currants;
- non-acidic berries and fruits.
The following dishes are considered prohibited:
- fresh baked goods;
- dairy products;
- compotes based on dried fruits;
- raw vegetables;
- fatty fish and meat dishes;
- carbonated and alcoholic drinks;
- tea and coffee with milk;
- pearl barley, barley and millet cereals.
In the first days of acute pathology, doctors advise stopping eating altogether.
On the first day you should drink only filtered water. After the discomfort subsides, you can gradually begin to eat.
Chronic pathology is characterized by periodic exacerbations. To avoid relapse for as long as possible, you must also adhere to a special menu.
In such cases, the patient is prescribed diet number 3.
The features of this diet are:
- availability of products that accelerate intestinal motility;
- eating small portions;
- taking fluids up to two liters per day;
- compliance with daily caloric intake. Its limit should not exceed 2500 kilocalories;
- eating lean fish and meat foods;
- eating boiled and baked foods.
Squid and shrimp will have a positive effect. Sour milk, butter, apples and dry cookies have a beneficial effect on internal organs.
In case of chronic obstruction, it is strictly forbidden to consume dishes in the form of:
- semi-finished products;
- smoked meat and fish;
- sausages;
- cocoa;
- strong tea and coffee.
If you follow all the tips, you can avoid relapses for a long time.
Many patients are interested in the question of what can be eaten with partial obstruction of the intestinal canal. In this case, the menu should be aimed at reducing the risk of putrefactive processes in the digestive canal. It is necessary to completely exclude products that have even the slightest possibility of irritating the mucous membrane of the gastric and intestinal walls. The total number of calories per day should not exceed 1850, while the amount of salt should be minimal.
The menu should include products in the form of:
- white crackers;
- boiled porridge. They should be cooked only with water;
- low-fat soups with meat and fish broth;
- boiled eggs;
- drinks. The patient can have weak black and green tea, rosehip infusion, currant infusion, coffee, freshly squeezed juices, but they must be diluted with water in a ratio of two to one;
- dietary types of meat and fish;
- crushed non-acidic fruits and berries;
- vegetable decoctions;
- low-fat cottage cheese;
- butter, but not in large quantities.
If acute intestinal obstruction is observed, then it is necessary to completely exclude:
- fresh baked goods;
- dried fruit compotes;
- milk;
- raw vegetables;
- fatty meats and fish;
- carbonated drinks, coffee and strong tea with milk;
- porridge in the form of pearl barley, millet and egg.
You should avoid salt and spices altogether. The basis is the drinking regime. It is better to refuse food on the first day.
If a patient has a chronic intestinal obstruction, then the goal of the correct menu is to improve bowel movements. If you do not follow a diet, then an exacerbation of the disease and a deterioration in the patient’s condition is possible.
The basis of the diet consists of liquefied dishes. The menu can include porridge in the form of buckwheat, rice, oatmeal, soups in low-fat broth with grated vegetables, mashed potatoes, baked vegetables. Instead of sugar and sweets, you can eat a little honey if you are not allergic.
Such a diet for partial blockage should be followed throughout life. The main thing is that the menu is rich in vitamins, minerals, proteins and carbohydrates. Fats should also be present in the diet, but not in minimal quantities.
Diet is one of the important aspects in treatment. Therefore, doctors create a sample menu for their patients. It might look like this.
- The next morning, oatmeal is prepared in water, as well as cottage cheese soufflé. Everything is washed down with weak tea.
- For an afternoon snack, you can drink a blueberry decoction.
- At lunchtime, doctors advise making soup with low-fat meat broth and adding semolina. Steamed meatballs, rice and jelly are also added to the diet.
- A rosehip based decoction is suitable as an afternoon snack. You can add a little honey to sweeten it.
- In the evening, prepare a steamed omelette and buckwheat, which is pre-ground. Everything is washed down with tea.
- Before going to bed, you can drink a glass of low-fat kefir or yogurt without additives.
Making a menu for the day
When drawing up a zero diet, doctors calculate calories. They should not be more than 1020 kcal per day. The daily diet contains:
- carbohydrates - approximately 150-200 g;
- fat - no more than 20 g;
- proteins - approximately 10 g.
The amount of liquid drunk per day ranges from 1.8 to 2.2 liters.
Mostly food during this period is prepared in the form of jelly or thoroughly pureed. When serving, monitor the temperature of the food, since cold and hot will be detrimental to the intestines. The diet is based on decoctions that have a jelly-like consistency and broths made from meat, but are low-fat.
You will have to completely exclude from your diet foods that have a dense consistency and any carbonated sweet drinks.
Chronic or acute intestinal obstruction requires a certain diet, since digestion is not proceeding properly. This diet will prevent fermentation and putrefactive processes from forming.
Fats should be present up to 60 g, and carbohydrates - 250 g, but simple carbohydrates - no more than 50 g. Proteins are also included in the diet - about 80 g, but the majority should be animal proteins.
Anything that can irritate the stomach and intestines should be excluded from the diet.
The volume of liquid allowed is from 1.5 to 2 liters, and it is advisable to avoid salt altogether. The total calorie content should be approximately 1900 kcal.
Nutrition, if intestinal obstruction is detected, should not burden him, now he should rest, and what nutrition is best for him in this difficult time, the doctor will tell you.
Intestinal obstruction is a disease that is accompanied by partial or complete blockage of the lumen of this organ with the contents of the digestive tract. This often occurs due to impaired intestinal motility, the formation of various neoplasms, or an irrational diet. The diet for intestinal obstruction will differ depending on the nature of the disease and the general condition of the patient. In addition, there are several types of gentle nutrition - before and after surgery.
In most cases, intestinal obstruction can be eliminated by taking medications - in the chronic form, or by performing surgery - in the acute form. But to consolidate the positive effect of such types of therapy, it is recommended to adhere to a specially formulated gentle diet for intestinal obstruction.
Causes
The following factors can provoke this condition:
- polyps of the small intestine;
- presence of tumor processes;
- change of diet;
- altered organ motility;
- poisoning with nerve agents;
- severe infectious diseases;
- spasm of the intestinal wall;
- abdominal adhesions;
- fecal and gallstones;
- roundworms;
- volvulus;
- swallowed objects.
Intestinal obstruction is expressed by the following manifestations:
- abdominal pain of a cramping or bursting nature;
- bloating;
- violation of the symmetry of the peritoneum;
- stool retention;
- nausea and vomiting;
- loss of appetite;
- inability to perform an act of defecation;
- in some cases, blood is released from the anus.
Why is a diet needed?
Intestinal obstruction means that everything contained in the digestive tract cannot completely or partially pass through the intestines because its peristalsis is impaired or some mechanical obstruction occurs.
The main reasons causing this problem include:
- Wrong diet: without a certain time, with incorrectly selected products or a radical change in diet.
- Polyps formed in the small intestine.
- Decreased muscle tone on the intestinal wall.
- Thyroid gland dysfunction, clinical manifestation - constipation.
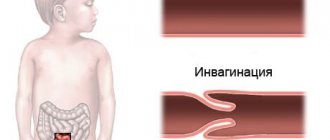
- Intussusception. A special type of obstruction when part of the intestine penetrates into the lumen of another part.
- Intestinal dysbiosis. It is observed when the microflora is disturbed, and this causes an increased process of decay, as a result, the motor activity of the intestines decreases.
- Iron deficiency anemia. When there is not enough iron, the intestinal muscles do not receive enough oxygen, and then muscle weakness occurs.
- Food allergies. It leads to the fact that if any food is not accepted, inflammatory changes of an allergic nature occur in the intestinal wall.
- Formation of tumor processes in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Constipation after surgery.
- Obstruction due to long-term use of medications.
Symptoms of poor bowel function. By eliminating the cause, you can normalize stool retention, but this will require following a diet and a special drinking regimen.
To recognize intestinal obstruction, you need to learn to identify the problem by symptoms. They are:
- pain in the lower abdomen, bloating;
- lack of appetite;
- stool retention, as well as gas accumulation;
- streaks of blood may appear in the stool;
- nausea and vomiting;
- painful bowel movements contribute to the development of fear when required to go to the toilet;
- rectal cracks appear;
- if constipation persists for a long time, prolapse of the rectal mucosa may occur;
- encopresis appears - a process in which solid feces accumulate in the rectum, and feces, which have a liquid consistency, are spontaneously released because nothing restrains control over the muscular apparatus of the rectum.
In case of intestinal obstruction, it is necessary to visit a therapist so that he can determine which specialist needs to be referred to. This could be an endocrinologist, surgeon or neurologist.
The primary task is to restore the previous level of consistency of the intestinal contents and return to the speed with which feces should normally pass through the colon. There are several types of treatment: conservative and surgical.
Diet after surgery
Often, with complete intestinal obstruction, intussusception, constipation and adhesions, surgical intervention is performed. During the operation, the damaged area is removed and the cause is eliminated.
After this, for a quick recovery, the patient should adhere to a strict diet.
In the first days, the organ should be cleansed. Therefore, eating and drinking is completely prohibited. To avoid dehydration, the patient's lips are soaked with water. During this time, the wounds in the digestive canal will heal a little.
On the second day the patient is allowed to take water. Eating after intestinal surgery can be resumed only on the third day. The patient can eat grated dishes that are steamed. This therapeutic diet after intestinal obstruction should be followed for two to three months.
After eating a portion, you need to take a short break. If the pathology is accompanied by constipation, then the food should be as diluted as possible. Then attention is paid only to soups and decoctions.
Intestinal obstruction also occurs with cancer. This type of disease is considered very life-threatening, so doctors strongly recommend adhering to only a zero diet.
For cancer, the amount of protein and fat should be minimal. But carbohydrates, on the contrary, should be enough. The basis of this menu is juices, decoctions, jellies and cereals. If you experience pain or constipation, you can take low-fat chicken broth for several days.
If the patient had an obstruction of the intestinal canal before the operation, then he must follow a strict diet for the rest of his life, this will avoid serious complications and repeated relapses.
After surgery to remove polyps in the intestines, the patient must follow a special menu. On the very first days following the operation, the organ should be clean. The patient is prohibited from eating or drinking anything at all. You are only allowed to wet your lips with water. During this period, postoperative wounds in the organ will heal slightly.
On the second day after surgery, the patient is allowed to drink water, and in the evening you can drink a few tablespoons of lean chicken broth. On the third day, the diet includes pureed, steamed dishes with a minimum amount of toxins. The therapeutic diet must be followed for 2-3 months - this time is enough to restore the intestines.
Patients who have undergone surgery will have to limit their food intake for several months. Following a special diet will normalize digestion, as well as stabilize the functioning of the intestines. For 2-3 days after the operation, during which adhesions or other formations were removed, patients must fast.
Patients begin a diet after surgery for intestinal obstruction a week later (the exact time is determined by the doctor individually, just as with cancer). Its principles are to reduce the load on the gastrointestinal tract. Patients are advised to consume meals every two hours in liquid form, prepared without fats, salt and spices.
Nutrition for intestinal obstruction depends on whether the patient has undergone surgery or not. If surgery is done, then in the first 12 hours it is strictly forbidden to eat anything. But you should adhere to a strict drinking regime.
All necessary vitamins and microelements are administered to the patient in the form of special solutions and mixtures through a vein or tube. As soon as the patient's condition improves, he is given permission to eat on his own.
The diet for intestinal obstruction is as gentle and relaxed as possible. The specialized menu includes foods that are easily digestible. When the patient recovers a little, the diet is expanded and food with proteins and carbohydrates is added. The basis is fiber. You need to limit your intake of hot, spicy and salty foods.
In some situations, patients experience complications in the form of adhesions. This type of disease can provoke the development of organ failure, so treatment should be carried out in any case. The basis of the therapeutic course is the same diet, but it involves a complete rejection of heavy foods that increase gas formation.
A gentle diet after surgery for intestinal obstruction should be followed for at least 10-14 days. When the body recovers, other products can be introduced. In case of pathology with constipation, it is allowed to drink fermented milk products in the form of kefir and yogurt. But their fat content should be small, maximum 1%.
This diet after intestinal surgery should be maintained for another two to three months. In the future, the diet can be expanded with new products, but you need to be extremely careful with them.
Signs of intestinal obstruction
Every person must know the signs of acute intestinal obstruction, which include pain, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, uneven bloating and the inability to defecate. Sometimes blood comes out of the anus.
Vomiting serves as an indicator of the location of intestinal obstruction. If the small intestine is blocked, vomiting occurs very often, the vomit has a specific green color due to the high content of bile and intestinal juices, with a terrible repulsive odor.
This indicates the presence of intestinal contents in the vomit, exiting through the stomach when intestinal motility stops. This symptom is called fecal vomiting. But if the obstruction is low in the colon, vomiting may not occur.
The presence of pain is an integral part of intestinal obstruction. The pain can be so severe that a painful shock occurs when the skin turns pale, cold sweat appears on it, and the pulse becomes weak.
If the pain seems to surround the navel and appears again literally in a matter of minutes, these are undoubted signs of small intestinal obstruction. Colonic obstruction pain occurs over a much longer period of time and is usually felt below the navel.
To establish a diagnosis of intestinal obstruction, the doctor can help by interviewing the person seeking help, palpating the abdomen, palpating the rectum, listening to the abdominal cavity, performing X-rays, irrigoscopy, and ultrasound examinations.
Computed tomography is a very accurate and effective diagnostic method. The patient’s blood must be taken for a general analysis. If improvement occurs (stool appears, pain subsides), intestinal conductivity is checked with barium, which is a contrast agent.
Without improvement and with the development of peritonitis, surgery must be performed. The main goal of the operation is to remove the obstruction in the intestine and allow chyme to move freely along the entire length of the intestine up to the anus.
Before bowel resection surgery, the patient is given broad-spectrum antibiotics into a vein. When the operation is completed, a tube is inserted through the patient's mouth to drain the contents of the stomach.
The operated patient is prohibited from eating and drinking for half a day after surgery. Therefore, the first time after surgery is quite difficult: nutrition consists only of nutrient solutions that are administered intravenously. Then the probe comes to the aid of the patient again, and nutrition is provided through it.
The concept of a zero diet
After surgery, corrected intestinal obstruction is treated with a gentle diet. In medicine it is called zero. The main limitation is salt. Its amount per day should not exceed two grams. Nutritionists advise eating six to eight times a day. In this case, the size of one serving should not exceed 200 grams.
The amount of protein per day on a zero diet should not exceed 150 grams. You also need to think about your drinking regime. The norm for intestinal obstruction is at least two liters per day. The basis is fresh vegetable and fruit juices, decoctions, jellies, slimy porridges and low-fat meat broth.
It is strictly forbidden to eat foods in the form of whole milk, carbonated water, solid foods, spicy and fried foods, and fatty foods.
How to identify intestinal blockage
A doctor may suspect an obstruction based on the patient’s complaints, clarification of the circumstances from the appearance, as well as examination data, percussion (tapping), palpation (palpation) and auscultation (listening) of the abdomen:
- bloating, swollen loop, with swelling of the peritoneum - hard stomach, tense muscles;
- metallic drum sound;
- the sound of splashing, the sound of a drop at the final stage;
If such signs are detected, diagnostics is prescribed using x-rays. He shows:
- arches of swollen hinges;
- bowls - a light dome above the horizontal levels of liquid;
- cross-striated intestine.
Ultrasound is of less importance, since swollen loops interfere with the passage of ultrasound.
About drinks and secrets of a tasty diet
A diet for intestinal obstruction can contain very tasty dishes.
If you have intestinal obstruction, the diet will not seem so sad if you include:
- Peel 4 large potatoes. Place in cold water overnight. Then grate on a fine grater and add to 1 liter of boiling water. Let it boil for 1 minute. Add 1 tbsp. l. butter and 1.5 tbsp. l. oatmeal. Place over low heat until the oatmeal is cooked through. Grate the sweet pepper on a coarse grater. Add and boil for 1 minute. Add 1.5 tablespoons of finely chopped herbs. Stir and turn off.
- Prepare mashed potatoes only from soaked potatoes. Boil the peeled potatoes until they begin to disintegrate. For 1 liter of water it should take 1 tsp. salt. Instead of butter, the puree can be seasoned with kefir or hot boiled milk.
- The work of the gastrointestinal tract will be helped by salads made from boiled pureed vegetables. Grate 1 small carrot and 1.5 small beets on a carrot grater. Season with sour cream or kefir. Salt to a minimum. You can season it with herbs. If there is any odor from the food eaten in the burp, there are not enough enzymes or bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract to digest this fiber.
- Grate 4 sweet, baked apples on a coarse grater. Add 3 tablespoons of steamed ground prunes. Season with honey and sour cream. If you season the salad only with sour cream, it effectively fights constipation.
- If someone doesn’t like green tea, you can replace it: 1 liter of water, 100 g of dried fruits, 1 tbsp. l. mint, 200 g pomegranate juice, 200 g honey. The drink is effective against cancer. Facilitates the activity of the gastrointestinal tract, normalizes stool and cardiac activity, helps the formation of red blood cells.
Important! The above dishes can only be eaten in the third week after surgery or in preparation for it.
The diet for intestinal obstruction in people prone to low blood pressure should contain many dishes from boiled pureed meat, veal liver, fish, oatmeal, beets (if there is constipation), those prone to diarrhea - blueberry juice, flax decoction.
If the intestines are blocked, it is advisable not to include foods with dense fiber in the menu; it is advisable to go gray on a fruit, vegetable and fermented milk diet for 7 days. Then switch to decoctions of flax and chamomile. On the second day, you can add 150-200 g of boiled milk per 1 liter of decoction to the decoction.
Causes of fecal obstruction and bloating
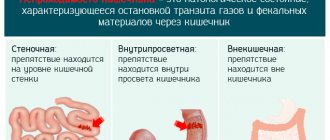
But what can cause fecal obstruction and severe bloating in a person? First, it should be pointed out that intestinal pain can be caused by two types of intestinal obstruction:
- Mechanical, which occurs due to foreign bodies entering the intestines, including tumors, gallstones, balls of worms, adhesions in the abdominal cavity (may appear after inflammation or surgery);
- Dynamic, arising due to a violation of the motor function of the organ. Also, intestinal obstruction (and, as a result, bloating) can occur during pregnancy, during childbirth, or after it. In this case, the disease develops very quickly and is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- constant, cramping or periodically increasing abdominal pain;
- vomit;
- stool retention;
- increasing intoxication.
If intestinal obstruction occurs during pregnancy, the woman should immediately seek medical help, since if left untreated, the consequences can be catastrophic. In particular, the development of peritonitis may begin - a disease that equally threatens the life of the mother and fetus.
In children, the following symptoms indicate intestinal obstruction:
- sharp paroxysmal pain in the abdomen;
- severe green vomit;
- absence of bowel movements;
- pallor;
- sweating;
- rapid increase in symptoms.
The main diseases that can lead to fecal obstruction and bloating:
- Intestinal tumors. When inflammation increases in size, it can block the intestinal lumen, preventing the passage of its contents. Tumors can be located both on the outside of the organ and on the inside - blockage of the lumen occurs in any case. The most common causes of such tumors are:
- heredity;
- improper diet and regimen;
- regular and heavy drinking of alcohol;
- smoking;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- chronic forms of diseases of the digestive tract;
- long-term use of certain medications (antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, etc.);
- Tumors of the abdominal organs. Such formations in some cases can compress adjacent areas of the intestinal tract and, as a result, cause intestinal obstruction. Tumors can occur as a result of the following diseases:
- pancreas cancer;
- liver cancer;
- peritoneal cancer;
- mesenteric cancer;
- gallbladder cancer;
- Cysts of the abdominal organs. These pathological formations are filled with fluid, which, over time, increase in size and can lead to compression of the intestines, making it difficult for the organ to function;
- Crohn's disease. This disease is characterized by inflammatory processes (the appearance of tumors, ulcers, erosion) in the digestive tract caused by disturbances in the functioning of the body's immune system. Often the pathology is complicated by intestinal obstruction, which appears as a result of narrowing of the lumen of the inflamed parts of the intestinal tube;
- Intestinal tuberculosis. This infection occurs as a result of a significant increase in the body of bacterial bacilli that are part of the “tuberculosis complex,” which includes six types of mycobacteria that cause tuberculosis;
- Abnormalities of intestinal development. This is a congenital disease that occurs during the embryonic period. Cases of such anomalies are not very frequent, but, for the most part, they create many problems, including difficulty in the outflow of contents through the intestines;
- Hernias. With these pathologies, internal organs move between cavities. Intestinal obstruction (and, as a result, constipation and bloating) can be caused by both internal (intra-abdominal) and external hernias, and occurs as a result of strangulation of the intestinal loops and mesentery in the hernial orifice;
- Adhesive bowel disease. This disease can be caused by injuries or inflammatory processes in the abdominal cavity (peritonitis, appendicitis, pancreatitis, cholecystitis, etc.), since adhesions are connective tissue bridges that prevent further spread of infections in the body. But, when they appear in the abdominal cavity, they can block the intestines and cause fecal obstruction and bloating;
- Ascariasis. This parasitic disease is caused by roundworms, roundworms, which enter the human body when eating dirty berries, fruits, vegetables or any other dirty food. When a significant number of these parasites accumulate, their balls can lead to blockage of the intestinal tract and, as a result, to fecal obstruction and bloating;
- Cholelithiasis. With this disease of the digestive system, stone formation is observed in the bile duct or bile ducts. In rare cases, when the disease is complicated, a pathology such as a gallbladder fistula occurs, which can lead to the entry of stones into the intestinal tract and, as a result, to its mechanical blockage;
- Hypokalemia. This pathology is characterized by a significant decrease in the concentration of potassium in the blood plasma. The reasons for the occurrence can be very different - from a small amount of potassium-containing products in a person’s diet to regular use of certain medications (antibiotics, laxatives, insulin, etc.);
- Injury or tumor in the brain and spinal cord. If such pathologies have damaged the nerve centers that regulate intestinal motility, sphincters and secretion processes, then the normal functioning of the intestines may also be disrupted;
- Stroke. This brain pathology is rarely associated in people with intestinal problems, but “failures” caused by bleeding in the brain, as well as accompanying inflammatory processes in the body, can also lead to fecal obstruction and bloating;
- Heavy metal poisoning. The most common human poisoning is lead. At the same time, he has lead colic, which is accompanied by severe pain in the abdominal cavity, constipation, bloating, metallic taste in the mouth, stomatitis, bradycardia, and some other symptoms. This all happens due to the effects that lead has on the body. First of all, it leads to overexcitation of the autonomic parts of the human nervous system, which are responsible for the stable functioning of intestinal motility (a similar effect in mercury poisoning);
- Thrombosis and embolism of the intestinal mesentery vessels. When blood vessels are blocked by foreign bodies, intestinal infarction can occur, and, as a result, the death of its tissues. This leads to disruption of its functions in the digestive process, secretion of mucus and pushing food through the intestinal tract;
- Spasmophilia. Pathology in which there is a violation of phosphorus-calcium metabolism. It is most often observed in children between 2 months and 2-3 years of age. The pathological syndrome is characterized by a low concentration of calcium and an increased content of phosphorus and vitamin D in the child’s blood. May be accompanied by the following symptoms (except bloating and stool obstruction):
Nutrition depending on intestinal obstruction
Intestinal obstruction is divided into 2 main types:
- Dynamic – there is no peristalsis due to paralysis of intestinal smooth muscles.
- Adhesive – the movement of feces is prevented by adhesions. Adhesions are caused either by complete or partial blockage of the intestines with feces, or by accidentally swallowed foreign objects that are not broken down by enzymes of gastric juice (usually in young children); due to intestinal volvulus (intussusception) or tumor. If the obstruction was caused by a blockage or adhesions, surgery is performed. The diet for adhesive obstruction is prescribed by the attending physician, depending on the patient’s condition after surgery.
When dieting after surgery for intestinal obstruction, you should adhere to the recommendations for consuming the amount and composition of food recommended by your doctor:
- Eating after bowel surgery should not be seen as a taboo on tasty treats. Familiar delicacies can be gradually introduced into the diet in the third month after surgery.
- Starting from the first postoperative day, the patient will receive some still water to wet the lips.
- By the middle of the second day - a few spoons of broth plus droppers with polysaccharides.
- By the end of the first week, you can start eating liquid pureed low-fat soups, mainly on an oatmeal basis.
- In the first 3 months you will have to eat small portions of 200 g 4-6 times a day.
If you feel constant suction in the stomach, then there is not enough solid fiber, and this is a sure way to an ulcer, you should consult with your doctor about adding variety to the menu. If constipation often occurs, then exclude potatoes and crackers from the diet. You can get rid of it with boiled beets and chamomile tea.
Variants of course and stages
If the blockage occurs in the small intestine, then the obstruction is called small intestine; it can be high (initial sections) and low (closer to the large intestine). A third of all cases are associated with the colonic variant of the pathology. The entire lumen may be blocked (complete) or there may be slight advancement, which is not enough for emptying (partial).
Obstruction has several stages in its development:
- acute – from 2 hours to 12. Severe pain, bloating, cramps;
- intoxication - imaginary recovery. The symptoms subside, but the gases do not pass and there is no stool. The abdomen has an asymmetrical shape. Lasts up to 1.5 days;
- final, terminal - severe circulatory disorders, extensive inflammation of the peritoneum.
What foods can you eat after surgery?
Irritating (spicy, bitter, sour, sweet) and hot foods should not be eaten after surgery. Products that cause increased gas formation and fermentation, as well as difficult to digest foods, are excluded from the diet.
After surgery, the following are prohibited for use:
- Sour fruits and berries.
- Preparations for the winter - pickles, smoked meats, marinades.
- Canned food.
- Sweets – candies, cookies, chocolate, etc.
- Mushrooms.
- White and fresh bread, baked goods.
- Nuts.
- Cold drinks.
- Legumes.
- Alcohol.
Important! It is recommended to avoid these foods for at least three weeks after surgery. It is advisable to maintain such a diet for 2 months.
Types of diet therapy
In case of intestinal obstruction, a menu is drawn up based on the characteristics of the disease: the form of development of the pathology, an operation to remove damaged areas of the mucosa. You need to follow a diet during the period of treatment and rehabilitation of the body.
Exacerbation of intestinal obstruction
The goal of diet therapy during an exacerbation is to prevent the formation and spread of pathogenic microorganisms. On the first day of the appearance of symptomatic signs of obstruction, it is recommended to refuse food for 24 hours. To relieve the manifestations of pathology, only the drinking regime should be observed in the first 24 hours.
During a diet in case of exacerbation of intestinal obstruction, the following should be excluded:
- fatty meats and fish;
- fresh vegetables;
- cereal:
- pearl barley;
- barley;
- millet;
- fermented milk ingredients;
- fresh bread, rolls;
- dried fruits;
- tea, coffee with added milk, cream;
- herbs, spices, salt, sauces;
- sweet carbonated drinks;
- alcohol.
The diet for obstruction involves the exclusion of ingredients that contribute to increased gas formation, the occurrence of the fermentation process, and irritation of the damaged intestinal mucosa.
Allowed products of a gentle diet are low-fat cottage cheese, eggs, soups cooked with vegetables and secondary meat broth, liquid cereals, butter, crackers, crushed sweet berries, rosehip infusions, diluted carrot juice. The amount of calories eaten should not exceed 1800 units.
Chronic obstruction
The goal of diet therapy in the chronic course of the disease is to prevent the progression of pathology and observe relapse of exacerbation. Features of the treated nutrition for intestinal obstruction include the use of foods that normalize intestinal motility, peristalsis, frequent meals in small portions, the volume of which does not exceed 200-250 g, and drinking at least 1.5-2 liters of filtered water per day. The daily calorie intake is no more than 2500 units.
The basis of the diet for chronic obstruction corresponds to treatment table No. 3, which includes permitted products:
- lean meat, fish varieties;
- seafood: squid, shrimp, octopus, mussels;
- fermented milk ingredients, cheese;
- liquid soups;
- cereals;
- butter;
- baked vegetables, fruits;
- biscuits;
- honey;
- dried fruits: dried apricots, plums, figs;
- decoction of flax.
Regular consumption of baked peeled apples, rich in fiber, relieves abdominal muscle spasms during fecal obstruction. Seafood, consisting of healthy compounds, enriches the body with protein. Dried fruits normalize stool in case of regular problems during bowel movements: alternating diarrhea and constipation.
During the diet, complete abstinence from prohibited foods:
- fatty, salty, smoked, spicy dishes;
- semi-finished products, fast food;
- broths based on fish and seafood;
- legumes;
- vegetables: cabbage, beets;
- tea, coffee, cocoa.
The daily diet menu for chronic intestinal obstruction includes ingredients rich in vitamins, minerals, and containing a sufficient amount of quickly digestible carbohydrates and proteins.
Minimal fat consumption helps thin stool. A healthy diet in chronic pathology must be maintained throughout life until complete relief from intestinal obstruction.
Postoperative diet
Intestinal obstruction in adults can be eliminated surgically, which involves removing the inflamed areas of the mucous membrane. Features of the rehabilitation period are adherence to the most gentle diet. 24 hours after surgery, the consumption of food and water is prohibited. The diet after surgery to eliminate intestinal obstruction involves eating only for the 3rd day. To avoid blockage of the canal with solid feces, you can only eat liquid, ground, crushed foods, fermented milk ingredients, and dried bread.