Have you been struggling with GASTRITIS and ULCERS for many years without success?
“You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure gastritis and ulcers just by taking it every day.
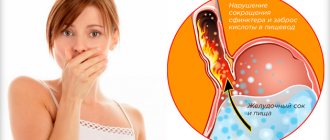
Among the ancient Slavs, the words “life” and “belly” were synonymous. And, truly, it is difficult to enjoy life when the pain in the pit of the stomach in the upper middle part of the abdomen does not allow you to breathe, hinders your movements, makes you suffer and suffer. Let's consider the causes of the condition, what it depends on, and its treatment.
In the pit of the stomach - where is it?
A spoon is a depression in the form of a triangle, bounded by an imaginary horizontal line connecting the lower edges of the ribs with the costal vault itself. It is especially visible in thin people.
Discomfort in different parts of the spoon or epigastric (epigastric) zone is already a diagnostic sign. In 95% of cases he talks about stomach problems. It rarely disguises itself as a heart attack, but in this case it is not accompanied by belching, vomiting and heartburn.
Causes and treatment of pain in the pit of the stomach
There are different types of stomach diseases. The most common among them are:
Peptic ulcer
The ulcer is indicated by a sharp pain, similar to a stab with a knife (dagger). It becomes unbearable if the ulcerations are perforated and intensifies with inhalation and sudden movements. The localization of the pain syndrome changes from the center above the navel and right hypochondrium to the entire abdominal area, to the back and right shoulder. At the same time, the stomach itself hardens and becomes “wooden”.
You cannot hesitate in such situations. Internal bleeding can be fatal. He is recognized by low blood pressure, severe pallor, sudden weakness, and an ambulance is urgently called. The severity of a stomach ulcer and its location affect the severity of the discomfort. In case of a perforated ulcer, urgent surgical intervention is indicated.
Gastritis
You can distinguish gastritis from an ulcer on your own. There is a connection between the acidity of gastric juice and the time of onset of discomfort. In the hypoacid form, a dull aching pain appears after eating and does not bother you on an empty stomach. With hyperacid it is the opposite. The pain may be barely noticeable or unbearably severe. It can be triggered by smoked foods, rough, spicy foods.
Chronic gastritis is characterized by:
- heartburn;
- rumbling in the stomach;
- nausea;
- belching;
- unpleasant taste in the mouth.
The type A form of gastric inflammation is characterized by: diarrhea, intolerance to fatty and dairy products. Over time, B12 deficiency anemia may develop.
Often, pathology in the stomach involves the pancreas, duodenum, and bile ducts, which complements the clinical picture with symptoms characteristic of pancreatitis, as well as cholecystitis.
The reasons for the feeling of heaviness in the pit of the stomach may be associated with duodenitis or peptic ulcer. In such cases, there is a complete lack of appetite as the body refuses to digest food.
Causes of pain in the pit of the stomach after eating
Pain at night from 10 pm to 4 am worries patients with stomach or duodenal ulcers. May occur on an empty stomach or be associated with meals. May be a reaction to spicy, fatty foods. In case of diseases of the duodenum, discomfort occurs on an empty stomach, and in case of stomach pathologies, for example, peptic ulcer, after eating. Sometimes relief comes after sour vomiting.
Soreness is called early if it appears an hour after eating and disappears after 1.5 hours when the food leaves the stomach. It may be late, it bothers you 2-3 hours after eating. It is due to the fact that gastric juice entering the duodenum irritates its mucous membrane. Hunger pains appear 5-7 hours after eating and are relieved while eating.
Pain in the pit of the stomach and physical activity
An important point is the connection between discomfort in the epigastric region and body position and physical activity. When diagnosed with adhesions, it occurs if the patient lifts weights or changes body position. When diagnosed with “prolapse of the stomach”, it is the other way around if the person assumes a horizontal position.
Burning in the pit of the stomach
A burning sensation accompanies the course of acute gastritis. The disease develops very quickly. The clinical picture is complemented by vomiting, diarrhea, bloating, and an unpleasant taste in the mouth. Fever and herpes rashes are also possible.
A burning sensation in the middle of the stomach is most likely a sign of functional dyspepsia. It is characterized by impaired motor activity of the stomach and duodenum. Provocateurs of the condition are considered to be smoking, drinking alcohol, certain medications, in particular aspirin, hypersensitivity of the stomach and disorders of the nervous system.
Pain in the pit of the stomach in different locations
If you are worried about pain in the right hypochondrium, it may indicate problems in various organs, including:
- heart and blood vessels;
- liver and pancreas;
- esophagus, stomach, duodenum;
- lungs.
Pain in the left side of the epigastric region may be associated with:
- pyelonephritis;
- gastritis;
- pancreatitis;
- hiatal hernia.
Pain in the pit of the stomach that radiates to the back can be a symptom of chronic or acute pancreatitis. The cause is often related to stones stuck in the bile ducts. They arise due to errors in nutrition, nervous and physical stress. When the gallbladder becomes infected, acute noncalculous (stoneless) cholecystitis may develop.
The pain can radiate to the base of the neck, shoulder blade, and collarbone. It can be paroxysmal or constant. Accompanied by fever, nausea, vomiting. The patient is forced to constantly change body position in search of a less painful position.
Pain in the epigastric region
Above, we figured out that several largest organs are projected into the epigastric region. Accordingly, discomfort and pain “in the pit of the stomach” can indicate a variety of ailments. Let's briefly look at what diseases can manifest as epigastric pain.
Epigastric region of the abdomen
Bloating due to overeating or stomach diseases, as well as functional dyspepsia (rapid filling of the stomach with a small amount eaten) are factors that cause discomfort in the epigastric region. In the epigastric zone, a person may feel pressure, burning, and complain that there is a burning sensation in the pit of the stomach. Typically, with these problems, discomfort increases gradually and subsides after a short time. If these sensations occur from time to time and are associated with food intake, and are also associated with a feeling of nausea or even vomiting, examination by a gastroenterologist cannot be postponed.
Symptoms of functional dyspepsia
In 80 percent, pain in the epigastric area is associated precisely with lesions of the digestive tract and typical diseases: gastritis (especially of autoimmune origin), pancreatitis, inflammation of the duodenum, and so on. Girdle pain with a nagging character, which is accompanied by permanent nausea, is a characteristic symptom of pancreatitis. Acute and continuous pain in the pit of the stomach, accompanied by vomiting and fever, is a signal of an inflammatory or infectious condition of the internal organs.
First aid for pancreatitis
Severe weakness, vomiting associated with dull pain in the epigastrium are associated with inflammation of the small intestine or duodenum. If a person feels stabbing, “dagger” pain in the pit of the stomach, or strong spasmodic tension in the abdominal muscles, these are characteristic manifestations of an ulcer in the stomach.
You can read more detailed information about stomach ulcers in our article.
Locations of ulcers
In this case, discomfort in the epigastric region may be associated with lung diseases (pleurisy, pneumonia, inflammation), heart attacks, chondrosis and pinched muscles, and circulatory disorders. With renal colic, nagging pains of a paroxysmal nature also appear in the intergastrointestinal tract.
Causes of pain in the pit of the stomach
In most cases, pain in the pit of the stomach is accompanied by other, more specific symptoms. Together, these symptoms can indicate serious and dangerous pathologies, therefore it is necessary to plan a trip to the clinic in the near future.
Table 1. Causes of pain in the pit of the stomach
| Which organ is affected? | Description of the problem |
| Lungs | Since the epigastric region goes around the lungs from below, a person often feels pain and discomfort in this area during bronchitis, pneumonia, tuberculosis and similar ailments. |
| Diaphragm | If pain in the epigastrium intensifies with inspiration, and also radiates to the neck and shoulders, one should suspect ailments such as diaphragmatic hernia or relaxation of the diaphragm. |
| Spleen | If this organ is damaged (for example, splenic infarction), the pain comes from the left hypochondrium and can flow through the center of the epigastrium to the neck. |
| Heart | Cardiac diseases often “hit” the epigastric region, radiating to the sternum, shoulders and even jaw. The pain is accompanied by pressure fluctuations and rapid heartbeat. |
| Liver | Spasmodic pain in the right hypochondrium indicates liver problems. |
| Appendix | If a person has an inflamed appendix, with sudden movements or turns, pain may be felt in the right hypochondrium. Its nature will not necessarily be acute - “in the pit of the stomach” appendicitis often manifests itself as dull, increasing pain. |
| Stomach | Pain in the epigastric region associated with stomach diseases can be either sharp and stabbing, or pulling, cramping, spasmodic. Pain is often accompanied by tension in the abdominal muscles, nausea, vomiting, and bowel movements. |
| Pancreas | The nature of the pain is similar to that accompanying gastric ailments: it can be shingles, sharp or aching. |
| Intestines | “In the pit of the stomach” the pain is strong and sharp, often the pain is accompanied by vomiting, which does not bring relief. |
| Gallbladder | Acute cramping pain radiates to the center of the epigastrium and radiates to the neck and shoulder blades. The pain intensifies with deep breaths. |
| Kidneys | Kidney diseases have the following symptoms: pain is localized in the center of the epigastric region, and when moving it radiates to the perineum and lower back. |
Diagnostics
Only a doctor can say exactly what caused the pain in the epigastric region based on test results. Pain in the pit of the stomach is a multivariate symptom. To find out its true cause, the doctor collects data on the history of the disease, finds out how the pain syndrome manifests itself, what kind of lifestyle the patient leads, what medications he takes.
A number of priority studies will be required using laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- ECG;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy;
- probing method;
- stool analysis to detect occult blood;
- general urine and blood tests.
Treatment can be symptomatic or aimed at eliminating the underlying cause of the condition. If acute appendicitis, oncology, or rupture of an internal organ is detected, surgery is indicated. Drug treatment and supportive therapy are prescribed by a specialist in the appropriate field. The patient can only strictly follow the medical recommendations of the gastroenterologist, including those related to nutrition.
Dysfunction of the liver and bile ducts
Biliary dyskinesia is characterized by impaired excretion of bile. This occurs due to a problem with the contraction of the gallbladder and ducts. Women are more prone to developing the disease. There are two forms of biliary dyskinesia.
With dysfunction of the liver and bile ducts, the patient is tormented by aching, sharp and paroxysmal pain.
They are localized in the peritoneum and right hypochondrium, radiating to the scapula and shoulder on the same side.
The presence of such symptoms indicates biliary dyskinesia:
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- worsening mood;
- weakness throughout the body;
- insomnia;
- lack of appetite;
- loose stools or constipation;
- decreased libido;
- disruption of the menstrual cycle.
Attending doctor
Gastroenterologist
Diagnosis The following studies will indicate an accurate diagnosis:
- blood test for biochemistry;
- ultrasound examination of the gallbladder and liver;
- bile analysis;
- X-ray of the gallbladder.
Treatment
One of the main methods of treating liver and bile duct dysfunction is diet. For a certain form of dyskinesia, it is necessary to adhere to a specific diet.
Antispasmodic and choleretic agents are used among the drugs.
Diet therapy
A diet without animal fats, spicy, fried foods, and alcohol brings relief. Warm porridge made from oatmeal or buckwheat is beneficial. The most gentle way of cooking is steaming. Fractional meals from small portions are recommended.
Any food with a long shelf life that is produced by the food industry and intended for snacking on the go is contraindicated. We are talking about chips, corn sticks, chocolate bars, crackers, and salted nuts.
Snacks, as a rule, are high in calories and can satisfy hunger, but are empty in terms of the content of useful minerals and vitamins. Such refined foods are considered extremely unhealthy. Alternatives to snacks include fresh vegetables, fruits, homemade crackers without butter, and dried nuts.
Prevention
Pain in the pit of the stomach is an extremely unpleasant symptom. To avoid ending up in a hospital bed or, worse, on the operating table, you should follow the simplest recommendations:
- Control your weight.
- Eat often, but in small portions.
- Include foods high in fiber in your diet and avoid fried foods.
- Limit the consumption of products containing dyes and emulsifiers.
- Learn to relax and avoid nervous breakdowns.
- Stop smoking, do not abuse alcohol.
- Move more, walk in the fresh air.
- After meals, rest for at least half an hour.
- Follow the drinking regime, drink in small sips.
And finally, be attentive to your health, identify diseases at an early stage, and, if necessary, do not delay going to the doctor.
Probably every person has heard the expression “sick in the pit of the stomach” at least once in his life. It is interesting that when asked where this spoon is located and what this feeling is, most people find it difficult to answer clearly. And everything would be fine, just a saying, but when pain is felt in the pit of the stomach, this is no longer a joke or folklore, but a consequence of the development of some kind of disease.
What is pain when coughing
The occurrence of an unpleasant symptom – pain when coughing – must be treated responsibly. The cough is distinguished between wet and dry (barking), paroxysmal, with sputum production, and with shortness of breath. Sometimes the cough reflex is accompanied by pain, which is localized in:
- sternum;
- left or right side;
- back;
- stomach;
- temples, head;
- under the ribs on the right or left.
Where is it located and why should it hurt?
In medical language, this place on the body is called the epigastric region - the point of connection of the anterior ribs. Why is it called a spoon? Yes, because this depression under the urinary process is shaped like a teaspoon. True, if we look at ourselves in the mirror, we won’t see any spoon. It is only visible on the human skeleton, but it is not difficult to determine exactly where the above-mentioned area is located.
The importance of this place lies in the fact that it is a projection of the internal organs. An experienced doctor can make a preliminary diagnosis based on how severe the pain in the pit of the stomach is: dull or aching, whether it is felt on the right or left. In other words, discomfort in the pit of the stomach is evidence of problems with internal organs. The main thing is not to panic, but to quickly find out the causes of the symptom and begin treatment.
Summarizing
If a person feels severe pain in the pit of the stomach, you should not wait for complications; you should immediately go to see a doctor. Only a specialist will be able to identify the true cause of pain in the pit of the stomach and prescribe a course of necessary therapy. It is important to remember that timely treatment is the key to a quick recovery.
information revision
: June 4, 2020.
- 1. WHO – https://www.who.int/ru/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases-(cvds), https://www.who.int/ru/news-room/ fact-sheets/detail/pneumonia
- 2. US National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute - https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/pneumonia, https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/heart-attack
- 3. Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research - https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hiatal-hernia/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20373385
- 4. US National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases - https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/pancreatitis/symptoms-causes, https://www.niddk.nih. gov/health-information/urologic-diseases/kidney-stones/clinical-trials, https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/gastritis
Found an error? Select it and press Ctrl+Enter.
Have you been struggling with GASTRITIS and ULCERS for many years without success?
“You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure gastritis and ulcers just by taking it every day.
Among the ancient Slavs, the words “life” and “belly” were synonymous. And, truly, it is difficult to enjoy life when the pain in the pit of the stomach in the upper middle part of the abdomen does not allow you to breathe, hinders your movements, makes you suffer and suffer. Let's consider the causes of the condition, what it depends on, and its treatment.
Provoking factors and causes of pain
Why does discomfort occur, and in what ways can it be eliminated? The principles of treatment depend on the factors that provoked the appearance of the pathological symptom.
Among the most common causes of discomfort in the pit of the stomach, doctors include the following:
Developing stomach ulcer
A very likely and dangerous cause of aching pain in the pit of the stomach may be an ulcer on the gastric mucosa. Here you need to pay attention to the following clinical manifestations:
- frequent pain and belching;
- nausea immediately after eating;
- lack of appetite;
- problems with stool (diarrhea, constipation);
- flatulence;
- bloating;
- sour taste in the mouth.
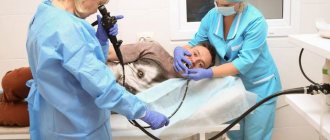
If such factors occur, then it is better to go to the hospital and do an endoscopic analysis of the stomach. Or, as people say, swallow a tube. Alas, this is the only way to identify a stomach ulcer and begin treatment at a more or less early stage.
There is a general principle that allows you to understand even before going to the doctor whether your stomach is bothering you or not. If discomfort occurs immediately after eating, this is a stomach problem. If it hurts before eating, on an empty stomach, and after eating, on the contrary, it goes away, then this is a lesion of the duodenum.
Duodenal ulcer
Aching pain on the right, which radiates to the back, may signal the appearance of an ulcer in the duodenum. The disease is caused by the bacterium Helicobacter Pylori, as in the case of stomach ulcers, but not only it. Additional causes of the disease:
- endocrine disorders;
- unbalanced diet;
- alcohol abuse;
- increased acidity in the gastrointestinal tract;
- too frequent use of antipyretics (Aspirin, Ibuprofen, Nurofen).
The development of ulcers is facilitated by a lack of microelements and vitamins in the body. They take part in redox reactions, the disruption of which can lead to destruction of the duodenal mucosa;
Pancreatitis
Acute constant pain in the epigastrium on the left side is a characteristic symptom of the development of pancreatitis. In the case of an acute course of the disease, it may also be of a shingles nature. Pancreatitis is essentially a malfunction of the pancreas. That is, enzymes for digesting food are not produced, which leads to decay of the duodenal contents. Food is not digested or absorbed by the intestines, which causes nausea and profuse vomiting.
Factors that cause pancreatitis include:
- a large amount of fried, fatty and smoked foods in the diet;
- alcohol abuse;
- long-term use of medications (especially hormonal ones).
Pancreatitis, alas, can be not only an independent disease. Very often it is preceded by the development of a stomach ulcer.
Appendicitis
With appendicitis, pain is first felt in the pit of the stomach, then in the navel, and then moves to the right side. The disease is accompanied by nausea and pain in the right side, which can intensify with deep breathing. As you know, appendicitis cannot be treated with medication; you will need the help of a surgeon.
Lesions of the esophagus
If discomfort in the pit of the stomach on the right is episodic, most likely the symptom is caused by damage to the esophagus, in particular, gastroesophageal reflux. When swallowing, pain radiates to the throat. Factors that provoke diseases of the esophagus are chemical or mechanical damage, inflammation of the ENT organs, and excessive physical activity. If you have such symptoms, you should contact a gastroenterologist.
Pancreatitis
Pain in the pit of the stomach may be due to pancreatitis, an inflammatory disease of the pancreas. The disease is divided into acute and chronic forms, each of which manifests itself with its own symptoms and requires appropriate therapy.
Women, men and even children are not immune from pancreatitis. Men suffer more often due to neglect of the symptoms that appear. They prefer to visit the hospital when the disease has almost completely consumed the organ, which entails long-term treatment.
“The most common cause of chronic pancreatitis is alcohol consumption.” – US National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
Experts have been able to identify a number of causes causing pancreatitis:
- Alcohol abuse;
- Eating fatty foods;
- Cholelithiasis;
- Long-term use of medications;
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Viruses or parasites.
Signs of illness
Signs of acute pancreatitis include:
- Severe pain in the pit of the stomach, which may result from painful shock or loss of consciousness;
- Fever;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Cardiopalmus.
Aching pain in the pit of the stomach may mean a chronic form of the disease, which does not manifest itself with pronounced symptoms. Signs of this form of pancreatitis include :
- Loss of body weight;
- Nausea;
- Vomit;
- Diarrhea;
- Fast fatiguability;
- Deterioration in general health.
When the chronic form of the disease worsens, a person experiences all the symptoms of the acute course of the disease. A sudden exacerbation often leads to tissue necrosis, which leads to acute pain in the pit of the stomach. In this case, the person needs urgent medical intervention and hospitalization.
Treatment options
Treatment for pancreatitis that causes stomach pain may include pain medication, antibiotics, a low-fat diet, or even surgery to remove the gallbladder.
Only timely therapy will help slow down the development of pancreatitis. To avoid various complications, it is recommended to consult with a qualified specialist rather than self-medicate.
Diagnostic methods
Since the causes of pain in the epigastric region can be different, treatment methods depend on the disease that provoked the appearance of the symptom. In addition to general recommendations, such as a balanced diet and giving up bad habits, each disease will have its own specific treatment recommendations.
First of all, when pain appears in the pit of the stomach, it is necessary to establish an accurate diagnosis. To do this you will need to do a full examination:
- abdominal organs;
- pancreas;
- liver and kidneys;
- gallbladder.
If pancreatitis and gastroesophageal reflux are suspected, an additional endoscopic examination and ultrasound of the pancreas may be required.
Hiatal hernia
When asked why there is pain in the pit of the stomach, doctors often answer – hiatal hernia. A hernia is a protrusion of abdominal organs, often the esophagus, stomach, or, less commonly, other organs.
The photo on the right shows a hiatal hernia © shutterstock
Hiatal hernia is divided into sliding or axial, paraesophageal, and combined forms of flow. The disease also has several degrees of severity, each of which manifests itself with its own symptoms and requires appropriate treatment.
Experts have identified some reasons that provoke the development of the disease:
- Changes in the diaphragm associated with age;
- Injuries;
- Birth defect;
- Pressure on nearby muscles when lifting heavy objects.
“The risk of getting a hernia hernia increases with age, and they often occur in people over 50.” – US National Institutes of Health
Signs of illness
- Heartburn;
- Reflux of stomach acid into the esophagus;
- Difficulty swallowing;
- Pain in the abdomen or chest in the pit of the stomach;
- Breathing problems;
- Vomiting blood or dark stools.
Experts recommend that if you experience pain in the pit of the stomach, immediately visit a hospital.
Treatment options
A routine doctor's examination will not help identify the presence of a hiatal hernia. To make an accurate diagnosis and determine the severity of the disease, the patient is prescribed an x-ray of the upper digestive system, endoscopy and ECG. The latter diagnosis is extremely important, since the specialist must exclude the presence of problems with the functioning of the heart.
Conservative therapy, including:
- Proper nutrition;
- Getting rid of bad habits;
- Antacids that suppress gastric secretion;
- Medicines to reduce acid production.
Surgical methods for treating hiatal hernia are associated with the lack of positive results from conservative therapy or with a too advanced stage of the disease.
Non-drug treatment
If discomfort in the epigastric area occurs immediately after eating, first of all, special attention will have to be paid to diet therapy. Rational nutrition has no effect on inflammatory processes in the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract, but helps eliminate pain and heaviness in the stomach. In addition, when ulcers form in the mucous epithelium, it is advisable to reduce food intake, since caustic gastric juice is released to digest it. It is this substance that contributes to the destruction of the walls of the intestines and stomach in the event of the formation of erosions and wounds on their surface.
How to quickly eliminate pain in the epigastric region? Doctors do not recommend resorting to the use of analgesics without an accurate diagnosis. This will only lead to a “blurring” of the symptomatic picture and make it difficult to determine the causes of the problem. If discomfort occurs continuously over several days, you should not postpone a visit to the therapist. After a preliminary examination, the doctor will most likely refer you to a gastroenterologist, infectious disease specialist or endocrinologist.
Preventive actions
The most common cause of discomfort in the abdomen and a lump in the throat is gastritis and stomach ulcers. A characteristic symptom of gastritis is hunger pain. Gastritis is caused by bacteria that damage the mucous membrane, which leads to disruption of the digestion process. To prevent the occurrence of gastritis, you should eat right, avoid stress, overeating, physical activity after meals, and a sedentary lifestyle.
Other effective preventive measures include:
- normalization of the daily routine, in which sufficient time should be allocated for proper rest, exercise, and walks;
- normalize nutrition, which should include lean meat, fruits, vegetables, dairy products, cereals, soups;
- quitting smoking and drinking alcohol;
- high-quality treatment of colds;
- daily walks and airing the room before bedtime;
- refusal to eat before bed, quick snacks, fast food.
Heaviness and a feeling of a coma are dangerous symptoms of various diseases. To eliminate these sensations, you need to consult a doctor who will help cure the underlying disease. Self-treatment can lead to dangerous health consequences.
Related video: Lump in throat
Anti-inflammatory therapy
Pain is one of the main signs of inflammation localized in the gastrointestinal tract. To alleviate the course of the disease and prevent its development, you need to take anti-inflammatory medications. Effective drugs and the treatment regimen itself can only be prescribed by a qualified doctor after a full examination of the patient.
So, what medications can be used if it is difficult to breathe due to pain in the epigastric area?
- “Mesalazine” – eliminates pain that occurs during exacerbation of gastrointestinal diseases;
- “Prednisolone” – prevents the development of inflammation in the stomach and extraintestinal areas;
- "Metronidazole" - destroys the cell walls of microbes that provoke the development of inflammation in the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract;
- "Budesonide" - eliminates generalized inflammation not only in the esophagus, but also in the respiratory organs.
Depending on the clinical manifestations and associated complications, patients may be prescribed medications in the form of rectal suppositories or intramuscular injections. In this way, it is possible to prevent even greater irritation of the mucous membranes in the event of the development of ulcers in the intestines or stomach.
Methods for treating heaviness in the sternum
Heaviness in the sternum, in the middle, pressing, with a different nature of pain is treated in several ways depending on the disease that caused it.
Most often, complex treatment is prescribed, including:
- taking medications;
- physiotherapy;
- special daily routine;
- diet;
- breathing exercises;
- homeopathy;
- traditional medicine recipes.
Medications
Medicines are the main method of treating diseases that cause a pressing sensation in the chest area.
There are several groups of drugs:
- sedatives;
- lowering blood pressure;
- cardiac;
- anti-inflammatory;
- antibacterial;
- choleretic.
| Name | Effect | Reception scheme | Well | Price |
| Hydrochlorothiazide | Normalizes blood pressure within 4 days. | 1 time per day, in the morning 25-100 mg | Maximum 4 weeks. | From 43 rub. |
| Verapamil | Reduces pressure within 4 minutes. | Adults 3 r. per day 40-80 mg; Children under 4 r. per day from 40 mg. | Determined individually by the attending physician. | From 50 rub. |
| Metoprolol | Reduces the frequency of attacks during angina pectoris, protects against myocardial relapse, and normalizes blood pressure. | 2 r. per day no more than 200 mg/day. | Minimum – 2 weeks. | From 36 rub. |
| Biseptol | Destroys pathogenic bacteria. | Children 3-6 years old: 120 mg 2 times. per day. Children 6-12 years old: 480 mg 2 times. per day. Adults 960 mg 2 times. per day | 7-10 days. | From 37 rub. |
| Allohol | It has a choleretic and antimicrobial effect, stopping the processes of fermentation and putrefaction in the intestines. | After meals, 1-2 tablets. | 3-4 weeks. | From 12 rub. |
| Zelenin drops (Kremlin) | Has a mild sedative effect, relieves spasms, eliminates renal colic. | Children over 12 years old: 1 drop per 1 year of life. Adults: 20-25 drops 3-4 times a day. | From 5 days, depending on the disease. | From 30 rub. |
Traditional methods
Traditional methods help to temporarily alleviate the condition and are not the main type of treatment. Most often, compresses soaked in various natural substances are used.
Black radish
Mode of application:
- grate the radish on a fine grater;
- apply the resulting mass to the source of pain;
- bandage;
- remove after the burning begins;
- Use once a day for at least a week.
Burdock
Mode of application:
- mix the crushed leaves and roots of the plant in a 1:1 ratio;
- heat the mixture in a dry frying pan;
- put in a fabric bag;
- apply for 5-6 hours to the source of pain;
- use if necessary.
Camphor and ethyl alcohol
Mode of application:
- mix 2 drugs in a 1:1 ratio;
- dilute 1/3 of the mixture with 2/3 of warm water;
- apply to the sore spot for 1 hour;
- apply several times a day;
- course of treatment is 7-10 days.
Agave
Mode of application:
- chop fresh leaves of the plant;
- squeeze the juice out of the resulting mass;
- soak the compress and apply it to the source of pain;
- use 2 r. in a day;
- course of treatment is 2 weeks.
All these methods help relieve muscle spasms and eliminate pain. As concomitant therapy for intercostal neuralgia, decoctions of medicinal herbs, ointments prepared at home, and relaxing baths are used.
Aspen bud ointment
Mode of application:
- thoroughly chop the dried tree buds;
- mix with butter in proportions 1:4;
- rub 2 times a day into the area where the pain is located;
- use if necessary.
Sage bath
Mode of application:
- pour 4 tbsp. herbs 250 ml warm water;
- leave for 1 hour;
- strain;
- fill the bathtub with warm water;
- add infusion;
- add 4 tbsp. sea salt;
- use the 1 p. method. a day before bedtime;
- course of treatment – 10 days.
The causes of pressing heaviness in the sternum can also be osteochondrosis. There are very effective recipes for its treatment in folk medicine.
Calendula tincture
Mode of application:
- 100 gr. pour flowers with equal parts of camphor alcohol, triple cologne and vodka (200 ml each);
- pour into a glass container;
- put in a dark place for 14 days;
- rub 2 times a day;
- course of treatment is 2 weeks.
Healing herbal rub
Mode of application:
- mix birch buds, dandelion root, mint and coriander fruits in equal parts;
- pour 100 ml of boiling water 3 tbsp. mixtures;
- bring to a boil over low heat;
- add 75 g to the broth. vegetable and butter;
- cook the mixture for 20 minutes;
- rub the source of pain;
- wrap in woolen cloth;
- Carry out the procedure up to 4 p.m. in a day;
- apply until complete cure.
Other methods
Other methods will be no less effective in treating heaviness in the sternum.
These include:
- Massage . Helps relieve muscle tension and eliminate pain. The course of treatment is 10 days. Repeat if necessary.
- Exercise therapy . It includes not only therapeutic exercises, but also swimming. Eliminates muscle spasms, strengthens the spine and reduces stress on it. The course is unlimited.
- Acupuncture (acupuncture). Helps get rid of pain and relieve muscle tension.
- Physiotherapy . Eliminates excess mucus from the lungs, normalizes blood circulation, restores lung tissue and strengthens the heart muscle.
- Homeopathy. Preparations made from natural substances lower cholesterol, relieve anxiety, and have a mild antispasmodic effect.
- Breathing exercises . This method relieves muscle tension, improves the functioning of organs located in the sternum, and normalizes overall health.
Most often, when treating heaviness in the sternum, complex treatment is prescribed, which includes all of the methods described above.
Symptomatic treatment and prevention
If a patient complains that his throat hurts after eating, in 95% of cases we are talking about the development of the so-called gastroesophageal disease. The cause of discomfort often lies in the penetration of gastric juice into the upper esophagus or respiratory tract. Duodenal contents cause severe irritation of the mucous membranes, resulting in soreness, soreness, pain and a feeling of dryness in the throat.
You can eliminate the manifestations of diseases that cause discomfort in the pit of the stomach with the following medications:
- “Albumin” – corrects metabolic processes, thereby restoring the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- “Hemodez” – accelerates blood circulation in the affected mucous membranes, which promotes their healing;
- “Beefy-form” – restores normal microflora in the intestines and stomach, thereby increasing local immunity;
- "Drotaverine" - eliminates spasms that cause pain in the epigastric zone;
- "Actiferrin" - accelerates the onset of remission in the development of chronic gastrointestinal diseases.
The most effective treatment for gastrointestinal diseases is their prevention. To prevent the occurrence of pancreatitis, ulcers and other pathologies, you need to follow simple rules:
- Eat a balanced diet;
- Treat constipation in a timely manner;
- Lead a healthy lifestyle;
- Drink at least 1.5 liters of water per day;
- Take vitamin and mineral complexes.
In any case, if discomfort appears in the pit of the stomach, you need to undergo a hardware examination by a gastroenterologist. Timely detection and treatment of diseases helps prevent the development of chronic diseases and systemic complications.
Stomach diseases are classified into several types according to etiological principles.
Clinical gradation of gastric diseases:
- Inflammatory (gastritis);
- Organic (tumor);
- Destructive (ulcer);
- Autoimmune.
The most common causative agent of bacterial gastric infections is Helicobacter. The microorganism parasitizes in the acidic environment of the gastrointestinal contents, processes hydrochloric acid and pepsin to form carbon dioxide. The compound irritates the mucous membrane and enhances the progression of peptic ulcer disease. There are carriers of the bacteria who do not develop ulcers. Treatment of such people is carried out with antibiotics, since there is a lot of experimental evidence that eradication of Helicobacter accelerates the healing processes of erosions, ulcerative defects, and helps normalize acidity.
Symptoms of common stomach diseases
Gastritis is inflammation of the gastric mucosa. The damage does not penetrate deeply. According to morphological features, the following categories of disease are distinguished: catarrhal, superficial, atrophic, erosive varieties of nosology.
The superficial (catarrhal) form is formed in people with a prolonged increase in intragastric secretion. The disease is provoked by irritation of the epithelium with hydrochloric acid.
The cause of the erosive form is poor quality nutrition, intake of toxic substances, consumption of rough food, and insufficient chewing of food. Americans often experience nosologies associated with long-term consumption of hot dogs, hamburgers, and cheeseburgers.
Symptoms of erosive gastritis:
- Nausea;
- Dull pain in the upper abdomen;
- Unpleasant taste;
- Heartburn;
- The presence of occult blood in the stool.
The atrophic form is characterized by complete degeneration of the epithelium, in which the functional tissue loses its properties. The nosology is considered a precancerous disease, so it needs to be treated from an early stage. The disease is often combined with secondary pathology: cholecystitis, colitis, pancreatitis, appendicitis.
Treatment of gastritis of the stomach
Treatment of inflammation of the gastric wall requires eliminating the cause of the pathology. Helicobacter eradication is carried out with antibiotics (clarithromycin, oxacillin). An increase in intragastric secretion is eliminated by antisecretory drugs of the h2-histamine blocker group, Na/K-ATPase inhibitors (omez, esomeprazole, ranitidine). Along with pharmaceuticals, diet therapy is prescribed with the limitation of spicy, fatty, fried foods. If you have gastritis, you should not eat:
- Canned food;
- Sparkling water;
- Spicy foods;
- Alcohol;
- Cold or hot food.
Gastric ulcer: symptoms and treatment
Gastric ulcer is characterized by a violation of the structural integrity of the mucous membrane of the organ, leading to destruction of the wall. The main difference between an ulcer and erosive gastritis is damage to the deep part of the mucous membrane, which results in alternating remissions and exacerbations.
A stomach ulcer is accompanied by severe pain in the pit of the stomach, which is in some way associated with eating. Night pain in the stomach is a typical symptom of a duodenal ulcer. High severity of the nosology leads to belching, heartburn, and decreased motor function of the stomach. Manifestations of the disease intensify with the following complications:
- Bleeding;
- Penetration – perforation into surrounding organs;
- Perforation is a rupture of the wall with the release of free gas.
Urolithiasis disease
Oddly enough, severe pain in the pit of the stomach may indicate urolithiasis.
The population at risk is in the age category from 21 to 60 years . Men are more likely to develop kidney stones than women.
According to scientists, urolithiasis, which leaves pain in the pit of the stomach, is a consequence of an imbalance in the human body. Because there is no single reason that causes this disease.
You are more likely to develop kidney stones if you have certain conditions, including:
- blockage of the urinary tract;
- inflammation in the intestines;
- cystic kidney diseases;
- digestive problems;
- gout;
- obesity;
- taking diuretics.
People at risk should be attentive to the signs that their body gives them. Hence, visit hospital facilities on time.
Signs of illness
The manifestation of symptoms depends on many factors, including the shape, degree, size and location of the stones. Small tumors may not cause discomfort to a person for many years. At that moment, one uneven pebble can cause significant inconvenience.
In medicine, there are several main signs:
- Pain when urinating;
- Acute pain in the back, side, lower abdomen or groin;
- Blood in the urine;
- Cloudy or bad-smelling urine;
- Inability to urinate.
If such symptoms occur, you should immediately visit a qualified specialist.
Treatment options
Pain in the pit of the stomach caused by urolithiasis can be relieved using conservative therapy.
Unfortunately, drug removal of formations does not bring 100% positive results . Experts consider this method of treatment more of a preventative measure that helps prevent the appearance of new stones and pain in the pit of the stomach.
A urologist can remove a kidney stone or break it into small pieces using the following procedures:
- Shock wave lithotripsy;
- Cystoscopy and ureteroscopy;
- Percutaneous nephrolithotomy.
Gastric dyskinesia: symptoms and treatment
A rare nosological form is gastric dyskinesia. In pathology, there is a disturbance in the movement of food due to the pathology of the movement of the food bolus (peristalsis). Signs of nosology appear rarely, but they are somewhat specific:
- Overflow;
- Heaviness in the stomach;
- Stomach pain (epigastric);
- Vomit;
- Hiccups;
- Bursting pain in the pit of the stomach.
Treatment of dyskinesia is carried out by probing for small defects. Using a diagnostic probe, doctors administer reparative agents (sea buckthorn), stop bleeding, and take gastric contents for examination. A biopsy helps identify cancerous tissue transformation in the early stages. The procedure is carried out by probing. After examining the internal contents of the stomach, the doctor removes a piece of material from the suspicious area. Constant drainage is carried out until the stomach tone is restored. At the same time, medications are taken to stimulate peristalsis.
Stomach diseases: volvulus as a life-threatening condition
Gastric volvulus is a rare and severe disease characterized by rotation of the organ around the anatomical axis.
Predisposing factors of the disease:
- Ligament lengthening;
- Developmental defects;
- Weight loss;
- Diaphragmatic hernia;
- Muscle weakness;
- Lifting weights;
- A sharp change in intra-abdominal pressure;
- Eating large amounts of rough food.
Symptoms of stomach disease accompanied by volvulus depend on the degree of compression of the organ tissue.
Why do stomach pains occur?
Stomach pain can occur with all of the above types of stomach diseases. There are about 15 variants of different types of stomach pain. The most common manifestation is pain associated with eating.
With chronic gastritis, stomach pain appears immediately after eating. Localization of a stomach ulcer along the greater or lesser curvature is accompanied by pain no later than 1.5 hours after eating.
With a pyloric ulcer, the appearance of pain in the stomach is observed 1.5 hours after eating. Clinical symptoms of nosology depend on the quality of food. Alkaline foods provoke early onset of pain (sour milk, pork, chicken).
Early pain syndrome often provokes a psychological complex in patients. Lack of food intake leads to weight loss in a person.
The symptoms of duodenitis and duodenal ulcers are somewhat different. The nosology is characterized by the “hungry” type. Pain appears at night and is relieved by drinking soda.
Increased pain is observed with increased physical activity and neuropsychic stress.
Other causes of pain in the pit of the stomach
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract are accompanied by different types of pain. Increased sensations are observed under the influence of secondary nosology:
- Physical fatigue, abdominal muscle tension, overwork;
- Bacterial infections, allergies;
- Stomach pain intensifies with spasms, diarrhea, vomiting, nausea caused by food poisoning. In children, the symptoms of dyspepsia intensify with sore throat and colds;
- Pain in the stomach is provoked by atypical forms of appendicitis, cholecystitis, and renal failure;
- Lactose intolerance occurs in a rare number of people. In the initial stages, the pathology manifests itself as nagging pain along the navel;
- Abdominal pain in a child after attending school due to stressful situations, nervous tension. The condition is typical for children with an unstable mental system.
What kind of stomach pain occurs:
- After eating if the products are incompatible;
- Nausea, heaviness of the stomach, fever;
- Dull aching pain appears when there is damage to the large intestine, pancreatitis, spasmodic contractions of the diaphragm;
- Radiation of pain to the back;
- Night pain syndrome;
- Compression of the intestines by an enlarged uterus during pregnancy.
Hormonal imbalance causes disharmony in the gastrointestinal tract.
Regardless of the cause, symptoms of gastric pathology are often accompanied by pain under the ribs below.
Food intolerance
Acute poisoning with chemical compounds always has a noticeable effect on the functions of the gastrointestinal tract. Diarrhea, as a characteristic symptom, is most often present with mercury or arsenic poisoning.
The first signs of acute mercury poisoning appear several hours after its onset.
In addition, in most cases there is severe abdominal pain and mucous diarrhea, often mixed with blood. Inflammation of the lungs is also observed. swelling of the upper respiratory tract, chest pain. the appearance of cough, shortness of breath. severe chills and increased body temperature to 38-40 °C.
Food intolerance to certain substances is usually genetic. In such people, the body is not able to produce enzymes. necessary for the absorption of certain chemical compounds.
One of the most common types of food intolerance is lactase deficiency - a disorder in the production of lactase. an enzyme that is necessary to break down lactose (milk sugar).
In young children, lactase deficiency may also result in restlessness, crying after eating, and chronic constipation.
Another disease associated with food intolerance is celiac disease. It develops in cases where the enzymes of the human body are not able to break down gluten (gluten), which is found in cereal plants (rye, wheat, barley).
The presence of this pathology is usually determined in the first year of a child’s life, and often coincides with the introduction of complementary foods containing flour products into his diet. Frequent, abundant, foamy stools with a pungent odor appear, having a light or grayish tint and a greasy consistency.
In this case, pathogenic microorganisms are usually not found in feces. The child becomes pale, lethargic, loses body weight and begins to refuse food.
Over time, dystrophy may develop. and the child acquires a typical appearance for this disease: severe emaciation, brightly colored mucous membranes and a pronounced enlargement of the abdomen.