Belching is considered a completely natural process and is an expression of the normal functioning of the digestive system. However, some of its types, in particular, sour belching, can be a signal that a person is experiencing some kind of disorder in the stomach or duodenum.
- Etiology
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Prevention
There are several predisposing factors that explain the appearance of such an unpleasant symptom. They are usually divided into two large groups – physiological and pathological. This symptom has no restrictions regarding gender and age, which is why it often manifests itself even in children. Often, sour belching is accompanied by other symptoms, and the most common of them is heartburn.
Comprehensive laboratory and instrumental diagnostics are aimed at identifying the causes of this manifestation. Treatment is often carried out using conservative methods - prescription of medications, diet therapy and the use of traditional medicine recipes.
Symptom Description
The accumulation of gases in the stomach cavity is a common phenomenon, most often occurring due to the swallowing of air during food intake (aerophagia), consumption of carbonated drinks, or due to fermentation processes in the digestive tract. Thus, burping is a natural process of reducing excess gastric pressure. If it does not recur too often, accompanied by a feeling of pain or irritation, then there is no reason to worry.
An alarming sign is the presence in the air mass of small particles of gastric juice, felt at the root of the tongue as something sour or burning. This type of belching may indicate serious pathologies of the digestive system.
Sour belching is a sign of possible stomach problems
Other reasons related to food intake
Nausea and belching of air in healthy people have other causes associated with improper food intake:
- When air is swallowed while eating, a belch is formed.
- After eating a large amount of food. In this case, both belching and nausea occur.
- Eating foods that produce gas in the stomach.
- If you do physical work immediately after eating.
- After eating fried or fatty foods, you usually feel nauseous.
- If you eat stale food, you start to feel sick.
- Pregnant women may experience belching after eating as a result of pressure on the diaphragm and nausea due to toxicosis.
Preventing nausea with belching is quite simple; you need to watch what you eat at every meal, unless you have a disease that causes this unpleasant symptom.
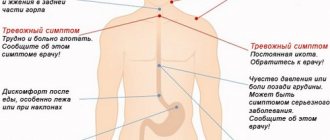
Associated symptoms
Anatomical and physiological disorders of the body that provoke sour belching are also accompanied by other unpleasant symptoms that can occur periodically or be constant. Among them:
- Pain in the throat, heart, stomach, behind the sternum;
- Hiccups;
- Cough (including at night);
- Impaired swallowing reflex;
- Dyspnea;
- Nausea;
- Heaviness in the abdomen;
- Hoarseness of voice;
- Feeling of a lump in the throat.
Diseases that can cause regurgitation with an unpleasant sour taste
If the sour taste in the mouth is an almost constant phenomenon, disturbing after every meal, you should be wary. It’s just that acid will not be regularly thrown into the esophagus and oral cavity. There are many known dysfunctions that provoke this process. Among them are the following:
- Insufficiency of the gastric cardia. The valve connecting the latter to the esophagus does not close tightly. The appearance of sour belching usually appears immediately after eating.
- Enzyme deficiency, in which the stomach is not able to completely break down food, and fermentation processes begin in it. If there are not enough enzymes in the gastric juice, belching appears about half an hour after a meal. Particles of undigested food often escape along with the air. The phenomenon may be temporary. The constant occurrence of a sour taste is characteristic of chronic pancreatitis.
- Gastritis. Sour belching appears a few hours after eating.
Also, the cause of the symptom can be a duodenal ulcer, inflammation of the gastric mucosa, impaired motility of the digestive organs, infectious gastroenterocolitis, and the consequences of surgical interventions affecting the gastrointestinal tract. As a rule, with all the above-mentioned deviations, regurgitation occurs against the background of increased stomach acidity. Often accompanied by heartburn. The patient is especially worried at night, when the body is in a horizontal position, and the juice is easily thrown into the esophagus. In the presence of pathologies, sour belching is enhanced by heavy food intake.
Exacerbation of diseases is provoked by various factors. Among them are decreased immunity, general weakening of the body after operations or other ailments, and abuse of alcohol or cigarettes. Most often, relapses of pathologies manifested by sour belching occur in the fall or spring.
Causes of sour belching
The most common cause of sour belching after eating is GERD, or gastroesophageal reflux disease. It occurs due to pathology of the muscles of the digestive system. Contractile fibers located in the locking sphincters can no longer create a sufficient narrowing of the lumen, and the walls of the gastrointestinal tract reduce the intensity of oscillatory movements (peristalsis). Due to such phenomena, the digested mass begins to stagnate, and the processes of fermentation, rotting and gas formation are activated in it.
The development of GERD depends on the condition of the muscles of the gastrointestinal tract
The mechanism of development of gastroesophageal reflux disease is described in its very name. Translated from Greek, “gaster” means “stomach”, “esophagos” means “esophagus”, and the Latin word “refluo” means reverse flow.
Many external factors can accelerate the development of GERD:
- Bad habits: Smoking;
- Drinking alcohol;
- Dopamine;
In most cases, GERD is accompanied only by emissions of an acidic gas mixture, and the contents of the stomach do not rise high up the esophagus. If peristalsis is severely impaired, the digested lump can begin to move in the opposite direction, splashing out into the upper sections of the tract with acidic liquid. At the same time, pancreatic enzymes and bile can penetrate into the stomach from the duodenum, adding a bitter taste to the belching.
Frequent exposure of gastric juice to the walls of the esophagus can damage its mucous membrane, which further contributes to the development of the inflammatory process - the so-called reflux esophagitis. The harbinger of this condition is heartburn - a burning sensation behind the sternum, which develops due to the influence of acid on sensitive nerve endings.
GERD can develop as an independent pathology, or as a symptom of other, more dangerous diseases.
Table: diseases that cause sour belching
| Painful condition | Reason for development | Distinctive symptoms |
| Non-atrophic gastritis | Inflammation of the gastric mucosa due to the proliferation of harmful bacteria (Helicobacter pylori), poor diet, and frequent stress. | Excessive production of digestive enzymes leads to increased acidity. The liquid contents of the stomach often penetrate into the pharynx, and heartburn is painful. |
| Hiatal hernia | Weakening of the diaphragm due to:
| The phenomenon of belching occurs with the slightest increase in pressure in the stomach. Refluxes are very common and occur not only after eating, but also in a state of hunger, rest, and during sleep. |
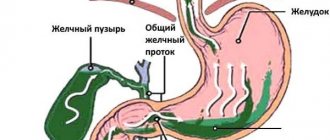
| Duodenostasis | Reduced patency of the duodenum. Probable reasons:
| There are releases of bile into the stomach cavity, giving the belching a bitter taste. |
| Scleroderma | Autoimmune damage to connective tissue, including the lining of the digestive tract. The walls of the esophagus and stomach become covered with scars and ulcers, lose their shape, and reduce motor activity. Sphincters are not able to limit different sections from each other. | The belching has a putrid or bitter-bilious taste. Stagnation in the stomach and intestines provokes the appearance of nagging pain throughout the tract. There may be difficulty swallowing, joint pain, pale skin, and weight loss. |
| Pyloric sphincter stenosis | Reduction of the lumen or complete closure of the valve separating the stomach and duodenum. Possible reasons:
| Due to the fullness of the stomach, fluid emissions up the esophagus are unusually abundant. Symptoms develop immediately after eating. |
| Peptic ulcer | Damage to the gastric mucosa due to increased acidity, poor diet, bad habits, past stress or illness (autoimmune pathologies, HIV infection, diabetes, cancer). | Heaviness and pain in the stomach, becoming more frequent when the condition worsens or after eating food. |
Article on the topic: How to restore and strengthen the nervous system with the help of herbs?
Belching with gastritis
Belching, as well as nausea and vomiting, which do not bring relief, are dyspeptic symptoms of the disease. The accompanying symptoms include discomfort, accompanied by sharp and aching pain, poor appetite, and heaviness in the stomach.
No matter what type of gastritis a person suffers from: autoimmune, infectious, toxic - the disease will be followed by belching of air. Depending on the form of gastritis and the reasons for its occurrence, it can be different. In the atrophic type of the disease, belching air acquires a rotten smell. In this case, pain in the epigastric region, rapid satiety with food, general weakness, a strong urge to defecate, and diarrhea are also characteristic.
When belching occurs along with decreased performance, pale and dry skin, brittle nails and hair loss, then there is a deficiency of iron in the blood and a lack of vitamin B12. This is due to poor absorption of these nutrients against the background of exacerbation of chronic gastritis.
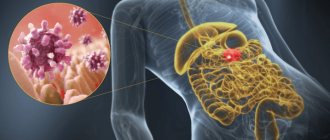
When gastritis occurs due to infection of the body by Helicobacter pylori, belching alternates with heartburn and pain on an empty stomach in the epigastric region
Belching and sour odor are observed with gastritis with high acidity. In case of an illness that occurs due to infection of the body by Helicobacter pylori, belching alternates with heartburn and pain on an empty stomach in the epigastric region.
Belching with gastritis with high acidity
Sour belching is characteristic of gastritis with increased secretion, as well as peptic ulcer disease. In addition to sour belching, there is pain of varying severity, heartburn after eating, a tendency to constipation, and the tongue is coated with a thick white coating. Chronic hypersecretory gastritis is characterized by increased production of hydrochloric acid. The acidity of belching depends precisely on the increased production of hydrochloric acid, which is an integral part of gastric juice.
Belching with gastritis with low acidity
Rotten belching indicates either stagnation and putrefactive fermentation of food in the stomach, or the inability of the stomach to digest it. The latter happens with chronic gastritis with decreased secretion. Rotting in the stomach is possible only in conditions of complete absence of hydrochloric acid - achlorhydria. However, the same can be observed with total secretory insufficiency - achylia, when both hydrochloric acid and the digestive enzyme pepsin are absent.
Often, rotten belching is one of the first symptoms of exacerbation of chronic gastritis with decreased secretion. In addition, there is heaviness and aching pain in the pit of the stomach, a feeling of fullness after eating, nausea, and regurgitation. Due to stomach discomfort, some patients try to eat as little as possible, which leads to weight loss. The disease is characterized by a tendency to diarrhea, with stools usually occurring 2-3 times a day, mushy, without mucus and blood. Palpation of the abdomen can reveal moderate pain in the epigastric region.
The disease proceeds in waves, exacerbations are replaced by rather long remissions, but chronic gastritis with secretory insufficiency is difficult to completely cure. Moreover, this disease is considered precancerous, since it is often combined with atrophy of the cells of the gastric mucosa. Therefore, it is necessary to carefully follow a diet that differs significantly from that for gastritis with normal and increased secretion.
Diagnosis of the causes of sour belching
Diagnosis of gastrointestinal diseases leading to the development of sour belching is carried out by a gastroenterologist . His external examination of the patient is usually accompanied by palpation, which makes it possible to identify some distinct signs:
- Deterioration of the patient's general condition;
- Bloating of the stomach or intestines;
- Frequency of reflux;
- Presence of accompanying symptoms (nausea, heartburn, etc.);
- Nature and localization of pain syndrome.
When the doctor communicates with the patient, an anamnesis of the current condition is established, its possible causes are bad habits, dietary habits, past diseases, hereditary factors.
Endoscopic examination of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum, or esophagogastroduodenoscopy, allows us to study the integrity of the walls of the corresponding organs, the presence or absence of inflammation, scars, ruptures, adhesions, ulcers, tumors and other damage on their surface.
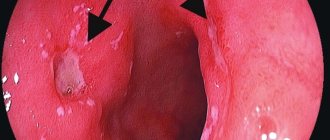
Endoscopic examination of the esophagus makes it possible to identify foci of inflammation on its walls
If necessary, a fragment of suspicious tissue can be removed for subsequent histological analysis. The preparation obtained in this way is fixed, treated with dyes, sections are prepared, which are then studied using microscopic technology. During the study, malignant changes in organs, accumulations of harmful bacteria, and areas of death can be identified.
Histological examination of the tissue around the gastric ulcer reveals numerous accumulations of Helicobacter pylori
The degree of increase in the acidity of gastric juice is determined by intragastric pH-metry. The readings are taken using a probe inserted through the esophagus. The activity of peristalsis in the upper parts of the digestive system is studied by the method of esophagomanometry - essentially, measuring the pressure of the walls of the esophagus using a multicapillary catheter and a specially designed pressure gauge. Contrast radiography allows you to determine the relative position of internal organs, changes in their size and shape, major injuries, and activity disturbances. Computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and ultrasound (US) serve the same purpose.
When conducting a blood test, the content of formed elements in it (erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets), changes in biochemical properties (enzyme composition of plasma, ESR), the presence of autoimmune proteins and antibodies to pathogenic bacteria are determined.
The use of these diagnostic methods allows you to accurately determine the cause of sour belching.
Table: differential diagnosis
| Disease | What diseases is it differentiated from? | Features of the condition | Diagnostic methods |
| GERD | Dyspepsia, biliary colic, infectious esophagitis, ischemic disease, drug esophagitis, esophageal tumors. | There are no pathological changes in the cardiovascular system. Pain as a bolus of food passes down the esophagus is a rare occurrence. The tissue walls may be inflamed, but are not subject to an oncogenic process. | External examination, endoscopy, histology, radiography |
| Non-atrophic gastritis | Atrophic gastritis, stomach tumors. | Helicobacter pylori bacteria are found in the gastric mucosa, and antibodies to them are found in the blood. In this case, autoimmune proteins are not detected. The tissues of the walls are not changed. | Blood test, histology, endoscopy |
| Duodenostasis | Duodenal diverticulitis, tumors. | The intestinal walls do not bear the protrusions characteristic of diverticulitis. The tissues are not susceptible to the oncogenic process. | Endoscopy, radiography, histology |
| Scleroderma | System atrophy, lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis. | The disease does not affect the processes of growth, joint formation, and mental development. The activity of the kidneys and the secretory function of the pancreas are not inhibited. | External examination, blood test, radiography, CT, MRI |
| Pyloric sphincter stenosis | Adrenal insufficiency, gastroenteritis. | The exchange of urea and sodium ions is not impaired. Diarrhea occurs in extremely rare cases. | External examination, blood and urine tests |
| Peptic ulcer | Chronic gastritis, gastroenteritis, cholelithiasis, pancreatitis, gastric tuberculosis, syphilitic lesions, cancer. | The pain syndrome is localized in the upper abdomen, clearly periodic, has pronounced exacerbations, and is not tied to the type of food consumed. Gastric secretion is moderately reduced. There are no antibodies in the blood to Treponema pallidum and Koch's bacillus. The mucous membrane does not have foci of the oncogenic process. | External examination, blood test, histology, endoscopy, radiography |
Medicines
If you feel discomfort from constant attacks, you should always have medications with you. In this case, you need to consult a doctor. The wrong medicine can have the opposite effect. You can alleviate the condition with:
- Almagel suspensions;
- Motilium tablets and suspensions;
- chewable tablets "Rennie";
- "Gaviscon".
These are just a few titles. It should be remembered that they all have contraindications. And what helped one may harm another.
Treatment methods
Sour belching requires special treatment only if it recurs regularly, is accompanied by painful sensations, or simply causes psychological discomfort in the patient. The treatment strategy is determined by the attending physician after performing the necessary diagnostic procedures .
Video: combating high stomach acidity
Drug therapy
Antacids and antisecretory drugs can be used to combat increased gastric acidity. Agents from the first group (Almagel, Maalox, Rennie) neutralize the acid by direct interaction with it, forming easily excreted salts and water. Antisecretory drugs (Omeprazole, Pantoprazole, Ranitidine) interfere with the production of acid by the walls of the stomach.
The peristaltic activity of the digestive tract is increased by prokinetics (Ganaton, Domperidone, Itomed, Motilium). Enzyme preparations (Mezim, Pancreatin) are used for low pancreatic functionality. In case of excessive proliferation of pathogenic bacteria, antibiotics are used (Azithromycin, Amoxiclav, Klacid).
Surgical treatment
Surgery is used in extremely severe cases that cannot be corrected with medication. Such situations include:
- Significant weakening of the esophageal opening of the diaphragm;
- Numerous adhesions and ulcers;
- Tumor process;
- Complete obstruction of the stomach and duodenum;
- Displacement of organs inside the abdominal cavity.
Diet
Diet correction is the most common and effective method of combating sour belching . The main principle should be fractional, orderly meals. It is advisable to delay the last meal and bedtime by at least 2–4 hours. Half an hour before meals, you need to drink up to 1 glass of warm water to activate the process of peristalsis. Light porridges (oatmeal, pumpkin) and jelly have a beneficial effect on the digestion process.
Article on the topic: How to prepare for an MRI of the brain
It is necessary to avoid foods that irritate the walls of the stomach:
- Alcohol;
- Mutton;
- Sparkling water;
- Mushrooms;
- Excessively hot and cold food;
- Cocoa and chocolate;
- Pickled vegetables;
- Smoked meats;
- Coffee;
- Marinades;
- Korean style carrots;
- Pearl barley porridge;
- Sweets;
- Sour cream;
- Sauces;
- Tomatoes;
- Fast food;
- Citrus.
Gallery: foods prohibited for sour burps
Display shock and 18+ content
Ethyl alcohol strongly irritates the walls of the stomach Coarse cereals are contraindicated for heartburn Astringents from cocoa beans can reduce the activity of the stomach and intestines Caffeine increases the acidity of gastric juice Nutrients contained in mushrooms are difficult to extract Lamb is too heavy for a weakened stomach “Fast” food creates unnecessary stress on the stomach and duodenum Sugar slows down digestion and promotes fermentation Fermented foods contain too many organic acids Smoked meats are hard on the digestive system Sauces contain a lot of hot spices Cold irritates the nerve endings of the esophagus and stomach Excess acids in citrus fruits can irritate the walls of the stomach
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine has discovered numerous means to improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, reduce acidity, and reduce the inflammatory process at the initial stage. Using these methods allows you to successfully combat sour belching. However, it should be remembered that many herbal remedies by nature have high biological activity, and therefore can cause harm if used carelessly.
Table: folk remedies against sour belching and heartburn
| Product name | Composition and method of preparation | Reception mode |
| Walnuts | Crush the peeled fruits. | Take 1 tbsp. l. every day. Used for preventive purposes. |
| Potato juice | Add 1 tbsp to freshly squeezed potato juice (1 glass). l. honey. Stir. | Drink half a glass in the morning and evening. |
| Calamus root | Grind dry calamus root into powder. | The powder, which fits on the tip of a teaspoon, is washed down with plenty of warm water. Used to treat heartburn |
| Celery root | Grind the fresh root. | Consume with water, 1 tbsp. l. three times a day, 30 minutes before meals. |
| Angelica infusion | 1 tsp. Pour a glass of boiling water over the crushed root, leave for half an hour, filter. | Drink a glass of the product in small portions throughout the day. |
| Baking soda | 1 tsp. Stir baking soda in a glass of warm water. | Drink the solution if you have severe acid reflux or heartburn. |
| Infusion of wormwood | 1 tbsp. l. pour a glass of boiling water over the herbs, leave for 2 hours, filter. | Take half a glass once a day, half an hour before meals. Considering that wormwood alkaloids have a toxic effect, this remedy should be used with great caution. |
ethnoscience
Nature's pharmacy contains the necessary herbs, plants, berries and other ingredients needed to help a person with sour burping. Unlike drug treatment, traditional medicine helps the body cope with the disease without side effects and without harm to other organs not involved in the process
. First aid at home after a sour dish: quickly drink milk.
1 recipe
Fresh goat milk helps regulate the function of the digestive organs and a person gets rid of belching. You need to drink 3 glasses a day every day for two to three months.
. The period of admission depends on the speed of health restoration.
2 recipe
Physical exercise has a beneficial effect on the human body. Health problems arise when physical activity decreases while constantly sitting in one place.
. The tone of the internal organs decreases, and malfunctions occur.
Lying on your back, raise your straight legs 45 degrees and hold for 2 minutes, then gently lower. Repeat several times
. At first, the belching will increase, but gradually the symptoms will begin to weaken and stop completely.
This recipe is not a way to treat a disease, but a method of quick relief for an acidic taste in the mouth. In any case, you should consult a doctor to get an accurate diagnosis.
Treatment prognosis
Sour belching itself does not pose a direct threat to life and health, causing only physical and psychological discomfort. Its manifestations are easily eliminated with drug therapy and diet correction.
The main danger lies in the disturbances in the functioning of the body that were imperceptible for the time being and provoked the appearance of the symptom in question. Their untimely diagnosis and ignoring can lead to severe damage to the gastrointestinal tract:
- Secondary infections;
- Bleeding ulcers and fistulas;
- Necrosis;
- Obstruction of the stomach and small intestine;
- Narrowing of the lumen of the esophagus;
- Oncogenic process.
Preventive measures
- Get rid of the root cause of regurgitation and prevent its recurrence.
- Get rid of bad eating habits. Start consuming food in small quantities and in a balanced manner. Eliminate heavy, unhealthy foods from your diet. Food should be taken in small portions before the feeling of hunger arises.
- Seek medical help in a timely manner for the treatment of ulcers, gastritis, and gastrointestinal pathologies.
- Avoid stress and do not have an adverse effect on your own psycho-emotional state.
- Introduce dosed physical activity and switch to an active lifestyle.
Return to contents
Prevention
Measures to prevent sour belching are extremely simple. They consist primarily of correcting the diet, avoiding excessively fatty and spicy foods, alcohol, and caffeine. You should limit the amount of food you consume, distributing it in fractional portions throughout the day. You need to completely get rid of the tendency to eat heavy dinners.
You can reduce the acidity of gastric juice by giving up smoking - it has been proven that nicotine and tar, when entering the digestive system with saliva, have an irritating effect on the mucous membrane.
Diseases
Sour belching after eating may indicate the presence of serious gastrointestinal diseases:
- Gastritis. Manifestations of gastritis are possible in two forms: chronic and acute. A characteristic accompanying symptom is excessive production of hydrochloric acid. Hydrochloric acid is one of the components of gastric juice, which helps to break down and disinfect foods that enter the stomach (all food products must be disinfected with gastric juice and acid to avoid infection getting inside). When the level of stomach acid increases, a person experiences heartburn, nausea, or acid belching.
- GERD. This disease is characterized by impaired motor function of the stomach. Stagnant processes occur in the body, which provokes unpleasant belching.
- Chronic pancreatitis. In chronic pancreatitis, enzymatic production is disrupted (which affects digestion and absorption of foods).
- Various disorders in other parts of the body.
- Depressed state of the protective function of the immune system.
Return to contents
Possible complications
- failures in the functioning of internal organs, which can lead to disruption of the digestion process;
- development of ulcerative formations;
- permanent heartburn, increased duration and severity of belching;
- opening of internal bleeding of the gastrointestinal tract.
- development of Barrett's esophagus syndrome (a precursor to cancer);
- narrowing of the esophagus (stenosis), disruption of the process of swallowing food;
- pathologies of the respiratory system.
Belching occurs naturally during the digestion of food. But the action should not be accompanied by discomfort and bad breath. Sour belching is a deviation from the norm. It is worth taking a closer look at the body and finding out the causes and methods of quick treatment.
During ingestion, food enters the stomach along with air, which, after the food passes further along the tract, is removed by the body through the esophagus to the outside. The action, accompanied by a sour taste or rotten egg smell, means that undigested food has returned to the esophagus. Many people suffer from sour belching and heartburn at night when the body takes a horizontal position. And this happens for various reasons - both harmless and serious.