The composition of urine reflects almost all processes occurring in the body. Therefore, its analyzes are carried out in the diagnosis of many diseases. The number of leukocytes, erythrocytes, and protein is taken into account. Often, a general urine test also reveals epithelial cells, mucus and other impurities. This is not always a sign of pathology, but such results are a reason for additional examination of the patient. After all, they may indicate the presence of an inflammatory process in the body, infection or kidney dysfunction.
Presence of mucus
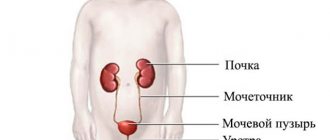
All urinary tracts are covered from the inside with mucous membrane. Special cells produce mucus, which protects their walls from the acidic component of urine and from urea. In addition, mucus is a natural barrier against the proliferation of bacteria and viruses, and it also accelerates the removal of salts from the body and prevents the formation of stones.
In a healthy person, almost no mucus is excreted in the urine. During the inflammatory process, the outer layer of the mucous membrane is often renewed, so such cells can enter the urine in small quantities. It is impossible to detect mucus with the naked eye; it is usually detected only during laboratory examination.
The presence of mucus does not always indicate some pathological processes in the body. Sometimes it is detected in a urine test if the patient has collected the sample incorrectly.
To avoid this, you need to know the basic rules for collecting urine for analysis:
- it should be collected in the morning immediately after waking up, unless the doctor gives other instructions;
- before collecting urine, you must thoroughly wash the perineum with warm water and soap;
- You need to collect samples in sterile containers, preferably specially purchased for this from a pharmacy; you must not touch its inner walls with your fingers;
- You only need to collect a medium portion of urine;
- It is advisable for women to cover the vagina with a tampon, and during menstruation it is irrational to take a test, since it will not be informative;
- You should not store collected urine for longer than 2–3 hours.
Some features of the appearance of mucus in women
Epithelium in the urine that appears in representatives of different sexes can be due to various reasons. So, in women, the causes of excess mucus may be:
- Incorrect urine collection. This phenomenon is observed when washing before the procedure is not thorough enough, the sample is submitted to the laboratory more than two hours after urine is excreted, or the use of a non-sterile container.
- The development of pathological processes - urolithiasis, urethritis, pyelonephritis and other problems.
- The appearance of cystitis - in women, this disease occurs quite often, and the result is inflammatory processes in the mucous layer of the bladder.
- Another of the many reasons for the appearance of mucus in the urine can be autoimmune inflammatory processes.
Pregnancy deserves special consideration, in which OAM helps to assess the course of diseases and identify possible abnormalities much earlier. If a woman urinated to check the tests while carrying a child, the indicators should not exceed 1+. If there are no other pathological results during the examination, level 2+ falls into the list of moderate and acceptable indicators.
When mucus appears in the urine of pregnant women, leukocytes or bacteria appearing in parallel should cause special concern. Such indicators indicate an infectious lesion, which is dangerous for both the woman and the fetus. In this case, bacteriological culture is required, which will identify the causative agent of the pathology, and sometimes PCR is used as an additional research method.
Interpretation of urine tests
Only a doctor can determine what this or that indicator indicates in the results of urine tests. After all, accurate diagnosis requires an integrated approach. Deciphering urine tests is not an easy process, since many other indicators need to be taken into account: the patient’s age, gender, and the presence of chronic pathologies. Although the norm for various parameters is often indicated on the form, minor deviations from it are not always evidence of pathology.
But some indicators from the test form can accurately indicate the development of inflammatory processes in the human body. First of all, this is the presence of mucus. This indicator is a sign of inflammation if it is present in large quantities, and also if, at the same time, red blood cells, white blood cells, protein and other substances are found in the urine.
In addition, during the analysis, the laboratory technician determines the color of urine, its transparency, odor and density. The chemical composition may contain a small amount of glucose, epithelial cells, leukocytes, erythrocytes, protein, and salts. It is also important to determine the external characteristics of the mucus itself. White color means that inflammatory processes are developing in the body. This coloration may also indicate poor personal hygiene or stagnation of urine. Red mucus appears in cases of serious infectious pathologies, circulatory problems, or acute poisoning.
Laboratory tests evaluate urine according to various criteria.
Important: with any test results, it is necessary to conduct additional examinations that will help clarify the diagnosis.
Indicators of the presence of mucus and other components may indicate the possibility of pathological processes. Impaired kidney function is indicated by the presence of mucus along with an increase in the level of red blood cells. This may be an infectious disease in which bacteria are found, as well as tumors or kidney stones.
If protein is detected in the urine along with mucus, the doctor may conclude that the filtration functions of the kidneys are impaired. True, an increase in protein can also be observed when the body is hypothermic or overworked, heart failure or hypertension.
When a large number of leukocytes are released along with mucus in the urine, most often this means that there is an inflammatory process in the urinary tract or a malignant tumor has formed. Sometimes various salts are also detected simultaneously with this indicator. This indicates a metabolic disorder. This condition can cause the formation of stones.
Is treatment necessary if mucus is detected in urine?
The need for therapy depends on the volume of mucus contained in the urine, the presence of additional components and the nature of the epithelial cells. Treatment is necessary in the following cases:
- an increase in mucous elements is accompanied by difficulty urinating, pain or fever;
- in addition to mucus, leukocytes, blood, salts or protein were detected;
- renal or primary epithelium was detected in the urine.
If there are no acute symptoms (pain, blood clots), a repeat urine test is prescribed. This is necessary because deviations may be caused by dietary habits, heavy loads, or improper collection of material for analysis. Repeated examination will help eliminate diagnostic errors.
The appearance of mucus in the urine may be normal, or it may indicate a serious pathology. In addition to the volume of the mucous component, other components of urine are additionally taken into account. This helps to identify possible deviations.
Norm of mucus and its excess
A healthy adult should have no mucus in their urine at all. Only a little clear mucus is allowed if other indicators are normal. But when it is detected in large quantities for the first time, a repeat study is usually prescribed. Only when the results are confirmed can the doctor conclude about the presence of pathology.
How to submit a urine culture for flora
When interpreting test results, the laboratory technician uses certain criteria. There are four levels of mucus presence, which are indicated by a “+” sign:
- normal state of mucus in urine – 1+;
- mucus in urine 2+ means a moderate amount;
- an increased level is indicated by three pluses;
- if there are 4 pluses next to the word mucus on the analysis form, this means that there is a lot of it and special treatment is required.
If there is a high level of mucus, it can even be detected visually. The urine becomes cloudy and contains sediment. Sometimes clearly visible flakes of mucus may appear. This condition most often indicates a serious inflammatory process, in which the body intensively produces mucus to protect the organs from the penetration of bacteria.
And a moderate increase in the level of mucus almost does not manifest itself externally. The patient can only feel the symptoms caused by the pathologies that cause this condition. If such sensations appear, it is advisable to undergo an examination in order to take timely measures to eliminate the disease. Most often, this is a violation of urination: retention, too frequent, strong urges that do not lead to the release of urine, urinary incontinence. When urinating, a burning sensation, stinging or pain may occur. Sometimes itching of the external genitalia, rash, redness, discomfort during sexual intercourse and pain in the lower abdomen also occur.
How is a mucus test evaluated?
The presence of mucus in the urine, which in Latin is called “mucus,” is confirmed by specialists in clinical laboratories. At the same time, in the process of studying urine, a number of related indicators are assessed - the color of the liquid and its transparency, specific gravity and acidity, odor and protein, and the amount of glucose. Red blood cells and white blood cells in the urine, the presence of salt, fungi, and ketone bodies are checked.
The rejection of the epithelium, which is mucus when it penetrates into the urine, is a constant process. In the testing laboratory, the number of epithelial cells is assessed not by number, but by a specially developed system of pluses in the range from 1 to 4. Accordingly:
- 1+ – the result falls within the norm.
- 2+ – if the laboratory gives two pluses, the level of mucus is considered slightly elevated, but may be a variant of the norm.
- 3+ and 4+ - such indicators of mucus during a urine test indicate the presence of various pathological processes, including urolithiasis, malignant neoplasms in the bladder, the presence of infectious agents, including those transmitted through sexual intercourse - chlamydia, trichomonas, mycoplasma. When testing urine in women or girls, this is how vaginal discharge that is included in the sample manifests itself.
Important. We can conclude that even if there is mucus in the urine and determining what it means, the reason will not always be the presence of pathology.
If repeated interpretation shows that the mucus in the urine is again increased, a more complete diagnosis is required to clarify the cause of the pathology. It should be taken into account that the norm of epithelial cells in urine is influenced by age and gender.
When mucus appears in urine, it may have a thick consistency; if it meets the norm, the secretion is transparent or white, which indicates its benign basis. In the case when the shade becomes yellow, it is an indicator of the disease. You should be wary of the appearance of greenish, brown or gray secretions in urine products.
More often, the penetration of mucus into the urine causes concern for a woman, since a thick secretion can form during ovulation, menstruation, pregnancy, or when using oral contraceptives. However, in men it is also possible to include mucus in a urine test, but more often this is not a consequence of improper sampling, but the presence of genitourinary infections.
Causes
A small amount of mucus is not usually a sign of illness. It can get into the urine if the rules for collecting tests are not followed or if there is insufficient perineal hygiene. For example, urine collected in a non-sterile jar or stored for more than 3 hours may show such results. When collecting urine from women, mucus from the vagina may get into it, which is due to the anatomical structure of the female body. This parameter is also detected when the patient holds urination for a long time before collecting the analysis.
During pregnancy, a small amount of mucus is also not a pathology. The woman herself cannot determine what this indicator means. Only a doctor can explain that bearing a child leads to changes in the functioning of many organs. Progesterone levels rise and the activity of the endocrine glands increases, which leads to increased mucus production. But there should still be a little of it in the urine.
A small amount of mucus in the urine is normal during pregnancy.
Attention: a little mucus may be released if the diet is unbalanced. This is caused by increased consumption of sweets, pork, poultry, white bread and fast food.
There are also more serious reasons for increased mucus levels. This could be hypothermia, overwork, severe stress, or poor nutrition. A lot of mucus in the urine appears with the following pathologies:
- infectious diseases of the genital organs: chlamydia, ureplasmosis;
- inflammatory gynecological pathologies in women, for example, vulvitis or vaginitis;
- urolithiasis: the presence of stones in the kidneys or bladder and their movement;
- trauma to the urinary tract during the movement of stones or diagnostic procedures;
- malignant neoplasms;
- prostatitis and other pathologies of the prostate gland in men;
- inflammation of the bladder - cystitis;
- urethritis - inflammatory processes in the urethra;
- kidney inflammation – pyelonephritis;
- chronic renal failure.
Most often, similar test results are found in women due to the peculiarities of their anatomical structure. Mucus in the urine of men is usually detected with inflammation of the prostate. Sometimes this condition is associated with poor hygiene, improper collection of tests, or prolonged retention of urination.
Mucus can also be detected in a child’s urine. Moreover, most often the causes of this condition are the same as in adults. But in addition to infectious and inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system and malignant neoplasms, this condition can also occur if personal hygiene rules are not followed. In boys, a common cause of such test results is a pathology such as phimosis. This is an anomaly in the development of the foreskin, in which the head of the penis cannot be completely exposed. Therefore, secretions accumulate on it and bacteria multiply. In girls, a similar condition appears with vulvitis, which develops with insufficient hygiene of the external genitalia.
Treatment
After determining the exact cause of the formation of mucous discharge in the urine and confirming the diagnosis, the specialist prescribes a specific therapy. The treatment must be comprehensive:
- taking medications to relieve inflammation, pain, and, if necessary, antibacterial therapy,
- a plentiful drinking regime, including not only plain water and fortified drinks, but herbal preparations with an anti-inflammatory effect,
- elimination of bad habits, balanced diet.
If a lot of mucus is found in the urine of women, it is strongly recommended to consult a doctor. With proper treatment, possible negative consequences and complications for the body can be avoided.
A general urine test is in many cases an effective way to confirm suspected diagnoses. In a normal state, the excreted fluid is transparent, but with the development of various pathologies affecting the genitourinary system, its quality characteristics may change. One sign of problems is mucus in a urine test.
Epithelial cells in small numbers may not cause concern, but if during the study their number exceeds the established norm, it is worth thinking about the possibility of inflammatory processes occurring in the kidneys or urinary tract.
What to do
If mucus is found in the urine during laboratory tests, the doctor usually immediately prescribes treatment for the pathology that is the cause of this condition. Special renal antiseptics, herbal decoctions and plenty of fluids are usually used to flush the urinary tract. Decoctions of rosehip, bearberry, cranberry or lingonberry juice, and mineral water are suitable for this.
For cystitis or pyelonephritis, antibiotics, nitrofurans, and Biseptol are used for treatment. The drugs Canephron, Monural, Cyston are effective. Diuretics are also needed, for example, Furadonin or Phytolysin.
Attention: any medications can be used only as prescribed by a doctor after diagnosis.
If such a pathology is detected, the doctor will prescribe the necessary medications.
Treatment of various pathologies that cause the appearance of mucus in the urine must begin as early as possible. Only with timely elimination of pathological processes and inflammation can complications be avoided. After all, sometimes you can get rid of mucus in the urine only through surgery. It is needed in the presence of a malignant tumor, polyps or stones.
But the need for such consequences can be prevented. To do this, you need to carefully observe the rules of personal hygiene and it is very important to visit the toilet regularly to prevent stagnation of urine. In addition, it is necessary to eat properly, providing the body with all the necessary vitamins, and drink enough fluids.
The appearance of mucus in men
In the adult male population, phimosis may join the pathologies already listed. In this situation, mucus in the urine of men is formed as a symptom accompanying the pathology of the head of the penis. What are we talking about in this case? With phimosis, the head of the penis cannot fully open, and under the fold of the foreskin mucus is secreted, the excess of which is quite problematic to get rid of.
A large amount of mucus in the urine can provoke hypertrophic changes affecting the prostate tissue. Problems can also be caused by sexually transmitted pathologies. In some cases, inflammatory phenomena in the kidneys provoke neoplasms in the prostate or a narrowed urethral canal, which leads to stagnation of urine and the inability to urinate normally.
Quite often, in cases where a lot of mucus forms in the urine, a number of other symptoms also appear, indicating the formation of kidney or urinary diseases:
- When urinating, the volume of fluid released begins to decrease.
- Painful sensations occur in the lumbar region.
- During urination, a burning sensation appears, and a suspicious sediment can be seen in the liquid.
- The desire to get rid of urine becomes more and more frequent.
- In some cases, mucous discharge is accompanied by pain in the groin and perineum - usually such signs accompany inflammation of the prostate.
- In some cases, the above processes are accompanied by fever.
In the acute form of the pathology, when assessing the condition, an increased number of proteins and leukocytes is observed. In the case of a chronic pathology, in addition to impaired urination, representatives of the stronger sex may experience fatigue, nervousness, and low sexual activity. Often situations in which mucus is found include the formation of benign neoplasms.
With urolithiasis, in addition to epithelial detachment, lumbar pain of a pulling nature and colic occur. If you lift heavy objects, you may experience an involuntary urge to urinate. Sometimes bloody inclusions appear in urine, and the process itself can be interrupted unexpectedly. This phenomenon indicates that the urethral canal is blocked by a stone, resulting in urgent need for treatment.
In children, both a small number of epithelial cells and increased mucus production occur for the same reasons as in an adult. Most often these are inflammatory processes - problems with the bladder or kidney pathologies, the development of urolithiasis.
conclusions
The detection of mucus in a general urine test is not always a sign of pathological processes. This may be a temporary phenomenon or the result of improper collection of tests. By following preventive measures and personal hygiene rules, this condition can be avoided. But often such test results indicate the presence of pathological processes in the body, which without treatment can become chronic. The development of serious complications can be prevented with regular examination. It is recommended to donate urine annually, even in the absence of symptoms of pathology.
How to eliminate negative phenomena
We looked at what mucus is, how its presence is indicated during analysis in cases where the norm is exceeded. It was also explained where and for what reasons mucous inclusions appear in urine. It remains to discuss how to treat pathological conditions accompanied by the detection of a mucous mass in urine. And here pathology, accompanied by negative signs, plays a huge role. For example, if cystitis is detected, you must:
- Prescribe antimicrobial treatment - it is usually recommended to take Augmentin, Nolitsin, and other pharmaceutical substances.
- To avoid the pathology becoming chronic, inflammation in the kidneys is eliminated with the help of Nalidoxic acid, Nitrofuran substances, Biseptol and antibacterial substances.
- If the volume of mucus increases, the recommendation of the attending physician may be the use of the herbal remedy Caneon.
- If you have cystitis, you will need to reconsider your drinking regime - within 24 hours you need to consume approximately 2.5 liters of purified liquid. It is also allowed to drink rosehip and oatmeal infusion and herbal teas.
If kidney stones are found, surgery will be required. During attacks of urolithiasis, antispasmodics and painkillers are prescribed. In some cases, doctors prescribe medications to help dissolve salt deposits. But for the most part, the effectiveness of such drugs is highly questionable.
If mucus and snot are produced in men during inflammatory processes in the prostate, medications may be prescribed that relax the muscles and reduce the volume of the inflamed organ.
Important. The mucus itself is not a disease, but only indicates that there may be a malfunction in the functionality of the organ. To eliminate possible errors, it is best to retake an unfavorable analysis.
The attending physician develops a treatment regimen only when the underlying pathology is determined. Medicines are selected based on the cause of mucus. Kidney pathologies are eliminated with the help of Biseptol. This medicine belongs to combined antibacterial drugs that kill pathological pathogens of inflammation.
When treating pathology, preventive measures are important to avoid the formation of increased volumes of mucus. So, regular bowel movements are necessary to avoid stagnation of urine. It is necessary to urinate before intercourse and carefully maintain the cleanliness of the genitals. You will need to drink more fluids and regularly include fresh fruits and vegetables in your diet. It is necessary to take special complexes containing vitamin C. Regular testing and examination by a specialist is also required.
How does deviation from the norm manifest itself?
If a person is completely healthy and no inflammatory process occurs in the body, urine should be virtually transparent and have a uniform consistency, and there should not be any neoplasms present in it.
Depending on the individual characteristics of the body, the shade of urine can vary from pale yellow to rich sand. The smell of the liquid should not be pronounced; the appearance of a sweetish aroma is a sign of abnormalities. If white flakes float in the urine of men and women, in some cases this is not a cause for concern; the reaction can be triggered by simple stress. But in most cases, the causes of this disease are quite serious; as a rule, they are associated with dysfunction of the urinary system.
Experts note that in approximately 60% of cases, a white film in the urine, balls, grains and plaque appear precisely because of illiterate collection of fluid and untimely delivery to the laboratory.
- The day before collection, it is not recommended to eat foods that can color the urinary pigment (beets, compotes, carrots).
- You should not take medications that contain iron (the largest amount is found in multivitamin complexes and various nutritional supplements).
- Before collecting biomaterial, you need to thoroughly rinse your genitals, this will help avoid the transfer of germs into urine. In this case, you should not use various gels and other products that can be difficult to wash off.
It must be remembered that when urinating, the middle part of the urine should be collected, since it is most suitable for analysis.
In order to be able to independently determine violations of the composition and quality of urine, you need to know what parameters the biological fluid of an absolutely healthy person should meet. According to variants of accepted standards, urine should have a number of the following characteristics:
- The liquid should be absolutely transparent and light. The exception is morning urine; the portion collected after a night's sleep is characterized by a slightly darker color. Slight turbidity is also acceptable, which may result from the consumption of certain foods or medications.
- Urine with flakes is a sign of disruption of the body. According to generally accepted versions of the standard, there should not be any foreign veins, threads, lumps, or other foreign components.
- A sharp, specific odor is also considered a deviation from the norm. Most often, in people suffering from various diseases, for example, infectious, viral etiology, urine acquires a putrid or acetone odor.
The volume of fluid released during urination can also indicate the development of possible pathologies. A small amount of urine, changes in color, structure, composition are direct indicators of dysfunction of individual organs and systems.
Goblet cells that secrete mucus are found throughout the urinary tract, in the kidneys, and urethra. Their main function is to protect the mucous layer from mechanical damage and the aggressive effects of uric acids. Normally, mucus is secreted in small quantities, which is sufficient to maintain functional abilities.
In a healthy body, the production of the substance occurs moderately, it is not visible to the naked eye. Mucus is determined in a general urine test and is marked in the form of crosses during laboratory diagnostics. Its significant content is a sign of pathological disorders.
| Quantitative indicator | ||||
| Deviation from the norm | Minor | Moderate | Strong | Expressed |
| Meaning | Conditional norm |
| Chronic recurrent inflammatory process or its exacerbation |
|
Normal urine values:
- color palette in the range of yellow;
- no turbidity;
- transparency;
- lack of protein, glucose, ketone bodies, casts, bilirubin, hemoglobin, salts, bacteria;
- the presence of single erythrocytes, leukocytes and epithelial cells;
- There should be no white flakes.
Any changes in normal indicators indicate the course of the pathological process. In infectious diseases, the number of leukocytes increases; in kidney pathology, blood and protein appear in the urine; in liver diseases, the color changes; when kidney cells are destroyed, cylindrical inclusions appear.
An acceptable norm is also considered to be darkening of urine in the morning due to its increased concentration, as well as a change in color due to taking special medications or foods.
It is recommended to do a urine test twice a year for prevention and timely detection of the onset of diseases.
If you notice any regular changes in your urine (color changes, odor), you should immediately consult a doctor to rule out dangerous pathological problems.
Diagnosis of infections
The main diagnostic criterion is the growth of uroinfectious bacteria in a urine sample of more than 105 microorganisms in 1 ml of urine.
In almost all cases, inflammatory cells - leukocytes - are also present in the urine: more than 10 leukocytes per ml of urine, or more than 5 in the sediment. It is important to know that establishing the presence of leukocytes in the urine is not definitive proof of the presence of infection.
They can be found at elevated temperatures due to
- inflammation outside the urinary tract
- inflammation of the penis
- and as a reflection of urine contamination, which almost all children have.
After the first suspicion, the disease is confirmed by ultrasound examination of the urinary system. Ultrasound is a non-invasive method that does not use ionizing radiation and is therefore the first choice when choosing a diagnostic method in children with possible urinary tract infections. Ultrasound evaluates
- state
- kidney shape and size
- existence and extent of expansion of the channel system
- appearance
- renal tissue thickness
- and bladder wall thickness.
In most cases, after the first urinary tract infection in girls under five years of age and boys of all ages, further treatment is required. The first method is further urination cisterography. This is an x-ray method used for diagnosis
- vesicoureteral repeated UCS
- or restoration of urine from the bladder to the urethra and kidneys.
Reflux is the most common urinary tract abnormality in children and occurs in 30-50 percent of children with urinary infections.
- In boys, as a rule, primary or congenital disorders of the connection between the ureter and bladder occur during the first year of life.
- In girls, it usually occurs between 4 and 8 years of age, and then secondary to or due to high pressure inside the bladder, causing urodynamic voiding disorder.
It is important to note that today, the recommended diagnostic methods for monitoring and diagnosing UTIs around the world use small amounts of radiation, such as radionuclide cystography or the more popular ultrasound cystography, which does not use radiation.
Ultrasound cystography has been recommended as the first method for diagnosing recurrent UKSA girls, or as a method for monitoring those already diagnosed with recurrent flow. If your little one is diagnosed with vesical REFL UCS, further diagnosis, treatment and follow-up for these abnormalities may result in permanent damage to the bladder and kidneys.
Dr. Komarovsky: everything about urinary tract infections in children.
How to take a urine sample
One of the main problems is collecting urine samples from young children who cannot control their urination. Special sterile containers are glued to the skin of the genital organs.
It is important to thoroughly wash the genitals with warm water and mild soap, and leave the collection container for a maximum of one hour.
If the child does not urinate, the container is removed, the washing process is repeated and a new container is attached. The urine sample must be delivered to the laboratory within one hour. Numerous studies show high rates of urine sample contamination due to failure to follow these guidelines (up to 60 percent). Thus, a large number of children are subjected to unnecessary treatments and further diagnostic procedures.
Children's doctor: urinary tract infections in a child.
Infants under one year of age need to undergo regular urine tests to monitor the health and development of the baby. Based on the test results, doctors can diagnose various pathologies of the urinary system, kidneys, as well as the presence of infection in the body.
Alarming indicators, in addition to the increased content of protein, mucus and sand, also include the presence of bacteria. What do bacteria in urine mean? What are the reasons for their appearance and how dangerous is it? How is pathology diagnosed and treated?
Why does this disorder occur in adults and children?
If during an examination you find mucus in your urine, what does this mean? The appearance of this secretion in female urine is due to the anatomical features of the structure of the patient’s genitourinary system. In some women, the opening of the urethra is located too close to the entrance to the vagina, so vaginal discharge during collection of the analysis may accidentally get into the biomaterial being studied. If the results of the study indicate the presence of such a secretion in an insignificant amount, then this is not yet a pathological sign.
Norm
In a healthy child, mucus can be detected in extremely small quantities. It forms in the urethra, after which it is excreted along with urine into the pot, which frightens parents. If the indicators are normal, they are designated as “traces”, “+” or “1”.
To get an accurate interpretation of your results, contact the doctor who gave you the conclusion. This way you will receive reliable information about your baby’s health and, if necessary, take timely and effective treatment.
Symptoms and their elimination
What symptoms appear if a white suspension appears in the urine?
- painful sensations during bowel movements;
- secretion of a large amount of mucus;
- irritation of the mucous membranes of the genitals;
- frequent urge to go to the toilet.
It is impossible to delay treatment for such disorders, since in the absence of treatment for a long time, the disease can become severe and treatment will take longer.
To choose the optimal treatment method, the specialist first needs to understand why white neoplasms in the form of flakes have formed in the urine. Very often, flakes occur due to contact with the outer epithelium, in which case the patient will be sent for re-analysis.
If a secondary study confirms the presence of an inflammatory process, the patient is prescribed certain medications.
- antibiotics;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Self-medication is strictly contraindicated, as it can only worsen the situation.
If the disease is caused by urethritis or prostatitis, the prescribed therapy may not bring improvement, and the only solution will be surgery.
The main sign of the presence of a large amount of mucus in the urine is its turbidity. If you fill a glass jar, then after a while mucus and other pathological impurities will settle to the bottom. You can often find mucous fibers that circulate through urine in the form of an independent suspension.
Pathological inclusions of mucus in urine
| Pathological condition | Features of development and course | Symptoms |
| Pyelonephritis | Develops against the background of an infection that has penetrated the kidney parenchyma. It often becomes chronic, cannot be completely cured, and when provoking factors appear, it worsens. There may be a constant presence of mucus in the urine, the indicator is 2-3 crosses | Nagging pain in the lower back, increased urge to urinate, increased nocturnal diuresis, weakness, increased body temperature, malaise |
| Cystitis | Often develops at a young age. Primary inflammation occurs against the background of infection, and if it is not completely eliminated, it becomes chronic. During periods of exacerbation, a pathologically large amount of mucus is diagnosed, 3-4 crosses | Frequent urge to urinate, up to 30 times a day. Severe pain when emptying the bladder, discomfort and pain in the pelvic cavity. Body temperature often rises, weakness and malaise increase |
| Venereal diseases | Many sexually transmitted diseases develop at lightning speed and cause mucus to appear within 1-2 weeks. Pathological impurities are temporary and almost always disappear after treatment of the underlying disease | Women experience an unpleasant odor from the vagina, itching, burning, discomfort, and pain during sexual intercourse and immediately after it. Mucus in urine usually has a rich color and is detected in the form of individual fibers. White, yellowish, green, blood streaks indicate a serious pathological process that requires urgent treatment |
| Diseases of the female reproductive system | Diseases of the female genital organs of a non-infectious nature can be caused by the formation of cysts, tumors, an increase in opportunistic microflora, etc. Pathological impurities in the urine are predominantly temporary and completely disappear after treatment of the underlying disease. The average is 2-3 crosses | Accompanied by unpleasant sensations in the vagina, itching, burning, discomfort during sexual intercourse, shifts in the menstrual cycle, impossibility of pregnancy, unpleasant odor |
| Autoimmune disorders | In the process of autoimmune disorders, a restructuring of cellular immunity occurs, as a result of which the body’s own cells are perceived as foreign agents. In response, an inflammatory reaction develops, a change in the structure of the mucous layer | Autoimmune damage is characterized by a long asymptomatic period. The patient's main complaint is cloudy urine and discomfort in the pelvic cavity caused by a chronic inflammatory process. Intoxication rarely develops, and therefore no specific and pronounced symptoms are observed. |
| Gastrointestinal diseases | Some diseases of the gastrointestinal tract lead to changes in all body systems. This is due to long-term inflammation and changes in the mucous membranes. Pathogenic microorganisms enter the urinary system through the blood and lymph. Especially often, changes occur against the background of helminthic invasions of the digestive tract, which is caused by the production of toxins during the life of parasites. When bile stagnates in the ducts, a large amount of urobilin is formed in the blood, which colors the urine deep yellow or brown. It becomes more aggressive towards the epithelium lining the kidneys and urinary tract, and in response to this, a strong release of mucus by goblet cells develops | The pronounced clinical picture of diseases of the digestive system is obvious. Among the main signs: disturbances in appetite, frequent nausea and vomiting, pain in the epigastrium and abdomen, stool disorders, constipation that alternates with diarrhea. Long-term chronic conditions lead to general intoxication of the body, increased body temperature, weakness, malaise, fatigue, etc. are observed. |
| Urolithiasis disease | Stones form in adults against the background of a pathological accumulation of salts and minerals. They have an irritating effect on the mucous membrane of the bladder; symptoms especially increase if the stones are directed towards the urethra, scratching and damaging it. Glandular tissues respond to microtraumatic lesions with inflammation and the release of mucus. Immediately after healing, pathological impurities disappear | Urolithiasis itself rarely provokes symptoms and discomfort. The clinic suddenly appears if the stone leaves its usual position and enters the environment. The patient notes spastic pain, unbearable constant discomfort in the lower back and pelvic area. Blood and mucus appear in the urine. If the stone is large, it clogs the lumen, causing urine to be excreted sparingly. |
| Oncology | Oncological diseases of the genitourinary system are quite common. The kidneys, uterus and ovaries have a pronounced mucous membrane, which often results in atypical cell development. The stronger the pathological process, the more mucus is detected in the urine. In order to prevent oncology, people with the constant presence of pathological impurities of 2-3 crosses are recommended to undergo a thorough examination | At the initial stages of development, mucus in the urine is invisible, like the underlying disease. A person notes a set of small signs in the form of fatigue, loss of appetite, weakness, etc. With the active growth of a cancer tumor, reaching large sizes and the formation of metastases, the clinic increases, the patient sharply loses weight, almost all organs and systems suffer. An impressive amount of mucus is detected, the urine is cloudy, after a few hours a significant sediment appears |
Experts put forward certain requirements for urine excreted in the absence of health problems. In many cases, when a person is not bothered by discomfort during urination, white discharge may be found in the biological fluid itself. They are the first signal of the formation of serious pathologies of the genitourinary system.
In most cases, when white discharge appears in the urine, patients also experience pain in the lower abdomen, as well as characteristic discomfort during and after bowel movements. If you notice the very first signs, you should immediately consult a doctor. If left untreated, complications may even lead to the need for surgery.
What analysis reveals
A general analysis can determine the presence of mucus in a baby’s urine. At the conclusion of the study results, parents will see whether discharge was detected and in what quantity.
If mucus is found, the attending physician will prescribe a repeat examination, which will reveal what was the real cause of the discharge. This disease is a symptom of pathologies that most often relate to the renal area. But don’t panic ahead of time, because discharge in a child’s urine may be normal and not pose a danger to the body and health in general.