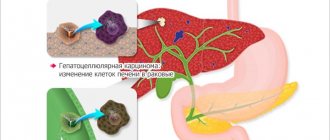
Liver echinococcosis is a dangerous parasitic invasion, which is characterized by the formation of hydatid cysts in the gland. Most often, the disease occurs in a chronic form; at the initial stage there are no negative symptoms. In the absence of timely treatment, liver dysfunction develops.
Detection of echinococcal liver damage is difficult, which is associated with an asymptomatic course at the early stage of infection. A general examination of blood and stool does not help determine the presence of helminths.
Treatment of a parasitic disease includes a set of measures - diet, hepatoprotectors, anthelmintic drugs, surgery. Without treatment, complications develop that cause disability and death.
Methods of infection, types and stages of the disease, clinical signs and treatment features are detailed in the article.
Mechanisms of development of symptoms of echinococcosis in humans
Growing echinococcal cysts lead to the development of sensitization of the body and have a mechanical effect on the organ, disrupting its functioning. Under the influence of the parasite's waste products, chronic inflammation of the affected organ develops. If the bubble is large, it can rupture and fester.
Sensitization of the body during echinococcosis
Metabolic products of the parasite lead to the development of hypersensitivity of both immediate, current and delayed types. Urticaria and eosinophilia are the most common allergic reactions. And in the event of a rupture of the bladder wall and the release of cystic fluid into the abdominal or pleural cavities, anaphylactic shock develops. In the case of multiple echinococcosis, various immunopathological reactions develop.
Mechanical impact
An hydatid cyst grows extremely slowly, but over many years (20 years or more) it can reach enormous sizes. Cases of findings of echinococcal blisters weighing 12 kg or more have been described. Multiple echinococcosis is rare. The severity of the symptoms of echinococcosis in humans is determined by the size and location of the cysts, which lead to compression of the organ and its atrophy.
Based on their diameter, cysts are classified into small (up to 5 cm in diameter), medium (6 to 10 cm in diameter), large (11–20 cm in diameter) and giant (21 cm or more).
The outer fibrous wall of the bladder reaches 0.5 cm or more. The inner shell is thin. Many brood capsules are formed in it, in which embryonic scolex are located, up to 100 in one capsule. Some of the scolex come out of the capsules and float freely in the fluid of the cyst (“echinococcal sand”). Number of scolex in 1 cubic meter. a milliliter of echinococcal sand reaches 400 thousand. Often daughter bubbles form within the bubble.
- Death and suppuration of the bladder lead to the development of acute purulent inflammation of the wall of the parasite.
- A rupture of the wall leads to the release of the contents and the implantation of scolex and daughter blisters into neighboring organs.
- Excessive infection with echinococcal eggs leads to the formation of many blisters localized in different organs.
- When the parasite dies, it becomes calcified.
Echinococcosis often occurs under the guise of a tumor process.
Rice. 2. The photo shows echinococcal cysts.
Rice. 3. Giant echinococcus in the liver.
Rice. 4. Shells of echinococcal cysts.
Features of pathogenesis
From helminth eggs in the human stomach and intestines, larvae are released, which penetrate through the wall of these organs first into the blood and then into the liver. The bulk of the larvae linger here, others can spread to other organs through the bloodstream. These can be the lungs, the brain and spinal cord, the kidneys, the heart, and the spleen.
Having lingered in any organ, after about 4-6 months a larval stage, or echinococcal cyst, up to one centimeter in size is formed, which is covered with a connective tissue capsule. Every year the cyst grows another 2-3 centimeters.
Thus, in some cases, with a long absence of symptoms, the bubble can reach gigantic sizes and contain up to several liters of fluid inside.
A growing cyst compresses the surrounding organs and tissues, causing various (nonspecific) symptoms. It is important to note that there can be several hydatio cysts in one organ.
When the parasite dies and a secondary bacterial infection attaches, the hydatid cyst turns into an abscess (the contents of the cyst are replaced with pus).
An hydatid cyst is a time bomb. If the integrity of the membrane of the bladder is violated, protoscolexes and small daughter cysts can spread through the bloodstream into the surrounding tissues and other organs, where new cysts will form. Also, damage to the shell of echinococcus can cause a severe allergic reaction, including anaphylactic shock, which can lead to serious consequences and result in the death of the patient.
Symptoms of echinococcosis in humans
Symptoms of echinococcosis in humans are polymorphic. They depend on the location of the cysts, their number and size, growth rate, as well as the age of the patient, the reactivity of his body and concomitant pathology. The disease develops slowly and lasts for years. The first symptoms of the disease often appear many months and even years after infection. Often, hydatid cysts are detected by chance. For example, with fluorography of the lungs or ultrasound of the liver.
The rate of increase in symptoms of echinococcosis in humans depends on the location of the cysts in the affected organ. So, when localized in the peripheral parts of the liver, cysts do not show themselves for quite a long time. When localized at the gate of the liver, as the cyst grows, it begins to compress the liver ducts quite early, which is manifested by jaundice; when the portal vein is compressed, ascites develops.
There are 4 stages of echinococcosis in humans: latent, stage of mild symptoms, stage of a detailed clinical picture and the fourth stage of complications.
Rice. 5. Echinococcosis of the brain.
Symptoms of echinococcosis in humans in the latent stage
The duration of the latent stage of echinococcosis (from the moment of infection to the appearance of the first clinical symptoms) is difficult to establish. It is often not possible to accurately determine the time of invasion. The appearance of the first subjective symptoms depends on the location of the hydatid cyst. When the cyst is localized in the peripheral parts of the liver, the latent phase lasts for years. With echinococcosis of the spinal cord, the latent phase is short, since even the slightest growth of the cyst already puts a certain pressure on the organ, which immediately leads to complications - paresis and paralysis of the limbs and disorders of the pelvic organs.
In some cases, echinococcosis is asymptomatic throughout life and is discovered unexpectedly on sectional findings in the form of calcified cysts in people who died from other diseases.
Symptoms of echinococcosis in humans in stage 2
Following the latent stage comes a period of mild subjective manifestations of the disease. Symptoms of echinococcosis in humans during this period depend on the location of the cysts. So, with echinococcosis of the liver, patients may complain of a feeling of heaviness and pain in the right hypochondrium, with lung disease - shortness of breath and difficulty breathing, with damage to the brain, patients complain of headaches.
Symptoms of echinococcosis in humans in the 3rd stage
In the stage of pronounced clinical manifestations, the symptoms of echinococcosis are significantly expressed, symptoms of allergy and intoxication appear, and the cyst itself is determined by palpation, x-ray examination or ultrasound.
Complications of echinococcosis
Complications of echinococcosis at the stage of cyst growth occur at any location.
- Almost immediately, already in the latent stage of the disease, complications arise when the cyst is localized in the spinal cord. The slightest growth of the formation puts pressure on the spinal cord, which is complicated by paresis, paralysis and disorders of the pelvic organs.
- When the cyst is localized in the peripheral parts of the liver, complications occur late. When localized at the portal of the liver, the echinococcal bladder begins to compress the liver ducts quite early, which is manifested by jaundice; when the portal vein is compressed, ascites develops.
- When localized in the lung tissue, the pressure of the growing cyst on the bronchi manifests itself as atelectasis. The pressure of a large echinococcal bladder leads to displacement of the mediastinal organs.
- Growing cysts cause pathological bone fractures.
Dangerous complications of echinococcosis are associated with suppuration of the cyst and rupture of its walls.
Suppuration of a cyst during echinococcosis occurs when a crack forms in its shell, through which bacteria freely enter. The source of infection is the biliary and respiratory tract. Suppurated echinococcal blisters appear as abscesses and occur with symptoms of purulent intoxication and severe pain in the affected organ.
When the wall ruptures, the contents of the cyst spill into the body cavity, which is accompanied by pain and anaphylactic shock and bleeding. When the contents of the echinococcal bladder come out, the scolex is implanted into neighboring organs.
- When localized in the liver, the contents of the cyst spill into the abdominal cavity, which is accompanied by anaphylactic shock, the development of peritonitis and the spread of the pathological process.
- When localized in the lung tissue, the contents of the cyst spill into the pleural cavity, which leads to the development of pleurisy.
- Often, when the walls of the bubbles rupture, the contents pour into hollow organs: bile ducts, stomach, intestines or bronchus.
The causes of death in patients with echinococcosis are toxic shock, which developed as a result of a breakthrough of the cyst contents into the pleural or abdominal cavities, metastasis to vital organs, and amyloidosis.
Rice. 6. Echinococcal blisters in the lungs look like metastases.
Diagnostics
The rate of increase in symptoms when a person is infected with echinococcus is associated with the area of formation of the echinococcal bladder; the disease can progress up to 10-20 years, without bringing any subjective disorders to the patient. Clinical manifestations are also nonspecific:
- in the blood, as with any helminthiasis, the level of eosinophils increases;
- the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and platelets increase;
- signs of allergic reactions appear (itching, rash).
At the first symptoms, an urgent comprehensive diagnosis is necessary, which consists of instrumental examination methods - ultrasound, MRI, CT, puncture of the affected area, serological diagnostic method to detect IgG antibodies to echinococcus.
Symptoms of liver echinococcosis in humans
Echinococcosis of the liver in humans occurs in 45 - 85% of cases. Most often, oncospheres settle in small capillaries of the right lobe of the liver. Echinococcal cysts grow slowly. When the cyst is localized in the peripheral parts of the liver, the latent phase lasts several years, complications occur late. As the echinococcal bladder grows, patients begin to complain of a feeling of heaviness and pain in the right hypochondrium.
When localized at the portal of the liver, the cyst quite early begins to compress the ducts of the liver, which is manifested by jaundice; when the portal vein is compressed, ascites develops.
Suppurating cysts appear as abscesses and occur with symptoms of purulent intoxication and severe pain in the affected organ. The source of infection in this case is the biliary tract.
When a cyst ruptures, its contents enter the abdominal cavity, which is accompanied by the spread of the pathological process, the development of peritonitis, and anaphylactic shock. Death can occur from toxic shock. The contents of the cyst can enter the pleura and cause purulent pleurisy, into the biliary tract and cause purulent cholangitis.
The Katsoni test, radiography and ultrasound of the abdominal organs are the main methods for diagnosing the disease. Surgical removal of an hydatid cyst with its contents and membranes is the main method of treating liver echinococcosis.
Rice. 7. Echinococcal blisters in the liver.
For more information about liver echinococcosis, read the article “Hepatic echinococcosis: symptoms, diagnosis and treatment”
Indications for the study
Echinococcosis may not manifest itself in any way for a long time. A person can notice deviations in health after several months, and sometimes even years. You should consult a doctor if you notice the following symptoms:
Diagnosis of toxocariasis
- increased fatigue, fatigue and constant weakness;
- skin rashes in the form of small rashes on any part of the skin;
- sudden and causeless changes in temperature;
- severe headaches, difficult to relieve with painkillers;
- formation of cysts in the liver, lungs, abdominal cavity, brain, etc.
The examination results are deciphered by a surgeon, infectious disease specialist or parasitologist. All tests are performed in immunological laboratories.
Symptoms of pulmonary echinococcosis
In the general structure of the incidence of echinococcosis, 20 - 30% of cases are due to pulmonary echinococcosis. This is the second most common localization after liver echinococcosis (80%).
The asymptomatic stage lasts a long time. Often the disease is discovered by chance on an X-ray examination.
- As the echinococcal bladder grows, certain symptoms associated with its localization begin to appear. The cyst can compress the lung tissue, blood vessels, bronchi and pleura. Shortness of breath, difficulty breathing, cough and chest pain are the most common symptoms of pulmonary echinococcosis.
- Inflammation of the lung tissue is manifested by an increase in body temperature to subfebrile levels. When the cyst suppurates, the temperature rises to 39 °C and bothers the patient for a long time.
- With pulmonary echinococcosis, patients develop symptoms of intoxication and allergization of the body (urticaria, eosinophilia and pathological immunological reactions).
- The pressure of a large echinococcal bladder leads to displacement of the mediastinal organs. With pressure on the bronchi, atelectasis develops.
- The appearance of cracks in the membrane leads to suppuration of the cyst. Suppurating cysts appear as abscesses and occur with symptoms of purulent intoxication and severe pain in the affected organ. They cause pneumonia (long-term pneumonia) and aggressive allergic reactions. In 90% of cases, the cyst breaks into the bronchus, less often into the abdominal cavity, pleura, pericardium and bile ducts.
Immunological tests, chest X-ray, CT and MRI are the main methods for diagnosing the disease. The basis of treatment is combination therapy, including the prescription of antiparasitic drugs and surgical techniques.
Rice. 8. Echinococcus in the lungs. The left radiograph of the lungs shows two homogeneous shadows in the left lung; the right radiograph shows the shadow of a cyst in the lower lobe of the right lung.
Echinococcus and children
Echinococcosis in children is often detected
.
The risk of getting sick in children is higher, as they actively learn about the environment and interact with pets. Since the parasite grows slowly, the disease is detected after several years (in adolescence). In young children, detection of a cyst is an accidental finding. They may be detected during an x-ray or ultrasound for another reason. Diseases can be detected after the Mantoux test. Echinococcosis in children occurs with the following symptoms:
- weight loss, stunted growth;
- decreased attention, sleep disturbances, memory;
- skin changes - rash, itching, jaundice;
- loss of appetite, nausea, abdominal pain.
If these signs are present, you should contact a pediatrician or infectious disease specialist for an in-depth examination. Diagnosis of the disease in children necessarily includes serological tests.
When a test for antibodies to echinococcus is prescribed, parents may have a question - what is it?
Antibodies are protein molecules
in a child’s blood that can be detected using special reagents. In addition to echinococcus, the cause of these symptoms can be Giardia, roundworms, and toxocara.
Echinococcosis of the brain
Echinococcosis of the brain is characterized by a long asymptomatic course. This is due to the slow growth of cysts. As a rule, patients consult a doctor when the cyst has reached a large size and the patient has developed focal symptoms and hypertension syndrome.
- The focal symptoms of cerebral echinococcosis depend on the location of the cyst. In 20% of patients with the disease, cortical epileptic seizures occur, but most often (up to 60%) patients experience paresis of the limbs.
- With a long course of the disease, a number of patients develop mental disorders in the form of delirium, depression and dementia.
- Intracranial hypertension syndrome manifests itself in the form of dizziness, vomiting and congestive optic discs. Patients often experience secondary optic atrophy and blindness.
In 30% of cases, patients with cerebral echinococcosis have an increased number of eosinophils. The cerebrospinal fluid exhibits elevated protein levels and pleocytosis. Pleocytosis may sometimes be absent.
Echinococcosis often occurs under the guise of a brain tumor. Facilitates the diagnosis of the disease by CT and MRI of the brain, detection of echinococcal cysts in other organs, conducting a skin allergy test and serodiagnosis.
Echinococcosis of the brain is continuously progressing. Removal of the cyst followed by antiparasitic treatment is the only treatment method. Otherwise, the disease invariably leads to the death of the patient.
If the cyst is removed without capsule rupture, the prognosis is favorable. If the capsule ruptures and the parasite disseminates through the cerebrospinal fluid spaces, the prognosis is unfavorable. Relapse in such cases, even with antiparasitic treatment, occurs after 1 - 2 years, followed by death.
Rice. 9. Echinococcosis of the brain. The MRI image on the left shows multiple cysts in both hemispheres of the brain. The picture on the right shows a single huge cyst in the frontal region.
Disease prognosis
With timely seeking help and adequate surgical treatment using anthelmintic therapy in the postoperative period, the prognosis remains favorable.
In the presence of complications, the prognosis mainly depends on the spread of the infectious process and the severity of the patient's condition. Patients who have been treated for this disease should be followed up in the clinic over the next few years. They need to take blood and urine tests, undergo X-ray and ultrasound examinations at least once a year.
Video Photo Tables
Echinococcosis of the spinal cord
If, during infection, Echinococcus larvae hematogenously from the intestine enter the epidural tissue of the spinal cord or the capillaries of the spongy substance of the vertebral bodies, then they speak of primary echinococcosis of the spinal cord. If the parasite larva has invaded the structures of the spinal cord from neighboring organs (for example, when a cyst ruptures), they speak of secondary echinococcosis.
- With intradural localization, the latent stage is short-lived, since even the slightest growth of the cyst already puts a certain pressure on the organ, which immediately leads to complications - paresis and paralysis of the limbs and dysfunction of the pelvic organs.
- The vertebral bodies are affected less frequently. As the echinococcal bladder grows, the vertebral body gradually begins to collapse, then the arches, and the spinal cord is compressed. Initially, the patient experiences pain that intensifies with sudden movements. Further, the mobility of the spine is limited, and kyphoscoliosis is formed. The rectus dorsi muscles thicken in the form of a roller.
Echinococcosis of the spinal cord should be distinguished from tuberculosis and spinal tumors.
Surgical treatment is the main method of treatment.
Rice. 10. The photo shows an echinococcal cyst of the spinal cord.
Causes of the disease
The main host of Echinococcus is the dog. It becomes charged with the pathogen when eating meat. A person can become infected with echinococci after contact with animals
or due to poor hygiene. In some cases, infection occurs through vegetables or fruits. They may contain oncospheres of the parasite.
Cases of infection often occur among hunters (when cutting meat and animal skins) and shepherds (from sick animals). Is Echinococcus transmitted from person to person? With everyday and physical contact - no. Humans are the definitive host, as they do not transmit the disease to anyone. Infection can occur during surgery, so surgeons are at risk of infection.
The term cystic echinococcosis has been heard, but not everyone knows what it is. There are two types of disease: alveolar and cystic.
With cystic echinococcosis, a cyst forms in the right lobe of the liver. In some cases, several formations occur at once. The alveolar type of disease occurs when the lungs are affected.
Echinococcosis of the kidneys
An hydatid cyst develops in the renal cortex. The left kidney is most often affected. There are several types of hydatid cysts:
- A cyst whose wall is not damaged is called closed.
- A cyst that protrudes into the renal calyx and is washed by urine with an intact wall is called pseudo-closed.
- A cyst that protrudes into the renal calyx and is washed by urine with a damaged wall is called open. In this case, the contents of the cyst constantly leak into the urine (echinococcuria).
With echinococcosis, the kidney is deformed, its calyces and pelvis dilate, the renal parenchyma atrophies, the mobility of the organ is impaired, and its displacement is noted. Upon death, the parasite undergoes calcification.
Weakness, malaise, increased fatigue, pain, even renal colic are the main symptoms of kidney echinococcosis in humans. The cause of renal colic is the discharge of daughter echinococcal blisters. During this period, blood appears in the urine. When the echinococcal bladder suppurates, an increased number of leukocytes appears in the urine. With an open cyst, free-floating daughter blisters can be seen during cystoscopy.
Removal of the hydatid bladder is the main type of treatment for kidney echinococcosis.
Rice. 12. Echinococcosis of the kidney.
Symptoms
Talking about what echinococcosis is, it should be noted that it can be asymptomatic in humans for decades. If clinical symptoms occur, then pathognomonic signs do not appear.
Whether it is echinococcosis of the brain or liver, there are three stages of development.
The first (latent) begins from the moment when the parasites invade the tissue. This period lasts until the first symptoms appear. Then comes the second stage, when the following clinical manifestations make the disease known:
- Pain in the place where the cyst is formed.
- Hives.
- Severe weakness.
- Nausea.
- Weak appetite.
- Intermittent diarrhea.
- Pain and heaviness in the right hypochondrium.
- Skin itching.
- Other specific manifestations, depending on which organ is affected.
The third stage is complicated. The disease is already advanced, and the cyst may rupture. This is fraught with serious consequences, such as pleurisy and peritonitis.
If the cyst festers, then severe intoxication and high fever occur. Obstructive jaundice, ascites, and pathological fractures often occur.
Echinococcosis of the heart
Cardiac echinococcosis is rare. Its share among all cases of the disease ranges from 0.2 to 2% of cases. The parasite larvae settle in the myocardium (usually in the left ventricle). Cysts are extremely rarely localized in the pericardium.
Cysts grow slowly - from 1 to 5 years.
- Compression of the coronary vessels leads to the development of coronary disease and cardiac conduction disturbances. Chest pain and shortness of breath are the main symptoms of echinococcosis in humans of this localization.
- Some patients develop myocardial infarction and malignant cardiac arrhythmias.
- Cases of complete transverse heart block have been described.
Suppuration followed by rupture of the cyst ends in the death of the patient.
Removal of the cyst is the main type of treatment for cardiac echinococcosis.
Rice. 13. Echinococcus in the heart.
Prevention measures
Prevention of echinococcosis in humans includes sanitary education among city residents, especially those groups of the population who are employed in the agricultural sector. Medical measures are also aimed at identifying and medical examination of infested individuals by examining people engaged in fur processing, manufacturing fur and leather products, and hunting.
Improving hygiene in slaughterhouses, following the rules for destroying the organs of sick animals, checking animals for infection and timely deworming them reduce the incidence of echinococcosis in domestic animals.
Measures to catch street dogs and destroy rodents also prevent the spread of infection among the population. Following personal hygiene rules, including limiting contact with street dogs, regularly washing hands after going outside, and washing food, helps maintain people's health.
Echinococcosis of the spleen
Echinococcal cysts in the spleen can be single or multiple. They are localized in its different departments.
- With a single hydatid cyst, the spleen acquires a dense elastic consistency, its capsule thickens, and the organ acquires a dark cherry color.
- With multiple cysts, the surface of the spleen becomes lumpy, its tissue atrophies, and the organ resembles a sac (“hydatid sac”).
If the course is complicated, the cyst may fester. When the wall ruptures, the contents of the cyst enter the abdominal cavity, which is accompanied by pain and anaphylactic shock; when the contents of the echinococcal bladder escape, scolex implantation occurs in neighboring organs.
Treatment of echinococcosis of the spleen is only surgical.
Rice. 14. Echinococcosis of the spleen. The photo on the right shows a huge cavity at the site of the hydatid cyst.
Treatment
After the diagnosis of echinococcosis is established, treatment begins immediately. Surgery
is used to eliminate cysts . In case of multiple formations, several operations are performed or all cysts are eliminated during one, if their location allows.
The parasite is removed along with the capsule and affected tissues. If the formation is gigantic in size, the liquid is removed from it by puncture, and then the capsule itself is removed.
To prevent the spread of echinococcus throughout the abdominal cavity, the walls of the cyst are treated with formaldehyde.
Important!
Echinococcosis can be slowed down using drug treatment.
Antihelminthic drugs are prescribed for the entire period
.
They are taken before surgery and in the postoperative period. An example of drugs that eliminate parasites are Vermox, Wormil. The drugs contain mebendazole and are available in tablets. The dose is increased gradually, from 1000 mg to 3500 mg per day. Treatment lasts 1-1.5 months.
For the pulmonary form, expectorants are prescribed. These include ACC, Ambrobene, Abrol. They are taken in tablets, 3 times a day. The course of treatment is from 5 to 7 days.
To reduce the inflammatory process, glucocorticoids (prednisolone) are used. After surgery, antibiotics are prescribed - Cefepime, Ceftazidime.
What it is
Echinococcosis is a disease caused by the parasite Echinococcus. The disease is typical for animals and humans; in the body, the pathogen affects any organ, often the liver and lungs. The highest prevalence of echinococcosis is recorded in regions where the main activity is agriculture associated with raising livestock . The disease is equally dangerous for adults and children; at the first symptoms, you should go to the hospital for diagnosis. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, surgical treatment is performed by removing tissues and cysts affected by echinococcosis.
Pathogen
This disease is caused by a pathogen called echinococcus, which is a larva that is introduced into the body in various ways. In appearance, the larva looks like a bubble with one or several chambers. Inside the vial is filled with liquid contents necessary for the development of the embryo. The bubble has an endogenous property when, due to some of its areas, new copies of the pathogen are reproduced. As a result, reproduction occurs, during which the volume and number of bubbles constantly grows, which is reflected in the surrounding tissues.
Photo 1. Appearance of the pathogen and cyst
Life cycle of helminth
Life cycle of the helminth Echinococcus photo
The intermediate hosts of the parasite are herbivores (sheep, cows) that eat grass contaminated with parasite eggs, as well as pigs that can eat the feces of sick dogs. In the body of intermediate hosts, the embryo is released from the eggs of echinococcus, which penetrates the bloodstream and spreads to various organs of the animal. There, an echinococcal cyst begins to form from the embryo, containing many vesicles containing the larvae of the parasite.
Predators, as well as dogs fed meat from infected animals, swallow hydatid cysts, after which they become infected with echinococcosis. In the intestines of predators, Echinococcus larvae are released from the cysts, which then turn into sexually mature tapeworms. Segments of echinococcus, which contain parasite eggs, come out of the intestines along with feces and can get on the dogs’ fur.
Echinococcal cyst (echinococcus) in the liver
Symptoms of liver damage during the growth of an hydatid cyst increase gradually and are absent at an early stage. Depending on which vessel or bile duct is compressed, there will be one or another symptom.
A patient with a significant size of the cystic formation (hydatid cyst) will experience heaviness in the area of the right hypochondrium, soreness, and rarely expressed pain, which may occur during complications (rupture of the echinococcal cyst, entry of its contents into the abdominal or pleural cavities).
Pain in liver echinococcosis intensifies after an error in nutrition and changes depending on the position of the body and palpation of the liver area. When palpating the right hypochondrium, there is pain, an increase in the size of the liver, the liver begins to protrude from under the edge of the costal arch.
When the bile ducts, and especially the common bile duct, are compressed, when the ducts grow and are compressed by an echinococcal cyst, yellowing of the skin is observed, and there may be itching.
Initially, jaundice with echinococcosis is mild. Slight yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes (subictericity) after some time turns into true pronounced obstructive jaundice.
Compression of the venous outflow system by an echinococcal cyst leads to the formation, increase and progression of edema of the lower extremities and ascites. Ascites - the accumulation of liquid blood in the abdominal cavity - is observed in the late stages of echinococcal liver damage. Following the liver, the spleen enlarges, upon palpation of which its significant enlargement is revealed.
Basic principles of disease treatment
Echinococcus oncospheres, which are formed during the development of helminthiasis of internal organs, migrate and spread throughout the human body in two ways - lymphogenously and hematogenously. Tissues and internal organs are at risk when the oncosphere forms at the site of the cyst.
To eliminate echinococcus, treatment can be carried out according to two basic principles:
- Conservative therapy is the treatment of echinococcosis without surgery. During this course, the doctor prescribes either drug treatment, according to indications, or chemotherapy with antiparasitic drugs. In the first case, all sorts of remedies are appropriate that relieve symptoms and help the body recover, as well as direct administration of anthelmintic tablets.
Symptoms can be relieved with antihistamines, anti-inflammatory and antiseptic medications, as well as hepatoprotectors and other agents, according to the clinical picture.
Chemotherapy is carried out if surgical removal of cysts is impossible, if the cyst has ruptured, with multiple cyst lesions (their size is not more than 5 cm), if non-viable cysts are found and for prophylaxis after their surgical removal.
- Surgery . This method is not used often, since 57% of cases lead to complications. According to statistics, 3-54% of patients, after removal of cysts, experienced relapses and needed repeated surgery, which leads to disability. To carry out such treatment, there is a strict list of indications that the specialist follows.
- Mixed treatment . In some cases, doctors resort to this method of treatment when, after surgical removal of echinococcosis cysts, concomitant antiparasitic drug treatment is required. Such measures will significantly reduce the risks of relapses and re-formation of formations.
Classification
The most common form of this disease in humans is cystic echinococcosis, also known as unilocular echinococcosis. Its causative agent is E. Granulosus sensu lato. The second most common form of the disease is alveolar echinococcosis, also known as multilocular or alveococcosis. It is caused by E. multilocularis. And the third is polycystic (neotropical) echinococcosis, caused by E. Vogeli or, extremely rarely, E. Oligarthra. Alveolar and polycystic types of echinococcosis are rarely diagnosed in humans and are not as widespread as cystic. But the polycystic type is a relatively new concept in medicine, which is often not mentioned separately, but is associated with the other two types. However, it is a serious disease with not only a high mortality rate, but also the potential for increasing incidence in many countries.
In humans, echinococcosis caused by E. Granulosus, E. Multilocularis, E. Oligarthra and E. Vogeli is localized in the liver (75% of cases), lungs (5-15% of cases), as well as other organs such as the spleen, brain, heart and kidneys (10-20% of cases). When the disease occurs in the body, the presence of slowly growing formations, which are often called cysts, is observed.
Cysts are filled with a clear substance (hydatid fluid) and have a spherical shape in all types of the disease. But in the cystic form of echinococcosis, they consist of a single compartment (chamber) and can usually be found in only one area of the body. While in the alveolar and polycystic type of the disease, the cysts have several compartments (chambers) and are accompanied by infiltrative (grow into adjacent tissues), rather than sudden growth.
Echinococcosis - what is it? (photo)
Echinococcosis is an infection of a person with the parasite Echinococcus. The adult, a long jointed tapeworm, lives only in the intestines of carnivores (dogs, foxes, wolves, etc.). In humans, the parasite is encapsulated and can grow in any organ.
Echinococcosis photo
Routes of infection:
- Contact route - infection from wild animals (during hunting, when cutting skins) or through contact with the fur of domestic animals, which have become infected with echinococcus larvae;
- Airborne droplets - inhalation of air containing parasite larvae is possible only in epidemically disadvantaged areas (hot countries, southern Russia and the Caucasus, South America);
- With food - food contamination also occurs when the parasite enters the larval stage through the air (food that has been left in the open air for a long time).
Many myths have been created around echinococcosis. To accurately know the risks of infection and the effect of the disease on the body, you should know:
- Echinococcus is very stable in the environment: it survives for a long time (from 1 month to several years) in the shade and tolerates low temperatures. Sunlight and drying out are harmful to the parasite.
- A person with echinococcosis is absolutely not contagious to others. Close contact, living together, sex, kissing and shared hygiene items are excluded from the link of infection with echinococcus.
- There is no echinococcus in the meat of animals, even carnivores; infection through meat food is excluded.
- When inhaled, the echinococcal larva (oncosphere) enters the intestines when coughing and swallowing mucus. Its further development always occurs through the gastrointestinal tract.
- Cleaning your hands with antiseptic solutions and soap will not reduce the risk of infection with echinococcus. Antibiotics, as well as antiseptics, have no effect on the parasite.
- The intrauterine route of infection with echinococcosis (from mother to child) is excluded.
- Echinococcus does not crawl through the body from organ to organ; its path lies through the bloodstream. By boring into the intestinal wall, the parasite enters a vein and migrates through the bloodstream to the organ.
- The first target of Echinococcus is the liver. Without staying there, the parasite migrates to the lungs and then to other organs: the brain, muscle tissue, kidneys, etc.
- Echinococcus does not reproduce in the human body. Infection occurs simultaneously, by one or several larvae. This is confirmed by the detection of living parasitic cysts of equal size in one or several organs.
The echinococcal larva, having settled in the organ, becomes overgrown with a dense capsule (the thickness of the walls reaches 5 mm) and begins to grow, feeding on the human body.
An hydatid cyst is a sphere with a diameter of 3-5 cm filled with fluid. Without treatment, cysts reach sizes of 10-20 cm or more.
The smallest oncospheres are attached inside the dense shell (visible during instrumental examination - ultrasound, x-ray, CT). Some encapsulated parasites die and become sclerotic. During the examination, irregularly shaped cysts are found without signs of development (dynamic observation).
What is echinococcus
Echinococcus is a tapeworm that originates and develops inside animals, parasitizing to humans and disrupting the functioning of organs. Through the fecal-oral route, the parasite is transmitted to humans or other animals and parasitizes internally. Echinococcosis is a pathological condition provoked by an echinococcus larva parasitizing a child or adult. The disease can be in remission for a long time without causing any signs of ill health.
Varieties
The type of echinococcus is classified according to the location of the parasite in the body and the nature of the cyst. There are two types of echinococcosis: single-chamber (cystic), alveolar (multi-chamber).
There are two main types of worms:
- Hydatid echinococcosis is localized in the liver.
- Alveolar echinococcosis is localized in the lung.
Worms enter the human body in eggs (vesicles). The echinococcal membrane has 2 layers, outer and inner. A liquid forms inside the bubble where small tapeworm embryos live. The bubble rapidly increases in size, squeezing and disrupting the functioning of internal organs. If it bursts, serious complications are possible.
Body structure
The tapeworm, having reached adulthood, has a length of 4-9 mm. Its body has a white tint and consists of a head and 3-5 segments, of which:
- 1 – immature;
- 2 – hermaphrodital;
- 3–4 – mature and reaches 5–6 mm in length.
The parasite has 4 suckers on its head and a hook-shaped trunk with which it feeds.
Life cycle
The life cycle of Echinococcus can be divided into 6 stages:
- The mature parasite develops and lives in the body of animals (dog, cat).
- With the animal's feces, eggs with worm larvae enter the environment.
- Herbivores ingest the eggs when they consume plants outside. As a result, the tapeworm larvae penetrate the body of the intermediate host.
- Having penetrated inside the animal, the larvae disperse through the bloodstream to all organs and lay eggs. Typically, the larvae lodge in filtering organs (liver, lung, heart).
- Cysts form at the site where the larvae are located, which inhibit the functioning of the organ and destroy it. Protoscolexes are formed in the animal body.
- They enter the body of dogs, cats or humans (the definitive host) by eating meat or other organs of a sick herbivore. Once in a living organism, the larvae attach to the small intestine and within 40 days develop into sexually mature individuals. After which their cycle ends.
Humans are both intermediate and final hosts in the development cycle of echinococcus. Usually, people become infected with echinococcus larvae when personal hygiene and preventive measures are not observed. You can also become infected through bodily contact with infected animals.
Signs of presence in people
Signs of echinococcosis appear in a child and an adult after 2–3 weeks, when the individual reaches adulthood. The disease is dangerous because it does not show visible signs for a long time. Initial symptoms of infection:
- nausea followed by vomiting;
- appetite disappears;
- dull nagging pain and tingling appear in the area of cyst formation;
- weakness, drowsiness, malaise;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- a rash all over the body similar to an allergic reaction;
- bloating;
- fever;
- pain on palpation of the chest and abdomen.
Painful sensations during echinococcosis appear in those places where the larvae are localized. Most often, pain manifests itself in the right hypochondrium. Diagnosis reveals an enlargement of the liver and spleen by 1.5-2 times. In the acute form of the pathology, the cyst can be easily felt upon palpation. Fever or chills are not observed during the development of pathology.
When liver larvae infest the liver, an abscess often forms. Due to severe compression of the gallbladder, the patient may develop jaundice. The urine becomes dark brown, the stool becomes discolored, and the skin becomes yellowish.
If a tapeworm infects the lung, the following symptoms appear:
- hard breath;
- dry cough;
- shortness of breath;
- sharp pain in the chest area;
- blue skin.
Typically, worm eggs are sent to the portal vein or pulmonary circulation. Because of this, when diagnosed, the cyst is found in the liver or lungs.
Diagnostics
The initial symptoms of the disease are difficult to determine. The patient can go to doctors for a long time, however, no positive dynamics of treatment will be identified. In this case, it is better to immediately go to an infectious disease specialist. To identify a tapeworm in a clinic, you need to do laboratory diagnostics and give a blood sample for biochemical analysis.
Diagnostic measures for identifying echinococcosis include:
- General blood analysis. If a person is infected, the level of eosinophilia increases by 15–20%.
- Katsoni's reaction. A sterile echinococcal substance is injected into a vein and the reaction is observed. A positive result is detected in 85% of patients. After removing the helminthic infestation, a negative reaction is visible a year later.
- X-ray. The image shows large domes of the diaphragm if the patient is infected.
- Radioisotope scanning. This is done to determine the size of the worm.
- CT and echolocation.
The alveolar form of the disease is detected with a tumor of the liver or other organ. It is important to correctly test for antibodies to make an accurate diagnosis.
ELISA for lung damage by parasites shows a positive result in 75% of cases, for liver damage in 95% of cases.
When a cyst ruptures in the body, a person develops a wet cough and the color of the urine changes. During laboratory tests, daughter echinococcal eggs are found in the duodenal contents.
When diagnosing pathology, the main thing is to correctly diagnose and identify the exact type of tapeworm. Symptoms of the disease can be confused with tuberculosis, polycystic disease or hepatitis. Therefore, it is important to carry out all the tests correctly to treat the real problem.
Treatment methods
If you are infected with echinococci, it is difficult to heal on your own. If the cyst has reached a large size, then when opened, there is a risk of breaking its shell and starting a purulent process.
When performing an echinococcectomy, it is possible to completely remove the cyst only in 10% of cases, if it has not reached a large size. If the tumor is large, then a puncture is made to remove the contents. This minimizes the risk of cyst rupture and prevents relapses.
Drug therapy is also provided. Treatment with Albendazole lasts 3-4 courses of 30 days. The number of courses depends on the severity of the disease. There is a 14-day break between doses of the medicine. With this treatment regimen, leukopenia often occurs as a side effect. Positive dynamics of therapy when using Albendazole is observed in 53% of cases.
If the patient's parasite larvae were localized in the brain, then a surgical treatment method is performed. With a multi-chamber form of pathology, operations are prohibited, and the further prognosis is disappointing.
Prevention
To avoid infection, it is recommended to deworm your pets and regularly observe personal hygiene rules. In enterprises and public places where people are served, it is necessary to comply with sanitary standards and regularly conduct tests for the presence of echinococci among employees. You should purchase animal products only from trusted places and avoid contact with stray animals.
As an individual prevention, you should thoroughly wash your hands after going outside and wash your food before eating. Meat and other animal products must be heat treated. By following these simple rules, you will be able to protect yourself and your family from parasite infection.
Treatment of echinococcus
If a single echinococcus has been detected, then there are all indications for surgery to remove it, and everything points to a favorable prognosis and outcome of the operation. As for multilocular echinococcus, unfortunately, in this case, the prognosis is disappointing. Because this case is inoperable. The most effective treatment method is surgery
Operational
There are several types of operations. If we are talking about radical echinococcectomy, then it is worth explaining what the essence of this operation is. During this procedure, the echinococcal cyst is completely excised. The connective tissue capsule is also cut out along with the cyst. There is a second way to solve the problem - excision of the cyst. When removing the liquid, all additional bubbles with all chitinous capsules are cut out. The formed body cavity is treated with special solutions or sutured. During the opening of an echinococcal cyst, special emphasis is placed on isolating the echinococcal fluid in the resulting cavity. If you do not remove all foci of possible infection, then if it gets on body tissue or a wound, this will lead to re-infection.
Medication
In the early stages, echinococcal brain damage can be healed without surgery.
If echinococcal cysts with a diameter of less than 3 cm are found, you should take an anthelmintic, Albendazole. It is necessary to complete a course of treatment within 28 days. Based on body weight, it is calculated how many milligrams need to be taken. To overcome echinococcosis, you need to drink 15 mg/kg per day if your body weight is less than 60 kg. If your body weight is greater, then 400 mg twice a day. To recover, you need to undergo 3 treatment courses, taking a break of up to two weeks. An indispensable part of treatment is taking absorbent drugs in order to cleanse the human body of toxins and minimize unwanted symptoms. At the same time, the attending physician prescribes analgesics, antibacterial drugs, antisecretors and others. If this course of treatment is ineffective, then the treatment regimen needs to be reconsidered.
Traditional methods
Alternative medicine for echinococcosis of the brain is appropriate only in the early stages and for prevention.
At the initial stage of development of echinococcosis in the human body, you can try to eradicate it with wormwood. In the larval phase, the helminth does not tolerate the effects of this plant, which is destructive for the parasite. The following plants have exactly the same effect on tapeworm embryos:
- mustard seeds;
- garlic;
- horseradish;
- radish;
- cinnamon.
Black peppercorns can also kill echinococcus. You need to eat one pea per day, chewing it slowly. A potion made from ginger can also be an effective method in the fight against helminths. It is necessary to grind the ginger root to the consistency of powder. Then dissolve one teaspoon of chopped ginger in about 50 g of milk or water. Drink the powder once every 2 days until you fully recover. Lemon peel is also used to deal a fatal blow to helminth larvae. To prepare the medicine you will need dried lemon zest. Grind the zest into powder and dissolve it in hot water. Treat yourself with this powder every day, taking it on an empty stomach.
Diagnosis of echinococcosis
Diagnosis of the disease depends on the area affected
Diagnosis of echinococcosis in the early stages is very difficult due to the lack of specific symptoms of the disease. As a rule, echinococcosis is diagnosed already at the stage of advanced clinical manifestations when the hydatid cyst reaches a certain size. To diagnose echinococcosis, ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs is used, first of all.
If pulmonary echinococcosis is suspected, an X-ray examination of the chest organs is used in diagnosis. To confirm the diagnosis, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are used. Carrying out serological tests to detect specific antibodies is not always effective in diagnosing helminthiasis due to the large number of cases of false negative test results.
A cyst biopsy is not used to diagnose echinococcosis, since it violates the integrity of the cyst and can lead to anaphylactic shock and the spread of the pathogen in the body.
Echinococcus: symptoms and treatment
- Characteristics of echinococcus Mechanism of human infection
- The effect of echinococcus on the body
Echinococcus is often found in the human body, the symptoms of which are rather nonspecific. To date, a large number of different parasitic worms have been studied. All of them can be divided into 3 types: round, flat (flukes) and ribbon. Echinococcus is a tape parasite. Unlike other representatives of this group (bovine and pork tapeworm), this parasite is small in size. Nevertheless, its presence in human internal organs poses a certain danger. What are the features of echinococcus, and how is echinococcosis characterized?
Have you been trying to get rid of PARASITES for many years?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to get rid of parasites by taking every day...
Read more "
Characteristics of Echinococcus
These helminths parasitize the body of humans and some animals. Humans are the intermediate host. In our country, dogs act as the final host of echinococcus. The intermediate host can be livestock (cows, pigs). For humans, Echinococcus granulosis is of greatest importance in the development of the disease. The size of a mature individual is about 3-5 mm. The body of Echinococcus consists of several parts (segments). In addition, there are suckers, hooks (bothria) and a head. The second and third segments contain the genitals, and the last segment contains the eggs.
Echinococci are able to separate their segments. The latter can move independently. This is of no small importance during the infection process. The parasite cycle is simple. The definitive host (dog) excretes echinococcus eggs along with the feces. They end up in the soil, grass, and water.
Next, the eggs must enter the body of the intermediate host. Infection of herbivorous domestic animals occurs in the process of eating grass.
At the same time, the segments of the parasite themselves can enter the body if they are on the grass. After this, larvae (oncospheres) emerge from the trapped eggs. The larvae penetrate the intestinal mucosa and are carried by the blood to various organs. The liver and lungs are most often affected. There are 2 types of echinococci: alveolar and hydatios. In the internal organs, the larvae form into fins. Finns often reach 5-10 cm or more.
Mechanism of human infection
A person becomes infected orally. This is most often observed in close contact with dogs. Currently in Russia, dogs, wolves and foxes are the main hosts of echinococcus. Children who often play with pets are also at risk of getting sick. Parasite eggs or its segments can enter the human body. The latter are often found on the fur of dogs. They get there after animals defecate. The segments may burst, and the eggs may be released and spread to surrounding objects. In this case, the eggs are brought into the person’s mouth along with dirty hands or food.
Echinococcus eggs cannot be detected with the naked eye. They are microscopic in size. After entering the bloodstream, the eggs settle in the liver, bones, muscles, and lung tissue. Bubbles form from the oncospheres. Finns grow very slowly. Within six months they reach a size of about 1 cm. Sometimes giant blisters filled with nutrient fluid form. It contains many larvae. Some people have hydatid cysts for 10 years or more. However, there are no specific symptoms of the disease.
There is another way to infect a person. The larvae can enter the human stomach and intestines by consuming contaminated meat (beef, pork) or liver.
A prerequisite is that the meat must contain larvae at the Finnish stage, and they must be viable.
A predisposing factor in this situation is insufficient heat treatment of meat. This is why it is so important to boil and fry meat well, especially large pieces.
The effect of echinococcus on the body
The negative impact of the parasite on humans is manifested in the following:
- in the formation of specific cystic formations in internal organs;
- in the formation of allergic reactions;
- in mechanical action.
Cysts can be found in any organ. Liver damage is observed in approximately 8 out of 10 people. In medical practice, there have been isolated cases when hydatid cysts were located in the pericardial sac. Large bubbles are very dangerous for humans. Under certain circumstances, they may burst, releasing liquid contents and larvae.
This is often the cause of anaphylactic shock.
The allergic effect is associated with the release of various toxic substances. As a result of this, reactions of delayed and immediate type are formed.
Large echinococcal blisters can compress organ tissue, causing atrophy.
You will be surprised how many parasites will come out if you drink a glass of regular...
Parasites will leave the body in 3 days! You just need to drink on an empty stomach...
Fibrosis may develop in the liver (replacement of normal connective tissue), and pneumosclerosis is often observed in the lungs. At the same time, the airiness of the lung tissue decreases.
Clinical signs of echinococcosis
Symptoms of this helminthiasis may be absent for a long time. If you have echinococci in your body, symptoms may include:
- nausea;
- decreased appetite;
- pain at the location of the cyst;
- weakness;
- malaise;
- bowel dysfunction such as diarrhea;
- the appearance of a rash on the body;
- vomiting;
- an increase in the size of the abdomen and its pain on palpation.
The localization of pain during echinococcosis varies. Most often, pain is felt in the right hypochondrium or epigastrium. During a medical examination, an increase in the size of the liver and spleen is often detected. In some patients, the cyst can be felt. It is defined as a dense formation. There is no increase in temperature during echinococcosis (except for complications). Fever may be the result of a secondary bacterial infection.
Damage to the liver by the parasite is dangerous due to the possible formation of an abscess. In cases of compression of the bile ducts of the liver, obstructive jaundice develops. In this situation, the skin and visible mucous membranes acquire a yellowish tint. The color of the urine may change (it becomes dark). Discoloration of stool occurs. If a person has a cyst in the lung, the following symptoms are possible:
- cough;
- difficulty breathing;
- pain in the chest area;
- blue discoloration of the skin.
Most often, when eggs enter the body, they rush into the portal vein system and into the pulmonary circulation. Hence the frequency of detection of cystic formations in the liver and lungs.
Diagnosis and treatment of echinoccosis
Before treating echinococcus, it is necessary to make a diagnosis. Diagnosis of the disease includes collecting a life history, epidemiological history and anamnesis of the disease. In this case, the fact of contact with animals or consumption of insufficiently cooked meat is important.
The risk group includes persons in contact with wild and domestic animals (foresters, shepherds, hunters, dog handlers). Laboratory diagnosis involves a blood test. General analysis and biochemical analysis can reveal eosinophilia, increased levels of enzymes (AST, ALT), bilirubin. To detect the pathogen, serological research methods (ELISA, RNGA) or polymerase chain reaction are used.
Treatment of echinococcosis is most often surgical. Conservative therapy can be used only for small cystic formations.
The safest method is to remove the cyst without opening it, because otherwise there is a risk of spreading echinococci. Tissue insulation is required. If surgical treatment is not possible, anthelmintic drugs are used. The most powerful drug is Albendazole.
The drug is contraindicated in case of liver failure, retinal pathology, during pregnancy and breastfeeding. It should also not be given to children under 6 years of age. An alternative option is the use of Mebendazole.
Prevention of the disease includes veterinary supervision, periodic examination of dog breeders, foresters, livestock breeders, washing of vegetables and fruits, personal hygiene, careful heat treatment of meat and liver of killed domestic animals. Thus, echinococcosis requires timely detection and treatment.
How to get rid of echinococcus
Treatment of echinococcosis is prescribed by an infectious disease specialist after specifying the stage of the disease, the size and number of cystic blisters. Getting rid of the parasite becomes possible thanks to:
- taking medications;
- carrying out the operation.
According to medical statistics, taking medications leads to the complete disappearance of echinococcal infections or their reduction in only 20-30% of patients. In especially severe cases, the effectiveness of drugs for echinococcosis decreases even more, which requires surgery.
Medication course for infection with echinococcus
After ekinococcosis has been confirmed, drugs are used to eliminate small and medium-sized Finns. Therapy is carried out using:
- Albendazole;
- Vormina;
- Mebendazole;
- Vermoxa.
Taking Albendazole for echinococcosis provides paralysis of the muscles of the parasites. The drug suppresses the breakdown of glucose and the production of ATP molecules, resulting in the death of the worms.
Thanks to the use of Vormin, the metabolism in the body of echinococcus larvae is disrupted. The death of helminths occurs quickly. They are eliminated from the patient’s body on the second day.
Mebendazole tablets cause negative changes in the energy processes occurring in the body of worms. The drug is also effective for mixed invasions.
Vermox deprives parasites of the ability to feed on glucose. Lack of nutrition provokes the death of helminths on days 2-3 of treatment.
The listed drugs for echinococcosis have certain contraindications. It is prohibited to carry out a treatment course in case of severe renal pathologies or poor tolerability of the active components of the drugs.
Drug treatment of elderly patients requires increased caution. This category of patients can be prescribed folk remedies for echinococcosis.
Surgical treatment of echinococcosis
The basis for surgery for echinococcosis is the extensive spread of parasites in the patient’s body, the course of the disease with relapses, and the presence of a large cyst. The intervention is performed under general anesthesia.
To remove Finnish echinococcus, use:
- laparoscopy method (minimally invasive percutaneous intervention);
- removal of the cyst and adjacent tissue areas.
At the stage of preparation for surgery and after the intervention, a course with anthelmintic drugs is required. Next, patients will need annual diagnostics, including ultrasound, radiography, and determination of antigens to echinococcus. Such measures help prevent the possibility of relapse.
Persons who show no signs of re-infestation over the next 5-7 years are removed from the register and considered healthy.
Treatment of echinococcosis
To treat echinococcosis, anthelmintic drugs and surgical removal of the cyst are used.
Treatment of echinococcosis is long, complex and expensive. As a rule, complex therapy is used - surgical removal of cysts and treatment with anthelmintic drugs.
For cystic echinococcosis, the most common treatment is surgical removal of the cysts in combination with the use of albendazole (Vormil) or mebendazole therapy.
For inoperable cases of echinococcosis, an alternative treatment method is the use of PAIR - a technique (puncture of the cyst, aspiration of its contents, injection into the cavity of the cyst of a scolitic drug that destroys the membranes of the parasite and its subsequent re-aspiration). PAIR - the technique is more effective in combination with treatment with albendazole or mebendazole. If for some reason its use is impossible, treatment with albendazole is prescribed for a period of three to six months.
For alveolar echinococcosis, the only treatment method is surgical removal of cysts using albendazole as monotherapy or its combination with mebendazole. If surgical treatment is not possible, I use a long-term (more than six months) combination of albendazole and mebendazole.
Liver transplantation is proposed as an alternative treatment for liver echinococcosis. However, this treatment method is very risky, since the patient may be re-infected with echinococcosis.
Spreading
Granulosus is very common. In very few countries it is believed to be completely absent. Regions where there is a high prevalence of infection often coincide with rural areas, grasslands, where dogs are capable of eating infected animals or parts of their carcasses.
multilocularis is most common in the Northern Hemisphere, including Central and Northern Europe, Asia and North America. However, its distribution was not always like this. For example, until the end of the 1980s, the existence of this type of echinococcus was known only in France, Switzerland, Germany and Austria. But there was a shift before the early 2000s, thought to be caused by an increase in the number of infected foxes in parts of France and Germany. As a result, new endemic areas appeared - Switzerland, Germany, Austria. As well as the countries closest to them - the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, Poland, the Czech Republic, Slovakia and Italy. Although alveolar echinococcosis is not yet very common, it is believed that it may become more common in some countries in the near future. This may happen due to the ability of E. multilocularis to spread.
Unlike the previous two species of Echinococcus, E. Vogeli and E. Oligarthra are limited to Central and South America. In addition, polycystic echinococcosis caused by these parasites is considered an extremely rare infection.
Lungs
This paired organ often becomes the “target” of the disease. Since we are talking about the symptoms and diagnosis of echinococcosis in humans, it is necessary to list the signs indicating its development in this case. They can be identified in the following list:
- Dry cough. Over time, sputum begins to appear, sometimes even with blood.
- Severe chest pain of a pressing nature.
- Dyspnea.
- Protrusion of intercostal spaces.
- Chest deformity.
Often this condition is complicated by exudative or dry pleurisy, perifocal inflammation of the lung tissue.
The cyst can fester and break into the pleural cavity or bronchi. This is accompanied by coughing attacks and the release of light sputum mixed with blood in huge quantities. Other symptoms also appear:
- Lack of air.
- Cyanosis.
- Acute chest pain.
- Fever.
- Chills.
- Anaphylactic shock.
In the early stages, with timely diagnosis in the clinic, echinococcosis is treated with medication. But if complications develop, urgent surgery is necessary. With timely intervention, the prognosis can be favorable.
Folk remedies
Treatment of parasites with folk remedies is used only as an addition to the main therapy. Refusal to undergo surgery may worsen the patient's condition and cause complications that are incompatible with life.
Antiparasitic plants include wormwood, tansy, and ginger. They are brewed and drunk as tea. Tansy and wormwood can be consumed dry, washed down with water. The use of herbs is acceptable if there is no allergic reaction to them.
Kinds
Experts distinguish 2 main forms:
- Hydatiosis – echinococcosis of the liver.
- Alveolar - the life activity of the microorganism occurs mainly in the pulmonary sacs.
In the human body, microscopic creatures live, develop, and reproduce only in the form of small larvae, which have a uniform appearance, reminiscent of bubbles.
How is echinococcosis transmitted?
Petit transmission of echinococcosis photo
A person becomes infected with echinococcosis by ingesting the eggs of the parasite. This occurs when personal hygiene rules are not observed - when eating unwashed vegetables and fruits that are contaminated with the feces of animals infected with infection, when contacting sick animals (dogs) whose fur may contain parasite eggs. Humans are an accidental intermediate in the transmission of infection. It is impossible to become infected with echinococcosis from a sick person.
Children are more often infected with echinococcosis, which is associated with their more frequent failure to observe personal hygiene, in contrast to adults. Infection often occurs in the summer, since echinococcus eggs remain viable for a long time in warm conditions.
Prevention of echinococcosis
Prevention of echinococcosis involves washing hands, vegetables and fruits
Prevention of echinococcosis presents some difficulties due to the fact that the disease in animals is asymptomatic. The main measures to prevent helminthiasis include deworming dogs and fighting stray dogs. In addition, preventive measures include ensuring hygiene in slaughterhouses and excluding dogs from access there.
In private households, to prevent echinococcosis, it is necessary to prevent dogs from eating the entrails of slaughtered livestock. A new method for the prevention of alveolar echinococcosis is vaccination with the echinococcus antigen. The method has already shown its safety and effectiveness in research.
Personal preventive measures include maintaining hygiene - washing hands before eating, eating well-washed vegetables and berries.
Tags: Parasitic
2 Comments
- Gulbarshin:
02/13/2015 at 11:07Great. I liked it very much. Thank you.
Answer
- PAVEL:
24.11.2017 at 14:12
Zdravstvuite.2 goda nazad na levom liogkom bil 400ml.exinakok ugalili.sdelali tomografiu i obnarujili na selezionke ocen malenki. oktyabre2017g. sdelali operaciu udalili selezionku.sdelali povtornuiu tomografiu vsio cisto.dlia profilaktiki kakoi preparat prinimat v kakoi dozirovke i kakoe vremia.zaranee blagodariu.
Answer