Execution method
- The patient lies down on a hard, flat surface. In a doctor's office, this is an examination couch in a horizontal position.
- The patient relaxes for a minute and restores breathing. The abdominal muscles should not be tensed before the examination.
- The doctor feels the patient's abdomen, determining the source of pain.
- When a sensitive spot is found, the doctor slowly presses his finger or stethoscope on the anterior wall of the peritoneum and quickly removes his hand.
With the Shchetkin-Blumberg symptom, pain is the main indicator of pathology. If the doctor relieves the pressure on the peritoneum and the pain intensifies, then the symptom is positive. If it remains the same, then it is negative.
A positive reaction is a sign of peritoneal irritation
What is Shchetkin-Blumberg symptom
The essence of the diagnostic examination is that with the help of a certain palpation technique it is possible to cause a persistent attack and confirm the presence of acute inflammation. If it is limited, the symptom is determined locally. With diffuse pathology, the whole stomach will hurt.
A questionable result is recognized when the patient experiences pain, but it is mild or unexpressed. When the level of discomfort after manual examination does not change in any way, the presence of acute surgical pathology is excluded. The described symptom is ineffective in situations where the patient has excessive tension in the muscles of the anterior wall of the peritoneum, accumulation of fluid inside its cavity, the presence of gases in the intestines, and the presence of a massive subcutaneous fat layer. In this case, additional palpation techniques are used to clarify appendicitis.
https://youtu.be/scBTWmdACXM
Differential diagnosis
Features of diseases that are detected by palpation.
| Diagnosis | Where does it hurt | Characteristic symptoms |
| Acute appendicitis | The pain is localized in the right iliac fossa | Percussion is accompanied by pain in the lower right quadrant of the peritoneum. When turning on the left side while lying down, the pain in the right side intensifies |
| Diffuse peritonitis | Pain manifests itself in all parts of the abdomen | The reason is a breakthrough of the stomach and the entry of contents into the peritoneum |
| Attack of acute pancreatitis | The pain is localized near the left hypochondrium | On palpation, the beating of the abdominal aorta is absent or weakly palpable. Amylase level increased in urine test |
| Stomach or duodenal ulcer | The pain affects the entire abdomen | An x-ray shows a layer of air resembling a sickle between the liver and diaphragm |
| Ectopic pregnancy | My whole stomach hurts | The muscles of the abdominal wall are slightly tense. The patient complains of delayed menstruation, rapid pulse and weakness. When making a diagnosis, data from an external examination of the uterus are taken into account. |
Symptoms of appendicitis
Appendicitis can manifest itself in different ways depending on the anatomical location of the appendix. It can be located in the retroperitoneum, near the liver, and even move to the pelvis during pregnancy. For this reason, no doctor can unambiguously make a diagnosis based solely on complaints of pain in the abdominal area.
The following are considered classic signs:
- pain in the epigastric region that migrates down and to the right. This is due to the pathogenesis of appendicitis and the characteristics of the innervation of the appendix;
- gradual increase in pain;
- lack of appetite;
- vomit. As a rule, with appendicitis it occurs once or twice. In this case, nausea and vomiting appear after the onset of pain;
- slight increase in temperature (up to 37-38°C);
- diarrhea or frequent and painful urge to have bowel movements;
- frequent urination;
- increased heart rate;
- occasionally there is an increase in blood pressure;
- Children with appendicitis typically experience pain during urination. This is due to the fact that an inflamed appendix irritates the bladder.
Important! If a person experiences severe abdominal pain, under no circumstances should they be given painkillers before a medical examination. Anesthesia can cause a blurred clinical picture, which, in turn, will lead to a diagnostic error that can cost the patient his life.
Women's diagnostics
Women also have specific manifestations of appendicitis. Considering that the symptoms of the appendix often resemble gynecological pathologies, additional diagnostics make it possible to identify the disease.
- Promptova - when examined by a gynecologist, the cervix moves, the appearance of pain indicates the development of gynecological pathology, excluding appendicitis.
- Zhendrinsky - when you press your finger on the Kümmel point, below the navel, pain appears, which intensifies when standing up and confirms the presence of appendicitis.
- Brando - pressing on the left rib causes pain during pregnancy.
The diagnosis of an inflamed appendix is not limited to the above symptoms. It is aimed at the initial examination of the patient, but is not able to fully guarantee the correct diagnosis. Accurate diagnosis depends on the results of instrumental and laboratory examinations.
Appendicitis in childhood
Symptoms of appendicitis in infants are somewhat different from those in older age groups.
Parents should be alert to the following points: poor appetite or the child’s refusal to eat, constant crying or screaming, nausea and vomiting (repeated), hyperthermia. In addition, the baby does not sleep well, his bowel movements are disturbed (usually in the form of diarrhea), and it is painful for him to urinate. During the examination, the child does not allow the doctor to touch him, taking a forced position - pulling his right leg towards his stomach.
If the baby is a little older, while running or playing, he suddenly crouches and starts crying.
In children, signs of appendicitis in most cases do not appear all at once. For example, the temperature in the initial stages may be normal or even drop. And if at the same time the baby screams all the time, refuses to eat and does not allow his tummy to be touched, it is necessary to urgently take him to the hospital.
Significance in diagnosis
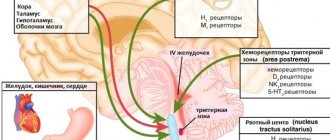
The positive Shchetkin-Blumberg symptom is caused by irritation of the peritoneum and is most pronounced in peritonitis. With limited peritonitis, the symptom is local in nature, for example, in patients with appendicitis it is determined in the right iliac region. When a hollow organ is perforated and the contents of the gastrointestinal tract enter the free abdominal cavity, the symptom is detected in all parts of the abdomen, which indicates generalized peritonitis.
With sharp tension in the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall (“board-shaped abdomen”) and in the initial stages of peritonitis, the symptom may be questionable. Also, the symptom may be less pronounced in the later stages of peritonitis due to degenerative changes in the nerve endings of the peritoneum.
Sometimes the symptom can be positive in patients with uremia, pneumonia, myocardial infarction (“pseudo-abdominal syndrome”), hemoperitoneum, acute pancreatitis, hematoma of the anterior abdominal wall or retroperitoneal tissue.
Laboratory research
After the initial examination, the patient is referred for additional examinations to differentiate the diagnosis.
| General blood analysis | Indicates inflammation in the body. With internal bleeding shows reduced hemoglobin |
| Urine amylase test | Required if pancreatitis is suspected |
| General urine analysis | Shows kidney condition |
| Blood chemistry | Necessary for diagnosing the condition of many internal organs: liver, kidneys, pancreas, etc. |
| Abdominal ultrasound | Detects cysts, tumors and stones |
| X-ray of the stomach | Shows accumulation of gas or fluid in the abdominal cavity |
| Visiting a gynecologist for women | Consultation and examination |
| Diagnostic laparoscopy | Used when other methods have not revealed anything |
Initial examination for acute manifestations
Appendicitis is almost always characterized by an unexpected onset, accelerated progression, and pronounced symptoms. A chronic course, in which inflammation develops over a long period of time, periodically exacerbating, is observed in only 1.5% of patients. The following proprietary syndromes are used to determine the disease:
- Kocher. Determines pain migration and is used most often. It is based on the gradual movement of painful sensations from the epigastric region to the iliac region. The accuracy of detecting appendicitis is above 50%.
- Voskresensky. Considered a sign of an abdominal irritant. To carry it out, the fabric of clothing is pulled over the stomach, along which a quick movement is made with the edge of the palm. If there is inflammation of the appendix, iliac pain appears on the right. Similar testing is carried out for other organs located in this area. Accordingly, painful sensations will change their localization.
- Shchetkin-Blumberg. It is the most accurate indicator of the presence of peritonitis in appendicitis and other pathologies. Diagnosis is made by deepening the palm of the hand into the abdominal wall. Appendicitis manifests itself as acute pain when suddenly raising the arm.
- Rovzinga. The technique is used quite rarely, although it is highly reliable. It is based on the artificial creation of a painful condition by pressure of the cecum with gas. The appearance of iliac pain indicates the presence of appendicitis.
- Sitkovsky. By placing the patient on his side, the intestinal loops are moved, causing compression of the appendix, which results in severe pain.
- Obraztsova. Used to determine pathology in the retrocecal location of the appendix. To do this, the patient lying on his back is forced to raise his right leg without bending. Muscle tension causes pain in the lower abdominal cavity.
The value of the technique is the ability to determine inflammatory processes in the peritoneum using conventional palpation - manual examination of the patient by pressing on the abdomen. In this case, the symptom manifests itself as sharp pain. During the examination, tension in individual or all abdominal muscles is noted. Increased pain upon abrupt cessation of palpation is caused by irritation of abdominal pain receptors. This manifestation has the most striking symptoms in the presence of peritonitis.
Localization of specific signs greatly facilitates diagnosis. In the case of limited peritonitis, the symptoms are local in nature, determined by the location of the pathological focus. For example, a positive reaction to palpation in the right iliac region indicates the existence of acute appendicitis.
Doubtful signs appear when the muscle layers of the peritoneum are overstrained, forming a disc-shaped abdomen, indicating the onset of the development of peritonitis.
In case of delayed diagnosis of pathology
this sign may also look dubious. Reduced activity of the abdominal nerve endings is due to their damage.
The manifestation of pain syndromes of different localization with this method of diagnosis may indicate the existence of the following pathologies:
- ulcerative damage to the digestive organs, complicated by organ rupture;
- acute appendicitis;
- myocardial infarction;
- pneumonia;
- peritoneal hematoma;
- pathologies accompanied by uremia;
- hematoma of the abdominal cavities.
Regardless of the location, a positive syndrome is a sign of an emergency condition that requires confirmation of the diagnosis and immediate assistance. When diagnosing a positive reaction of the syndrome, it is not enough, so other signs characteristic of a particular disease are taken into account:
- Acute appendicitis - localized in the right iliac region, characterized by pain in the lower quadrant of the peritoneum on the right during percussion.
- Acute cholecystitis - localized in the right hypochondrium. It is determined by pain at the moment of tapping the inflamed area with the edge of the palm.
- Diffuse peritonitis - distributed throughout the peritoneum. In the area of the right hypochondrium, the percussion sound is not dulled.
- Acute pancreatitis is determined by inflammation localized in the area of the left hypochondrium. It is determined by the weakening or complete absence of aortic pulsation at the time of palpation.
It is important to properly prepare the patient for the examination, otherwise the Shchetkin-Blumberg symptom may not appear or be misinterpreted. During examination, the patient lies on his back. A person should relax as much as possible and try not to move. Legs should be slightly bent at the knees, placing your feet on the bed. The specialist needs to palpate gently at first, gradually pressing on various areas of the abdomen, and then sharply remove the hand. The patient may feel pain in a specific area - this is how the area of inflammation or the affected organ is determined.
Such diagnostics make it possible to identify a serious disease in the shortest possible time. The symptom may indicate the presence of an illness, often requiring immediate surgical intervention.
Symptoms of appendicitis in children
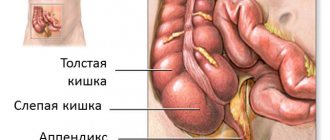
The appendix is an extension of the cecum, which, when inflamed, is burdened with life-threatening complications.
Acute appendicitis occurs due to:
- Blockage of an area of the intestine.
- Development of harmful microflora.
- Spasm of the walls of the appendix.
- Stagnation of blood.
- Infections.
- Overeating.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
https://youtu.be/kg1mINGa008
In pregnant women, appendicitis becomes inflamed due to the fact that the enlarged uterus damages the appendix.
The functions of the appendix are varied. Among them are the digestion of food and the effect on intestinal motility. It is believed that the appendix is a vestigial organ and some patients try to inflame appendicitis on their own at home.
Do not do this under any circumstances. According to statistics, people who have had their appendix removed have an increased risk of developing stomach and intestinal cancer. In addition, it is more difficult for people without an appendix to restore intestinal microflora after infections.
If appendicitis is suspected, symptoms in adults are as follows:
- Deterioration in health.
- Abdominal pain.
- Weakness.
- Abnormal stool.
- Rapid pulse.
- Nausea and single vomiting.
Scar after appendectomy in a man
Women more often than men suffer from inflammation of the appendix. In women, appendicitis occurs in the evening or at night. From the first minutes, abdominal pain appears, which shifts to the right iliac region.
With an anatomical anomaly in the location of the appendix, patients complain of pain in:
If the pain suddenly goes away during acute appendicitis, this is a reason for urgent surgery. Dulling of pain is associated with the development of peritonitis, a complication after appendix. With peritonitis, the contents of the stomach enter the peritoneum, and the nerve endings die.
Children and adolescents have bodies that are not as strong as adults. Children are a particular risk area: fragile health and the inability to speak complicate the disease. But in infants under 1 year of age, inflammation of appendicitis is rare.
Reasons for the problem
Appendicitis is an inflammation of the appendix - the cecum. Its progression can cause great trouble, even death. Accurate diagnosis that assesses the severity of inflammation is the most important factor in preventing tragedy. The manifestation of characteristic symptoms in appendicitis is due to inflammation of the deep layer, involving the surrounding structures.
Diagnosis of pathology is complicated by the variety of symptoms manifested in various inflammatory diseases. For timely detection of appendicitis, there are various types of diagnostic parameters proposed by qualified researchers.
They received names corresponding to the names of the authors. Such symptoms are aimed at determining the primary diagnosis using external signs and behavior of the patient. Its basis is an external examination, with elementary manipulations creating artificial conditions and postures.
There are four main categories of manifestations of appendicitis:
- pronounced signs of inflammation;
- painful sensations;
- dyspeptic symptoms;
- peritoneal.
The intensity of symptoms is affected by:
- location of the process;
- patient's individuality;
- duration of the development period;
- severity of the course;
- complicating factors.
Accurate determination of the necessary parameters of the disease is only possible with a more detailed examination.
Questionable symptom
A dubious variant of the symptom occurs. The patient notes pain in the peritoneum after the doctor’s manipulations, but not severe, as in patients who cry out during palpation.
Reasons that lead to a questionable symptom:
- Patient obesity.
- Bloating.
- Severe tension in the abdominal muscles.
Sometimes a dubious symptom is caused by advanced peritonitis, in which the nerve endings die in the peritoneum. This explains the inhibition of the patient's reaction.