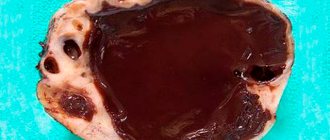
Rupture of a cystic formation of the ovary (the medical term “apoplexy”) is a complication of the presence of a cyst, in which it ruptures. The process is accompanied by a violation of the integrity of the formation and the release of blood contents directly into the cavity of the pelvic organs and abdominal space.
It occurs with approximately the same frequency in girls aged 15-18 years and in women of older reproductive age. Of all diagnoses, 12-13% require immediate surgical intervention, and 25-28% are classified as acute gynecological pathologies.
Rupture of an ovarian cyst is not an independent disease, but acts as a complication.
Ovarian cyst: what is it?
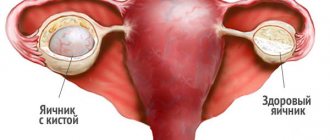
A cyst is a hollow tumor with liquid contents, localized on the surface of the ovary, one or both at the same time. Visually, the cyst looks like a sac containing a pathological secretion. The diameter of the formation can vary from an insignificant size of 1-2 cm to a very impressive size of 15-20 cm.
A functional cyst is almost always diagnosed, the cause of which is the overripening of the follicle - a structural component of the ovary formed from an egg.
A cyst is a benign formation; atypical cells do not develop in it. However, the tumor can cause many complications, including when trying to conceive.
Ovarian cyst
https://youtu.be/l0d_tHPPINo
Consequences
If the ovarian cyst is large or has non-sterile contents, serious consequences may occur. The most common complication is peritonitis (inflammation of the abdominal cavity). Its signs are rapidly growing abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting and a serious deterioration in the patient’s condition.
If a chocolate cyst, which forms on the endometriotic substrate, ruptures, there is a risk of the disease spreading to other organs through the implantation of endometrial fragments. If the cyst showed signs of inflammation from the very beginning, most likely it has purulent contents. In this case, the rupture leads to infection of the entire abdominal cavity. Signs of this phenomenon are rising temperature.
Functional cysts
Cystic formation of the functional type is the most common type of hollow tumor. They are formed from the stroma - the connective tissue of the gland, located on the surface of the ovary in the form of a sac. As a rule, they develop during the period of ovulation, during minor hormonal disruptions and disorders in the reproductive system.
There are two types of functional cysts:
- Follicular.
- Luteal.
The first type of formation, follicular, is benign and develops inside the ovary. It occurs in almost 90% of cases and is a kind of response to physiological disorders in the reproductive system. A follicular cyst is a follicle that is in the process of ovulation and has released an already mature egg filled with secretion.
Often, formations up to 5 cm are diagnosed. They do not manifest themselves clinically, but increase the concentration of estrogen in the blood. Therefore, the patient’s first complaint is menstrual irregularity. The cause of this type of cyst is often inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs.
The second type of cysts, luteal cysts, are also benign formations. It develops in the corpus luteum phase (luteal phase), which occurs immediately after ovulation and lasts about 11-14 days. Cysts appear during this period, which is where they get their name. The main reason for its development is hormonal imbalance.
If there are no complications, then therapeutic intervention is not required; such formations tend to resolve on their own. They also disappear during pregnancy, in the third trimester, sometimes in the second.
Consequences of a burst cyst
If medical measures are not taken in case of ovarian rupture, the following changes occur in the woman’s body:
- intoxication of the body due to fluid entering the peritoneal cavity;
- development of cystic formations into an oncological form;
- infection of other female genital organs.
If effective medical care is not provided, death is possible. With surgery, the worst thing a woman can expect in the postoperative period is infertility. The postoperative period passes quickly and very painlessly for the woman.
For complete rehabilitation and return to work capacity, restriction of physical activity for one month after surgery, rational vitamin nutrition and the use of hormonal drugs will be required.
A ruptured cyst can and should be treated. Modern medicine will quickly help a woman not only restore her health, but also remain as desirable and harmonious in her intimate life.
Can an ovarian cyst burst?
? Surely, many young ladies have heard about such a disease, but not everyone knows what very bad consequences it can result in if it is not eliminated in a timely manner. As a rule, an ovarian cyst does not cause discomfort and is not accompanied by severe pain, only sometimes slight discomfort is felt. Since cysts come in different types, they also develop differently. But the worst thing is when it bursts. This can often be recognized by severe pain, bleeding and high fever.
This phenomenon is called apoplexy in medicine. As a rule, a follicular cyst in women does not cause any discomfort, and it can only be identified during an examination by a gynecologist. If an ovarian follicular cyst bursts, the symptoms may be as follows:
:
- Severe pain appears in the lower abdomen; general body temperature rises to 39C; heart rate increases; weakness appears throughout the body; blood pressure may drop sharply; severe bleeding is observed.
These symptoms indicate that the woman urgently needs medical help. When a follicular cyst ruptures, surgery is usually not required unless there is severe pain or heavy bleeding. But when the corpus luteum cyst bursts (as a rule, this happens in the second half of the menstrual cycle), the listed symptoms worsen, so the problem can only be solved with the help of surgical methods.
Interesting on the web:
Reasons for the breakup
In most cases, rupture of follicular and luteal type cysts occurs. Such tumors have very thin walls, so they are more likely to be opened. In addition, unlike endometriotic ones, they are capable of self-resorption. Therefore, it is important not to confuse the first formations with endometriotic ones, which require mandatory removal.
A follicular cyst tends to rupture during ovulation, while a luteal cyst tends to rupture in the second phase of the cycle.
It was found that rupture of the cystic formation more often develops in the right ovary, which is explained by its more pronounced blood supply.
There are also a number of provoking factors that can lead to cyst rupture:
- disruption of the endocrine system;
- severe stressful situations, malfunctions of the central nervous system;
- inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system;
- violation of microcirculation in the area of the uterus and its appendages;
- menstrual disorder accompanied by absence of menstruation;
- neoplasms of various etiologies in the pelvis;
- various abnormalities of the uterus;
- long course of hormonal therapy.
Sometimes this happens without any cause-and-effect situation; it often happens in teenage girls after active physical activity. Intense sexual intercourse and gynecological manipulations can also cause rupture of the cystic formation. However, the rupture can also occur in a state of complete rest, for example, at night, during sleep.
Ovarian apoplexy
Treatment
As we said above, a ruptured ovarian cyst does not always require surgery. Surgical intervention is not used if the cyst is small in size and has sterile contents. In this case, it is recommended to carefully monitor the ovary, as well as prevent adhesions (they often occur after a cyst ruptures and can lead to infertility and other gynecological problems). We will tell you how to avoid complications and restore ovarian function using natural remedies.
Ortilia (hog queen)
This herb is especially loved by Siberian healers. It will help not only cope with the consequences of a ruptured cyst, but also prevent the reappearance of new cysts. It eliminates the very causes of these tumors – hormonal imbalance and gynecological inflammation. Therefore, after suffering a cyst rupture, be sure to undergo a course of treatment with the boron uterus.
Most often, an alcohol tincture is made from the plant, since decoctions and infusions have an unpleasant taste. Combine six tablespoons of dry herb with 500 ml of vodka and keep in a dark place for 2 weeks. Drink a tablespoon of tincture before each meal.
If alcohol is contraindicated for you, you need to grind dry ortilia grass, mix with the same amount of thick honey and eat a teaspoon every morning. This treatment can be used for complications after a rupture, as well as to normalize the functioning of the ovary. The therapeutic course lasts from 3 to 6 weeks, depending on the severity of the disease.
Raspberries
If you have experienced a cyst rupture, be sure to drink raspberry leaf tea for a while. This plant is a real elixir of women's health. It is not contraindicated even for pregnant women. Prepare tea according to your own taste, since it is impossible to overdose on raspberries. Add honey or raspberry syrup to the drink.
Herbal baths
Every day (except for menstrual days) you need to take warm herbal baths. They promote rapid resorption of the contents of the cyst and its membrane, prevent many complications, and help restore overall health. Use yarrow, thyme and horsetail herbs for baths.
The procedure is prepared as follows: during the day, pour 5 liters of cold water into a pan and throw in 50 g of herbs. In the evening, when you come home from work, heat this mixture, but do not bring it to a boil, then strain and pour into the bath. Swim in this water for at least half an hour (this time can be extended at the request of the patient).
Castor oil compresses
Every week you should do three castor oil compresses (except menstruation days) - for example, on Mondays, Wednesdays and Fridays. The procedure is prepared in this way: a clean flannel cloth, folded in three layers, is soaked in castor oil and placed on the stomach in the area of the affected ovary. Cover the fabric with a plastic bag or foil, with a towel on top, and place a bottle of hot water on the compress. As the water cools, you can remove the towel. The goal is to warm the ovary and speed up the resorption of residual fluid.
Herbal infusions
Be sure to undergo a course of herbal treatment. They act in several directions at once - improving the absorption of fluid, preventing inflammation and preventing the recurrence of the cyst. Here's a good recipe:
Twist all the plants through a meat grinder so that they are finely chopped, mix and use to prepare an infusion. In a thermos, mix a tablespoon of the mixture and 800 ml of boiling water, leave for 3-5 hours (if you don’t have a thermos, a pan wrapped in a towel will do). Drink a glass of medicine 4 times a day for two months. A collection of sweet clover grass, marigold flowers and mistletoe shoots (all taken in equal parts) helps well. This collection is used to prepare a decoction (a tablespoon per 3 cups of water, boil for 5 minutes). You need to drink 2-3 glasses of this drug a day, and after 1-2 months your reproductive system will work like a clock.
Another recipe:
- Elecampane rhizomes – 3 parts;
- Burnet root - 3 parts;
- Burdock roots – 2 parts;
- Calendula flowers – 2 parts;
- Red fortified wine.
Mix the herbs. Pour five tablespoons of the mixture into 500 ml of red wine, heated to a temperature of 90-95 C (almost boiling). Leave for 3 days, then strain. Take 25 ml of this wine before bed to restore women's health.
If an ovarian cyst bursts, the consequences can be fatal in the absence of emergency measures. Women, of course, know about the possible formation of cystic neoplasms, but not everyone realizes that after spontaneous opening of a cyst they should immediately seek medical help.
What symptoms indicate that the cyst has burst? What measures should be taken in this case? What consequences can occur if a cyst ruptures?
Symptoms of a rupture
The main symptom is severe and sudden abdominal pain, which is localized in the lower abdomen, on the side of the affected ovary. The condition may be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and dizziness.
In addition to the clinical picture of an “acute abdomen,” the following symptoms are observed:
- sharp, painful sensations in the lower abdomen, reminiscent of an attack of appendicitis;
- disruption of the functioning of the digestive system, development of acute constipation;
- pronounced tension in the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity.
The development of acute pain in the abdominal cavity is characterized by blood entering the gastrointestinal tract after a cyst ruptures.
In addition to abdominal pain, the following manifestations may appear:
- spotting, bloody vaginal discharge;
- alternating diarrhea with constipation;
- body temperature above 37°C;
- signs of hypotension (low blood pressure).
Pain in the lower abdomen should always alert a woman, especially if it is not associated with menstrual bleeding. The pathological process can affect every organ of the female reproductive system, ovaries, uterus, fallopian tubes. If assistance is not provided in a timely manner, the chance of developing peritonitis is extremely high, which will require emergency surgical intervention.
Treatment
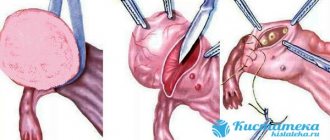
Rupture of the formation and tissue of the ovary is called apoplexy. The operation is carried out immediately. Two methods of surgical intervention are used:
- Laparotomy.
This is an abdominal operation that is performed under general anesthesia. - Laparoscopy.
The operation is performed through several punctures in the abdominal cavity.
The choice of technique depends on the patient’s condition. If the ovary is not affected, then only the cyst is removed. Partial or complete removal of the ovary is possible. The woman’s age, whether she has children, and plans for pregnancy must be taken into account.
Severity of the condition
Taking into account the clinical manifestation of the pathological process, apoplexy is usually divided into the following forms: anemic and hemorrhagic (with the development of bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract); pain (severe pain, up to loss of consciousness); mixed (combines several of the above-described forms at the same time).
Cyst rupture is almost always accompanied by bleeding of varying intensity, for this reason the pathology is usually divided into degrees of severity. In gynecological practice, there are three degrees of severity of apoplexy: mild, moderate, severe. The latter also includes an extremely severe degree, where the operation is performed on an emergency basis.
Popular articles:
|
When is the best time to see a doctor?
Women who have a cyst should monitor their well-being very carefully. Usually, some specific symptoms begin to be observed even before the ovarian cyst bursts! For example, pain begins to appear several hours, less often – a day before the rupture. At first, the pain is not intense, it is nagging in nature and gradually increases. If you consult a doctor at this moment, serious complications can be avoided with almost 100% probability.
https://youtu.be/wnsMF6-fkDU
Diagnosis of cyst rupture
In 90% of cases, patients are hospitalized with a diagnosis of “acute abdomen,” where surgeons, urologists and gynecologists are involved in determining the cause. It is extremely important to identify the rupture quickly and eliminate the bleeding process as soon as possible. A standard gynecological examination using speculum, ultrasound, and diagnostic laparoscopy are performed.
They also resort to laboratory tests of urine and blood. A urine test for proteins is performed. The presence of protein in the urine is typical for many pathological conditions, including its increase observed in apoplexy. A urine test for occult blood is required. Using a special test called phase contrast can distinguish whether red blood cells are entering through the glomeruli or whether they are coming from the lower pelvic organs. The blood is tested for the amount of hemoglobin, which decreases significantly during bleeding. An hCG test is performed to exclude ectopic pregnancy.
The diagnosis is made based on examination, the presence of pain and the results of diagnostic measures. The course of therapy will depend on the severity of the problem; both conservative and surgical techniques can be used.
What to do if an ovarian cyst bursts? Consequences and methods of treatment.
If an ovarian cyst has burst, the signs will determine the treatment
. If there is internal bleeding, a woman needs cold: it needs to be applied to the lower abdomen and completely relaxed. As a rule, this is how a ruptured follicular cyst is treated. As a rule, when a cyst ruptures with pronounced symptoms, resection is performed, that is, suturing the ovary. For this purpose, laparoscopy or laprotomy is used. In the most severe, advanced cases, absolute removal of the ovary is prescribed if it is completely infected.
Resection is never prescribed during pregnancy, as it can cause miscarriage or premature birth. Gestational age is often taken into account. With severe blood loss, a woman needs a donor blood transfusion.
If no measures are taken when a cyst ruptures, the consequences can be disastrous:
- Intoxication occurs because all the fluid in the cyst enters the abdominal cavity. After this, organs and tissues will become infected, which will lead to general poisoning. The likelihood that the cyst will develop into a malignant tumor increases. When an ovary is removed, a woman may become infertile, which will affect the functioning of the entire reproductive system. Other gynecological diseases will also appear, since all organs of the reproductive system are interconnected, and any infection spreads extremely quickly.
Treatment methods
Conservative therapy
A conservative treatment method is prescribed in the presence of mild forms of apoplexy, which are not accompanied by bleeding into the abdominal space. The patient is prescribed complete rest, a cold compress on the abdominal area, vaginal suppositories with an anti-inflammatory effect, and painkillers. After the acute process has been eliminated, a course of electrophoresis or other physiotherapeutic procedures is prescribed.
Physiotherapeutic procedures after rupture of an ovarian cyst
Surgical methods
Recently, experts recommend treating apoplexy promptly, even in the presence of its mild forms, especially if pregnancy is planned.
In most cases, surgery is performed laparoscopically. Laparoscopy is an endoscopic surgical method. The treatment procedure is carried out not through one large incision, but through several small ones, 1-2 cm long, which are used to insert a camera and working surgical instruments. After the operation, only a few small stitches remain. This significantly reduces postoperative recovery and the patient can usually return home within a few days.
As a rule, surgery is performed to preserve the ovaries, but in severe cases they are removed along with the cystic capsule. In such cases, oophorectomy is performed - the most gentle method of resection with minimal risk of complications.
When performing surgery, it is important to efficiently remove blood clots from the abdominal cavity, which will avoid adhesions.
Laparoscopy for ovarian rupture
Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation in the postoperative period consists of preventing the development of adhesions, normalizing hormonal levels, as well as the possibility of further successful conception. During the patient’s recovery period, hormonal contraception is selected taking into account the individual characteristics of the body. Additionally, a course of physiotherapeutic manipulations is prescribed, which will speed up the recovery process.
Recommendations and tips
After surgery, the woman is prescribed medication and follows all the doctor’s instructions. This complex includes:
- taking antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and painkillers;
- complete physical rest for a month;
- proper nutrition, avoidance of alcohol and smoking.
To prevent the formation of a cyst and prevent surgery, you should undergo an annual examination by a gynecologist.
https://youtu.be/ivU0pSFSSGo
Ultrasound and other diagnostic methods
Rupture of an ovarian cyst is an acute surgical condition. Its diagnosis includes the following methods:
- ultrasonography;
- puncture of the abdominal cavity through the posterior vaginal fornix;
- diagnostic laparoscopy, which can immediately proceed to a full-fledged operation.
Ultrasound examination has several purposes. During it, the following can be revealed:
- the presence of free fluid in the abdominal cavity;
- a formation on the ovary that looks like a cyst, sometimes a rupture is even visible;
- other diseases with a similar clinical picture can be excluded.
An ultrasound is performed using a vaginal sensor; to complete the picture, an abdominal one can also be added.
Expert opinion
Daria Shirochina (obstetrician-gynecologist)
An ectopic pregnancy with a ruptured tube and intra-abdominal bleeding is accompanied by similar symptoms. Therefore, to exclude this condition, it is recommended to do a urine test or a blood test for hCG during the examination.
If ultrasound results confirm the presence of fluid in the abdominal cavity, it is necessary to determine its nature. For example, it could be blood or a pathological effusion (as a result of inflammation, an oncological process). For this purpose, culdocentesis is performed. The procedure involves puncture of the abdominal cavity through the posterior vaginal fornix. The manipulation is carried out as follows:
- The girl lies down on the gynecological chair.
- Local anesthesia or intravenous anesthesia is performed.
- After treating the vagina, the obstetrician-gynecologist pierces the vaginal wall in the area of the posterior fornix with a special needle.
- If there is blood in the abdominal cavity, it begins to flow out; the pressure of the stream can be used to judge the blood loss.
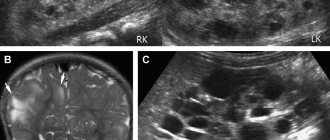
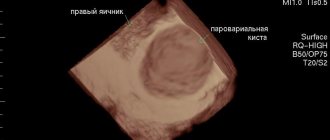
Rupture of an ovarian cyst on ultrasound.
Detection of blood is a direct indication for surgical intervention.
If the clinical situation does not clear up even after culdocentesis, diagnostic laparoscopy can be performed. During it, the ovaries are visualized, it is clear whether there is blood in the abdominal cavity and in what quantity. If necessary, they immediately move from diagnosis to treatment: removal of the cyst and, if necessary, part or the whole complex of appendages.
Watch this video about the picture of a pelvic ultrasound for a ruptured ovarian cyst: