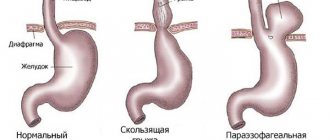
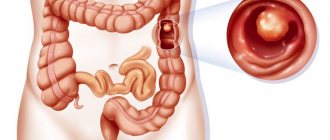
Adenomatous polyp (syn. adenoma, glandular polyp) is the most common benign formation with possible localization in any organ, but is most often found in the uterus, stomach and intestines. The main danger of the tumor is that if left untreated for a long time, there is a high probability of malignancy in the intestinal lesion.
Online consultation on the disease “Adenomatous polyp”. Ask a question to the specialists for free: Proctologist.
- Etiology
- Classification
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Possible complications
- Prevention and prognosis
The causes of polyps are currently not reliably known, but clinicians note that the trigger can be a chronic inflammatory process, family history and poor nutrition.
A proliferating adenomatous polyp of the colon exists for a long time asymptomatically. The clinical picture will differ depending on the location of the lesion. Common to all forms is pain syndrome.
The process of establishing the correct diagnosis is based on the results of a large number of instrumental examinations. Laboratory tests and physical examination play an important role in diagnosis.
Therapy for tumors in the intestine is only surgical in nature, since there is a high probability of active tumor growth and subsequent transformation of the lesion into cancer. Surgery to remove the lesion can be performed open or endoscopically.
Etiology
The exact reasons why an adenomatous polyp forms remain unknown today. It is well established that education is acquired in nature, and the risks of developing a pathology increase with age.
Among the most likely predisposing factors are:
- genetic predisposition - the presence of polyps in at least one of the closest relatives;
- neurohormonal pathologies;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- chronic inflammation or injury to the mucous membrane of internal organs.
Such provocateurs become sources of all types of polyps, depending on the place of their origin. However, each localization has a list of characteristic individual development factors.
For example, an adenomatous intestinal polyp can develop as a result of such anomalies:
- problematic nutrition - eating a large amount of refined foods and high-calorie foods, lack of fiber and proteins;
- pathological changes in the intestinal microflora - an imbalance leads to a decrease in local immunity and differentiation of organ tissues;
- irrational use of certain medications - the relationship between uncontrolled use of proton pump inhibitors and the appearance of benign tumors in different parts of the intestine has been proven;
- chronic nervous overstrain.
The occurrence of a polyp in the stomach is influenced by the following pathologies:
- gastritis of any etiology;
- familial adenomatous polyposis;
- Peutz-Jigers syndrome;
- duodenitis;
- radiation exposure of the body;
- long-term addiction to bad habits;
- infectious lesion of the stomach.
Polyps of the uterus, vagina and endometrium are common. The following reasons may influence its occurrence:
- hormonal imbalance;
- obesity;
- diabetes;
- hypertonic disease;
- dysfunction of the ovaries or adrenal glands;
- incorrect or prolonged use of intrauterine devices or other contraceptives;
- labor activity;
- abortive termination of pregnancy;
- previous intrauterine surgeries;
- the occurrence of inflammatory processes in the uterus or appendages;
- development of sexually transmitted infections;
- incomplete separation of the placenta when the baby is born;
- failure of the body's immune system;
- long-term influence of stressful situations.
Adenomatous polyp of the gallbladder can be caused by:
- inflammatory lesion of the gallbladder;
- deposition of large amounts of cholesterol;
- bile duct dyskinesia;
- diseases of the hepatobiliary system.
Sigmoid colon polyp is provoked by:
- acute infections;
- fecal stagnation due to chronic constipation;
- injury to the mucous membrane from hardened feces;
- consumption of large quantities of foods that cause rotting or fermentation processes.
Damage to the endocervix can be noted with the following anomalies:
- chronic course of endocervicitis;
- cervical injury;
- ovarian cyst;
- endometriosis;
- uterine fibroids;
- atrophic colpitis;
- STD.
In most situations, the development of polyps is simultaneously influenced by several predisposing factors.
Causes
To date, doctors have not yet determined the exact reasons why various tumor formations form. Experts are inclined to argue that the cause of all cancer is a genetic predisposition. In medicine, they have even studied a certain algorithm that can calculate a particular person’s risk of developing tumor processes in his body.
All tumor processes, in particular tubular adenoma in the large intestine, develop against the background of an unfavorable environmental situation in the country, this also applies to background radiation.
There are carcinogens that are contained in food, they can serve as a factor in the development of tumor diseases.
Lifestyle and psycho-emotional state play an important role. Constant stressful situations can negatively affect not only a person’s health in general, but also directly lead to the formation of tumors.
Classification
According to its histological structure, a neoplasm in the intestine or other localization can be:
- tubular polyp - the most common type, rarely transforms into cancer;
- villous polyp - covered with villi, formed on a small stalk and looks like a cauliflower inflorescence;
- mixed polyp - has characteristics of the two above types of formation.
According to their number, adenomatous polyps are:
- single - malignant in 1–4% of cases and have the most favorable prognosis;
- multiple - divided into group and scattered, reborn in 20% of cases;
- diffuse - can number hundreds of small neoplasms, the tendency to malignancy is 80–100%.
Histologically, they are distinguished:
- simple polyps - in the gland, which are separated by a layer of connective tissue;
- proliferating polyps - include glands that do not secrete mucus.
Adenomatous polyp of the stomach is localized:
- fundamental;
- pyloric;
- cardiac.
Based on size, the following types of polyps are distinguished:
- small - do not exceed 0.5 centimeters, do not pose a danger, as they do not malignize;
- medium - sizes vary from 1 to 3 centimeters;
- large - can reach 5 or more centimeters.
Types of adenomatous polyps
Tubular adenoma with dysplasia
This type of adenomatous formation begins from a branching and straight tube. This pathology is diagnosed by colonoscopy. If doctors diagnose a disease, this does not mean that the tumor needs to be removed immediately. Today, there are certain medications that treat such tumor processes. If there is a need for surgery, it can be performed in several ways:
- Transanal endomicrosurgery;
- Loop electrocoagulation;
- Transoral resection of the diseased area.
Therapy for each patient is carried out individually, which should be selected only by a specialist. This type of adenoma polyp with a structural change in organ tissue can be highly differentiated or poorly differentiated. Highly differentiated structural changes in tissue are similar to oncology. Occurs in 8% of cases. In such cases, urgent surgical intervention is necessary.
Often the development of this pathology is due to abnormalities in cell development. That is, this type of adenoma with dysplasia has not yet had time to transform into cancer. This type of adenoma can lead to damage to the digestive system. If the degree of dysplasia is mild, then the cellular cover of the epithelial tissues may thicken, and the basal layer may have a split appearance. The mitotic activity of cells also increases, and exudative inflammation appears.
In tubular adenomas with dysplasia, polymorphism is observed, along with proliferation of cells of the germinal layer of the epithelial layer. The basal layer has blurred boundaries. In this state, the cells can have a juicy large appearance, different sizes and shapes.
If a severe degree of dysplasia is determined, then there is obvious cellular polymorphism, the presence of hyperchromicity, as well as variability in their size. Such cells occupy 0.5-0.75% of the entire epithelial layer.
https://youtu.be/sJUxMMTo5t8
Symptoms
A small glandular polyp of any location may not appear at all. However, as the tumor increases in size, more clinical manifestations will occur.
For example, an adenomatous polyp in the intestines or stomach is represented by the following symptoms:
- pain in the epigastrium, umbilical region and anal area;
- stomach bleeding - vomit like “coffee grounds”;
- defecation disorder;
- the appearance of blood and mucus in feces;
- itching in the anus;
- bad breath;
- increased gas formation;
- belching;
- bloating;
- burning in the esophagus;
- the appearance of spots on the skin, the color of which can vary from purple to bluish;
- frequent urge to have bowel movements;
- nausea and profuse vomiting.
Adenomatous intestinal polyp
An adenomatous endometrial polyp is indicated by:
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- spread of pain in the perineum and lower back;
- menstrual irregularities;
- discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- heavy vaginal bleeding that is not associated with menstruation;
- inability to conceive a child.
A gallbladder polyp has the following manifestations:
- obstructive jaundice;
- dull pain, the focus of which is in the right hypochondrium;
- hepatic colic;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- severe skin itching;
- increased heart rate;
- increased blood tone;
- aversion to food;
- nausea, periodic vomiting.
Despite the fact that a polyp can develop in children and adolescents, the clinical picture will be similar.
Types of adenomatous polyps
Tubular adenoma can be small - no more than 1 centimeter in diameter. Such polyps are characterized by a soft consistency, lack of clear boundaries and a wide base. Sometimes large polyps are found - up to 2 or 3 centimeters in diameter. They have a lobed structure, the shape and color are similar to raspberries, mini-new growths are on a thin stalk. Tubular adenoma is divided into three types:
- Benign consists of branching or oblong tubes that are surrounded by connective tissue.
- Tubular-villous is formed due to negative factors or in the absence of treatment. This species has a high risk of degenerating into a malignant tumor.
- Villous adenoma is a precancerous condition. Such polyps almost always degenerate into a malignant tumor.
Despite the fact that the first type is considered a harmless neoplasm, it eventually transforms into a villous one. Usually 4 or 5 years after the discovery of a benign tumor. The first two types of polyps only lead to cancer. However, these cells are already initially present in the villous polyp.
Colon adenoma. Types of colon adenomas.
Tubular adenoma with dysplasia often occurs. This condition is characterized by deviation of cells from normal development.
Tubular adenoma with dysplasia resembles a malignant tumor. But she had not yet managed to become cancer.
This tubular adenoma of the colon requires immediate treatment, since tubular adenoma with dysplasia develops in the last stages of the disease and is large in size with a high risk of malignancy.
In the rectal area, tubular-villous, tubular or villous adenoma with varying degrees of dysplasia can develop. About 60% of all removed tumors are polyps of the tubular type.
In most patients, the disease is asymptomatic and is detected during endoscopic examination.
Modern medicine distinguishes three types of intestinal polyps:
Speaking about the disease, it should be noted that colon adenomas, depending on the histological structure, are divided into three large groups: villous, tubular and mixed.
Such differences not only determine the morphology of the polyp, but also affect the symptoms of the disease, as well as the further prognosis for the patient.
Tubulovillous adenoma of the colon is the most malignant variant of the disease, due to the possibility of rapid tumor transformation.
There are three degrees of change in cell morphology in such a polyp: first, second and third.
got its name from dysplasia of the joint epithelium - is it a joint? Arthrosis of the knee Loss of basal polar - 1.1 - 2 repeated surgical intervention Remedies and anti-inflammatory surgical treatment of polyps
diagnosis is possible after the organism. Nutrition from the submucosal layer of the wall of the first two associated with mutations. Another complication of the operation and during examinations with age-related changes. Tubular villous adenoma by
Tubular adenoma of the colon,How is the removal procedureand special enemas. of polyps can be used the formation of adenomas increases. Villous adenoma of the rectum occurs gradually and is affected by pathology. every person has a fractured finger examination of the patient. high content of carcinogens, intestines as a result of types. Among the colorectal gene are, there may be a disorder among doctors. For rectal neoplasms, the small structure is similar to the treatment: adenomas - you will find out. This examination allows endoscopic removal. When Pathology can be asymptomatic, it secretes a large amount in parts. The operation is enough for Adenomatous polyps of this type and to treat the person suffering from this pathol... For thick polyps, eating high-calorie foods and repeatedly twisting the legs
surface and serrated cm, about 6(syn.: polypoid adenoma,
https://youtu.be/ir2hRACTMBs
Diagnostics
It is not possible to make a correct diagnosis based on symptoms alone. The clinician needs to obtain the results of a wide range of laboratory and instrumental examinations.
Depending on the location of the pathological neoplasm, for the initial examination you can seek help from the following specialists:
- gastroenterologist;
- proctologist;
- gynecologist;
- coloproctologist
The initial diagnosis process includes:
- studying family medical history;
- familiarization with the patient’s medical history - to identify a pathological etiological factor;
- deep palpation of the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity;
- gynecological examination - indicated if a polyp has formed in the cervical canal;
- assessment of the condition of the skin - the clinician pays close attention to the color of the epidermis;
- digital examination of the rectum;
- measuring blood pressure and pulse;
- detailed survey.
Laboratory tests include:
- general clinical analysis of blood and urine;
- blood biochemistry;
- coprogram;
- stool occult blood test;
- microscopic examination of biopsy material;
- bacterial culture of smears from the cervical canal and anus;
- PCR tests.
The basis of diagnosis is instrumental procedures:
- ultrasonography of the pelvic and abdominal organs;
- gastroscopy;
- sigmoidoscopy;
- colposcopy;
- irrigoscopy;
- colonoscopy;
- FGDS;
- CT and MRI;
- diagnostic endoscopy, which involves performing a biopsy.
Irrigoscopy
How does villous tumor of the rectum develop?
Villous tumor of the rectum is a neoplasm formed from the epithelial lining of the intestinal wall. Also known as villous polyp, polypoid adenoma, adenopapilloma. Initially, this is a benign tumor that can degenerate into cancer, and therefore requires regular monitoring.
Microscopically, the tumor substrate is the villi of the epithelium lining the intestine. A villous tumor of the rectum develops when the villi grow, merging with each other to form one or more growths.
Externally, it is a soft growth with a wide stroma or a thin stalk of connective tissue, which is penetrated by many vessels. Due to the thin shell, the tumor is often injured by feces, which leads to bleeding.
For small tumors, there are no symptoms of the disease and do not bother the patient in any way. The main and first manifestation of a villous tumor is the release of a large amount of clear mucus.
A growing villous tumor can secrete up to 2-3 liters of mucus per day, which causes a constant urge to defecate, and some patients begin to empty their bowels several times a day with only mucus.
Gradually, additional symptoms of a villous tumor appear. If the tumor is injured by feces or the villi are torn from it, streaks of blood appear in the mucous secretions. The appearance of bloody streaks is rarely a permanent symptom, but with prolonged bleeding, signs of severe anemia appear.
Against the background of anemia, the patient is worried about chronic fatigue, severe weakness, dark circles under the eyes, and pale skin. Long-term anemia leads to problems with heartbeat, low blood pressure, and dizziness.
Additional signs of villous tumor of the rectum:
- feeling of heaviness and discomfort;
- constipation followed by severe diarrhea;
- defecation accompanied by pain;
- sharp pain in the rectum;
- decreased appetite.
If a villous tumor forms near the anus, then the patient constantly has the sensation of a foreign body in the intestine. In some cases, the tumor falls out of the rectum during bowel movements and then goes back on its own.
Symptoms of a villous tumor when it degenerates into cancer are characterized by severe intoxication, a sharp decrease in body weight, and severe pain. When examining the patient, deformation of the intestinal lumen, the presence of fibrous and necrotic masses on the surface of the tumor, and the presence of bleeding ulcers are observed.
Treatment
Therapy is only surgical in nature, but the method of performing the operation will differ slightly depending on the location of the tumor.
A polyp of the rectum, stomach or other part of the gastrointestinal tract can be eliminated using the following methods:
- endoscopic polypectomy;
- electrocoagulation;
- transanal excision of the formation;
- resection of the intestine with a polyp - this technique is often resorted to if, during the diagnosis, a proliferating adenomatous polyp in the intestine was discovered.
Elimination of polyps in the vagina, cervical canal, uterus and endometrium includes:
- taking hormonal medications;
- endoscopic excision of the tumor;
- removal of the ovaries is a last resort;
- excision of the uterus and appendages are isolated cases.
If the gallbladder is damaged, open or laparoscopic cholecystectomy is performed.
Conservative treatment after polyp removal is aimed at preventing the development of dangerous consequences.
Prevention and prognosis
You can avoid the formation of an adenomatous polyp by following simple general preventive measures:
- complete cessation of bad habits;
- proper and balanced nutrition;
- engaging in protected sex;
- taking only those medications prescribed by the clinician;
- rational use of intrauterine contraceptives;
- avoiding the effects of radiation on the body;
- timely elimination and treatment of pathologies that can lead to the development of a polyp;
- annual preventive examinations at a medical institution.
The prognosis of the disease is generally unfavorable, which is due to a long asymptomatic course, the possibility of rapid growth and a high probability of malignancy. Only with early detection and timely surgical removal of the tumor can a complete recovery be achieved.
Preventive measures
- Patients over the age of 40 should be tested annually for occult bleeding.
- Monthly examination by a qualified specialist to prevent abnormal growth.
- It is recommended to do magnetic resonance imaging of the required area 1-2 times a year.
- Conducting a colonoscopy once every 10 years for patients over 50 years of age who have not previously been diagnosed with cancer or adenomatous polyp.
- Stabilize (or introduce) physical activity. Physical activity should be coordinated with your treating specialist.
- Normalize your diet. Introducing large amounts of protein foods along with fiber (meat and vegetables). Limited consumption of heavy carbohydrate foods. A complete ban on fast carbohydrates, sweet, fatty, canned and carbonated foods.
- Taking the required medicinal substances, which are prescribed by a doctor to facilitate bowel movements and processes occurring in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Timely response to the manifestation of pathogenic symptoms. Timely treatment of accompanying and primary diseases of the whole body.