What is and why does diverticulitis of the sigmoid colon occur?
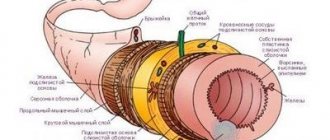
Diverticulitis of the sigmoid colon is an inflammatory disease associated with congestion in diverticula (spherical protrusions of the walls of the digestive organ). Diverticula are formed as a result of metabolic disorders, insufficient motor skills, poor nutrition, age-related changes, and the influence of external factors.
At risk:
- people over 40 years old;
- those who abuse laxatives;
- ignoring foods with fiber in the diet;
- obese patients.
The development of diverticulosis of the sigmoid colon is caused by constipation, excessive strain during bowel movements, and frequent pressure of gases on the intestinal walls.
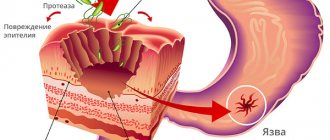
In the early stages, when diverticula have not reached a large size, the disease is asymptomatic. As the pouches increase, normal bowel function is disrupted. Diverticula are made of connective tissue and therefore do not participate in digestion. The accumulation of waste provokes the onset of the inflammatory process, rotting, and bacterial growth. The sigmoid colon is the terminal part of the colon that becomes the rectum. Feces can be retained in its stretched cavities.
Complications of diverticulitis of the sigmoid colon are abscesses, fistulas, tissue necrosis, peritonitis.
Etiology
The formation of pathological hernial protrusions in the area of the sigmoid colon is considered by specialists in the field of gastroenterology to be one of the most common types of damage to the large intestine.
The causes of the disease are:
- chronic intestinal obstruction;
- violation of colon motility;
- the development of any degenerative process in the organ;
- vascular disorders.
Among the predisposing factors are:
- age-related changes in the body;
- congenital weakness of connective tissue;
- poor nutrition - the predominance of fatty and spicy dishes in the menu, lack of fiber (therefore, the basis of treatment is gentle nutrition for diverticulosis);
- frequent overeating;
- atherosclerosis;
- cardiac ischemia;
- excessively high body weight.
The incidence increases as a person gets older. As a result:
- children and people under 40 suffer from this disease only in isolated cases;
- in the age category from 40 to 50 years, this diagnosis is given to every 3 people;
- in persons over 60 years of age, pathology is diagnosed in 50% of cases;
- Among older people, 80% are diagnosed with diverticular disease of the sigmoid colon.
Symptoms and clinical signs
It is impossible to recognize the appearance of sigmoid colon diverticulitis in the early stages. To make a diagnosis, an examination by a specialized doctor is required. Symptoms of inflammation of the intestinal sacs are nonspecific and are characteristic of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
As the disease worsens, when the diverticula increase or bacterial flora joins, characteristic symptoms appear. Patients note discomfort in the lower left abdomen. There is a disorder of bowel movements - constipation alternates with diarrhea. Constant bloating appears due to excessive gas formation, flatulence, belching. A person complains of a feeling of empty bowel movements even after several bowel movements.
A relative subsidence of pain occurs after bowel movements, without taking painkillers. But over time, the symptoms return.
Photo: Elvira Koneva / Shutterstock.com
Due to general intoxication associated with stagnation in the intestines, signs of malaise appear:
- increase in body temperature to 38-39°C;
- fever with chills;
- nausea, vomiting;
- weakness, dizziness;
- bloody or purulent discharge in the stool.
Upon palpation, the doctor notices tension in the abdominal wall. During the examination, the patient may complain of sudden attacks of pain, which are episodic in nature.
To obtain a complete picture of the form, severity of the disease and the presence of complications, it is necessary to conduct a thorough diagnostic study. When diagnosed with sigmoid colon diverticulitis, symptoms and treatment often coincide with those of other intestinal diseases.
Manifestations of uncomplicated diverticulosis (ICD-10 code - K57)
- Pain syndrome. As a rule, pain occurs that is constant, dull, and aching. In terms of localization, as a rule, they occur in the middle and lower parts of the abdomen (hypogastrium and mesogastrium) on the left. The reason for this kind of sensation is an increase in pressure in the sigmoid colon and a violation of its motility. Self-relief of pain is possible, but not always. Another feature is that pain sharply intensifies after eating and subsides after defecation. Often, pain with intestinal diverticulosis in some way resembles the symptoms of an acute abdomen caused by appendicitis.
- Constipation, which is periodically combined with diarrhea.
- Release of large amounts of foul-smelling gases, bloating.
- On palpation, pain sensations are especially clearly manifested in the peri-umbilical region and in the hypogastrium on the right. With a deep palpation examination of the sigmoid colon, it will be possible to feel diverticula. There is also some feature of this pathological process, which is in a certain way related to the localization of the pathological process. In the event that diverticulosis mainly affects the right parts of the large intestine, fragmentation of the intestine and thickening of the stool will be characteristic; Persons under the age of forty will be more susceptible; the tendency to bleeding is more pronounced. In the event that the left parts of the large intestine are affected by diverticulosis (ICD-10 code - K58), then pronounced atrophy of muscle fibers, reservation and formation of dense feces will be observed; This will be typical for elderly and senile people; the most likely complications in this case are diverticulitis (an inflammatory process in diverticula).
In order to understand whether in a certain clinical case there is a complication of diverticulosis (ICD-10 code - K57) or not, it is necessary to conduct a number of general clinical and special studies.
- In a general analysis of blood and urine, characteristic inflammatory changes will be visible (increased ESR, increased number of leukocytes, shift in the leukocyte formula to the left);
- Presence of blood in stool;
- Regarding the general condition – fever, severe pain in the abdomen.
To confirm the diagnosis and clarify the nature of the complication, several special studies will be necessary:
- Irrigoscopy - this study will help clarify the localization of diverticula by detecting a filling defect;
- CT scan;
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs.
https://youtu.be/3_vuPvwDPK8
Stages of the disease
Since 1978, the Hinchey classification system has been used to diagnose diverticulitis, which is based on the clinical presentation of the disease. In 1999, Hanson and Stock proposed a more precise definition system based on data obtained during research. Thus, a modern classification of sigmoid colon diverticulitis has emerged:
- Stage 0 - uncomplicated diverticulosis at the initial stage of development. It has no clinical symptoms and is discovered accidentally during colonoscopy or irrigoscopy.
- Stage 1 - uncomplicated acute diverticulitis. Characteristic pain in the left iliac region of the abdomen. During colonoscopy, redness of the walls of the diverticulum is noticeable. On CT, in addition to the general picture of diverticulosis, infiltration of the intestinal wall is visible.
- Stage 2 - complicated acute diverticulitis. The stage is divided into types. Each type has its own characteristics and signs, on the basis of which a decision is made on further actions regarding the patient.
- Stage 2 a. The probability of death is 0%. Acute phlegmonous diverticulitis with peridiverticulitis of the sigmoid colon. The presence of local symptoms of irritated peritoneum in the left side of the abdomen (“left-sided appendicitis”) is characteristic. During colonoscopy, the clinical picture has the same outlines as at the first stage. CT scan shows increased density of paracolic fat tissue. Conservative treatment is effective.
- Stage 2 b. Death is likely for 3.1% of patients. Diverticulitis of the sigmoid colon with abscesses, covered by perforation or the presence of fistulas. In addition to local peritonitis, a decrease in intestinal tone is noted. CT scan shows abscesses and multiple air bubbles.
- Stage 2 s. The patient's probability of death is 21.4%. Perforation of the sigmoid colon is determined at the initial stage of the disease. A plain radiograph shows obvious symptoms of an acute abdomen and free gas in the abdominal cavity. Urgent treatment is required.
- Stage 3. The disease is a chronic, receding form with irreversible damage to the walls of the sigmoid colon (stenoses, fistulas). There are characteristic symptoms with defecation disorder, acute abdominal pain, and periodic fever.
Having identified the stage of the disease, it is possible to determine the subsequent treatment tactics for inflammation of the sigmoid colon, the need for surgical intervention and the likelihood of adverse consequences.
Diverticular bowel disease - classification
The international classification is a single normative document that requires pathology to be assessed according to the same standards. This approach helps to obtain the most reliable information about the prevalence of the disease and its forms in different countries. For example, a study of diverticular disease revealed a clear dependence on the type of diet: people living in countries with a predominant consumption of plant foods (Africa, India) get sick less often.
The standards concern the use of the same terminology. A diverticulum is a pouch-like protrusion of the intestinal wall. Accordingly, their inflammation is called diverticulitis. The term “diverticulosis” in ICD-10 has been replaced by “diverticular disease”. It denotes the presence of single or multiple diverticula in different parts in the inflammatory phase, with or without a complicated course. The codes are the same for recording cases in adults and children.
At the same time, in Russia there remains a clinical classification that differs from the international one. She divides diverticulosis into:
- asymptomatic;
- confirmed by clinical signs;
- complicated.
Complications include:
- inflammation (diverticulitis, peri-intestinal infiltrate, abscess);
- perforation of the diverticulum wall;
- formation of fistula tracts into neighboring tissues and organs;
- bleeding.
Important! Proctologists believe that this approach more accurately assesses the patient’s condition and determines the optimal treatment tactics. A disadvantage of the ICD is the lack of mention of the acute or chronic course of the disease.
Diagnoses included and excluded from the list
Diverticular disease is included in the class of intestinal diseases and belongs to the group “Other diseases”. Based on morphological changes, the formations of the thin and thick sections are combined:
Diagnostics
Diverticulitis of the sigmoid colon, the symptoms and treatment of which are not characterized by specific features, is a rather dangerous disease. Without timely detection, the disease progresses and complications develop.
Early diagnosis is an important component of effective treatment, which helps to detect the disease, select a therapeutic regimen, and prevent the development of complications. For diverticulitis of the sigmoid colon, informative hardware technologies are used that make it possible to see even minor changes in the functioning of the intestine and its structure.
An effective method for diagnosing diverticulitis in the early stages is computed tomography. The hardware technique makes it possible to detect changes in the contour of the intestinal walls and determine destruction in the tissues. If the patient's condition allows, CT angiography is required to determine diverticular bleeding and exclude pseudoaneurysms.
Irrigoscopy (administration of a barium enema) is considered an informative method for diagnosing the sigmoid colon. The procedure helps to identify narrowing of the lumen of the sigmoid part of the intestine in cases of infiltration, as well as to fill the fistula space with a contrast agent. In acute, severe cases of the disease, irrigoscopy is postponed until the severity of inflammation subsides.
Ultrasound examination helps to determine thickening of the intestinal walls, intraintestinal and intramural infiltrates, the presence of fistulas, and identify inflammation of the paroxysmal tissue. With abundant gas formation in the intestines, ultrasound is not very informative. Therefore, a careful approach to each case of illness is necessary.
Photo: Khakimullin Aleksandr / Shutterstock.com
Colonoscopy is performed only in the absence of perforation of the walls of the sigmoid colon. Otherwise, the procedure will lead to pressure on the diverticulum with subsequent rupture and the development of peritonitis. Colonoscopy can be performed after exacerbations have subsided. The procedure reveals the overflow of blood vessels with blood, swelling of the mucous membrane. It is possible to determine the presence of blood clots, blood clots, and purulent masses that fill the diverticulum cavity. Colonoscopy data for bleeding are not very informative.
Based on the results of the x-ray, it is possible to determine the presence or absence of released air in the abdominal cavity.
Diverticulitis of the sigmoid colon is a disease that requires a comprehensive approach. When assessing the patient's condition, several diagnostic methods are used.
Treatment methods
Treatment of sigmoid colon diverticulitis is closely related to the stage, form of the disease, condition and age of the patient, and the presence of concomitant disorders. For patients with a mild form of an uncomplicated condition, outpatient therapy with symptomatic medications, diet, and rest is indicated. If there are no signs of acute inflammation with the development of pathologies, the condition quickly improves on its own.
Patients with moderate and severe forms of the disease require hospitalization. In cases of infection, taking antibacterial agents is indicated. If emergency intervention is necessary, surgery is prescribed.
Drug therapy
Treatment with medications is a conservative form of therapy, used as an independent method or in combination with other measures. Drug therapy for diverticulitis of the sigmoid colon involves taking medications to combat the causative agent of a bacterial infection and suppress the symptoms of illness.
For outpatients, compliance with all medical instructions is required, including ensuring rest, bed rest, and diet. Medicines are taken strictly according to the prescription, without allowing for independent adjustment of dosages or duration of therapy. To normalize the condition, the following drugs are prescribed:
| Pain syndrome | Improved intestinal motility | Nausea | Dysbacteriosis | Antibiotics |
| Drotaverine | Kalimin | Cerucal | Lactovit | Metronidazole+ fluoroquinol |
| Papaverine | Mestinon | Metoclopramide | Probifor | Metronidazole+ co-trimoxazole |
| Galidor | Motilium | Perinorm | Lactiale | Moxifloxacin |
The course is selected for each case of inflammation of the sigmoid colon. After the expiration of the period, the patient undergoes a re-examination.
Photo: S_L / Shutterstock.com
Patients in the hospital are prescribed intravenous antibiotics. Treatment is selected taking into account the patient’s condition, his age, and the risk of complications.
Drainage
Percutaneous drainage of the affected area of the sigmoid colon is a minimally invasive tactic that is indicated in the presence of abscesses. Allows you to get rid of fluid accumulation in the cavity of diverticula. Drainage prevents rupture of cavities, thereby preventing the development of peritonitis, sepsis and other dangerous conditions. After installing the drainage structure, observation with an ultrasound machine is required.
According to a study from the University of Minnesota, the success rate of drainage treatment is 76% of all cases of the disease. For small single-line abscesses, taking antibiotics into account, treatment is 100% effective.
The PAD technique is not relevant in case of an extremely serious condition of the patient, the presence of multiple diverticulosis, abscesses accompanied by fistulas, if the contents of the ulcers are of a semi-liquid or solid consistency. In such cases, surgical intervention is indicated.
Operation
The decision to perform surgical intervention is based on the results of the diagnostic study, the condition and age of the patient. The choice of tactics depends on the indications for elective or urgent surgery.
Urgent surgery is required if diagnostic testing reveals free perforation with peritonitis, bowel obstruction, abscesses that cannot be drained, or fistulas. The lack of effectiveness of conservative treatment is also taken into account.
Photo: gpointstudio / Shutterstock.com
Elective intervention is used in cases of intestinal obstruction, if the contrast agent leaks outside the intestine, or there is difficulty in differentiating cancer. Elective surgery is performed by resection (cutting). At least 6 weeks must pass from the period of acute inflammation to the actual event. Before the procedure, bowel preparation is performed with mechanical and medicinal manipulations, including antibiotic therapy.
Treatment is carried out in two ways - laparoscopic (through a small incision) and open (opening the abdominal cavity). The presence of adhesions or inflammation prevents the use of the first method. Resection as primary surgery helps reduce the risk of recurrence. Reduces the likelihood of mortality from 26 to 7% (compared to colostomy), increases life expectancy in operated patients. In addition, the hospital stay after primary resection is shorter than for other procedures.
Hartmann's operation is another method of primary surgery. It involves colectomy (cutting the sigmoid part of the intestine) with removal of the intestine into the anterior abdominal wall (applying a calostomy). In this way, a new path for excretion of feces is formed. Patients require regular care and training in how to change a colostomy bag. The second stage of the operation is to restore intestinal continuity.
Diet
Diet therapy is an important part of the complex treatment of diverticulitis with damage to the sigmoid colon. You need to change your diet in order to enhance the effectiveness of the drugs, reduce the load on damaged tissues and compensate for the deficiency of elements necessary for the full functioning of the body.
The main goals of the diet include:
- Restoring natural water balance. As symptoms develop, patients often experience vomiting, diarrhea, and fever. For this reason, the body loses fluid, which can lead to dehydration and the development of related complications. Drinking plenty of fluids and including liquid foods in the diet normalizes the imbalance and promotes rapid recovery without harm to health.
- Normalization of intestinal motility. Some patients experience alternating constipation and diarrhea. This affects intestinal health, immune defense and overall well-being. Proper nutrition reduces the likelihood of congestion, prevents the accumulation of feces in enlarged diverticula, and prevents the development of bacterial infections and related diseases.
- Activation of enzyme production. As a result of tissue destruction and disruption of the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, enzyme production is disrupted. The intestines have no direct function. It is necessary to artificially start the process with specific products.
The menu is compiled taking into account the introduction of vitamins, minerals, micro and macroelements. Small and frequent meals are recommended. The weight of one serving does not exceed 300 ml. Fried and smoked foods are completely excluded. Preference is given to steamed or oven-baked dishes.
| What is possible | What not to do |
| Baked vegetables | Alcohol |
| Dairy products | Chocolate, cocoa |
| Vegetable soups with broth | Rice or semolina porridge |
| Buckwheat or wheat porridge with vegetable oil | Carbonated water, jelly, strong coffee, caffeinated drinks |
| Vegetable stew | Pasta |
| Wholemeal bread | Premium bread |
It should be borne in mind that such nutrition is possible only during the stable phase of the disease. At the time of exacerbations, the patient needs to eat exclusively liquid food to prevent the development of constipation and excessive pressure on the damaged walls of the sigmoid colon.
Image: POLIGOONE / Shutterstock.com
Traditional medicine, principles of therapy
Treatment of diverticulosis with folk remedies is mostly symptomatic and can be used as an adjunct to drug therapy.
Herbal medicine has found its application in many countries around the world. Of course, it is best to use publicly available methods for uncomplicated forms of the disease, combining them with medications. Below, we will consider all possible folk remedies for diverticula and the most effective ways to combat the disease.
Recipe No. 1 - Flaxseed or olive oil.
Relieves constipation, relieves inflammatory reaction. Every day before bed, drink 1 tablespoon of flaxseed oil and add olive oil to vegetable salads throughout the day.
Recipe No. 2 - Herbal infusion.
Mix equal amounts of dried nettle leaves, motherwort, chamomile flowers, rose hips and dill seeds. Pour a tablespoon of the prepared mixture into a thermal mug and pour 250 ml. warm water (not boiling water). Then close and let it brew for about 1.5 hours. The finished infusion is decanted and drunk 125 ml morning and evening for 4 weeks.
Recipe No. 3 - Decoction of slippery elm bark.
Boil 250 ml of water with 0.5 tsp. powdered slippery elm bark and 1 tsp. granular or simple bark. The mixture should be kept on low heat for 15 minutes, strain and drink 1-3 glasses every day.
Recipe No. 4 - Plantain-based medicine.
Pour one tablespoon of seeds with water, juice, kefir or yogurt and mix well. The mixture must be taken immediately after preparation, in small sips. After half an hour, you need to drink another 250 ml of water. With a sufficient dose, the seeds, once in the stomach, swell and reach the large intestine in increased sizes. This stimulates peristalsis. The medication continues until the unpleasant symptoms of the pathology are completely eliminated.
Recipe No. 5 - Peppermint tea.
Add a few mint leaves to your tea each time and drink as often as possible. It has a calming effect on the gastrointestinal tract, reduces flatulence and pain. The drink is especially useful for those with esophageal diverticula.
Recipe No. 6 - Elderberry tincture.
Add more than 1 tablespoon of berries to a glass and pour boiling water. Drink the prepared tincture as tea. Strengthens the immune system, having a beneficial effect on intestinal function using folk remedies.
Recipe No. 7 - Oatmeal jelly.
It has a particularly incredible effect, eliminating constipation, bloating and activating intestinal motility and will return lightness and a sense of freedom. It is recommended to use it only in the morning.
To prepare such a healing drink, 250 mg of flakes must be poured into 3 glasses of cold boiled water, stirred and a piece of rye bread should be added to the mixture. Place in a warm place for 48 hours, while covering. Strain the fermented solution through cheesecloth. Place everything that remains in a blender and grind until liquid. This starter should be stored in the refrigerator and used to make jelly.
Recipe No. 8 - Introduction of bran into the diet.
This product is rich in fiber and other beneficial substances.
It is recommended to take about 50 g per day, no more. There is an approximate scheme for including bran in the diet, the main thing to remember is that this moment should proceed gradually. Here's an example:
| Day | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Quantity | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 |
| Tablespoons | 1,5 | 3 | 4 | 5,5 | 7 |
Of course, the exact amount of food you eat per day should be discussed with your doctor, taking into account your weight, age and other characteristics. Can be mixed with water, kefir, yogurt, compotes, soups and main courses
Recipe No. 9 - Thorn tincture
Sloe liqueur has a positive effect. For production, bush plums, sugar, and alcohol are used. It is prepared as follows:
- Place plums in any container and pour alcohol over the fruits.
- The bottle is closed and left in the room at a temperature of no more than 17 - 20 degrees.
- After 4 months, filter the tincture, adding 100 g of sugar for each liter of medicine.
- After the sugar has dissolved, the medicine is poured, sealed tightly, and left for another six months.
Afterwards, take a tablespoon no more than 1 – 2 times a day.
Recipe No. 10 - Chamomile infusion enema.
This method has wonderful medicinal properties and reduces pressure on the intestinal walls. The treatment consists of carefully injecting an infusion of about 1.5-2 liters, previously brewed and cooled to a temperature of 37°C, into the anus. The procedures are carried out once for 7 days, gradually reducing their number to one per month. This medicine can be taken throughout the day.
Complications
Diverticulitis of the sigmoid colon is dangerous due to the development of complications. If the disease is not detected in a timely manner, the risk of developing pathologies that pose a threat not only to the health, but also to the life of the patient increases.
A bacterial infection develops when there is stagnation in the diverticulum cavity. As the condition worsens, toxic damage to the body occurs and ulcers appear. The patient complains of acute pain, fever, diarrhea with impurities, and symptoms of general intoxication.
Fistulas (fistulas) appear as a result of abscesses, thinning and rupture of diverticula. A fistula is a through hole through which the contents of the sac leak into the general abdominal space.
Perforation is a rupture of a hollow organ, as a result of which the contents of the sigmoid colon (feces, blood, pus, gas) penetrate into the abdominal cavity.
Peritonitis is an inflammatory disease associated with intestinal contents entering the abdominal cavity. An extremely dangerous condition that requires immediate surgical intervention. If immediate treatment is not carried out, blood poisoning develops, which in most cases leads to the death of the patient.
Rules for traditional treatment for diverticulosis
Since diverticulosis causes disorders of the digestive system, the use of folk remedies is aimed at stabilizing the functioning of the digestive system, enhancing intestinal motility, preventing constipation and other conditions that provoke complications of the disease.
For colon diverticulosis, it is important to coordinate treatment with folk remedies with your doctor, since even harmless medications often cause undesirable consequences. For patients using natural products to treat a disease, experts recommend adhering to the following rules:
- The prescription, dosage and duration of taking the medicine are discussed with the attending physician.
- When preparing the product, you must strictly follow the instructions.
- Only high-quality products are used to prepare medicines.
- It is important to rule out allergies to the components of the recipe.
- If your health worsens, skin rashes or other side effects appear, you should stop treatment and consult a doctor.
The effectiveness of treating diverticulosis with folk remedies has not been officially confirmed. Independent use of medicinal recipes of traditional medicine will not only not be beneficial, but also dangerous to health.
Forecast
Diverticulitis of the sigmoid colon is a treatable disease if detected early. As a rule, patients complain of acute inflammation of the diverticulum, when symptoms of intoxication appear.
Carrying out a planned surgical operation with removal of a fragment of the sigmoid colon can reduce the likelihood of re-formation of protrusions. Uncomplicated forms of the disease can be treated with drainage and antibiotic therapy.
The prognosis for patients with a mild form of the disease is favorable. If you follow treatment tactics and proper nutrition, complete relief from symptoms occurs. Elderly patients with complicated inflammation of the sigmoid colon are not guaranteed a complete recovery.
Prevention
It is impossible to completely protect against the development of diverticulitis of the sigmoid colon. According to research results, there is a possibility of a genetic predisposition to the disease. However, it is possible to reduce the likelihood of intestinal destruction occurring. It is worth following simple steps:
- Do not abuse laxatives. Drugs that stimulate intestinal motility, with constant use, contribute to atrophy of the natural physiological actions of the organ.
- Enrich your diet with fiber. Fiber has a beneficial effect on intestinal function and normalizes the process of digestion and bowel movements. Fiber prevents gastrointestinal disorders and prevents the development of colon cancer.
- To refuse from bad habits. Smoking and alcohol are the main provocateurs of diseases of human internal organs. Nicotine and ethanol disrupt fermentation, reduce vascular tone, and weaken the immune system.
- Give preference to healthy eating. You need to increase the amount of fruits, vegetables, and nuts in your diet. Reduce or exclude smoked foods, pickles, instant foods, and sweets from the menu.
- Upon reaching 40 years of age or at an earlier age in the presence of obesity, regular examination by a proctologist is indicated. People at risk need to monitor their intestinal condition, undergo routine intestinal examinations and hardware diagnostics.
- If you experience chronic discomfort or pain in the abdominal cavity, seek help from a doctor. If symptoms increase, it is unacceptable to mask them with medications. Self-medication for diverticulitis is contraindicated. Any attempts to cope with the problem on your own can provoke the development of complications.
Following simple recommendations will reduce the likelihood of developing intestinal diseases and will have a positive effect on human health.
What is included in the concept of intestinal diverticulosis?
Diverticular disease is a pathological process in which a pouch-like protrusion of up to two centimeters or a diverticulum in the mucous membrane forms in the wall of the large intestine, but more often in the sigmoid region, due to a decrease in the tone of the muscle layer. But the term diverticulosis itself implies many such formations that cause discomfort in a person and are discovered by chance, for example, during a routine examination.
In more than 85% of all cases, this pathology occurs in the large intestine, namely in its sigmoid section. Much less often the rectum, stomach and other hollow organs are affected.
Diverticulosis is often an acquired disease and is diagnosed in people aged 40 years. It is usually asymptomatic until the first signs of inflammation appear.
In order to treat this pathology, or at least reduce the symptoms, it is necessary to normalize the diet and resort to natural medicines that restore lost functions of the digestive tract.