MRI of the pancreas can detect inflammation, oncology, and fibrous tissue changes. A significant advantage of the study is the ability to detect the disease at an early stage, when verification by other methods is not yet available. Numerous monographs describe issues of magnetic resonance diagnostics of the disease. If detected late, the disease inevitably leads to irreversible consequences.
MRI of the abdomen and pancreas
The lethal outcome is due to necrosis, destructive lesions of the pancreas tissue, and the formation of peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum). It is better to prevent a neglected process than to treat it.
Indications for MRI of the pancreas
The study is recommended in the following cases:
- An ultrasound revealed a formation similar to a benign or malignant tumor, especially if it is small in size, as well as to determine the stage, relationship with neighboring tissues, vessels;
- it is necessary to identify an anomaly in the structure of the gland;
- severe inflammatory process (pancreatitis) with tissue destruction (pancreatic necrosis), cyst formation;
- in preparation for surgical treatment;
- you need to examine the internal lumen of the ducts, which is not detected by ultrasound (it often contains stones and tumor metastases);
- assessment of the results of surgical intervention;
- to exclude tumor recurrence and metastases;
- it is necessary to distinguish pseudotumor pancreatitis from a neoplasm;
- suspicion of a tumor that produces insulin (insulinoma), leading to attacks of low blood sugar;
- symptoms of gastrinoma producing gastrin - the formation of many ulcers in the stomach;
- an unusual course of diabetes mellitus, probably associated with glucagonoma, a tumor formation that synthesizes glucagon;
- clinical manifestations of vipoma - diarrhea, loss of potassium and chlorides, carcinoid - hot flashes, abdominal cramps, loose stools.
We recommend reading the article about ultrasound of the pancreas for a child. From it you will learn about the indications for performing an ultrasound of the pancreas in a child, the preparation and features of the procedure, as well as the norms in indicators, deviations and their causes. And here is more information about CT scanning of the thymus gland.
Contraindications
Magnetic resonance imaging is not suitable for everyone. Its implementation is contraindicated in the following cases:
- serious mental or neurological disorders;
- claustrophobia;
- too much weight;
- pregnancy;
- the presence of metal structures in the body: stents, pacemakers;
- severe general condition.
Some restrictions are relative. In this case, the doctor can individually determine the appropriateness of the diagnosis. Relative contraindications include severe heart, liver and kidney diseases, and the third trimester of pregnancy.
Prescription restrictions
An absolute contraindication is the presence of a pacemaker or insulin pump. Their work in a magnetic field will be disrupted. Also, when a metal object enters the scanning area, it quickly heats up, which leads to tissue burns. Therefore, this method is not prescribed in the presence of any metal structures - stents, clips installed during surgery on vessels, fragments remaining in the body, implants.
During pregnancy, MRI is not used in the first months, and then it is prescribed for health reasons.
Relative limitations are the fear of confined spaces and a weight of 130 kg or more. For these categories of patients, it is possible to use an open-type device designed for significant excess weight. In cases of severe motor agitation and the inability to remain still, sedatives may be additionally administered.
How does a tomograph work?
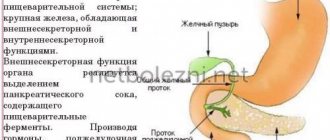
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is an advanced method of non-invasive study of the anatomy and structure of internal organs. The operation of the device is based on the interaction of a magnetic field with the human body. Under its influence, the atoms of the molecules that make up the human body change their vibration frequency to a resonant one. When they are in this state, the detector records their vibrations.
The vibration frequency of each molecule and each of its fragments is individual, therefore, using a computer program, it is possible to recreate a detailed image of the organ and examine it from all sides. Therefore, the tomograph is designed as follows: the magnetic source and detector rotate around the patient, who lies motionless on the couch. During the study, more than a hundred images of sections of the patient’s body are taken.
MRI allows you to identify the cause of pain and prescribe the correct treatment.
Indications for prescribing MRI are various, from clarifying the diagnosis obtained using other diagnostic methods, to its staging and control of the disease.
When prescribed with contrast
To identify a small tumor or, if necessary, determine the degree of its invasion into neighboring tissues, it is necessary to increase the clarity of the image. For this purpose, a contrast agent, a gadolinium-based drug, is injected into the vein.
Malignant tumors usually quickly accumulate contrast due to a well-developed network of vessels. In benign processes, absorption proceeds more slowly. MRI data in such cases are indicative, and only histology (tissue examination) can accurately determine the type of neoplasm.
Contrast is not indicated during pregnancy. During lactation, if it is necessary to use contrast, it is recommended to switch the child to infant formula for 2 days. Contraindications include severe renal failure and allergic reactions to the drug. Therefore, before conducting the study, a skin test is needed.
MRI of the pancreas
You should also check your kidney function using urine tests, blood biochemistry with kidney tests, and ultrasound.
Differences between MRI, computed tomography and ultrasound techniques.
When a CT scan of the pancreas is prescribed, patients must be given intravenous medications containing iodine. Without using this tool, it is possible to obtain a small amount of information.
Important information: What should be the diet for pancreatic cancer
A similar method is carried out using X-ray ionizing radiation.
Ultrasound is a more common and inexpensive method for diagnosing pancreatic diseases. You should not make a diagnosis based on ultrasound data alone, especially if the doctor is not very experienced. The quality of the study may be hampered by the patient's excessive weight and flatulence.
Preparing for an MRI of the pancreas
For two days, it is necessary to exclude from the diet foods that contribute to gas formation in the intestines: cabbage, legumes, black bread, milk. Carbonated drinks, alcohol, and fatty foods should be avoided. MRI is performed on an empty stomach. 2 hours before the procedure, activated charcoal is prescribed; in case of severe flatulence, it is combined with Espumisan. About an hour before, you need to take a No-shpa or Riabal tablet.
What a test can reveal
Using MRI, you can detect inflammation, cystic changes, tumors, reduction and enlargement of the organ.
Normal sizes and deviations
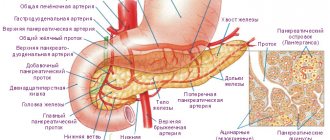
The most significant parameters are the length of the organ (15-22 cm) and the width of the head - from 3 to 7 cm. The body of the pancreas is approximately 1 cm smaller than the head, and the tail has an average thickness of about 2 cm. Weight in adult patients is 65-110 G.
Reduction in size (atrophy) is caused by general exhaustion of the body (starvation, tuberculosis, pituitary insufficiency), as well as age-related changes. The volume of the gland decreases by approximately 3 times due to a decrease in the number of functioning cells and their size in diabetes mellitus.
Also, wrinkling is caused by the replacement of working tissue with connective fibers as a result of chronic inflammatory processes. A peculiar type of weight loss is observed when a large amount of fat is deposited.
In the first stages of the inflammatory process, due to swelling of the iron tissue, it increases in size. It is most often associated with pancreatitis. There is a uniform increase in tissue volume. With a tumor, cysts, blockage of the duct with a stone or local suppuration, predominantly the affected part becomes larger than normal, the organ loses its normal structure.
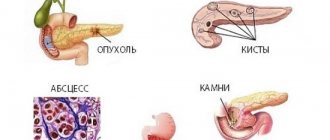
Cysts
They are cavities filled with liquid. Appear as a result:
- injuries, hemorrhages;
- acute, chronic inflammation;
- disturbances in the outflow of pancreatic juice due to blockage of the duct.
Using MRI, you can clearly detect the shell of the cyst, its contents, and distinguish the fluid from the disintegrated tissue. With malignant degeneration, there is pronounced heterogeneity inside, and the shell loses its clarity. When suppuration occurs, the signal becomes uneven.
Diffuse changes
Normally, the structure of the tissue is homogeneous; with inflammation, there is an alternation of areas with different densities throughout the gland. In this case, cysts appear as foci with low signal intensity, and calcium deposits, small ulcers and areas of connective tissue growth appear denser.
Such heterogeneous areas are randomly scattered throughout the organ; there is no pattern in their location, unlike a tumor.
Cancer
A malignant neoplasm is characterized by the presence of a focus with a signal of low intensity or close to the gland tissue. Its contours are uneven and unclear. There is usually dilatation of the ducts. Without contrast, MRI detects tumors as small as 2 cm, and when used, tumors up to 1 cm in size can be detected at a very early stage.
Decoding the results
The images obtained during the magnetic resonance examination are examined by a radiation diagnostics specialist. Its task is to identify and describe pathological changes presented in the images. He should also identify the connection between the existing disorder and other dysfunctions of the gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract).
Interpretation of the results usually takes about an hour. To guarantee the reliability of the study, the patient is given a specialist’s report with the doctor’s signature and seal, as well as photographs on film, paper and digital media.
A cystic lesion of the pancreas looks like a round formation with clear contours without obvious walls. Pseudocysts are presented in the form of multi-chamber structures with a thickened wall. Often such a formation extends beyond the contours of the pancreas. The presence of granulation tissue along the periphery and air bubbles inside indicate the formation of an abscess.
More than ninety percent of all tumor processes in the endocrine organ are adenocarcinoma. Most often, the neoplasm affects the head of the pancreas. The images show changes in the contours of the pancreas and a local increase in the affected part of the pancreas.
Dilatation of the pancreatic ducts cannot confirm the presence of cancer. This symptom also characterizes chronic pancreatitis and obstruction. Adenomocarcinoma may visually resemble a cyst. A specialist will be able to recognize cancer by the absence of calcification. The tumor will have a thicker and more uneven wall.