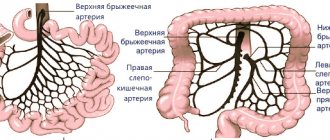
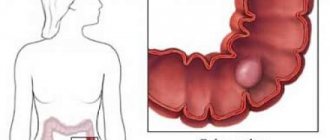
Benign tumors - colon polyps - develop as a result of changes in the glandular epithelium. They form in many patients and often occur without symptoms at all, making their presence known only when they grow strongly.
Some forms of neoplasms turn into malignant tumors and can cause acute intestinal obstruction. Treatment of colon polyps is often surgical - using surgical or endoscopic techniques.
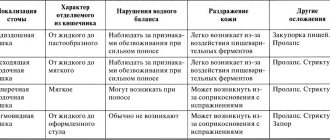
Classification by quantity and size
Colon polyps can be small or large in shape: pedunculated, mushroom-like, flat, sponge-like, and also in the form of clusters or a dense knot.
Important! Polyps can be single or multiple (appearing in different parts of the intestine). Familial polyposis of the colon also occurs.
Multiple polyps are characterized by groups of nodes, but usually there are few of them. With familial colon polyposis, there are hundreds, and in some cases thousands, of neoplasms. They are evenly distributed throughout the entire intestinal segment.
Classification by type of structure
Single and multiple familial polyposis of the colon can have a different structure and nature of origin:
- Glandular (adenomatous). Found in most cases of diagnosing colon polyps. Characterized by red or pink growth of the gastric epithelium. They have a dense texture and mushroom-shaped shape. Sometimes there are branching types that spread along the mucous membrane, but practically do not occupy the space of the intestinal passage. The average size of a polyp is 2-3 cm. They rarely become covered with ulcers and are practically not prone to bleeding, as a result of which they have the least danger of degenerating into a malignant tumor.
- Glandular villous polyps of the colon. Found in 20% of cases, they have a transitional form, combining the signs of glandular and villous neoplasms. Due to the peculiarities of their structure and development, they are prone to degeneration into malignant tumors.
- Villous polyps in the large intestine. They occur only in 14-15% of patients, usually presented in a nodular form, spreading along the intestinal mucosa. The color is rich, red, as they consist of vessels. When they reach a diameter of 3-5 cm, they begin to bleed, become covered with ulcers or die, leading to the development of necrosis.
- Hyperplastic neoplasms. Diagnosed in almost 70% of cases, they have the structure of soft nodes and rise slightly above the mucous membrane. The size is the smallest. They rarely exceed 5 mm and do not degenerate into malignant neoplasms.
- Cystic (juvenile) tumors. An abnormal shape of colon polyps, occurring mostly in children or teenagers. Most often, 1-2 pieces are formed in different parts of the intestine.
Classification of colon polyps is needed to understand the processes that may arise as a result of the detection of a particular neoplasm. However, many patients have multiple types of tumors at diagnosis, which complicates their treatment.
Folk remedies for polyps
You can get rid of hyperplastic growths using folk remedies, but they can be used after consultation with a doctor. Some types of tumors cannot be removed with natural medicines. Here are the most popular recipes:
- Infusion of agrimony. Has anti-inflammatory and absorbable effects. Brew 2 tbsp. l. dried herbs in a glass of boiling water (98-99 degrees). Infuse the decoction for 60 minutes, take a third of a glass three times a day. The course of treatment is at least 1 month, after which a break and re-examination is necessary.
- Viburnum decoction. The berries are collected away from the highways, from September to October. The first frosts make the berries juicier and healthier. Prepared from 2 tbsp. l. dried or 3 tablespoons of fresh berries. Brew 300 ml of hot water, leave for 15-20 minutes. Every day a new portion is prepared, and the resulting drink is drunk in 3 doses before meals.
- Celandine . When fresh, the herb has toxic properties; when harvesting, contact with eyes and mucous membranes must be avoided. When the grass dries, useful decoctions are prepared from it. For 1 tbsp. l. dry product take a glass of boiling water. Boil for 15 minutes over medium heat, cool and strain. You need to take 2 spoons twice a day.
- Enemas with celandine. The medicinal substance is applied gradually. The first time take a liter of water and 1 tsp. fresh celandine juice. They give enemas every day (15 days in a row). Then follows a seven-day break. In the second cycle, make a solution of 1 tbsp. l. juice and a liter of water. Again they give 15 enemas once a day with a similar break and begin to repeat the second stage.
You can understand that folk recipes work by reducing the signs of a hyperplastic polyp: the process of defecation improves, pain is less frequent or disappears completely, and blood is no longer found in the stool.
Causes of growths in the intestines
Colon polyposis is formed as a result of several factors, which most often depend on a person’s habits and behavior:
- Eating disorders. Neoplasms more often develop in people prone to refined foods and animal fats. Those who eat fiber, plenty of fruits and vegetables, as well as fish and vegetable oils have significantly lower risks.
- Perennial constipation. Due to the retention of food masses, bacteria develop, traumatic factors arise, which lead to the formation of polyps in the colon.
- Chronic gastrointestinal diseases. Medicine believes that neoplasms occur only on damaged mucous membranes. They are caused by inflammation: dyskinesia, colitis, Crohn's disease.
- Bad habits. Overeating, smoking and alcohol can trigger the formation of polyps in the colon.
- Heredity. Even children sometimes develop neoplasms, despite being in full health. Most often this is due to a genetic factor.
- Physical inactivity. Reduced physical activity causes gastrointestinal diseases, which lead to the formation of growths on the mucous membrane.
- Age. In people over 50 years of age, polyps in the large intestine appear from the slightest trauma to the mucous membrane. The risk is especially high if a person drinks alcohol, smokes, or is overweight.
Although colon polyps often cause no symptoms, they can cause discomfort. But it is often confused with other diseases.
Features in children
In childhood, the problem often manifests itself between 3 and 6 years of age. The main cause of the disease is heredity. Less commonly, the problem is acquired and occurs as a result of frequent dysentery, inflammatory complications and helminthic infestations. As a result of constant irritation of the intestinal mucosa, uncontrolled proliferation of epithelial tissue is observed, from which polypous growths subsequently form. The procedure for removing rectal polyps in a child is mandatory, because despite the initially benign etiology, there is always a risk of its degeneration into oncology.
Symptoms of growths in the large intestine
Colon polyps can be suspected by the appearance of severe itching in the anal area. This is due to the action of mucus produced by the neoplasm. Some forms of tumors cause bleeding that appears in the stool and on underwear.
With polyps of the large intestine, the passage of food is disrupted, since overgrown tumors interfere with its movement. Flatulence and constipation appear, and the patient often thinks that he has gastritis or pancreatitis.
Important! Pain during bowel movements is a common symptom of colon polyps.
Secondary signs: anemia, weakness and fever in the last stages of the disease. If the neoplasms have degenerated into a malignant tumor, severe lethargy, vomiting and other signs of cancer appear.
The disease can be suspected if there are frequent dizzinesses or pain in the lateral walls of the peritoneum. Sometimes symptoms of gastritis appear: nausea, sour belching, heartburn. Due to intoxication, colon polyps cause an unpleasant odor from the mouth. Temperature appears during periods of exacerbation or growth of tumors.
Diagnosis of the disease
Several methods are used to diagnose colon polyps. Sometimes 1 x-ray or MRI in combination with a blood or stool test is enough, but in some cases a combination of several techniques is required:
- MRI and CT. They give a complete picture of the condition of the epithelium in the area of the rectum and colon. Polyps ranging in size from 1 mm are detected.
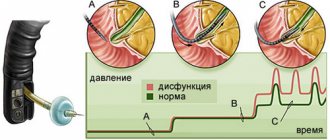
- Sigmoidoscopy. A modern method for diagnosing parts of the digestive system. Using a device equipped with a flexible tube, it is penetrated through the anus. The light bulb at the end of the device illuminates the mucous membrane well and transmits information to the monitor. The manipulator helps to take biomaterial for research.
- Colonoscopy. A painful but informative method for detecting colon polyps.
- General blood analysis. Used to confirm the diagnosis. If a person has a neoplasm, the hemoglobin level will be significantly reduced. This also indicates hidden bleeding. If the state of leukocytes is changed, then some kind of inflammatory process occurs in the body.
- Irrigoscopy. A barium solution that does not transmit x-rays is released into the intestines. After this, a picture is taken: colon polyps are clearly visible, their position and size can be assessed.
If neoplasms are detected, surgery is prescribed. However, conservative treatment is sometimes carried out before it.
How to help a cat who has blood in his stool
- Before starting treatment, you need to figure out why your cat has blood and mucus in his stool. Only after establishing a diagnosis can a treatment regimen be selected.
- If there is a foreign body or neoplasm in the intestine, only surgical intervention will help.
- In case of rat poisoning, the use of an antidote (vitamin K), a dropper, gastric lavage, and maintenance therapy will be required; in case of poor blood clotting, constant use of vitamin K and iron supplements is necessary.
- The treatment of a cat with a disease of the gastrointestinal tract must be approached comprehensively. First of all, eliminate the cause of the disease and prescribe specific and symptomatic treatment. The animal must be under the supervision of a veterinarian and undergo additional examinations (urine, blood and feces tests, ultrasound, and, if necessary, x-rays with contrast). Self-medication is extremely dangerous.
- For infectious diseases, specific (use of serums with ready-made antibodies, antibiotics) and symptomatic treatment is mandatory. If therapy is not started on the first day, then there is a high risk of losing your pet.
- For diseases caused by protozoa or parasites, it is necessary to identify the causative agent. This is the only way to choose the most effective drug that will help your pet.
You can also contact our site's staff veterinarian, who will respond to them as soon as possible in the comment box below.
Methods for removing growths
Before removal, they try to reduce colon polyps with courses of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Studies have proven that they resolve small tumors and significantly reduce the diameter of large growths.
Important! Aspirin is used when treating familial colon polyposis, but the risk of gastric bleeding and hemorrhagic stroke is taken into account.
If a single colon polyp is detected, a polypectomy method is used to remove it. Typically, the operation is performed immediately during a colonoscopy in an inpatient setting, when the patient comes for diagnosis. A year after the operation, a repeat procedure is necessary, since the colon polyp may reappear.
Intestinal resection is the removal of colon polyps using a classic surgical method. Indicated for focal lesions of the mucous membrane, as well as for the risk of dysplasia and the presence of ulcerative colitis.
Important! Resection is prescribed when large, ingrown tumors are detected that cannot be removed using gentle methods or constantly form again.
All surgical options, endoscopy and polypectomy, are discussed with the patient.
Treatment tactics
Depending on the degree of polypous lesion, the nature of the growth and the type of localization, surgical tactics are chosen.
The following methods are used for removal:
- Polypectomy. The traditional method of excision of a polyp using an electric knife, followed by cauterization of the wound surface with a laser or electrodes. The operation is performed using a rectoroscope or colonoscope.
- Transanal section. The method allows you to remove polypous lesions in the lower or middle parts of the colon using a rectoscope or colonoscope. A special loop is placed over the polyp, which is compressed and the polyp is excised. Next, the wound site is cauterized with an electric charge to prevent bleeding.
- Laparoscopic polypectomy. It is used when localizing a polypous lesion in hard-to-reach places. It involves several incisions in the peritoneum and further manipulation using surgical instruments.
- Resection. A radical method of polyp removal, prescribed for metastases and malignant tumors, may involve complete removal of the colon or part of it along with the affected mucosa.
Attention! Unfortunately, no operation guarantees the absence of potential oncogenic risks and the formation of a new lesion. In the overwhelming majority, surgery to remove polypous tumors is an adequate prevention against intestinal cancer.
Prognosis and complications
If a colon polyp is detected and removed on time, the prognosis is favorable. Not all growths degenerate into a malignant tumor. Surgery using the endoscopic method is a simple and safe procedure. It is recommended to all patients when growths are detected, since the operation reduces to zero the risk of the polyp degenerating into a malignant tumor.
Important! A balanced diet is followed regardless of the course of the disease, including after complete removal of tumors.
The diet for neoplasms should include dishes with calcium and folic acid. Doctors may prescribe supplements with these substances and additional antioxidants and vitamins.
Complications
With colon polyps, complications develop if the disease is not treated:
- more bleeding leading to anemia;
- degeneration into malignant cells;
- acute intestinal obstruction due to blockage of the intestine by large growths;
- inflammation of the intestine - acute enterocolitis, which can lead to intestinal perforation and death;
- the formation of fecal stones, which lead to appendicitis and other serious consequences, appear as a result of constipation.
During the operation, complications also arise - a hole in the area of the treated intestine. Through it, food can enter the abdominal cavity and cause peritonitis.
What kind of pathology?
Rectal polyps in children and adults are benign formations that grow on the epithelium of the rectum, but under a confluence of unfavorable factors they quickly multiply and increase in size. It is rare that such a disease can be detected in the initial stages, because the first symptoms of polyposis begin to bother you in the later stages, when the size of the tumor is impressive. If the polyp is not removed in a timely manner, the situation threatens to end in profuse hemorrhage, which can sometimes lead to serious consequences.
The signs of an anal polyp fully correspond to the characteristics of a benign tumor:
- the pathology does not affect the general condition;
- the atypical structure does not appear;
- a tumor from the rectum does not spread to neighboring organs and does not have the ability to metastasize.
If polyps are detected in a child or adult, the doctor will advise their removal, because if unfavorable factors coincide, the formations can become dangerous and become malignant at any time.
Prevention of neoplasms
You can avoid the appearance of polyps in the colon if you follow some rules. However, there are no uniform standards for prevention; neoplasms can appear even in completely healthy people who lead an active lifestyle and eat right.
Here are the main points that reduce the risk of developing the disease:
- diet correction – you need to adhere to proper nutrition;
- introducing more fiber into the menu - it improves bowel cleansing and prevents the formation of feces;
- giving up bad habits - low activity amid constant overeating, smoking and alcohol;
- examination at the first symptoms - especially in cases where spotting appears. After 50 years, all patients must undergo endoscopic examination;
- remove polyps as soon as they are discovered to prevent the formation of malignant cells.
The diet for the prevention of colon polyps deserves special attention.
Proper nutrition to protect against tumors
If you review your diet in time, get rid of the abundance of animal fats, carbonated drinks and refined foods with carbohydrates, you can improve your health. Not only in terms of the formation of growths.
Important! Proper nutrition encourages physical activity, but there are certain difficulties in making the transition. Endure the first month, and you will feel how much your mood, appearance has improved, and how much strength you have gained with a proper diet.
Plant-based foods with fiber are the basis of a healthy diet. This means that every day a person should eat a lot of vegetables, a little less grains and even less fruit. Animal fats are replaced with unrefined olive, sunflower, and pumpkin oil.
Useful for cleansing the body: apples, pumpkin, beets, carrots, cabbage and corn with zucchini. You need to eat in small portions, 5-6 meals a day. We must not forget about lean meat and fermented milk products, which have a positive effect on the intestinal microflora.
Removing polyps is the only way to cleanse the colon of tumors. This is necessary because some of the growths are prone to growing and degenerating into a cancerous tumor. After detecting neoplasms, be sure to review your diet and lifestyle - moderate physical activity and a proper diet significantly reduce the risk of recurrent polyposis.