Symptoms
In the acute phase, symptoms will be:
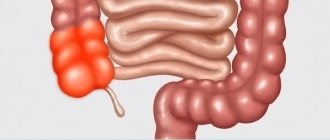
- pain in the right half of the abdomen, in the right iliac region;
- the nature of the pain is sharp and painful with possible irradiation to the groin;
- intoxication several hours after the onset of pain - nausea, vomiting, headache, increased body temperature, etc.;
- violation of bowel movements - constipation or diarrhea;
- flatulence.
On palpation, the abdomen is tense in the area of inflammation, the cecum is enlarged, and a loud rumbling can be heard due to accumulated gases.
The chronic form of the disease has more subtle symptoms and, as a rule, occurs due to non-compliance with the diet, psycho-emotional stress, or after a viral infection. Mild and moderate pain in the lateral abdomen, rumbling, and flatulence are observed. An increase in body temperature is not typical. There may be slight nausea, but more often the patient does not present such complaints. Possible weight loss, unmotivated weakness, fatigue.
Surgery
If the medical history records a calm course of the infiltrate and an obvious tendency to resolve, conservative treatment is necessary. In this case, the appendiceal infiltrate (dense and immobile) is the main contraindication to immediate surgical removal of the appendix.
This treatment for children and adults involves the following methods:
- strict bed rest;
- broad-spectrum antibiotics (gentamicin, ampicillin, ceftriaxone, etc.);
- a diet that is gentle on the intestines;
- physiotherapeutic procedures.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with: Rectal tumor: symptoms, surgery and consequences
Patients remain in the hospital until the tumor completely resolves (3-4 months, in children and the elderly - up to 6 months), after which a planned surgical operation is prescribed. It includes direct appendectomy (removal of the appendix), separation and fusion of organs, and sanitation of the entire abdominal cavity.
In cases where the diagnosis shows a mobile and loose appendicular infiltrate, as well as in early forms of the disease, a planned operation is permitted: appendectomy and separation of the omentum. After the operation, a drain is inserted into the right iliac region, through which the patient is administered antibiotics for 3-4 days.
If a purulent abscess is suspected, emergency surgery is necessary. The medical history reflects the following symptoms: fever, chills, increased pain, increased infiltration, increased leukocyte levels, etc.
Surgery for this diagnosis includes opening the abscess and emptying it, draining it. Then - postoperative treatment (antibiotics, bed rest, gentle diet, etc.). After 2 months, diagnostics are required:
Infiltration in acute appendicitis in most cases has the most favorable prognosis and does not pose any threat to the life of both adults and children. However, this disease has its own characteristics: recognizing and correctly diagnosing infiltration is not always easy, which is why it is so important to listen to any complaints of the patient and seek medical help in a timely manner.
Diseases of the cecum
Colitis
Main article: Intestinal colitis
A group of inflammatory bowel diseases that damage the intestinal mucosa.
Causes:
- hereditary predisposition;
- viral etiology;
- autoimmune effects (UC, Crohn's disease);
- chemical poisoning;
- psycho-emotional instability;
- bleeding of a section of the intestine (ischemic colitis).
Symptoms:
- pain in the right half of the abdomen or in the entire abdomen;
- constipation/diarrhea;
- chills;
- blood in stool;
- dry skin;
- intoxication;
- false urge to defecate.
Crohn's disease
Main article: Crohn's disease
It is a granulomatous inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, most often affecting the distal parts of the small intestine with the transition of the inflammatory infiltrate to the cecum.
We recommend reading:
Gastroenterocolitis: symptoms and treatment methods (diet, medications)
The reasons are not well understood, but there are several most likely ones:
- genetic predisposition;
- infectious theory;
- autoimmune inflammation.
Symptoms of Crohn's Disease:
- cramping pain in the right half of the abdomen after eating, the condition improves after defecation;
- flatulence;
- diarrhea;
- blood in stool;
- constant temperature from 37.1 to 38.0 °C;
- weight loss;
- headache, brittle nails, irritability, dry skin, etc.
Cecal diverticulosis
Main article: Intestinal diverticulosis
A disease that is a protrusion of a section of the intestinal wall.
The reasons may be:
- poor nutrition;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- overweight, high BMI.
Clinical picture:
- pain in the right half of the abdomen that does not disappear after defecation;
- flatulence;
- constipation;
- constant temperature from 37.1 to 38.0 °C.
In the initial stages of the disease, there may be no symptoms. Sometimes diverticula are an incidental finding during colonoscopy or irrigoscopy.
Cecal cancer
Main article: Colon cancer
This is a malignant neoplasm localized in the right iliac region.
Causes:
- chronic gastrointestinal diseases;
- genetic predisposition;
- exposure to harmful substances from food or occupation;
- age and gender: more often develops in men over 45 years of age;
- excessive consumption of fatty, smoked and spicy foods.
Symptoms:
- blood in stool;
- aching pain in the abdomen, mainly on the right;
- intoxication;
- weight loss
Prognosis of splenic angle syndrome
The prognosis in the initial stages and with appropriate treatment is favorable. The effect of surgery is good, but there is a risk of complications from surgery. I remind you: do not self-medicate. Seek help from your doctor.
If you find a typo in the text, please let me know. Select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags: anatomy, sphincter, colon
- Related Posts
- When the balance is out of balance: intestinal neural dysplasia
« Previous entry
Diagnostics
Laboratory methods
- general and biochemical blood test;
- general urine analysis;
- feces for occult blood.
Instrumental methods
- biopsy;
- colonoscopy or irrigoscopy;
- Ultrasound to assess the general condition of the digestive tract and identify concomitant pathologies.
When the first symptoms of cecal disease appear, you should consult a gastroenterologist.
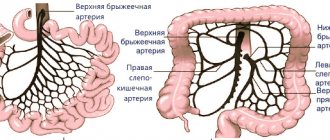
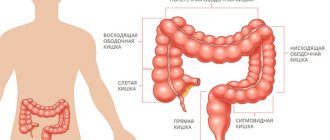
Role in the body, functions
The cecum is often confused with the appendix. Although these organs are related, they are completely different. The appendix is a branch from the cecum, its shape resembles a worm. It is separated from the cecum by the sphincter. The length can be between 2-13 cm.
The cecum is responsible for processing fluid and absorbing it. It performs this function due to its structure. Consists of a large number of absorptive cells. In addition, it contains Lieberkühn glands. This is a hyperplastic organ. The appendix plays a more important role in the body. It protects it from foreign cells.
Treatment
Aimed at the root cause that led to this pathological condition.
- In case of bacterial damage to a segment of the cecum, broad-spectrum antibiotics are used; in case of a pathogen identified, antibiotics to which the microorganism is sensitive are used.
- For a viral agent - antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs. In Crohn's disease, drugs that increase the immunological activity of the body are contraindicated. Since this disease is autoimmune, the following are prescribed: cytostatics (azathioprine), glucocorticosteroids (prednisolone), aminosalicylic acid derivatives (sulfasalazine).
- To reduce pain - antispasmodics (no-spa, duspatalin).
- To improve intestinal function during constipation - prokinetics (Ganaton, Motilium). Moreover, before prescribing treatment, diagnostic measures must be carried out in order to make the correct diagnosis. Thus, the prescription of prokinetics for diverticulosis not only will not solve the problem, but can also aggravate it, especially for diverticula that reach large sizes.
- For diarrhea - immodium.
- Probiotics to improve intestinal microflora - lactobacterin, bifidobacterin.
- A diet rich in plant fiber and the prescription of laxatives (Duphalac).
- Correction of the psycho-emotional background - tranquilizers, antidepressants, sedatives according to indications.
- For cancer of the cecum, radiation and chemotherapy, surgical removal of the affected segment, cytostatics, and painkillers are prescribed.
Prevention
- rejection of bad habits;
- fractional and rational nutrition (more plant foods);
- daily consumption of dairy products;
- normalization of the psycho-emotional background.
A scheduled examination by a gastroenterologist once a year with mandatory FGDS and colonoscopy will be able to identify pathology and begin treatment in a timely manner, which is very important, especially for cancer of the cecum.
In continuation of the topic, be sure to read:
- Typhlitis (inflammation of the cecum): symptoms and treatment methods
- Main symptoms of appendicitis
- Appendicitis: main signs and treatment of pathology + FAQ
- Details about the intestines: structure, sections and functions of the organ
- Caecum: location, structure and functions
- Large intestine: location, structure and functions
- Location and functions of the appendix
- Diseases of the colon: symptoms and signs of pathologies, treatment
- Intestinal colitis: symptoms and treatment in adults
- Proctitis: symptoms and treatment methods (diet, drugs, surgery)
MRSA: what doesn't kill us will make us stronger
Discussion: 4 comments
- Dmitriy:
2018-08-09 at 07:11Thanks for the review. Everything is clear and understandable. Is it possible to correct a defect using an endoscope? Is colon hydrotherapy used? I am a general practitioner, and my interest is not idle. I would be grateful for your answer.
Answer
Doctor:
2018-08-14 at 00:25
Hello! Do you mean laparoscopic surgery? Laparoscopic treatment is carried out. There are two options: laparoscopic reduction of the splenic flexure and resection of the elongated transverse colon. In the second option, it is technically very difficult to do completely minimally invasively, so a two-stage method was adopted. Mobilization of the intestine is performed entirely laparoscopically, while the anastomosis itself is performed extracorporeally. If by endoscope you meant colonoscope, then no - it cannot be adjusted “from the inside”. I have a rather reserved attitude towards colon hydrotherapy. But the siphon enema is our everything)).
2018-11-06 at 13:48
I also have Payr's syndrome (diagnosed by irrigography), well, the pain is in the ileocecal area, minor flatulence gives a severe pain. After the operation, how many months does it take to fully recover? (if a colon anastomosis was performed)
Answer
- Doctor:
2018-11-09 at 19:35
It all depends on the specific situation. The “strict” period after surgery is about 1.5 months (diet, limited physical activity).