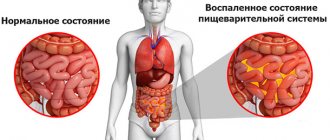
Causes of inflammation of the sigmoid colon
Most often, the sigmoid region becomes inflamed simultaneously with another section of the intestine (large intestine, rectum). So with colitis, proctitis or enterocolitis, the sigmoid colon is also affected by the disease. Less commonly, the sigmoid colon becomes inflamed on its own.
This happens in the following cases:
- irritation of the intestine with feces, when they become very hard and difficult to pass through the intestines;
- constipation, including during pregnancy, when the fetus grows and compresses the intestines, preventing feces from moving forward;
- insufficient blood supply to the intestinal walls due to atherosclerosis or thrombosis;
- Crohn's disease, diverticulitis, inflammation of the colon, paraproctitis;
- intestinal dysbiosis, may be due to long-term use of antibiotics;
- low physical activity, especially in a person who has a sedentary job;
- intestinal infections, as well as viral diseases;
- carrying out radiation therapy;
- formation of adhesions after intestinal surgery;
- abdominal injuries.
If you are having problems with your gut and you are not sure what is causing it, it is best to consult a doctor for advice. He will want to not only check the sigmoid colon, but also examine nearby parts of the intestine to get a more complete picture. Having established the causes of sigmoiditis, the doctor will prescribe treatment.
There is no need to do this yourself, because good modern drugs from advertising can only do harm if the diagnosis is incorrectly established.
Diagnostics
If at least one of the above symptoms appears, you should first contact a therapist or gastroenterologist. Based on the results of the survey and initial examination, the person is prescribed additional methods for examining the sigmoid colon:
- Sigmoidoscopy. With a sigmoidoscope it is possible to examine the rectum and the lower part of the sigmoid colon. Using this method, the mucous walls of the intestine are examined, polyps, tumors, and erosive processes are identified. It is possible to take biopsy material.
- Colonoscopy. A long, improved endoscope is used, which allows one to examine all parts of the large intestine, unlike a sigmoidoscope.
- CT (computed tomography). It is used to accurately determine the location of the tumor, its size, and the presence of pathological formations that displace the intestine. Using this method, the inflammatory process in the sigmoid colon is detected.
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging). A more informative method compared to computed tomography for cancer screening. High resolution makes it possible to detect tumors of the sigmoid colon without the introduction of contrast agents; it accurately determines the size of tumors and the presence of metastases to other organs and tissues.
- Irrigography. The method is based on an X-ray examination of the intestine with a contrast agent. Using irrigography, you can determine developmental anomalies, the shape of the intestine, its length, peristalsis, the presence of pathological formations, the presence of obstruction, and erosion.
We recommend reading:
Why does pain occur during bowel movements and how to diagnose the cause?
Causes
Common causes of irritable bowel syndrome:
- psychogenic factors - stress, overwork, increased nervous excitability, mental disorders, psycho-emotional lability;
- heredity - people who know about cases of IBS and IBS in close relatives are at risk;
- decreased motility of the intestinal tract of any nature - the condition is caused by a decrease in smooth muscle tone of a post-traumatic, medicinal, physiological nature;
- long-term drug therapy (especially antibiotics, hormones) - drugs often lead to the development of dysbiosis, chronic irritation of the intestinal lining;
- visceral hyperalgesia – a syndrome of decreased pain threshold, the body’s reaction to stimuli;
- exposure to hormonal, chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
Bad habits (tobacco smoking, alcohol abuse), homosexuality, internal hemorrhoids, chronic paraproctitis, proctitis, and abnormal development of the intestinal tract can contribute to the development of a pathological condition and functional disorder of the colon.
Causes
Inflammation of the sigmoid colon develops under the influence of the following factors:
- Causative agents of intestinal infections;
- Dysbacteriosis;
- Inflammatory diseases of nonspecific nature;
- Insufficient blood supply to the intestines (ischemia);
- Radiation sickness
Group of intestinal infections
Among diseases of infectious origin, dysentery, food toxic infections and amoebiasis are of primary importance. Most pathogens can produce toxins that differ in their tropism and type of action.
It is with shigellosis that the pathogen induces damage to epithelial cells, which leads to a decrease in the functional area of the hollow organ. The main mechanism of transmission is fecal-oral, and the source of infection is often a sick person or carrier.
The greatest danger to the patient is latent/erased forms of infectious intestinal lesions.
The incubation period of the disease and the severity of the clinical picture depend on the amount of incoming pathogen and the characteristics of the organism.
Dysbacteriosis
Inflammation of the sigmoid colon can occur due to disruption of the microflora in this section. The ratio of saprophytic bacteria depends on the state of a person’s immunity, as well as previous diseases. The following nosological units are of great importance:
- Shigellosis;
- Salmonella;
- Food poisoning infections (FTI);
- Parasitosis (amoebiasis, giardiasis).
The trigger factor for dysbiosis in inflammation of the sigmoid colon is considered to be long-term use of antibacterial drugs, the spectrum of action of which also covers representatives of one’s own microflora.
It is worth considering that the concept of “dysbacteriosis” does not exist in the international classification. It is also absent in the clinical practice of foreign doctors.
In maintaining the correct balance, diet and the presence of bad habits play a role. Addiction to alcoholic beverages and smoking, frequent consumption of poor-quality food causes changes in the conditions of the internal environment of the body.
Nonspecific inflammation
Sigmoiditis as a manifestation of nonspecific intestinal diseases may be one of the first pathological signs. These primarily include the following:
- Nonspecific ulcerative colitis;
- Crohn's disease.
The true causes and mechanism of development of these diseases are unknown to this day. Moreover, they manifest more often in people in the age group from 20 to 40 years. Inflammatory changes occur more often in the distal parts of the colon, so sigmoiditis is a characteristic manifestation.
Today, most researchers are inclined to believe that these diseases are of an autoimmune nature. People with a hereditary predisposition are at risk.
Ischemic command
The sigmoid colon has its own characteristics of blood supply, so in case of insufficiency, only this section is affected. The main reason for this is atherosclerosis. Manifestations develop gradually, reaching their peak after 60 years.
In this case, patients report complaints of extraintestinal symptoms of vascular damage in the form of one of the variants of coronary heart disease (angina pectoris, cardiosclerosis, history of heart attack) or cerebral insufficiency.
In more rare cases, the sigmoid colon is affected due to ischemia arising for the following reasons:
- In utero anomalies in the formation of vessels of the sigmoid colon;
- Diffuse connective tissue diseases;
- Compression of blood vessels from the outside by a tumor, enlarged lymph nodes;
- Spikes.
Chronic insufficiency of blood supply (hypoxia) can subsequently cause a secondary infection or narrowing of the intestinal lumen due to the proliferation of connective tissue with the formation of scars.
Radiation sickness
Chronic sigmoiditis can be a manifestation of radiation sickness, which is typical primarily for workers of hazardous enterprises and people injured as a result of the Chernobyl accident (liquidators, displaced persons, evacuated residents).
It should be taken into account that this form of the disease can occur in the long term - several months or even years after radiation exposure.
Inflammation of the sigmoid colon occurs as a side effect of radiation therapy in cancer patients with malignant lesions of formations in the pelvis (rectum, bladder, prostate, ovaries) or a metastatic process in the lymph nodes.
Features of treatment of the sigmoid colon
Treatment of sigmoiditis is considered a difficult and rather lengthy process. It requires the patient to follow all the doctor’s recommendations. The treatment process is based on diet and medication.
Nutrition for sigmoiditis
If the intestines are affected, the sigmoid colon will not be able to fully digest food and absorb water. As a result, the stool will stagnate or come out with undigested pieces of food.
In acute cases, nutrition should be gentle. It involves eliminating irritating foods from your diet.
Treatment of sigmoiditis with diet excludes the consumption of foods that are rich in carbohydrates and fats. This process leads to inhibition of digestion and the development of fermentation.
The following are completely excluded from the diet:
- fresh pastries and bread;
- fatty, fried foods;
- meat and sausages;
- soups and cereals with milk;
- strong meat broths;
- fish and canned food;
- caffeinated and alcoholic drinks;
- marinades, spices, seasonings, smoked meats.
For seven days, the menu should consist of vegetable broth and cereals. As a drink, you can use green tea, berry infusions, and rosehip decoctions. The diet should also include baked apples.
The menu can be gradually expanded. But the emphasis should be on preventing congestion in the sigmoid colon and constipation.
Drug therapy
If the sigmoid colon is affected, the location of the pain will be on the left side. An unpleasant feeling may occur during or after eating food, or when emptying the intestinal canal.
To get rid of this, the patient is prescribed treatment, which includes:
- painkillers and antispasmodics;
- antibacterial medications in the form of Doxycycline, Tetracycline, Phthalazole;
- adsorbent agents in the form of Smecta or Neo-smectin;
- enveloping and astringent medications. These include:
- Almagel;
- medications with anti-inflammatory properties.
Treatment of sigmoiditis also involves restoration of intestinal microflora. For this, the patient is prescribed probiotics in the form of Acipol, Bifidumakterin. The duration of treatment is from seven to fourteen days.
Traditional methods of treating inflammation of the sigmoid colon
You can restore the functioning of the digestive organ using folk remedies. They are used as additional therapy to reduce inflammation and stop diarrhea.
There are several effective recipes.
- First recipe: Herbs in the form of sage, mint, St. John's wort are taken in equal proportions.
The herbal mixture is poured into a mug of boiled water and infused for thirty to forty minutes. Then it is filtered. The finished product should be taken up to three times a day, one hundred milligrams, thirty minutes before consuming food. - Second recipe: Mix mint, motherwort and nettle in equal proportions.
The mixture is poured into a mug of boiled water and infused for about forty minutes. Then it is filtered. The medicine should be taken up to four times a day, sixty milliliters. The duration of treatment is three weeks. - Third recipe: To make the solution, take chamomile, sage and calendula.
Fill with a mug of boiled water and infuse. After which it is filtered and cooled to a temperature of 37 degrees. The solution is injected into the intestinal canal and held for at least ten minutes. These manipulations must be carried out before a night's rest for fourteen days.
When the first signs appear, you should urgently contact a specialist.
Prevention
Sigmoiditis often ends with total damage to the colon. The disease, even in a mild form, is fraught with dangerous complications. But you can prevent its development, for this you need to:
- stop smoking;
- do not forget about hygiene;
- eat right (not only choose healthy foods, but also follow the basic rules of eating);
- do not prescribe medications, especially antibiotics;
- treat other diseases in a timely manner.
At the slightest sign of sigmoiditis, you should consult a specialist. Only with the help of adequate therapy can severe complications, often resulting in death, be avoided.
Treatment of the sigmoid colon
Treatment of any stage of human intestinal inflammation is a long process that requires adherence to a regimen. Diverticulosis of the sigmoid colon is treated with medications, bed rest and a special diet. Drug treatment includes the following medications:
- antibacterial drugs: doxycycline, ampicillin, tetracycline, fluoroquinolones;
- painkillers and antispasmodics;
- drugs characterized by enveloping and astringent sedative effects;
- suppositories with methyluracil, corticosteroids and microenemas with chamomile decoction for acute sigmoiditis.
In case of exacerbation of the disease, treatment should include bed rest and diet, regardless of what symptoms are present. After the acute stage, the patient is recommended to take medications for several months, this will protect against cancer. Also, during treatment, conventional herbal medicine can achieve good results.
Authorized products:
- stale white bread and bread crumbs;
- steamed or boiled dietary meat: veal, turkey, rabbit, chicken. Meatballs, quenelles, soufflés, and cutlets are prepared from boiled meat. Instead of bread, boiled mashed rice is added to the minced meat;
- slimy and pureed soups in lean fish or meat broth. They add steamed meatballs, rice, meat puree, egg flakes;
- lean boiled or steamed fish. Dumplings and meatballs are made from minced meat;
- eggs in the form of a steam omelet or soft-boiled;
- low-fat and non-acidic pureed cottage cheese, steamed curd soufflé are allowed;
- Porridge can only be eaten pureed; it is boiled in low-fat broth or water. They use cereals such as oatmeal, rice, buckwheat;
- For drinks, it is recommended to drink black coffee without sugar, green tea, decoctions of bird cherry, blueberry, currant and rose hips;
- Allowed for consumption are sour mashed apples, jelly, bird cherry, currant, quince, pear and blueberry jelly.
Prohibited products:
- sweet bakery and flour products, fresh bread;
- fatty meats, lard in any form, meat products in the form of sausages and frankfurters;
- soups with a rich, strong broth, with the addition of pasta and vegetables. Milk soups are prohibited;
- canned fish, caviar, fatty fish;
- fried and hard-boiled eggs;
- any types of fats (vegetable oil and butter);
- fresh vegetables, fruits, berries, herbs;
- any sweets, honey, jam, chocolate;
- all herbs, spices, hot sauces;
- carbonated drinks, kvass, coffee and cocoa with added milk;
- pasta, pearl barley, millet, legumes;
- whole milk, fatty fermented milk products.
During the peak of an exacerbation, to prevent cancer from developing in the future, if there is severe pain and diarrhea, it is better to stop eating altogether for one or two days. At this time, it is recommended to drink as much liquid as possible: strong black and green tea, a decoction of rose hips, currants, and bird cherry. Too hot or cold foods should be removed from the diet and salt intake should be limited. You should not eat fatty, fried foods, marinades, smoked foods, spices, or alcohol. For normal functioning of the digestive system, it is useful to take decoctions of medicinal herbs: mint, oak bark, chamomile, St. John's wort, sage.
Treatment with folk remedies
In some cases, herbal decoctions help prevent the development of cancer; they help to subside inflammatory processes, improve intestinal function, have an astringent effect and stop diarrhea. We recommend that you drink tea made from medicinal herbs. To do this, take plantain leaves, dill seeds, chamomile flowers, celandine and rose hips in equal quantities (one teaspoon each).
The collection is brewed in a liter of boiling water and allowed to brew for six hours. The resulting infusion is drunk a quarter glass before meals 6 times a day. The duration of treatment should be four weeks. Then they take a break for a week and repeat the course of taking the herbal decoction again. To consolidate the result, it is advisable to repeat this course of treatment three times.
For prolonged diarrhea, juice from plantain leaves helps well. It has a pronounced astringent effect. The juice is squeezed from the crushed leaves of the plant. A tablespoon of juice will need to be diluted in a glass of boiled water, and taken half an hour before meals.
With the right treatment tactics, in most cases it is possible to achieve an improvement in well-being, avoid cancer and, ultimately, achieve a full recovery. The patient needs to be patient, as the treatment process is quite long and is accompanied by strict dietary restrictions. Only with strict adherence to all medical recommendations is it possible to recover and return to a full life.
Treatment
Relief of inflammatory processes on the mucous membrane of the sigmoid colon takes quite a long time. And the success of treatment directly depends on the patient’s ability to strictly follow all the recommendations of the attending physician.
How to treat sigmoiditis? The main points of treatment are drug therapy and strict adherence to diet.
Drug therapy
In the presence of an acute course of the pathology, the patient is prescribed bed rest. The effect of medications prescribed for diagnosed sigmoiditis is aimed at relieving the causes of the disease, inflammation of the mucous membrane, as well as symptomatic manifestations of the disease.
Thus, the drugs that form the basis of treatment include:
- painkillers (depending on the individual characteristics of the patient and the tolerability of certain components);
- antispasmodics;
- absorbent drugs - Neosmectin, Smecta (if there are contraindications - activated carbon);
- antibiotics - Doxycycline, Tetracycline (for more serious or extensive infections - Ampiox, Fthalazol);
- antacids - Almagel and others;
- anti-inflammatory drugs - Salofalk and others;
- probiotics - Linex, Hilak-Forte (mandatory use after a course of antibiotics or after relief of symptoms);
- rectal suppositories (suppositories) - suppositories for sigmoiditis are prescribed as an additional measure. Depending on the goals pursued, medications with mityluracil, sea buckthorn oil, and others may be prescribed.
In some cases, in particular, if catarrhal sigmoiditis is diagnosed (that is, the least dangerous and unexpressed), microenemas with medications are prescribed.
Diet
The main objectives of the diet compiled in the treatment of sigmoiditis are:
- avoiding irritation of the mucous membrane of the sigmoid colon;
- helping to relieve inflammation in this area;
- restoration of normal functioning of the digestive tract.
A diet for sigmoiditis, or rather with antisigmoiditis therapy, implies a serious reduction in consumed fats and carbohydrates.
The result is an almost complete absence of fermentation and putrefaction of the intestinal contents. There is an improvement in peristalsis, as well as the production of only the digestive juice necessary for normal digestion.
The minimum period for following this type of diet is 7 days. It also provides for the principle of fractional nutrition, that is, eating food often, but in small portions (the average number of snacks per day should be 6-7 times).
One of the recommendations would be to accustom the digestive system to a regular diet - eating food every day at the same time, this helps improve peristalsis and normal digestion of consumed foods.
Another feature is the type of food served - it should be grated, liquid or pureed. Hard large pieces are strictly not recommended.
The main thing is a diet for inflammation of the sigmoid colon, which involves excluding from the diet:
- freshly baked bread and pastries;
- fatty meats and fish;
- smoking and canning products (especially industrial);
- rich broths and soups made from milk;
- whole milk and its derivatives;
- fermented milk products with a high fat content;
- fresh vegetables, berries, fruits and herbs;
- hot spices and herbs, marinades;
- carbonated drinks (including homemade ones, for example, kvass), coffee, strong tea;
- alcoholic products.
Conversely, the basis of nutrition should be products from the following list:
- lean meat, fish and poultry (passed through a grater or blender);
- meat soufflé, steamed cutlets;
- vegetable puree;
- dried bread (white);
- steamed omelettes and soft-boiled eggs;
- porridge (oatmeal, rice, buckwheat), exclusively cooked in water and passed through a blender;
- fermented milk products with reduced fat content;
- weak green tea and fruit and berry compotes;
- apples (grated in small quantities).
In the acute form of the pathology, accompanied by pain of increased intensity, you need to generally limit food intake for 1-2 days, that is, fast.
Sigmoiditis
Sigmoiditis (sigmoiditis; Latin intestinum sigmoideum sigmoid colon + -itis) is inflammation of the sigmoid colon, a type of segmental colitis. First described in 1893 by A. Mayor. Isolated sigmoiditis is rare. It is often combined with proctitis (see full body of knowledge) and in these cases is called proctosigmoiditis.
The etiology, pathogenesis and pathological anatomy are the same as for colitis (see full body of knowledge).
Sigmoiditis can be acute or chronic. Acute sigmoiditis is characterized by the appearance of pain in the left iliac region, which, depending on the severity of the pathological process, can be moderate or cramping, a change in the nature of bowel movements and stool frequency; acute sigmoiditis is most often a symptom of dysentery (see full body of knowledge).
With chronic sigmoiditis, patients complain of pain in the left half of the abdomen, mainly in the lower part, which intensifies before or after defecation, with prolonged walking, shaking, or physical stress; There is an alternation of diarrhea and constipation, as well as false diarrhea (see the full body of knowledge: Constipation, Diarrhea). Patients are concerned about bloating, loud rumbling in the intestines, belching, and sometimes nausea and vomiting. In severe cases, there is weakness, a drop in body weight, and an increase in temperature. On palpation, thickening, compaction, and tenderness of the sigmoid colon are determined. Mucus, sometimes blood, and pus are found in the stool.
The inflammatory process in chronic sigmoiditis often spreads to the visceral peritoneum with the development of perisigmoiditis. As a result, fusions of the intestine with surrounding organs are formed. Perisigmoiditis can also occur due to trauma or abdominal surgery. The localization and nature of pain in perisigmoiditis do not differ from those in sigmoiditis. A characteristic sign of perisigmoiditis is the limitation or absence of mobility of the sigmoid colon during palpation of the abdomen. During X-ray examination, the sigmoid colon is fixed, its contour is flattened.
The diagnosis is made on the basis of clinical picture, results of bacteriological, microscopic and biochemical examination of stool, X-ray and endoscopic examination. Microscopic examination of stool reveals leukocytes, red blood cells, mucus, and intestinal epithelial cells. A biochemical study reveals increased excretion of enzymes and protein in feces (see full body of knowledge: Feces). The endoscopic picture (see the full body of knowledge: Colonoscopy), as well as the results of histological examination of the biopsy material, depend on the cause of sigmoiditis. X-rays reveal changes in the intestinal mucosa in the form of deformation, an increase in caliber, a decrease in the number of folds until they disappear, rigidity of the intestinal wall, unevenness barium column, filling defects and others (see full body of knowledge: Irrigoscopy).
Differential diagnosis is carried out with tumors of the colon (with cancer, early stenosis of its lumen often occurs), with diseases of the urinary tract, female genital organs, appendicitis with an atypical location of the appendix.
They recommend rest and a gentle diet with limited plant fiber. Antibacterial, antispastic, analgesic, sedative, astringent, enveloping agents are used; local treatment with suppositories and microenemas with starch, chamomile, fats, vitamin A, methyluracil, corticosteroids and others are widely used
With timely treatment and compliance with the recommended regimen, the prognosis is usually favorable.
Prevention of chronic sigmoiditis consists of preventing acute intestinal diseases, eliminating foci of infection in the body, rational nutrition and adherence to food intake.
Reasons for the development of pathological processes
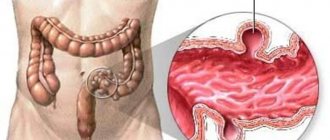
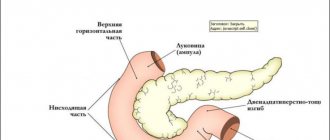
In appearance, the sigmoid colon resembles the Latin letter sigma. The length of the sigmoid colon is about sixty centimeters. Its main function is to digest food, absorb water and saturate the body with it. It also contains the formation of feces.
Where is the sigmoid colon located? This area is located on the left side in the retroperitoneal space. In the female half of the population, it is located directly behind the uterine cavity. In men, the sigmoid colon is located behind the bladder.
This type of intestinal tract is considered one of the largest. The unusual shape allows it to trap moving food, allowing it to be digested and formed into feces. From the sigmoid colon the mass passes into the rectum, from where it exits.
Often in practice there is a disease such as sigmoiditis. It is characterized by the development of an inflammatory process, which occurs due to stagnation of feces and the entry of an infectious agent as a result of injury to the mucous membrane.
The causes of the development of the disease in the sigmoid colon are:
- disturbance of blood flow in the pelvic organs;
- dilatation of venous vessels;
- diseases of the rectum in the form of fissures in the anus, proctitis, paraproctitis, Crohn's disease;
- colibacillary infections, dysentery, dysbacteriosis in the intestinal canal;
- malnutrition, lack of vitamins and minerals, lack of foods rich in fiber;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- constant constipation;
- deterioration of digestive peristalsis;
- diseases of the digestive system in the form of duodenitis, cholecystitis, enzyme deficiency;
- pathological processes in the prostate gland;
- chronic diseases in women;
- increased pressure on the intestines during pregnancy;
- surgical interventions on the abdominal cavity;
- abdominal injury.
If a person has experienced at least one of the above reasons, then it is worth visiting a doctor for consultation and further examination. The sooner the disease is detected, the easier and faster it will be cured.
Classification
The scope of therapeutic measures often depends on the characteristics of the disease, so there is a need to reflect them in the clinical diagnosis. Sigmoiditis is classified according to the following principles:
- Catarrhal sigmoiditis . Characterized by the development of superficial inflammatory changes in the mucous membrane. The clinical picture may be absent or mild, without causing severe discomfort to the person;
- Erosive sigmoiditis . Develops as a result of poorly treated or ignored catarrhal inflammation. Characteristic lesions appear that are prone to deeper damage;
- Ulcerative sigmoiditis . In this form, inflammation affects the deeper layers of the intestinal wall, which is accompanied by hemorrhages (bleeding).
- Perisigmoiditis . All layers of the wall are damaged up to the serous membrane, which leads to the formation of infiltrates and adhesions. Inflammation can spread to nearby organs and soft tissues of the gastrointestinal tract.
In some cases, the clinic of spastic sigmoiditis can be observed. This occurs when the autonomic regulation of intestinal activity is disrupted.
Diagnostic and treatment methods
Any disease of the transverse colon requires medical attention.
Symptoms indicating diseases of the transverse colon:
- stomach ache;
- difficulty defecating;
- flatulence;
- diarrhea;
- the urge to defecate immediately after eating;
- tarry stools with a foul odor.
The doctor can examine the transverse colon using different methods.
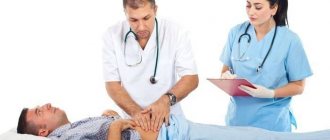
With the help of palpation, benign and malignant tumors can be detected. Palpation is performed with both hands. The patient is asked to take a deep breath.
After this, applying gentle pressure, the doctor pushes the skin of the abdomen upward and plunges his fingers into the abdominal cavity, reaching the posterior wall of the peritoneum. Usually the transverse section can be well palpated.
Irrigoscopy is an x-ray of the colon, previously filled with a contrast suspension. Irrigoscopy helps to detect tumors, chronic colitis, diverticula, narrowings, fistulas and other pathologies.
Colonoscopy is the most reliable method of examining the large intestine.
Colonoscopy is performed with a special device. There are many models of colonoscopy machines, all of which make it possible to examine the intestine from the inside along its entire length.
During a colonoscopy, you can take tissue for a biopsy, remove a benign tumor, stop bleeding, and remove a foreign body.
Having diagnosed the disease, the doctor will prescribe treatment. There are two main methods of treating the transverse colon (conservative and surgical) and several auxiliary ones.
Having detected inflammation in the transverse colon, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics and prescribe symptomatic treatment, which will consist of taking antispasmodics and other painkillers.
In some cases, local treatment will be useful: enemas with decoctions of medicinal herbs - chamomile, mint.
Some diseases of the transverse part of the large intestine require the use of enzyme preparations: Festal and others. After treatment with antibiotics, it is necessary to restore the intestinal microflora.
For this purpose, bacterial preparations are prescribed: Bifidumbacterin, Bactisubtil and others.
Instead of Bifidumbacterin, the doctor may prescribe a bio-cocktail that contains beneficial microbes, minerals, vitamins and medicinal herbs.
Drug treatment is well complemented by diet therapy, physiotherapy, and mineral water intake.
If conservative treatment does not help, surgery may be required. Surgeries on the large intestine are performed using classical and laparoscopic methods.
Video:
In the first case, a large incision is made in the abdominal cavity, in the second, the operation is performed through a small hole.
Surgical treatment may involve removing part of the transverse colon or cutting off the diverticulum.
In the case of hereditary polyposis and ulcerative colitis, it is sometimes necessary to perform a colectomy, that is, complete removal of the transverse part of the colon.
It can be concluded that diseases of the transverse colon are few in number, but many of them are life-threatening and require surgical intervention.
Most diseases of the transverse part of the large intestine are highly preventable. To do this, you need to eat right and make sure that the intestinal contents do not stagnate.
Do I need to take antibiotics?
Infectious sigmoiditis of bacterial origin usually does not require systemic antibiotics. The required therapeutic effect can be achieved by using selective drugs that include nifuroxazide. In severe cases, penicillin antibiotics may be prescribed: Ospamox, Flemoxin, Augmentin. Preference is given to combinations of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid, but the acid component may be contraindicated if there are signs of mucosal ulceration, so any antibiotics should be selected by the attending physician.
"Augmentin"
Diseases of the sigmoid colon
Diseases of this section of the digestive system become a consequence of fecal obstruction, arising due to a violation of the elasticity of the walls of the sigmoid intestine, with the detrimental effect of intoxication products on the gastrointestinal tract. All diseases of the sigmoid colon are accompanied not only by an internal inflammatory process and an acute attack of pain, but also by external changes in this section and its epithelial layer. Such changes can be tracked clinically - using ultrasound. Early diagnosis helps avoid serious complications in the future.
Dolichosigma intestinalis
Even a child can be diagnosed; it is important to treat the disease in a timely manner. Dolichosigma is a pathological elongation of the sigmoid colon or mesentery (mesocolon), resulting in impaired intestinal motility
In such a clinical picture, megadolichosigma is observed, i.e. abnormal thickening of the walls. Constipation and paroxysmal abdominal pain are eloquent signs of the disease, but in order to determine the fact of damage to the large intestine, a comprehensive diagnosis is required.
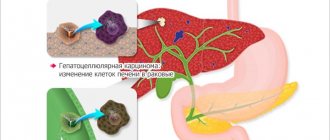
Cancer
Adenocarcinoma, neoplasia carcinoma, blastoma, distal tumor are malignant neoplasms that, with successful treatment, reduce the quality and life expectancy. For example, a villous tumor of the sigmoid colon is difficult to diagnose at an early stage; the symptoms are similar to classic food poisoning (bloating, flatulence, diarrhea, nausea). The approach to the problem is comprehensive and includes diagnostics of the body with biopsy and sigmoidoscopy. Treatment is carried out surgically - removal of the tumor with long-term rehabilitation.
Inflammation
If an inflammatory process occurs in the sigmoid part of the intestine, in medical practice this disease is called sigmoiditis, and is treated with conservative methods. Common causes of the disease are increased activity of intestinal infections and an imbalance of bacteria (dysbacteriosis). Doctors remind us of radiation sickness and intestinal ischemia, pressure of neighboring organs and impaired circulation as pathogenic factors that can provoke the first attack.
With progressive inflammation, doctors recommend taking painkillers and additionally drinking probiotics to restore intestinal microflora. To destroy pathogenic flora, treatment of sigmoiditis necessarily includes the prescription of antibiotics. Vitamin therapy and a therapeutic diet also become an integral part of an integrated approach to health problems. It all depends on the form of the characteristic disease. It could be:
- proctosigmoiditis (spastic colitis);
- focal sigmoiditis;
- bend;
- erosive sigmoiditis.
Diverticulosis
If the blood supply to tissues is impaired and improper transportation of feces to the intestines, the patient develops another disease. It is called diverticulosis and is relapsing in nature. The inflammatory process spreads to the sigmo-rectal sphincter, which connects the rectum and sigmoid colon and is responsible for the excretion of feces.
The disease starts with an acute attack of pain, which is localized in the left side of the abdomen. During the pathological process, intestinal motility is impaired, and high intraluminal pressure occurs. The patient cannot understand its cause for a long time, and the truth is revealed by ultrasound. Inflammation of diverticula of the sigmoid colon is treated conservatively in a hospital setting.
Find out in more detail what sigmoid colon diverticulosis is - symptoms and treatment of the disease.
Symptoms of the disease
Since the organs are located in a spacious area of the peritoneum, the patient may not feel a problem in his own body for a long time. The first signs of sigmoid colon disease are an acute attack of pain, which only intensifies with palpation of the sigmoid colon. This occurs during a progressive pathological process in which other structures of the gastrointestinal tract are involved, for example, the pancreas. The characteristic symptoms of the disease are presented below:
- upset stool, unusual color of stool;
- sharp pain during the resting stage or after defecation;
- belching leading to vomiting;
- increased signs of dyspepsia (flatulence, nausea, bloating);
- sudden weight loss;
- lack of appetite;
- loss of strength, weakness.
- Polyps in the intestines - first symptoms and manifestations, treatment
- Signs of polyps in the intestines
- Pneumatosis intestinalis - symptoms and signs. Treatment of pneumatosis intestinalis with drugs and folk remedies
Sigmoid colon hurts
This symptom does not appear at the initial stage of the characteristic disease. Severe pain in the sigmoid colon indicates a prolonged course of inflammation, increased pressure from the source of pathology on neighboring organs. The doctor cannot make a diagnosis; differentiated diagnostics is required. For example, upon palpation, an acute attack of pain only intensifies and radiates to the hypochondrium area. Taking painkillers helps it subside, but this is a temporary effect. It is important to look for the cause in order to avoid the chronic course of this disease.
Diseases
Where is the colon located and how does it hurt? First of all, a person who has inflammation of this part of the organ will feel pain in the lower abdomen and discomfort in the anus.
In addition, other signs of pathology may be observed:
- regular constipation;
- discharge of pus from the anus;
- the presence of blood impurities in the stool;
- flatulence;
- painful urge to defecate;
- loose stool.
If a person has pain in the upper, transverse, descending colon, symptoms of pathology may also indicate iron deficiency anemia. This occurs due to the formation of bleeding ulcers or erosions in the affected organ.
Diseases of the colon occur for the following reasons:
- lifestyle errors: physical inactivity, overeating, abuse of fatty foods;
- hypotension;
- chronic constipation;
- abuse of dietary supplements of dubious quality;
- long-term treatment with antibiotics.
The colon, the symptoms of inflammation of which cannot be ignored, is susceptible to many diseases, including the formation of a malignant tumor.
Hirschsprung's disease
This is a hereditary pathology that manifests itself in a person in infancy or early childhood.
A person with this disease suffers from prolonged constipation, which can last over several weeks.
In this case, enemas and laxatives are useless. However, constipation in Hirschsprung's disease alternates with debilitating diarrhea.
All these disorders of the functioning of the digestive system occur due to ganglion cells of the colon.
The parts of the intestine located above it hypertrophy due to constant contractions, which is why the intestines cease to empty themselves. With this disease, a person is indicated for surgery to remove hypertrophied parts of the organ.
Diverticulosis
The disease can be either congenital or acquired. Diverticulosis is a disease that is accompanied by protrusion of sections of the intestinal mucosa through its muscular layer. This is accompanied by the formation of sac-like formations in which feces can accumulate, which can provoke inflammation of the organ mucosa.
Typical symptoms of diverticulosis include lower abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhea and vomiting. Ignoring treatment for diverticulosis can lead to such serious consequences as organ obstruction, phlegmon and peritonitis.
Polyposis
A disease accompanied by the formation of growths on the mucous membrane of the organ, the size of which ranges from several millimeters to several centimeters.
Polyps are dangerous because they can degenerate into malignant neoplasms, that is, provoke intestinal cancer.
Symptoms of the disease include problems with defecation, since growths in the lumen of the organ interfere with the free movement and exit of feces.
If the polyps are large, the patient may suffer from hemorrhages inside the organ. Polyposis is treated surgically, as well as using cytostatic drugs.
Oncology
Often, inflammation of the colon, the symptoms and treatment of which is extremely important, leads to cancer of this part of the intestine. Oncologists consider colon cancer the least dangerous type of cancer of the gastrointestinal tract. However, the threat of this disease to human life lies in the fact that the symptoms of the disease resemble signs of a disorder in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
So, the patient suffers from symptoms such as diarrhea, pain and colic in the lower abdomen, slight discharge of blood and mucus during bowel movements. But as the disease progresses, symptoms such as anemia and prolonged constipation, caused by a narrowing of the lumen of the colon, increase.
In this case, cancer is treated surgically: the affected part of the organ is removed along with part of the mesentery and nearby lymph nodes.
If metastases occur after surgery, a course of chemotherapy is given.
In the first stages of the disease, the prognosis for patient survival is 70%, but in the last stages of cancer the probability of death is at least 80%.
Possible symptoms of colon cancer cannot be ignored, because timely consultation with a doctor will allow treatment of the disease to begin as early as possible.
Symptoms
The manifestations of the disease directly depend on the form of its course.
Thus, the acute form of inflammation of the sigmoid intestine has the following characteristic features:
- intense pain in the left side of the abdominal cavity (in some cases, the pain tends to radiate to the left leg);
- increased gas formation with all the ensuing consequences (flatulence, bloating);
- systematic diarrhea, accompanied by a strong unpleasant odor of feces, as well as the presence of mucous, blood or purulent fragments in them (in some cases);
- feverish state (pallor of the skin, general weakness);
- nausea, sometimes with bouts of vomiting.
In the chronic form of the disease (chronic non-ulcer sigmoiditis), the symptoms are not intense and include the following conditions:
- bowel dysfunction, with attacks of diarrhea and constipation alternating;
- pain during defecation;
- constant discomfort in the abdominal area.
Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the sigmoid colon is characterized by a disruption of the digestive processes, and therefore the ability of this and adjacent sections to absorb contents.
All this, naturally, negatively affects the saturation of the body with necessary substances, which often leads to a sharp decrease in body weight. And the prolonged presence of fecal matter in the intestines leads to gradual poisoning of the body with toxins and, as a result, the appearance of allergic skin reactions.
The chronic form is characterized by alternating periods of exacerbation and remission, during which the symptoms of sigmoiditis are practically or completely absent.
The pathology can worsen in the presence of favorable conditions for this, these include:
- non-compliance with the diet prescribed by the doctor;
- serious physical activity;
- serious stressful situations;
- infectious infection;
- various types of trauma (especially the abdominal cavity).
Diagnostic measures
Diagnosis of sigmoiditis is often carried out jointly with specialists such as a gastroenterologist, gynecologist, proctologist, surgeon and infectious disease specialist. For severe abdominal pain, the first priority is to identify life-threatening conditions. Before the manifestation of the form of the disease and its type, other inflammatory processes in various parts of the abdominal cavity (cholera, dysbacteriosis, manifestations of dysentery) are excluded. Diagnostic measures consist of the following measures:
- study of clinical history;
- investigation of complaints;
- palpation of the abdomen and iliac region;
- urine and blood tests (usually detailed biochemical tests);
- stool analysis for occult blood, dysbacteriosis, intestinal infections;
- sigmoidoscopy;
- X-ray;
- gynecological examination (in women);
- examination by a urologist (for men).
If all possible pathologies with a similar symptomatic picture are excluded, then sigmoiditis or inflammation of the sigmoid colon manifests itself. Usually, the diagnosis of primary sigmoiditis, if excluded by the symptom of “acute abdomen,” does not cause serious problems. Before checking the sigmoid colon, the doctor will familiarize you with the necessary preparation rules.
Types of sigmoiditis
As mentioned earlier, inflammation of the sigmoid colon can be acute or chronic.
- The acute form is accompanied by pronounced clinical manifestations. It develops soon after exposure to a traumatic factor, for example, an intestinal infection.
- The chronic form has less pronounced symptoms and often occurs due to dysbacteriosis.
The disease is also divided depending on the nature of the damage. Sigmoiditis happens:
- catarrhal - the mildest form of the disease, in which inflammation covers only the upper layer of epithelial tissue;
- erosive - usually develops as a result of untreated catarrhal sigmoiditis, when it forms erosions on the mucous membrane that can bleed;
- ulcerative is the most severe form of the disease, which is characterized by the formation of ulcers on the mucous membrane; either one ulcer or several foci of different depths and localization can occur. Often develops with ineffective treatment of erosive sigmoiditis.
Ulcerative sigmoiditis is the most severe form of the disease, which is characterized by the formation of ulcers on the mucous membrane.
Sigmoid colon cancer: symptoms and signs with photos
In the earliest stages, sigmoid colon cancer develops for a long time without external changes, and with the first visible symptoms it quickly progresses, increasing the speed of the disease. Such dynamics (asymptomatic progression) occur in all types of cancer, so the best solution is to fight, and not to neglect your health to the point of obvious symptoms. Minor manifestations are often harbingers of trouble, so you should not ignore them.
The onset of the disease is gradual. General weakness, unmotivated fatigue, poor appetite, decreased tolerance to physical activity are typical primary complaints of the patient. With a more detailed study, you can notice signs of paraneoplastic syndrome, which is expressed by spots on the skin, rashes of unknown origin, itching (see photographs). Later, constipation occurs due to partial occlusion of the lumen of the sigmoid colon, sometimes alternating with diarrhea.
Late signs include:
- • pain syndrome;
- • endogenous intoxication;
- • chronic intestinal obstruction.
The abdomen hurts in the left iliac region, the pain is aching, becomes more intense over time and becomes debilitating. Increased heart rate, increased body temperature, increased respiratory rate, disturbances in acid-base and water-electrolyte balance are characteristic features of endogenous intoxication. The doctor can also feel a lump-like formation.
The initial signals of the disintegration of a cancerous tumor are mucous or mucopurulent contents in the stool, often mixed with blood. It irritates the perianal area and causes a burning sensation.
General information
Sigmoiditis is a group of inflammatory processes of various etiologies affecting the sigmoid colon. It occurs acutely or chronically, can be isolated or combined with inflammatory damage to other parts of the large intestine. The most common condition is simultaneous inflammation of the sigmoid and rectum - rectosigmoiditis. Sometimes the symptoms of sigmoiditis prevail with colitis - diffuse inflammation of the colon. In the sigmoid colon, inflammatory processes develop more often than in other parts of the intestine. Sigmoiditis affects both sexes, with a predominance of women noted among patients. Adults suffer more often than children. The likelihood of occurrence increases with age.
Functions
The sigmoid colon performs important functions for the body:
- The sigmoid colon contains beneficial microflora. It helps strengthen the immune system, participates in the synthesis of vitamins, and promotes the digestion of food debris that does not disintegrate under the influence of gastric and intestinal juices.
- Absorption of water and electrolytes. Numerous studies have proven that the most water and ions are absorbed in the sigmoid colon.
- Removal of feces. Normally, the rectum is empty. Feces accumulate in the sigmoid colon, and when it moves into the ampulla of the rectum, a reflex urge to defecate occurs.
Disruption of the sigmoid colon leads to diseases. If the absorption function is impaired, a violation of hemostasis and vitamin deficiency occurs. And if the sigmoid colon inhibits the movement of feces, constipation occurs. The cessation of the inhibitory influence leads to diarrhea.
Risk group
The occurrence of epithelial neoplasia of the sigmoid colon is due to various reasons:
- Heredity. It has been proven that patients who have close relatives with colon cancer have a high risk of acquiring this type of cancer;
- Polyps and polyposis. In terms of their properties, they are benign formations, but they tend to develop into malignant tumors;
- Diseases such as sigmoiditis, Crohn's disease, chronic colitis, etc.;
- Age. Sigmoid colon cancer is detected in patients aged about 40-60 years;
- Peristalsis disorder, constipation;
- Abuse of alcohol and carcinogenic products;
- Smoking;
- Diabetes mellitus type 2;
- Poor nutrition, with uncontrolled consumption of unhealthy fats and fast carbohydrates.
Complications
If there is no timely treatment, then sigmoiditis most often progresses further, affecting other parts of the intestine. For example, proctitis is observed as one of the complications in patients. With the progression of ignored inflammation, proctosigmoiditis symptoms and untimely treatment lead to a violation of the intestinal tightness, which can provoke an outbreak of peritonitis. Peritonitis is an inflammatory process in the peritoneum, which is most often eliminated surgically.
If the patient consulted a doctor in time for medical help, underwent a detailed diagnosis and effective treatment prescribed by a specialist, then the result of such actions will be a complete recovery. However, you should not expect a quick effect of therapy. During medical procedures, patients are largely limited in nutrition.
Pathological expansion
Enlargement of the sigmoid colon can be a congenital pathology or an acquired disease. It usually occurs against the background of expansion of the rectal ampulla. Symptoms: constant constipation, abdominal pain. For several years, constipation may be the only symptom of the disease. In this case, defecation occurs 1-2 times a week. The stool has an abnormally large diameter and a dense consistency.
Over time, nagging pain in the abdomen occurs, which weakens or disappears after defecation. The release of a large volume of feces is possible only with strong straining. This leads to the formation of anal fissures, stretching of the anal sphincter, and the development of hemorrhoids.
Dilatation of the sigmoid colon occurs due to problems with peristalsis. In patients, the urge to defecate occurs only during a significant increase in intraintestinal pressure, which is not typical for healthy individuals. This leads to the accumulation of large amounts of feces in the intestines.
If symptoms are severe, consultation with a gastroenterologist and x-ray diagnostics are necessary. Treatment consists of diet, enemas, and laxatives.
Nutrition and sigmoiditis
The diet for intestinal sigmoiditis No4 (table No4) in clinical medicine involves limiting calories to 2000 kcal per day. This diet helps eliminate toxins and metabolic products, inhibits rotting and fermentation in the intestinal cavities, and reduces the symptoms of intoxication. The duration of such a diet is determined individually (about 7-10 days). Patients eat fractionally, in small portions. For chronic and acute sigmoiditis, it is allowed to use:
- dietary lean meat (rabbit, chicken, minced boiled meat cutlets);
- low-fat fish, steamed or boiled;
- stale bread;
- soups with lean broth (pureed);
- egg omelet, soft-boiled eggs;
- granular cottage cheese (additionally pureed);
- grated fruits.
Preferred drinks include sugar-free compotes, rosehip decoctions, lingonberry or cranberry juice, and clean drinking water. It is necessary to exclude carbonated drinks, aggressive foods, fresh baked goods, fatty fish or meats, legumes and pasta. In some cases, it is recommended to completely exclude food except drinking (rosehip infusion, chamomile).
Staging and prognosis
According to the worldwide classification of diseases, the ICD 10 code is C18.7.
The development of a malignant neoplasm of the sigmoid colon is divided into 4 stages:
Stage 1 . The tumor is located within the sigmoid colon. If detected at this stage, the survival rate is almost 100%.
Stage 2 . Divided into two subspecies.
- 2A , when the tumor occupies less than half the diameter of the intestine and grows inside the lumen;
- 2B , when the tumor grows into the wall of the sigmoid colon.
There are no metastases. The prognosis is good, the five-year survival rate in both cases is above 80 percent.
Stage 3 also consists of two options.
- 3A – The tumor occupies more than half the diameter of the intestine, without metastasis. Survival rate is about 60%;
- 3B – The tumor metastasizes to regional lymph nodes. Survival rate is about 40%.
Stage 4 . It is characterized by the growth of the tumor into neighboring organs, metastases in the lymph nodes and in distant organs. Chance of survival up to 10%.
Classification and types
Sigmoiditis is classified according to different clinical manifestations, which greatly facilitates diagnosis and subsequent treatment. Based on the type of inflammation, sigmoiditis is classified into acute and chronic forms. Based on the nature of the inflammatory process, sigmoiditis is divided into the following types:
- Catarrh. Catarrhal sigmoiditis - what is it? Catarrhal sigmoiditis covers only the surface of the intestinal mucous structures. There is swelling and severe redness. Against the background of catarrhal inflammation, mucus secretion increases, so some experts call this form of sigmoiditis mucous.
- Erosive. Erosion foci form on the intestinal walls, which do not have a destructive effect on the deep layers of intestinal tissue. Erosive sigmoiditis provokes the formation of ulcerative fragments.
- Ulcerative (otherwise purulent-hemorrhagic). Ulcerative lesions form on the intestinal mucous tissues, which destroy the deeper layers of the intestinal walls.
- Perisigmoiditis. The serous membranes of the intestine are involved in the pathological process. An infiltrate forms around the intestine itself, and adhesive segments form between the intestinal loops, which can spread to adjacent organs or connective tissue.
During differential diagnosis, several forms of sigmoiditis are often detected simultaneously, which is associated with a long-term pathological process and the presence of a burdened history of the epigastric organs.
Nutrition for chronic form
In case of chronic sigmoiditis during remission, to prevent constipation, foods rich in dietary fiber are included in the diet. Recommend:
- beet;
- carrot;
- pumpkin;
- dried apricots;
- prunes;
- vegetable and fruit juices;
- biscuits and bran bread.
If you are prone to constipation, the use of wheat and rye bran is very effective. Pour a tablespoon of bran into a glass of boiling water and let it brew for 30 minutes. Then the water is drained, and the resulting slurry is added to porridge, cottage cheese, soups, or taken in its pure form, washed down with water. The dose of bran can be increased to 6-8 tablespoons per day (in the absence of pain and diarrhea).
In case of stable remission, it is best to switch to a common table with the exception of fatty meat, spicy and salty foods, smoked and canned foods, pastries and alcohol. If the prescription of a general diet causes an exacerbation of the process, it is necessary to return to diet 4c.
The diet for chronic sigmoiditis during exacerbations is the same as for acute sigmoiditis. In cases where the disease is severe and the patient loses a lot of weight (15% or more of body weight), it is necessary to resort to parenteral nutrition. Solutions of protein preparations, essential amino acids, fat emulsions, solutions of glucose, and electrolytes are injected into the subclavian vein through a catheter.
Prevention and prognosis
The danger of the disease is reduced to the formation of peritonitis, proctitis or rectosigmoiditis with a prolonged or complicated course, as well as to the chronicity of the pathological process.
Formation of hemorrhages
Preventive measures are aimed at excluding acute sigmoiditis and exacerbations of the disease during chronic course. The main measures include:
- proper nutrition;
- healthy lifestyle;
- timely treatment of infectious diseases;
- prevention of intestinal infections;
- prevention of constipation.
Sigmoiditis requires accurate diagnosis and timely treatment. If all medical recommendations are followed in the chronic course of the disease, stable clinical remission can be achieved. Treatment of sigmoiditis is long-term and includes not only drug or surgical correction, but also maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
About Crohn's disease as a provoking factor of sigmoiditis:
Although the anatomy of the human body is the same for everyone, some organs may vary in shape and size from person to person. The most common differences occur in the body's digestive system, namely in the area of the large and small intestines. The sigmoid colon is located in the thick section, the proper functioning of which directly affects the human condition.
This intestine helps digest food by supplying water to the human body. It is usually located at the level of the iliac crest, but can also reach the hypochondrium. Inflammation of the sigmoid colon is a fairly common phenomenon, which is called sigmoiditis. The symptoms of the disease are quite clearly expressed; they will be discussed in this article. It is important to note that this is a fairly commonly diagnosed disease and affects a large number of people.