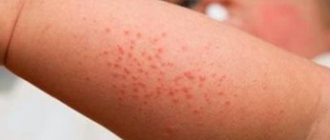
The main symptoms of hyperacid gastritis
In order to diagnose the disease in time and prevent its destructive effects, it is necessary to know the symptoms of hyperacid gastritis. The first signs of illness will be heartburn and stomach pain. Heartburn is often accompanied by acid belching; the stomach produces an excess of secretions. Nausea is considered a symptom of gastritis with increased secretion, vomiting is accompanied by a sharp sour odor.
Hypersecretory gastritis causes aching pain. They occur more often at night or early in the morning, “on an empty stomach.” Two to three hours after eating, pain is observed due to excessive secretion of gastric juice and pyloric spasm. As a rule, patients complain of burning and heaviness in the epigastric region. In some cases, pain intensifies in autumn and winter.
The main symptoms of hyperacid conditions are very similar to the symptoms of erosive gastroduodenitis or peptic ulcer.
With this disease, pain syndrome comes to the fore, which is characterized by the appearance of “hunger pains” that appear on an empty stomach or a few hours after eating. A rather specific symptom is a decrease in pain almost immediately after eating.
In most cases, the patient can clearly identify the connection between the symptoms of a given disease and the consumption of certain foods.
Often, increased acidity is combined with heartburn and sour belching.
Preventive measures
After treatment, in order to reduce the likelihood of exacerbation of the hyperacid form of gastritis, the patient must follow the following rules:
- do not violate the principles of diet in nutrition;
- exclude fatty, too spicy foods from the diet;
- give up alcohol and smoking;
- monitor your emotional state, avoid nervous stress;
- devote sufficient time to rest and sleep.
A person who discovers symptoms of high acidity needs to urgently contact a medical institution for examination, diagnosis and treatment. Timely initiation of therapy will help shorten the duration of the disease and avoid complications.
We recommend: What is catarrhal gastritis and how to treat it?
Causes of the disease
There are several factors that stimulate the secretory function of the stomach in hyperacid gastritis:
- Poor nutrition – heavy, irritating meals, alcoholic drinks, long breaks between meals, overeating. These disorders lead to increased production of HCl and pepsins, which eventually begin to corrode the organ wall.
- Smoking. Studies show that an increase in the acidity of gastric contents is associated precisely with smoking on an empty stomach, and smoking a cigarette after a meal does not significantly affect secretion.
- Infection with H. pylori is an acid-fast bacterium that destroys the inner lining of the stomach and leads to inflammation, ulcer formation, and cancer.
- Insufficient blood supply to the stomach associated with heart failure, atherosclerosis or vascular spasm.
- Zollinger-Ellison syndrome is a tumor of the pancreas that produces the hormone gastrin, which stimulates the secretion of HCl. This is a condition that is difficult to correct and often leads to the formation of deep ulcers with a high risk of bleeding.
- Violation of the nervous or hormonal regulation of the secretory function of the stomach. For example, against the background of stress and nervous tension, the regulatory influence of the vagus nerve on the digestive tract changes. Against this background, acidity can either decrease or increase. In women, hyperacid gastritis often develops during pregnancy due to hormonal changes.
This disease most often affects men at a young age, in some cases occurring against the background of complete general health.
Factors leading to the development of the described disease include smoking (especially on an empty stomach), abuse of black coffee (primarily instant) and strong tea, and poor diet.
It is important to note that hyperacid gastritis can occur for no apparent reason.
https://youtu.be/7FRICR-2OO0
Diagnosis of acidity disorders
If you suspect gastritis, you need to contact a gastroenterologist and endoscopist. Doctors will order tests, based on the results of which a diagnosis will be made.
The most characteristic symptoms of hyperacid gastritis:
- pain in the upper abdomen, worsening after eating;
- heartburn;
- belching sour, sour taste in the mouth;
- dense white coating on the tongue;
- nausea;
- vomiting of eaten food;
- constipation, less often - diarrhea;
- stomatitis, damage to tooth enamel.
Mechanisms of gastric damage in hyperacid gastritis
Hydrochloric acid in high concentrations corrodes the gastric mucosa. In advanced cases, the damage reaches the submucosal layer, then the muscular layer, and an ulcerative defect is formed. The situation is aggravated by enzymes that break down protein - pepsins. Since the internal organs contain a large amount of protein, pepsins, in the absence of adequate protection, begin to digest the gastric wall.
Violation of gastric digestion causes a malfunction of the intestines, leading to upset stool. For chronic hyperacid gastritis, constipation is more typical, but with Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, gastric secretion becomes so massive that digestive juices do not have time to be absorbed and diarrhea begins.
Etiology
Excessive production of hydrochloric acid and, as a result, hyperacid gastritis can be caused by the following factors:
- Helicobacter pylori infection;
- hypertonicity of the parasympathetic nervous system;
- frequent stress;
- smoking;
- alcohol consumption;
- poor nutrition;
- food allergies;
- some diseases of the liver and pancreas;
- endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus);
- chronic infections and diseases of the oral cavity, nasopharynx, etc.
Helicobacter is the most common cause of hyperacid gastritis, but it usually acts in conjunction with other unfavorable factors, such as stress or dental caries. You can learn more about the connection between oral diseases and stomach diseases from the video at the end of the article.
Treatment
https://youtu.be/fDPHQySmEcs
In the modern world, the diagnosis of “gastritis” has ceased to be something exotic and, unfortunately, has become a fairly common occurrence. By origin, gastritis is an inflammatory disease (in this case, the mucous membrane becomes inflamed). The disease can be accompanied by both high and low acidity.
Hyperacid gastritis must be treated with medication, while following a strict diet. Drugs for the treatment of hypersecretory gastritis are aimed at inhibiting (suppressing) the production of gastric juice and enzymes. With the help of medications, you can reduce the patient’s pain, cramps and reduce inflammation of the stomach tissue.
The state of increased acidity, like other pathological processes in the digestive organs, requires, first of all, adherence to a fairly strict diet.
Contrary to popular belief about the beneficial properties of broths, it should be noted that in case of the disease described, they are strictly prohibited. The more rich the soup eaten, the more gastric juice will be produced in the patient’s stomach and, accordingly, the more severe an exacerbation can be expected. Fresh herbs and black bread are also prohibited. It is also necessary to exclude fried meat and fish. Bread, millet porridge, alcoholic drinks and carbonated water, and ice cream are prohibited.
In case of severe exacerbation of the disease, it is usually advised to spend several days on a strictly limited diet: pureed vegetable purees, lean meat, porridge.
Depending on what structural changes in the gastric mucosa are accompanied by a hyperacid state, the qualitative and quantitative composition of food products permissible for consumption can be changed.
Among the medications in the treatment of the described disease, the leading role is played by drugs to reduce acidity and sorbent drugs. It is important that a specific drug and its dose should be selected only by a doctor, taking into account quite a few factors. It is strictly unacceptable to independently refuse certain medications, replace the drug, or change the dose.
Traditional methods of treating this disease also include following a diet with the intake of certain decoctions and infusions. Unfortunately, some common recipes may not only fail to cure hyperacid gastritis, but also cause the formation of erosions or ulcers of the gastric mucosa.
How to treat
To prevent the progression of the pathology, first of all, it is necessary to find out what provoked the increase in the acidity of gastric juice and why the protective mechanisms are not effective.
To visually assess the condition of the mucosa, specialists perform fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy (FEGDS).
The study also allows you to take a tissue sample for histological analysis, test for the presence of Helicobacter pylori infection, and determine the acidity of gastric juice. A flexible tube with a camera is inserted through the mouth into the stomach of the person being examined, which allows one to see how inflamed the tissue is and whether there are any neoplasms or ulcers.
Treatment of hyperacid gastritis includes taking medications, diet therapy, following a meal schedule (skipping meals is unacceptable), and physical procedures may be prescribed. You cannot treat the disease with pills or traditional medicine yourself, as this can harm the body and contribute to the transition of acute gastritis to chronic.
If acid-fast bacteria are present in the stomach, the patient is prescribed antibiotics that are not neutralized in an acidic environment. This may be Tetracycline, Azithromycin, Metronidazole, Levofloxacin, Amoxicillin, Clarithromycin, Tinidazole.
Triple therapy is considered standard, in which the patient takes two antibacterial drugs simultaneously with medications that suppress the production of hydrochloric acid (proton pump inhibitors). Bismuth-based agents can be added to this regimen to protect the gastric mucosa from the negative effects of acids.
The type of antibiotic and frequency of administration is determined by the doctor, based on the patient’s health condition and his or her tolerance to the medications. Duration of treatment is 7–14 days. If the three-component regimen does not work, then an additional antibacterial agent is recommended to the patient, and in extreme cases, the sensitivity of the bacterium to all antibiotics is checked and individual treatment is developed.
The treatment regimen for hyperacid gastritis includes drugs that normalize the acidity of gastric juice. These are drugs that inhibit the production of hydrochloric acid or neutralize it and protect the gastric mucosa.
The following drugs may be prescribed to reduce the production of hydrochloric acid:
To protect the gastric mucosa, it is recommended to take alginates. The drugs interact with gastric juice and form a protective film on the surface of the organ, preventing contact of acid and tissue. The product begins to act within 5-10 minutes after administration, so pain associated with irritation of the mucous membrane goes away quickly.
Under the influence of the medicine, insoluble bismuth oxychlorides and citrate are formed in the stomach, which protect the mucous membrane from acid and pepsin. The product promotes the regeneration of stomach tissue, has bactericidal activity against Helicobacter, and has an anti-inflammatory and astringent effect.
Drug treatment must be supplemented with diet therapy. It is recommended to steam or boil food; you need to chop it before eating. It is necessary to eat often so that hydrochloric acid does not corrode the stomach, but in small portions.
Seasonings and spices should be excluded, and the daily amount of salt consumed should be reduced. Alcohol, sour fruits (grapes, lemon, kiwi), fatty and pickled foods, butter, margarine, fermented milk products, coffee, strong tea are strictly contraindicated.
After the pain in the stomach has passed, you can gradually expand the diet, but you still need to avoid foods that stimulate the production of hydrochloric acid such as:
- spices;
- chocolate;
- sour fruits;
- sorrel, spinach;
- legumes;
- fatty meat and fish;
- canned food;
- rich broths (fish or meat);
- smoked meats;
- strong tea and coffee;
- fresh bread;
- carbonated drinks.
Proper diet for gastritis with low acidity
For people with high stomach acidity, a special diet number one has been developed. The diet includes products that are as gentle as possible on the mucous membrane and give it the opportunity to regenerate.
The first diet is considered one of the strict ones and is used in cases of treatment of acute or chronic gastritis. Basic principles of the diet:
- You should not cause temperature changes in the gastrointestinal tract. Such an action will cause pain and aggravation. Excessively hot and cold foods are prohibited.
- You should not eat fried food. Food is boiled, steamed or baked.
- The amount of salt is kept to a minimum so as not to irritate the gastric mucosa.
- Long breaks between meals should not be allowed. Food is taken in small portions 5-6 times a day.
- You need to eat about 3,000 kilocalories of food per day.
Diet No. 1 is very diverse, although many things are prohibited. Based on your diet, it is possible to form basic healthy eating habits. A diet for hyperacid gastritis promotes the patient’s speedy recovery and is considered a legitimate method of treatment.