Inflammation of the liver can be toxic, viral or autoimmune in nature. The most dangerous hepatitis is that caused by a virus. The body can be cleansed of toxins using medications and hemosorption methods. Autoimmune inflammation occurs more easily, although it is incurable. The viral agent is extremely difficult to remove from cells and is resistant to therapy. Hepatitis C, caused by a virus, is the worst. New drugs have been developed to treat such ailments. But the best option remains to prevent their occurrence.
Routes of infection and danger to others
There are several ways to become infected with the hepatitis C virus. It is transmitted through direct contact with infected blood when:
- transfusion;
- using non-sterile instruments for medical or cosmetic procedures;
- use of injecting drugs.
The infection can also be transmitted sexually through unprotected sexual contact. Also at risk are children who can be infected during the prenatal period if the mother has the virus.
Is hepatitis C contagious through household contact? HCV infection can pose a threat if the rules for using personal belongings are violated. In the immediate environment or in one’s own family, a person with hepatitis C can be a source of danger only if the rules of personal hygiene are not observed.
Infection is possible if you use personal items of a sick person with traces of his blood (toothbrush, razor).
Routes of transmission of hepatitis B and C
Is it possible to become infected with hepatitis, and how does it happen?
The virus enters the blood of a healthy person through:
- microtraumas and cracks;
- sperm;
- vaginal discharge;
- medical procedures without disinfecting instruments.
The dangerous virus is transmitted from a person diagnosed with acute (chronic) hepatitis B (C).
The infection is transmitted through blood. It enters through blood and fluids (unprotected sex, infected needles during intravenous drug administration; needles used for tattooing, acupuncture). Infection occurs when semen, vaginal secretions and infected blood enter the bloodstream of a healthy person. It can be transmitted to a child during birth through the mother.
Previously, infection occurred through transfusion of donor blood with the virus. But since 1972, laboratory testing of donor blood samples has eliminated this possibility.
https://youtu.be/Ggv3DxGV1cI
Which hepatitis is considered the most dangerous?
The hardest, most dangerous and most terrible of all is hepatitis C. The “gentle killer” is practically incurable today. Medicine can only make its development slower. The disease is terrible primarily because it can lead to cirrhosis and liver cancer. The worst thing is that the most dangerous hepatitis may not make itself felt for a long time. This fact makes quick treatment impossible. If the disease is detected in late stages, treatment may no longer stop it.
The incubation period for hepatitis C lasts a couple of weeks, a month or even a year. The symptoms of the “gentle killer” are poorly identified. It is characterized by weakness, nausea, jaundice, loss of appetite, pain in the right hypochondrium and joints. Such manifestations are characteristic of many diseases, and without special laboratory tests it cannot be determined. After an acute course, the disease in 20% of patients becomes a virus carrier, and in the majority it becomes chronic.
The chronic stage passes slowly - up to ten years. Statistics say that within 10 years of illness, half of patients die. This happens because the liver continues to perform its functions, and in the meantime the virus destroys the cells of the gland. Thus, a person may not be aware of the presence of the disease. When cirrhosis of the liver appears, symptoms occur - jaundice, enlarged liver, pain in the right side, ascites (fluid accumulation in the abdomen).
The disease occurs in 2% of the world's inhabitants. Due to the spread of drug addiction, the number of patients is growing. After diagnosis, it is necessary to begin treatment on time so that the terrible disease does not have time to develop into cirrhosis. The main thing is not to panic, follow the course of treatment, follow a diet, do not drink alcohol, and strengthen your immune system. In medicine, cases of recovery from the disease have been recorded after 25 years.
Attention! The information published on the site is for informational purposes only and does not constitute a recommendation for use. Be sure to consult with your doctor!
What is the danger of each type
Viral hepatitis
Type A is called Botkin's disease. It occurs due to poor hygiene and is considered a food infection that affects the liver. Hepatitis A occurs only in acute form and is easily treated. In case of illness, a person develops immunity and no longer faces this type of illness. The mortality rate for Botkin's disease is 0.5%. The danger is that it is the most common.
Hepatitis B is characterized by severe damage to the liver and spleen. Vomiting and fever appear. Its danger is that once it enters the body, it remains there forever and can develop into a chronic form. Fortunately, this type of disease does not lead to cirrhosis of the liver and is highly treatable. With timely diagnosis, the fatal outcome is minimal.
The next infectious agent, type D virus, enters the body and can multiply there only in the presence of hepatitis B. Its main difference is that type D aggravates the course of the disease and complicates treatment. It is characterized by a more severe pathogenesis, more often becomes chronic, and can lead to cirrhosis and liver cancer. Hepatitis D is a very rare type of disease but can cause death.
Type E resembles Botkin's disease in its symptoms, method of infection and treatment methods. It is also well treated, and in some cases the body itself defeats it. Often, in addition to the liver, it affects the kidneys. The main danger of this disease is that in the case of a pregnant woman in the last stages of pregnancy, it leads to the death of the fetus and in 9-40% of cases - to the death of the mother.
Other types
Attention should be paid to the danger of alcoholic and toxic hepatitis. Under the influence of aggressive substances, liver cells degenerate into adipose tissue
As a result, the organ cannot perform its functions normally, and liver cirrhosis occurs. The autoimmune type is dangerous because, for unknown reasons, antibodies begin to destroy organ cells. Thus, the liver is destroyed by the body itself. The metabolic type of the disease is distinguished by the fact that it develops due to hereditary pathologies. Secondary hepatitis is difficult to treat. In addition to this disease, they are fighting the pathology that caused it.
Which type is the most dangerous and incurable?
The most dangerous hepatitis is subtype C. It is curable only in rare cases. It can be contracted at a dentist, cosmetologist, tattoo parlor, ear piercing or piercing. It is also dangerous for the doctors themselves, since contact with the blood of an infected patient on the surface of the skin or mucous membranes leads to infection of the doctor. Virus C is transmitted through blood transfusions or surgical interventions using poorly sterilized instruments. New medications are being developed to treat it. The latest inventions of science are oral nucleoside polymerase inhibitors. But even long-term therapy does not always lead to a positive result and complete cure.
The danger of different types of hepatitis
Hepatitis A and E are similar in nature and course, as well as mode of transmission. The first is called Botkin's disease. The virus enters the human body through water contaminated with the feces of a patient. The duration of the incubation period is from seven days to two months. The disease is manifested by severe chills, nausea, a sharp increase in body temperature, and pain in the liver area. Then jaundice occurs, darkening of the urine.
To eliminate these forms of hepatitis, hospitalization is necessary. To reduce the destructive effect on the liver, droppers are placed to eliminate intoxication.
In some cases, home treatment is practiced. The patient needs a strict diet, complete rest and bed rest. The organ is supported with the help of hepatoprotectors.
Hepatitis B and D are considered more dangerous. They enter the body through sexual contact, during the use of syringes or infusion systems of a sick person. The virus can also spread to the fetus if it is detected in the mother’s body during childbirth. It is impossible to become infected through everyday means.
Damage to the organ leads to its increase in size. After penetration into the blood, the viral agent may not reveal itself for six months. In this case, the person does not feel any symptoms, the disease quickly becomes chronic.
Type B virus cannot be completely eliminated from the body. But if you use hepatoprotective drugs, follow a regimen and diet, you can maintain liver function at a normal level.
In acute forms, hepatitis in 90% leads to the death of the patient in the absence of timely assistance.
Hepatitis B can have serious consequences. It is often accompanied by hepatitis D. This significantly aggravates the course of the disease, but with proper therapy, good results are usually achieved.
Views D and G
HDV itself does not harm a person, since it can develop in the body only in the presence of hepatitis B. But it complicates the course of the disease, which leads to the rapid development of complications and increases the likelihood of death.
Hepatitis G still remains poorly understood. It is known that it is most often asymptomatic and the body is able to cope with it on its own. However, in some cases liver failure occurs. The fulminant type of infection is characterized by high mortality due to the rapid death of hepatocytes.
Varieties
There are 7 types of hepatitis, which are caused by different factors. Each of them carries its own dangers.
- Modification A. Caused by type A virus. Infection occurs through water and food.
- Modification B can be transmitted sexually. Infection through parenteral and household routes is also possible. The modification of this virus is concentrated in all biological fluids.
- Hepatitis C, transmitted through the enteral route, may not be diagnosed immediately. The most terrible of infections. At a late stage there is no treatment.
- Hepatitis D, transmitted by enteral transmission, is caused by an RNA virus. When diagnosing, combinations of viruses B and D are often found. This is explained by the presence of an obligate dependence of the viruses on each other.
- Modification E. Infection of this group occurs through the fecal-oral route.
- Hepatitis F is one of the new diseases that is caused by a pair of viruses. A person can become infected through a blood transfusion.
- Hepatitis G. The virus is easily transmitted sexually, during surgery, from mother to baby.
general information
Hepatitis has very different symptoms and severity. They have one thing in common: liver damage and inflammation. In most cases, hepatitis is a separate disease, but sometimes it is a companion to other ailments. Hepatitis can be a symptom of the presence of other diseases in a person (with a nonspecific reactive form). The most common is the viral type of disease.
Most hepatitises have a wide range of routes of infection. For hepatitis C, D, C, G, B, this is primarily contact with blood. This group includes blood transfusion, working with blood, injection with a non-sterile syringe, and drug addiction. D, C, G are also transmitted sexually and from mother to child. Diseases of types A and E are characterized by a fecal-oral mode of infection: the virus gets into food and water with feces, and then into the human intestines.
The symptoms of each type have certain differences associated with its nature, stage and degree of damage to the body. But all hepatitis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- weakness, headache and muscle pain;
- disruptions in bowel function;
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- enlarged liver and spleen;
- peeling and itching of the skin.
Features of form A and E
Both viruses enter the body through the intestines and are characterized by a similar course. Those at risk are those who do not observe personal hygiene rules, who consume water from untested sources and food without sufficient heat treatment.
Tourists can become infected when visiting Asian countries where these types of virus are common.
Main differences:
- Hepatitis A . The main patients are teenagers and young people. Outbreaks of infection are observed during the hot season. It proceeds relatively easily. The treatment prognosis is favorable, there is no chronicity of the process.
- Hepatitis E. The risk group is predominantly teenagers. As the disease develops, acute pain appears in the right hypochondrium and severe symptoms characteristic of intoxication. In the acute form, the probability of a woman dying during pregnancy is more than 50%. The fetus also dies. Possible autoimmune kidney damage.
Types of disease
Hepatitis, depending on its origin, is divided into:
- Viral.
- Autoimmune is a liver disease of an inflammatory-necrotic nature that causes cirrhosis and renal failure.
- Toxic - destruction of liver cells occurs as a result of penetration of chemicals through the skin, respiratory tract or stomach.
- Alcoholic – pathology develops if a person drinks alcoholic beverages for a long time. About a quarter of alcoholics are diagnosed with hepatitis five years after starting this lifestyle.
- Metabolic – liver damage occurs as a result of hereditary pathologies associated with metabolic disorders. This usually occurs with Wilson's disease or hemochromatosis.
- Cryptogenic – the origin of the disease could not be determined. This picture is observed in 15% of all cases.
- Nonspecific reactive - its development is associated with pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract or other abnormalities in the functioning of the body.
Acute and chronic course of the disease is usually observed. In the first case, poisoning of the body quickly occurs, the person weakens, and the body temperature rises significantly. In the chronic course, the patient does not feel any symptoms. Gradually, the liver increases in size, which is accompanied by heaviness and pain in the right side under the ribs.
What kind of hepatitis the patient cannot be treated for by any method is of interest to everyone. Hepatitis B and C are considered the most serious in this regard. It is almost impossible to completely cure the virus.
Methods to combat the disease
What is worse, hepatitis B or hepatitis C, worries many. The first disease is transmitted sexually and through blood. But there is a vaccine against it, the introduction of which will completely protect against the disease.
The presence of hepatitis C is mainly manifested by the carriage of the virus in the blood. Vivid manifestations are usually felt by people with HIV infection or suffering from AIDS. There are no vaccinations against the infection, and treatment can take many years and cost a large sum.
The virus is not completely curable. You can only reduce the antibody titer and make a person safer for others. Although today new generation drugs have already appeared that give hope for a complete recovery in a short course of treatment (Sofosbuvir and analogues).
With such a diagnosis, a person can fully exist with the help of constant diet and proper lifestyle.
According to the old regimens, patients are prescribed:
- Interferon – to activate the immune system;
- Ribavirin - in combination with interferon, the drug significantly improves the prognosis for hepatitis.
Ribavirin-interferon therapy has a positive effect on the condition of the liver, but after stopping the course, a relapse of the inflammatory process may begin.
In the chronic course of the disease, the patient does not feel symptoms, except for heaviness in the side. These sensations intensify and then stop, so many do not pay attention to it, which can have a bad effect on the overall situation.
So in advanced cases, with the development of cirrhosis, the spleen and liver become enlarged, bleeding from the nose and anus is observed, spider veins appear on the body, and body weight quickly decreases. This group of symptoms occurs due to liver failure.
Therefore, you should consult a doctor at the first symptoms. Since hepatitis often does not reveal itself at the beginning of development, for timely diagnosis you need to take a blood test once a year. This will help identify pathology in the early stages.
Source: hepatit.su
What is the danger
It’s worth starting to consider the topic with the question: why is hepatitis C dangerous? In fact, there are several parameters here. These include:
- difficulty recognizing the diagnosis;
- If you do not begin to take timely measures to treat the disease, then it can develop into such terrible diseases as steatosis or cirrhosis. The latter disease can lead to liver cancer, and this disease is almost impossible to fight.
- if the diagnosis is not made on time, the mortality rate among the population is 5-8 percent. These are official figures provided by the Ministry of Health.
Now everyone knows which version of hepatitis is the most dangerous, and how exactly this danger manifests itself for humans.
About other types of hepatitis
So, if it was previously stated that hepatitis C is considered the most dangerous, it is worth talking about other varieties of this disease. Hepatitis A, for example, also carries certain risks. This disease is much easier to detect in the early stages, and the mortality rate is only 0.5 percent, which is an order of magnitude lower than in the case of C.
As for the diagnosis itself, it is based on clinical and laboratory data. The clinical method is based on early detection of the disease. A person begins to have a short-term increase in temperature, and then an enlargement of the liver occurs. If a person complains about this, then all the signs are obvious. After a few days, the first signs of jaundice may appear.
As for laboratory tests, they can be specific and nonspecific. Specific ones are focused on identifying the causative agent of the disease.
As for non-specific methods, they are more important. They are able to determine the severity of the disease at a certain stage, and also provide the opportunity to search for the optimal treatment method
An example is the identification of an indicator of the activity of renal cell enzymes.
Hepatitis B is more dangerous than A. It is also quite common in the modern world. It is worth noting that it is well recognized by modern diagnostic methods. In addition, it does not lead to such complex diseases as cirrhosis. It is quite possible to cure it with chemicals. This makes the mortality rate minimal.
Diagnosis of hepatitis B is also quite simple. There are many methods. Just as with any other viral disease, a blood test can help identify pathogens. A biochemical blood test is also used. It determines the amount of liver enzymes.
One of the most effective methods is liver biopsy. This is done using a special needle, which allows you to remove a piece of tissue. Timely detection of the disease leads to the fact that the mortality rate drops to a minimum, unlike the most terrible hepatitis C. It is worth talking about it in more detail.
Prevention
To protect yourself and your loved ones from such a terrible disease, you need to keep the house clean and monitor personal hygiene for all family members. Adults need to explain to children that everyone should have their own items such as scissors, nail files, and toothbrushes. Unfortunately, with the increase in drug addiction, the number of patients with hepatitis B, C, D is also increasing.
Advice! Parents need to be attentive to their child. If his behavior has changed and has become alarming, it is better to seek help from a psychologist and, if necessary, a narcologist.
The hackneyed expression that it is easier to prevent a disease than to treat it later does not lose its relevance and topicality. Protecting yourself from hepatitis is not difficult. For timely detection of the disease, it is necessary to regularly visit a doctor and get tested. This will allow hepatitis to be detected at an early stage and the liver to recover as quickly as possible.
The process of regeneration and detoxification is long, sometimes taking several years. During treatment, as well as after it, the patient is advised to give up bad habits, follow a diet and maintain immunity.
Why screening for hepatitis virus infection is important
Screening means testing for carriage of hepatitis viruses in presumably healthy people. Why presumably? We have already told you that there is an incubation period during the disease. During this period, the disease does not manifest itself, the person feels healthy and has contact with other healthy people. But during this time, which can last up to six months if infected with hepatitis B and up to 26 weeks if infected with the hepatitis C virus, the person is a source of infection for others. To prevent such unhindered spread of the virus, examinations are carried out. In any public or private laboratory, such tests are carried out after taking blood and examining it. The price of tests for hepatitis B and C is approximately the same. If a person is infected with the hepatitis B or C virus, specific antigens or antibodies to parts of the virus will be found in his blood.
Hepatitis B and C markers: what are they? Antigens are parts of material foreign to our body. Antibodies are what our immune system produces against foreign material (antigens) in order to destroy it. Antigens and antibodies are determined by ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay). Moreover, the detection of special antibodies against antigens can indicate the time of infection (acute process or past infection) and distinguish the infection from the formed immunity after vaccination. It is worth noting that there is no vaccine against the hepatitis C virus. In addition, parts of the DNA of the virus can be detected by PCR (polymerase chain reaction)
Now you understand the importance of this examination. And if you are asked to undergo this examination at work or at university, do not be discouraged
On the contrary, it is better to learn about your health for the benefit of yourself and the people around you. After all, the earlier treatment for viral hepatitis is started, the better and faster the positive outcome in the form of recovery occurs. Let's look at these questions about treatment in more detail.
Find out more about virus detection from the articles “All about tests for hepatitis C” and “Tests for hepatitis B”.
Preventive measures
Other types of hepatitis can be prevented through vaccination. Since these actions are impossible with hepatitis C, measures aimed at protecting against the entry of the virus into the body are considered mandatory. In addition, it is necessary to perform general strengthening actions.
Hepatitis C is transmitted exclusively through contact of a biological fluid containing the virus with a wound or subcutaneous tissue. Therefore, disease prevention includes the following actions:
- compliance with the rules of sanitation and hygiene when visiting medical, cosmetology or dental institutions, it is worth abandoning the multiple use of one syringe by several people;
- You should avoid constantly changing sexual partners and be sure to use contraceptive methods during sex;
- If work activities take place in conditions with a high risk of hepatitis infection, then it is imperative to be regularly tested for markers of the virus.
It is worth noting that in 20% of infected people, the appearance of the virus does not have a clear etiology. Infection occurs even in those people who lead a healthy lifestyle, have not undergone blood transfusions or organ transplants, have one regular sexual partner and do not use drugs.
If an infected relative lives in the house, you should not allow the same razor to be used, as there is a risk of cuts. Also, you should not share a toothbrush with someone who is sick. In cases where an infected person receives a domestic injury and drops of his blood fall on any surface, it is imperative to disinfect it. It is preferable to carry out disinfection with a chlorine solution.
Hepatitis is an inflammatory process in the liver. The pathological condition can go away on its own or cause scarring, cirrhosis, or cancer. The most common causative agent of the disease is the hepatitis virus, but no less often the cause of the disease is exposure to toxic substances, taking certain medications, and alcoholic beverages.
Transmission of the disease is possible through consumption of contaminated foods, water, blood transfusions, and invasive medical procedures. A person becomes infected during a manicure, a tattoo session, unprotected sexual contact, from mother to child. Hepatitis occurs acutely or chronically; acute infection produces limited symptoms.
Symptoms
Contact your doctor if you suspect an infection. Symptoms show signs of being infected by a virus if:
- jaundice appeared;
- the stool became light;
- urine darkened;
- decreased appetite;
- physical condition is alarming;
- soreness in the right side.
After diagnosis, immediate hospitalization is required.
The time from the onset of the lesion to the onset of symptoms varies. With form B - up to six months. During this time, the viral infection adapted and began to manifest itself. Symptoms at first are similar to those of the flu:
- headache;
- malaise;
- joint pain;
- rashes.
There is no sharp increase in temperature, although it is rising.
Manifestations of form C are limited to loss of appetite and weakness. After a couple of days, pain appears in the right hypochondrium, nausea, darkening of the urine, lightening of the stool, and vomiting. When palpated, the organ is enlarged. Signs characteristic of hepatitis are found in the blood:
- high bilirubin;
- virus markers;
- liver tests increase 8-10 times.
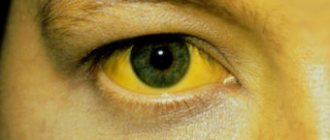
After yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes appears, the condition improves.
The clinical picture can be in mild, moderate and severe stages of development. There is also a fourth stage – the fast stage (fulminant). A dangerous virus quickly attacks an organ. This is the most severe course of the disease. It is characterized by extensive tissue necrosis, after which death is possible. The danger is the chronic course of the disease. Signs are characterized by the following symptoms:
- fatigue;
- itching of the skin;
- darkening of urine and lightening of stool;
- bleeding;
- sudden weight loss;
- organ enlargement;
- the appearance of spider veins;
- jaundice.
Consequences of hepatitis B and C
The mixed form of hepatitis B and C is considered the most dangerous. The simultaneous presence of 2 viruses in the body contributes to the rapid destruction of liver tissue.
The affected liver is deprived of the ability to fully cleanse the blood of poisons. This can lead to brain damage.
According to doctors, with the simultaneous development of pathologies, the hepatitis C strain can displace the hepatitis B strain. This is observed in 40% of cases.
When the hepatitis B virus is defeated, antibodies are formed in the blood. It is impossible to get sick again. Group C virus is able to attack the body again and again.
Treatment of hepatitis
Treatment of both forms is carried out in a hospital. Based on the symptoms, treatment of the organ and associated diseases is prescribed.
During the period of complications, it is necessary to increase the body's immune defense. Therefore, immunostimulants and vitamin preparations are prescribed.
Inflammatory processes are eliminated with special drugs. The infection is suppressed by antiviral therapy: Interferon, Biboverin, Pegintreferon. "Sofosbuvir" together with "Riboverine" or "Harvoni" will stop the proliferation of a viral infection inside the cell.
Nucleotide agents are used: Tenofovir, Sebivo, Zeffix or their analogues. Along with drug treatment, herbal medicine can be prescribed. It is prescribed and monitored by the attending physician. Folk recipes based on mumiyo, bee products, and medicinal plants are used. They support the functioning of the diseased organ, relieve inflammation, and destroy infection. Unlike drug treatment, there are no side effects.
In the treatment of hepatitis B and C, antiviral drugs, immunostimulants and hepatoprotectors are used
What is hepatitis and what is its danger?
The term hepatitis combines all pathological inflammatory changes that occur in the human liver in acute or chronic form. Under the influence of the virus, organ cells are destroyed.
The liver is the most important organ that supports the functioning of the entire body at the required level.
It has the following functions:
- Responsible for the production of bile, which promotes the digestion of fatty foods.
- Produces albumin and other types of proteins.
- Promotes the disinfection of toxic substances and breakdown products of ammonia, nicotine, and alcohol.
- Participates in the metabolism of vitamins, hormones, proteins and glucose.
- Synthesizes fats and blood clotting factors.
Hepatitis occurs in different forms. A person may not even notice a mild course of the disease. But in severe forms, normal liver tissue is completely destroyed.
Hepatitis C is considered the most dangerous. This is due to the fact that it is extremely difficult to identify the disease in the early stages, and without proper therapy, cirrhosis of the liver will develop, which subsequently develops into cancer. Hepatitis C kills 8% of patients.
The pathology can proceed for many years and even decades without the slightest manifestation, destroying liver tissue. The main route of transmission is the patient's blood.
The prognosis for this disease can be influenced by many factors.
It is especially important to make a diagnosis on time
Therefore, you need to pay attention to the state of your health and donate blood for analysis once a year, especially for those people who are at risk for infection (medics, donors, patients with hemophilia, etc.)
It is advisable to be especially careful when choosing a tattoo parlor, beauty salon and medical institutions. In dubious establishments, they do not pay enough attention to sterilizing instruments, so infection can occur
The development of cirrhosis with hepatitis C occurs in 20% of cases. Everyone else continues to live with the virus; it cannot be cured on its own. There have been only a few such cases in history.
Risk of complications
The most common complications from hepatitis: cirrhosis, liver cancer, liver failure, portal hypertension, autoimmune diseases. All of them develop in the last stages of the chronic course of the disease.
In order to reduce this likelihood and detect the disease at an early stage, it is necessary to undergo regular medical examinations.
If the patient leads a healthy lifestyle, does not use drugs or alcohol, and eats right, then the likelihood of complications is reduced. In the presence of alcohol or drug addiction, the risk of concomitant pathologies increases many times over. But the most dangerous variant of the development of the disease is the presence of co-infection (HIV, AIDS, a combination of several hepatitises).
Routes of infection and features of manifestation
The main route of transmission of the virus is through blood. You can become infected after using a patient’s toothbrush or razor, visiting beauty salons, tattooing or piercing, dental offices and hospitals. But drug addicts have the highest risk of infection. Infection with the virus can also occur through sexual contact or during childbirth. But the likelihood of transmitting infection in this way is low (up to five percent). In some cases, it is not possible to find out how it enters the body.
Hepatitis C is not transmitted through airborne droplets. Infection in domestic conditions is possible only through microtrauma, contact with an object that contains the blood of a patient or a carrier of the virus. Hepatitis form C develops slowly and is most often asymptomatic. The carrier may not know that he is infected for a long time, sometimes up to ten years. This is what is associated with the high mortality rate among patients with this disease. The clinical picture of hepatitis C is mild. In the first stages of its development, the same symptoms occur as with hepatitis B:
Symptoms and signs of HCV
- weakness;
- apathy;
- decreased appetite;
- fast saturation.
You may also experience: dyspepsia, a feeling of heaviness and discomfort in the right hypochondrium. As the disease progresses, nausea, vomiting, joint pain appear, and the color of stool and urine changes. Fever and intoxication syndrome are not typical for hepatitis C. Yellowness of the sclera and skin in the first stages of its development appears extremely rarely: these symptoms are characteristic of the late stage of the disease, when it has led to the development of complications.
The disease is most severely experienced by alcoholics, patients with HIV status, elderly patients and people with concomitant liver pathologies.
Sources
- https://medgepatit.com/getatit/kakoj-vid-gepatita-samyj-opasnyj-dlya-cheloveka/
- https://gepatologist.ru/vospalenie/profilaktika/kakoj-gepatit-samyj-opasnyj.html
- https://progepatity.ru/gepatit-b/chto-opasnee-gepatit-b-ili-gepatit-c
- https://blotos.ru/gepatit-kakoj-samyj-opasnyj
- https://zpppstop.ru/zppp/hepatitis/kakoj-gepatit-samyj-opasnyj.html
- https://bolitpechen.ru/disease/gepatit-disease/drugie-gepatity/kakoj-gepatit-samyj-opasnyj-82
- https://simptomov.com/pechen/vidy/gepatit/opasnee/
Types of viral hepatitis hepatitis C, B and others
Viral hepatitis is divided into groups. There are acute viral hepatitis and chronic viral hepatitis. According to the ICD-10 classification (International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision), which is used by all doctors, viral hepatitis is divided into:
- Acute hepatitis A
- Acute hepatitis B
- Other acute viral hepatitis
- Chronic viral hepatitis
- Viral hepatitis, unspecified
In turn, chronic viral hepatitis is divided into:
- Chronic viral hepatitis B with delta agent
- Chronic viral hepatitis B without delta agent
- Chronic viral hepatitis C
- Other chronic viral hepatitis
- Chronic viral hepatitis, unspecified
From these classifications it is clear that it is important to indicate the “letter” of hepatitis. What does this letter mean and what does it determine for the further prognosis of the disease? In this article we talk about several types of hepatitis: hepatitis B, hepatitis C, hepatitis D
These are completely different viruses, which are united by liver damage with further replication in this organ. Read more about each of these viruses below.
Principles of therapy
Despite the fact that hepatitis C is an incurable disease, therapeutic measures should not be abandoned. It is necessary to begin treatment of this pathology with lifestyle changes. In particular, it is required to completely abandon bad habits such as smoking and drinking alcohol.
The “Table No. 5” diet is being introduced. Its main function is considered to normalize liver function, improve bile secretion and provide protection to the intestines and stomach from various types of damage.
The features of this diet are as follows:
- exclusion of fried foods from the diet (all foods should be steamed or boiled);
- you need to eat 5–6 times a day, portions should be small;
- you need to drink more liquid - the daily dose of clean water is at least 1.5 liters;
- in the daily diet there should be no more than 100 grams of proteins and fats, about 450 grams of carbohydrates. Sugar is no more than 50 grams, and salt is 10 grams.
Regarding drug treatment, in the case of hepatitis C, there is nothing more effective than antiviral therapy. The patient is prescribed direct-acting medications that act on viral proteins, which are considered the main elements in the development of pathology.
Just a few years ago, pegylated interferons in combination with ribavirin were widely used, but now they are not used due to low efficiency (up to 50%).
There are a number of situations when antiviral therapy is contraindicated for people:
- the presence of individual intolerance to drugs whose action is aimed at combating viruses;
- experience of ineffective therapy with antiviral drugs.
In such situations, in order to slow down the progression of pathology, as well as the development of complications in the form of cirrhosis and liver cancer, the use of medications is prescribed, the action of which is aimed at reducing the inflammatory process and the rate of progression of fibrosis. Sometimes these therapies are carried out in parallel.
Regardless of what antiviral drugs are prescribed to patients, the doctor must prescribe hepatoprotectors - these are drugs that increase the liver’s resistance to pathogens, have a restorative effect on hepatocytes, and normalize their work.
Hepatitis C is a disease, treatment of which with the help of folk remedies will not give any effect.
According to studies that were conducted on patients with hepatitis C, it was noted that if interferon therapy did not give the desired result, then inflammation and the degree of fibrosis can be reduced with the help of drugs based on glycyrrhizic acid. Therefore, if there are any contraindications to antiviral therapy, after consultation with a doctor, you can start taking glycyrrhizic acid, the positive effect of which after therapy will be confirmed by laboratory tests.
Sources
- https://JKTguru.ru/diagnostika/samyy-opasnyy-vid-gepatita
- https://OGepatite.ru/zhizn/kakoj-gepatit-samyj-strashnyj.html
- https://venerologia03.ru/gepatit/samyj-opasnyj-vid.html
- https://gepatit.polovye-infekcii.ru/gepatit/gepatityi-bc-chto-eto-takoe
- https://InfoPechen.ru/gepatity/drugoe/kakoj-gepatit-samyj-opasnyj.html
- https://medgepatit.com/getatit/kakoj-vid-gepatita-samyj-opasnyj-dlya-cheloveka/
Botkin's disease or hepatitis A
Infection occurs by drinking dirty water, food, or through unwashed hands. Hepatitis A occurs once, most often in childhood, after which lifelong immunity is developed. The clinical picture in adults has pronounced symptoms. An experienced doctor can easily make the correct diagnosis.
It is more difficult to diagnose jaundice in a child, because in children it is often either asymptomatic or has symptoms similar to influenza or ARVI. In this case, it is necessary to undergo tests to determine elevated levels of bilirubin and liver enzymes.
Treatment of Botkin's disease is aimed at the rapid removal of toxic substances from the body in general and the liver in particular. Patients are prescribed IVs, dietary nutrition, B vitamins, rest and rest.
Types of disease
Hepatitis is a common liver pathology, which can also be non-infectious in nature. The disease can develop against the background of:
- food or drug poisoning;
- alcoholism;
- autoimmune diseases.
Different types of the disease have different symptoms, but some signs can be identified that are common to all types of pathologies. This:
- general weakness;
- intestinal dysfunction;
- enlarged liver and spleen;
- flaky skin;
- pain on the right in the area of the ribs.
Types of disease:
- Hepatitis A, or Botkin's disease in other words, appears as a result of violation of hygiene rules. The disease responds well to treatment, never becoming chronic. This type is the most common.
- Hepatitis B causes severe liver damage. This type of disease is transmitted through blood or sexual contact, as well as from mother to children during childbirth. It has severe symptoms, such as vomiting and fever, but responds well to treatment.
- Hepatitis D is a virus that can attack the body only if it already has a type B virus. In this case, a significant deterioration in the patient’s condition occurs, there is a risk of cirrhosis or cancer, and the pathology can become chronic. Type D is a rare disease, but terrible in its consequences.
- Hepatitis E is in many ways similar to Botkin's disease. However, this type is dangerous for pregnant women, as it can lead to the death of not only the child, but also the mother. The disease often affects the kidneys along with the liver. In most cases it is successfully treated.
The most dangerous hepatitis is type C, which often leads to severe and incurable diseases.
Why is hepatitis B dangerous?
HBV is one of the hepatitis that can cause death. This situation becomes possible if the disease takes a chronic form (in 10% of cases). With a strong immune system and proper treatment, the infection is often cured.
The danger lies in the carcinogenic properties of the pathogen and the ability to activate other viruses that arrive in a latent state. It does not directly destroy hepatocytes. But the liver cells suffer from the action of the immune system aimed at destroying the infection. This form most often leads to primary cancer of the gland.
There is an effective vaccine against the disease. Three-time administration of the vaccine protects against infection by more than 90%.
The most dangerous virus
Scientists believe that the most dangerous for human health and life is hepatitis C. This is due to the fact that specialists have not been able to find effective drugs against it. While it is possible to vaccinate against other types of hepatitis, there is no such vaccine against hepatitis C.
Dangerous hepatitis C is very often accompanied by severe complications, such as cirrhosis or liver cancer. What is especially dangerous is that when infected with this disease, a person does not suspect anything for a long time; the initial stage of the disease is asymptomatic, affecting the body day after day. First of all, damage to the liver begins, since the lesion develops there, thereby destroying the cells of the organ.
Irreversible processes begin that lead to disruption of the liver and its destruction. This process can last absolutely asymptomatically for ten years.
During the incubation period, which can last up to one year, a person experiences slight discomfort, manifested in the form of increased fatigue, general weakness of the body, indigestion, and joint pain. Since these symptoms may indicate the presence of other diseases in the human body, most people do not pay special attention to such signs, and certainly do not associate their condition with infection with the terrible hepatitis C.
The transition of this disease to a chronic form occurs gradually, in proportion to the growth of fibrosis and an increase in the number of affected hepatocytes. Despite this, the organs continue to function and do not attract attention for a long time. The result of this process is cirrhosis of the liver, the initial symptoms of which are the following:
- increase in abdominal size;
- appearance of spider veins on the skin;
- excessive weakness and fatigue;
- jaundice.
The first signs of the disease
After being infected with such a terrible disease, a person does not suspect anything for a long time, since the initial stage of the pathology is asymptomatic, but every day the internal organs are increasingly affected. Initially, the liver begins to suffer, since the focus of hepatitis is located there, provoking the destruction of organ cells.
Irreversible processes develop that cause deterioration in the functioning of the liver, and then its destruction. These changes are completely asymptomatic and take decades.
During the incubation period, which lasts about a year, a person feels some discomfort, which manifests itself in the form of excessive fatigue, a feeling of weakness, problems with digesting food, and painful sensations in the joints. Since such symptoms are also inherent in many other pathologies, a person does not pay due attention to such manifestations and does not associate his condition with a disease such as hepatitis C.
If treatment is not started at this stage, then a gradual transition of hepatitis C into a chronic form occurs, which is characterized by a proportional increase in fibrosis and an increase in the number of affected hepatocytes. But despite these changes, the organs continue their work, and the person does not even suspect that he is contagious.
As a result, such manifestations lead to the development of liver cirrhosis, which is characterized by the following symptoms:
- increase in abdominal volume;
- spider veins form on the skin;
- there is a constant feeling of weakness, the person gets tired quickly;
- the skin turns yellow.
Possible manifestations of hepatitis C
If the virus is already in your blood, it may show symptoms, but not earlier than two weeks from the start of the incubation period and no later than 6 months after.
- The temperature rises sharply;
- Weakness and aches throughout the body;
- Headache attacks;
- Manifestations of ARVI symptoms;
- Loss of appetite;
- Heaviness and pain in the right hypochondrium;
- Nausea;
- Vomit;
- Darkening of urine to the color of strong tea;
- Discoloration of stool;
- The skin takes on a yellow tint;
- The whites of the eyes take on a yellow tint.
All these symptoms refer to the acute form of hepatitis C. Extensive intoxication processes occur in the body, and relief does not occur, as with other diseases, for example, acute respiratory viral infections.
How to determine pathology?
What type of hepatitis is the most dangerous? As mentioned above, the most serious type of the disease is form C.
The particular danger of the disease lies in the fact that it has no clinical manifestations. Only when nausea, chronic fatigue and joint pain occur does the patient begin to suspect the development of hepatitis C. The skin gradually turns yellow.
A feature of hepatitis C is not pronounced intoxication and increased transaminase, as in types A and B.