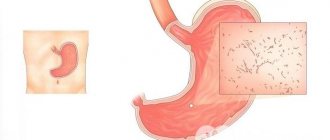
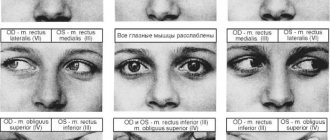
According to the international classification of diseases, there is no such independent disease as catarrhal bulbitis. However, doctors recommend not to delay and to promptly seek medical help if there are signs of such stomach gulbit. Catarrhal type bulbitis can cause many serious complications. The disease indicates the presence of a serious inflammatory process that occurs in the gastric mucosa, namely in the zone of transition to the duodenum. In simple words, the bulb becomes inflamed, which provokes severe bile stagnation and evacuation of secretions.
What are the symptoms of the disease?
Stomach bulbitis, as a rule, does not have any special symptoms that would characterize this particular disease. Superficial bulbitis is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Painful sensations when feeling hungry.
- Discomfort and rumbling sounds in the abdomen.
- Yellow coating on the mucous membrane of the tongue.
- After eating, you still feel hungry.
Periods of pain most often occur in the evening and at night, and are aching and cramping in nature. Sometimes the pain radiates to the navel or to the right upper abdomen.
The next stage is focal gastric bulbitis, which has the following symptoms:
- Signs that accompany superficial bulbitis.
- Addition of flatulence (excessive gas formation).
- Remaining food in the bulbous area of the duodenum causes bad breath.
- Attacks of heartburn and belching.
- Defecation disorders (difficulty bowel movements, diarrhea).
- Increased acidity or bitterness in the mouth is especially noticeable in the early hours of the day.
Digestive disorders provoke an exacerbation of the disease and all symptoms.
Feeling worsens and includes high body temperature, dizziness and headaches, muscle weakness, abnormal sweating, both at night and during the day.
Forms and stages
Catarrhal bulbitis can have different forms. Each form of pathology is expressed by certain specifics.
The following types of bulbite are distinguished:
- Surface. It is a mild form of the disease. In the superficial form, only the outer zones of the mucous membrane are affected. This type can occur hidden, the patient is unaware of the problem with the digestive tract for a long time. When the disease is neglected, there is a risk of developing an erosive form of pathology. The erosive type of bulbitis is expressed by deep damage to the layers of the epithelium.
- Erosive. Manifested by nausea and vomiting, mainly after eating. In complex cases, this type can cause ulcerative lesions.
- Follicular. This form of catarrhal bulbitis is rare. The pathology is accompanied by serious disorders of the digestive tract, which negatively affects the patient’s quality of life.
- Moderate. Most often, the pathology occurs hidden. Patients may experience headaches, nausea and vomiting. Such symptoms are recorded when the disease relapses.
- Focal. Characteristic of this form is the defeat of individual sections of the 12th bulb - the rings of the intestine. This species is quite dangerous to health; timely treatment prevents the development of serious complications.
- Atrophic. This form of the disease is expressed by impaired functioning of the duodenum. As a result, the patient experiences frequent vomiting. The patient with this type experiences rapid weight loss.
In accordance with the morphological characteristics, bulbite is classified as follows:
- First degree. Defined as weak. The preservation of the structure of the mucous membrane is recorded, infiltration with lymphocytes and plasma cells is observed;
- Second degree or moderate bulbitis. Damage to the surface layer and structural changes in the microvilli of the mucous membrane are recorded;
- Third degree or severe. It is expressed by deformations of the villi, lymphoplasmacytic infiltration is observed, and there is a possibility of the appearance of erosive formations.
Chronic catarrhal bulbitis
The chronic type of the disease develops as a result of neglect of catarrhal bulbitis, manifested by the duration of the disease, periods of remission and exacerbation, the body's immunity decreases, headaches and muscle weakness occur. Lesions of the intestinal lining may be microscopic. Chronic gastric bulbitis has certain symptoms. Basically, the pathology is accompanied by pain of varying degrees of intensity; the presence of ulcers is excluded.
Focal catarrhal bulbitis
Against the background of hormonal disorders, focal bulbitis often occurs. The inflammatory process covers various zones of the mucous membrane of the bulb, located between the stomach and duodenum. The lesions are not localized; they are located in different parts of the affected organ. In severe cases, inflammation spreads, moving towards the intestines and stomach.
Pain with focal bulbitis is similar to the symptoms of a peptic ulcer. The patient has an intestinal disorder, in the morning the patient feels nausea, after eating he often experiences sour belching, bloating, and a feeling of heaviness that turns into pain in the epigastric region.
Exacerbation occurs against the background of the development of vitamin deficiency, alcohol abuse, and prolonged fasting. The duration of catarrhal focal bulbitis is about 7 days, in some cases up to 2 months. Stomach acidity may remain normal. With focal bulbitis there is a risk of bleeding.
Erosive
Erosive bulbitis is characterized by the formation of erosive foci on the walls of the duodenum, which can cause destruction of the walls of the stomach. This type of inflammation is provoked by irregular diet, constant stress and a genetic predisposition to gastrointestinal diseases. Advanced erosive bulbitis is dangerous due to the risk of gastric bleeding, the appearance of ulcers, and various complications in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Follicular
Follicular bulbitis is one of the rare types of disease. This type belongs to the varieties of gastroduodenitis and is often a harbinger of its development. Factors that negatively affect the mucous membrane of the bulbus lead to a malfunction of the motility of this zone and an increase in the reaction of lymphoid tissue in this part of the intestine. An increase in the amount of gastric juice produced, as well as a decrease in the protective functions of the bicarbonate layer, enhances the aggressive influence of HCL in this area of the gastrointestinal tract and the growth of lymphoid follicles. This leads to the formation of white vesicles on the mucous membrane of the bulbus, which indicate the development of follicular bulbitis.
Currently reading: Main symptoms and treatment methods for follicular bulbitis
Surface
With superficial bulbitis, the upper part of the mucous membrane becomes inflamed. This form of the disease is the initial stage of the disease. In most cases there is no severe pain or vomiting. The patient feels heartburn, heaviness and slight pain. Most often, this form of bulbitis occurs due to poor nutrition, smoking, and alcohol abuse. If neglected, the disease can progress.
What causes the formation of bulbite
People of absolutely all gender and age categories are susceptible to the disease. According to statistics, the majority of victims are young women.
Among the many causes of the disease, the following are the most common:
- Severe poisoning.
- Prolonged smoking and consumption of alcoholic beverages and drugs that cause stomach irritation. The same effect is possible from the use of aggressive forms of medications.
- Mental disorders, constant nervousness, which provokes abnormal spasms in the gastrointestinal tract, blood flow disorders.
- Excessive amount of hydrochloric acid in the stomach.
- Foreign objects getting inside, causing injuries.
- Chronic or hereditary pathology associated with disturbances of peristalsis, modifications of the intestine.
- Infection of the stomach with various pathogenic bacteria, including Helicobacter pylori infection.
- Poor nutrition. Irrational consumption of food, mainly spicy, fatty and heavy foods.
- Chemical burn of the gastric mucosa.
Over a long period of time, focal gastric bulbitis may have a sluggish course and not manifest itself with severe symptoms.
A noticeable exacerbation of the pathology is possible under the influence of off-season vitamin deficiency, taking special drug therapy and excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages.
Treatment for adults
Drug therapy in the treatment of focal bulbitis in adults consists of prescribing drugs with the following effects:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs with antacid action with a predominant content of bismuth (Almagel, Maalox, Gastal);
- Antispasmodic analgesics that help relax muscle muscles and eliminate discomfort (No-shpa, Drotaverine, Spasmolgon, Papaverine);
- Drugs that slow down the action of dopamine receptors (Motillium, Cerucal);
- Medicines for accelerated restoration of damaged mucous membranes, which help improve metabolism (Liquitorin, Actovegin, Solcoseryl);
- Preparations for neutralizing hydrochloric acid (Fatotidine, Omez, Omeprazole);
- Antibiotics to destroy pathogenic microorganisms in the form of Helicobacter pylori (Metronidazole, Clarithromycin, Amoxicillin);
- Sedatives for severe nervous system disorders (valerian, motherwort).
Surgical intervention is carried out in the presence of clear indications and a severe course of the disease in an erosive form. Physiotherapy (electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, mud baths) is effective for general recovery.
Diagnostics
Despite the fact that bulbitis has a wide range of symptoms, difficulties may arise when choosing a diagnostic method.
Manifestations of pain can confuse the specialist and cause the assumption of inflammation of appendicitis or some neurological disorders.
A full examination of the patient with palpation and examination of the surface of the tongue helps to exclude false diagnoses.
When palpated, the pain will be concentrated precisely in the final part of the stomach, and the surface of the tongue will have a dense coating of yellow or white color.
Of course, the initial diagnosis does not allow us to determine exactly the development of bulbitis, but it gives the necessary direction for further action.
Diagnostic measures include a list of the following actions:
- General blood analysis. With an exacerbation of the disease, the presence of an inflammatory process will be indicated.
- Blood chemistry. Even in the sluggish stage of the disease, excessive production of pancreatic enzymes and C-reactive protein can be detected.
- Kcal test for occult blood.
- FGDS (fibrogastroduodenoscopy). During diagnosis, it is possible to recognize the type of damage to the mucous membrane, detect possible microtraumas, and inflammatory processes. During the procedure, gastric juice is collected for laboratory testing to identify the pathogen and its sensitivity to antibiotics.
- X-ray using contrast agent. The results of the study will display data on the presence of stagnant food in the bulbous area, impaired peristalsis and an enlarged organ.
- Ultrasound. Examination of the gastrointestinal tract using ultrasound can detect pathologies of the liver, duodenum and pancreas.
During a consultation with a specialist, you must talk about all your symptoms. To make a correct diagnosis, every moment in the patient’s well-being is important.
If you are using any medications, you should also inform your doctor.
Symptoms of the disease
A disease such as gastric bulbitis is very difficult to diagnose, especially in the early stages. The diagnosis can only be made using special equipment. The fact is that the signs of the disease are not expressed clearly enough and are not characteristic only of this disease.
Only subtle signs may appear during the disease, mainly nausea. In the meantime, inflammation of the bulb - the so-called duodenal bulb - may already be in full swing.
The causes of bulbitis can be medications that irritate the mucous membrane, food containing any caustic substances, for example, acid. As a result, the symptoms of bulbitis include weakness and loss of strength, lack of appetite, severe pain in the head, pain in the abdominal area can become unbearable and have the character of cutting. After eating, attacks of nausea appear. A bitter taste appears in the mouth due to increased secretion of bile.
When diagnosing bulbitis, an important point is the initial examination of the patient; such an examination allows you to outline ways and methods for further diagnosis. However, the main means for making a correct and comprehensive diagnosis are laboratory tests.
The reason for examination and diagnostic studies is the patient’s complaints. In this case, the patient usually complains of pain attacks in the right abdomen. A visual sign may be a yellow coating on the patient’s tongue. Pain may also appear around the navel. Such pain with bulbitis has the character of periodic spasms. The cause of exacerbation is food intake.
Patients with bulbitis develop an unpleasant odor in the mouth. Belching from the mouth, sweating, headache and malaise are constant companions of patients. This is due to the fact that an increased amount of toxins is produced in the stomach during bulbitis.
Treatment options
Focal gastric bulbitis requires a multi-stage treatment regimen. The impact on the disease will certainly be complex.
The fundamental requirement before starting therapy is a radical change in lifestyle, nutrition, and elimination of bad habits.
Treatment options include the following:
- Medication. Drug therapy includes several stages of treatment. Each stage is necessary to achieve a specific goal.
- Anti-inflammatory therapy. Designed to stop the process of inflammation and relieve pain.
- Antispasmodics. To relax the intestinal muscle tissue and stabilize gastric motility.
- Biogenic stimulants. They improve the healing process of ulcerative lesions of the mucous membrane, normalize metabolism in tissues.
- Antibiotics. To eliminate the bacterial pathogen that caused the formation of focal or superficial gastric bulbitis.
- Herbal medicines. Taken in the form of dietary supplements to help restore gastric microflora.
- Vitamin and mineral complex. They have the effect of replenishing micronutrients throughout the body, which have become deficient after problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
- Physiotherapeutic.
- Electrophoresis with the use of painkillers.
- Magnetotherapy.
- UHF therapy.
- Surgical.
- Ligation of bleeding vessels and use of a surgical clip.
- Ethnoscience.
- Herbs do not have a therapeutic effect, but only help improve the therapeutic effect of medications taken.
- Pharmaceutical propolis tincture (to reduce pain and accelerate mucosal regeneration).
- Rosehip infusion (to support immunity).
- Fresh potato juice (neutralization of aggressive gastric juice).
- Chamomile infusion, licorice, St. John's wort (promote healing of the mucous membrane).
The need to use herbal infusions must be confirmed by the attending physician.
The entire stage of treatment is accompanied by adherence to dietary nutrition. The therapeutic diet is prescribed by the attending physician on an individual basis.
Most often, it is necessary to avoid eating aggressive foods, which can provoke excessive production of gastric juice and prolonged irritation of the mucous membrane.
How to treat
The treatment method for focal bulbitis is based on the use of complex therapy using various rehabilitation techniques according to a specific scheme:
- Carrying out preventive examination and necessary research;
- Prescribing drug therapy with drugs of varying degrees of impact;
- Compliance with a therapeutic diet;
- Establishing a correct lifestyle;
- Physiotherapeutic procedures as necessary;
- Compliance with recommendations for disease prevention.
The recovery process is prescribed individually by the attending physician, who studies the presented clinical picture and monitors the overall established treatment.
What are the preventative measures against bulbitis?
Prevention against bulbitis consists of the following recommendations:
- Maintain immunity. Take vitamin complexes necessary for a certain age category.
- Avoid nervous and mental stress. If you have difficulty resolving such problems on your own, seek help from a specialist.
- Develop a consistent habit of proper nutrition. Permanently give up coffee containing alcohol, alcoholic beverages, fatty and highly seasoned foods.
- Consult your doctor promptly if you experience problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
- Complete smoking cessation.
- Regularly undergo diagnostic tests to identify the bacteria Helicobacter pylori and fully treat it.
- Wash your hands, vegetables and fruits thoroughly.
- Include moderate exercise in your lifestyle to maintain good gastric motility.
Simple rules of prevention will not only help to minimize diseases such as focal gastric bulbitis, but will also protect the overall health of the entire body.
What is the prevention of focal bulbitis?
Preventive measures include:
- Passing a medical examination;
- Treatment of other inflammatory processes in the body;
- Rejection of bad habits;
- Proper nutrition, avoiding overeating and excessively fatty foods;
- Maintaining hygiene rules.
After treatment with antibiotics and medications, following a diet and certain lifestyle rules allows us to hope for a complete recovery.
We recommend: How to properly brew and drink Chaga when treating gastritis
Useful video
https://youtu.be/5lu-xgrVf6s
What is surface bulbite? This is the mildest stage of inflammation of the mucous bulb, which is located at the border of the junction of the stomach and intestines. All diseases of both organs are projected here. In addition, the ducts of the pancreas and gall bladder exit into the bulb. With the development of one or another pathology, swelling of the mucous membrane of the organ being described develops. As a result, difficulties arise in the release of secretions, which provokes stagnation of bile and enzymes necessary for the digestion and absorption of food.
In this case, characteristic symptoms appear, indicating the development of superficial gastric bulbitis. This is a constant rumbling in the stomach, the formation of a feeling of hunger even after eating, general malaise, a tendency to constipation, and sometimes nausea. On an empty stomach, pain often occurs that is vague in nature.
Intestinal motility is impaired, and its contents are often thrown back into the stomach. Therefore, belching and vomiting with a bitter aftertaste appear.
Superficial gastric bulbitis is diagnosed by fibrogastroduodenoscopy. During this procedure, the doctor sees changes in the color of the mucous membrane. It becomes slightly brighter than normal, the capillaries are slightly dilated. Observing such manifestations of pathology, the doctor writes “superficial gastritis bulbitis” in the diagnosis.
Causes of bulbitis
The main causes of inflammation in bulbitis prove a connection with stomach diseases. The people most susceptible to the disease are:
- those who do not know how to organize a proper diet, who are addicted to fast food, chips, fried and spicy foods that irritate the mucous membranes;
- smokers who drink alcoholic beverages immoderately;
- often exposed to stressful situations, nervous stress;
- infected with Helicobacter pylori infection, helminths or parasites;
- with reduced immunity;
- with hypofunction of the adrenal glands;
- from families with a hereditary predisposition.
The bulb undergoes serious changes during reflux disease - the backflow of the contents of the duodenum with bile and pancreatic enzymes into the stomach. In this case, the mucous membrane is affected due to additional mechanical and chemical irritation.
What can provoke such a clinical picture?
Many factors can lead to the development of focal superficial bulbitis. We list only the most basic of them. This:
- Infection caused by the microbe Helicobacter pylori.
- Giardiasis, helminthic infestations.
- Crohn's disease (chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract).
- Poor nutrition, constant overeating, abuse of spicy, fatty, fried foods, incorrectly chosen diets.
- Constant drinking of alcohol, smoking.
- Decreased body immunity.
- Injury to the bulb caused by foreign objects entering the intestines.
- Hereditary predisposition.
Inflammation of the bulb mucosa can also be caused by drinking too hot a liquid or eating too hot food. At the beginning of the development of the disease, characteristic symptoms rarely appear, so focal superficial bulbitis quickly develops into other more severe stages, which we will talk about below. Therefore, it is so important to identify pathologies in time and begin adequate treatment.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosing the disease is not difficult for an experienced doctor; there are several methods for this:
- direct conversation with the patient, clarifying his complaints and symptoms;
- studying the abdomen using the palpation method, which helps to detect painful areas in the patient or the presence of compactions in the organ;
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy is a method of visually examining the condition of the intestines, in which a special device in the form of a tube is inserted through the patient’s mouth, which allows studying the organ from the inside;
- A common method is also radiography of the stomach and duodenum;
- impedancemetry of the gastrointestinal tract, which helps to study the state of the digestive tract by introducing probe electrodes and obtaining resistance between them;
- antroduodenal manometry is a method that studies the pressure inside organs;
- the state of the environment inside the stomach and intestines is also studied by studying the acidity inside the organs;
- Blood tests are collected to study changes in the body's condition after the onset of the disease.
What is the help?
Superficial bulbitis is easy to treat - diet quickly leads to relief.
It is necessary to completely exclude salty, spicy, fried foods, fatty meat products, canned food, smoked foods, and alcohol from the diet. During the first two weeks, only chicken broth with crackers, liquid milk porridge and jelly are allowed. Later, meatballs or steamed cutlets are prepared from minced meat. Vegetables and fruits that have a rough texture will first have to be softened by baking. The patient must not only change his diet, but also the nutrition system itself. Now you need to eat often, five to six times a week, but in small portions. To prevent relapses of chronic superficial bulbitis, doctors recommend radically changing your entire life: try not to worry, learn to get rid of stress, give up night shifts at work and use sedatives if necessary.
Features of drug treatment of superficial bulbitis
Drug treatment is prescribed only during periods of exacerbation of the disease, after identifying the cause of inflammation of the mucous membrane. So, for example, if the cause of the illness is Helicobacter pylori, superficial bulbitis is treated with a course of antibiotics.
For parasitic superficial gastric bulbitis, sedatives are prescribed. After recovery, herbal decoctions and tinctures are used as prophylaxis.
In other cases, medications are prescribed that normalize stomach acidity. These are "Almagel" and "Phosphalugel". They help neutralize high acidity, eliminate heartburn and stomach grumbling. Relevant medications are those that enhance the regeneration of duodenal cells, tablets that regulate the motility of the gastrointestinal tract, enveloping and astringent agents, and antispasmodics for pain.
Often the described disease is accompanied by gastritis; it often happens that superficial gastritis bulbitis becomes a type of duodenitis. Then drug treatment is complex.
Folk remedies
Inflammation of the intestinal mucosa can be easily eliminated with folk remedies. Plantain juice is especially effective in this case. It is mixed with honey in proportions of 3x1 and drunk three times a day before meals, 50 mm. This remedy has an anti-inflammatory effect and promotes the regeneration of cells in the gastrointestinal mucosa, so the superficial bulbitis goes away quickly.
When people go to the doctor with severe abdominal pain, as a rule, they order an examination and write down the pathology found in the conclusion. In some cases, a chronic erosive process is discovered in the duodenum called gastric bulbitis - what it is and how to treat it will be described below.
Prevention
There is no specific prevention for this pathology. To prevent the development of catarrhal bulbitis, a person needs to adhere to general recommendations:
- Lead a healthy lifestyle;
- Treat digestive system pathologies in a timely manner;
- Follow a diet;
- Perform physical exercises systematically;
- Have a medical examination at least 2 times a year.
Catarrhal bulbitis is a fairly serious pathology that leads to negative consequences. To avoid this, you must consult a doctor in time and strictly follow the specialist’s recommendations.
What is stomach bulbitis?
The pathology is characterized by inflammation of the duodenal bulb; for the same reason, the disease is also called bulboduodenitis. The inflamed area is only adjacent to the stomach, so the presence of the name of this organ in the diagnosis is incorrect. Knowing what bulbitis is and how to treat it, you should understand that we are talking more about the duodenum. They began to call it a pathology of the stomach only because in most cases this disease is accompanied by gastritis.
Both diseases have a common and similar pathogenesis, often arise from each other, and complicate the course of inflammatory processes. Bulboduodenitis and gastritis have similar symptoms, so often inflammation of the bulb in the duodenum occurs hidden, masquerading as attacks of gastritis. These two diseases greatly reduce a person’s level of comfort in life and require treatment.
Surface
This is one of the forms of pathology that is diagnosed in humans. Superficial gastrobulbitis differs in that abdominal pain is not the main symptom. It can be determined by fibrogastroduodenoscopy; it is characterized by slightly swollen folds of the gastric mucosa, a brighter color, and dilated capillaries. Superficial bulbitis can provoke reflux phenomena, in some cases even into the esophagus from the bulb. A patient with this form of bulboduodenitis may notice the following symptoms:
- tendency to constipation;
- chronic rumbling in the stomach;
- irritability;
- cardiopalmus;
- chills;
- nausea (rare);
- general malaise;
- constant strong feeling of hunger.
Catarrhal
This type of pathology is characterized by superficial inflammation of the bulb, swelling of the intestinal wall, and desquamation of the epithelium are observed. Catarrhal bulbitis can be purulent, mucous, serous, this factor determines the nature of the effusion. Sometimes there is a gradual change in exudate during the development of gastric bulbitis. More often, the catarrhal form occurs in acute form and without pus. Doctors say that this kind of gastric bulbitis occurs quickly, is easy to treat and goes away without residual effects.
Follicular
This type of gastric bulboduodenitis is regarded as a separate form, because the pathology becomes the result of an immune reaction to the penetration of aggressive agents or infection. Inflammation occurs, an increase in lymphoid follicles in the intestinal wall, which forms a clinical picture that is very similar to the catarrhal form of the disease.
Erosive
This pathology is often called ulcerative bulbitis, because erosive areas form on the mucous surface of the intestine, which develop into ulcers. This form of pathology requires special attention and urgent treatment, because there is a high probability of developing a secondary peptic ulcer, the appearance of intestinal bleeding (if wall perforation occurs), and peritonitis. Acute and chronic forms of erosive gastric bulbitis are diagnosed with equal frequency. The erosive form is more difficult for patients to tolerate; it is more difficult to treat this type of disease.
What changes occur with bulbitis?
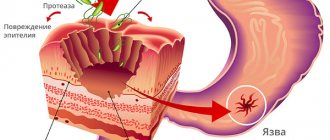
When the digestive process in the stomach is disrupted, acidified, undigested food comes to the bulbus. Additional enzymes are required to process it. Retention of the food bolus contributes to stagnation of the contents and inflammation of the mucous membrane.
At first, the bulbite is in the nature of a superficial lesion, then it penetrates deeper, causing the formation of cracks and small wounds (erosions). The folds of the mucous membrane swell, dilated vessels fill the surrounding tissues with blood (the phenomenon of hyperemia). If bulbitis is not treated in time, the damage goes to a deeper level, the submucosal and muscle layers. Thus, a duodenal ulcer is formed.
Isolated inflammation of the bulb practically does not occur; the causes of inflammation are the same as with gastroduodenitis
Causes of the disease
In medicine, the traditional etiological factor in the development of chronic and acute inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract is considered to be the bacterial infection Helicobacter Pylori. A proven fact is that this microorganism is present in the duodenum, stomach during ulcers and inflammation. Whether it is the cause or only accompanies these gastrointestinal diseases is still unknown. The main eating disorders, which, according to experts, cause the development of gastric bulbitis are:
- abuse of smoking and alcohol on an empty stomach;
- spicy, fatty poison, fast food;
- overeating;
- sweating;
- dizziness;
- increased fatigue;
- frequent headaches;
- irregular meals.
All these factors cause changes in the acid-base state, which further provokes chronic, acute inflammatory processes. Another probable cause is helminthic infestation, giardiasis, which is often found in children and people with an asocial, marginal lifestyle. A rare but reliable cause of this gastric pathology is granulomatous enteritis, Crohn's disease. In patients, disorders in the immune system and genetic predisposition are clearly visible.
In Crohn's disease, bulbitis will be one of many symptoms, syndromes of the disease; it will not be the only manifestation of the disease. This is due to the systemic nature of the gastrointestinal tract pathology, and not focal manifestations. The reasons for the development of bulbitis include taking certain medications, harmful working conditions, and working with aggressive substances that can penetrate the intestines.
Causes
There are several types of bulbite:
- erosive;
- surface;
- spicy;
- focal;
- chronic;
- catarrhal
Bulbit occurs against the background of existing pathologies or is a consequence of poor nutrition and bad habits.
There are several reasons for the development of bulbitis:
- preservation of the embryonic mesentery, which provides mobility to the duodenum. Because of this, the intestines can twist, and food fragments can linger in it. Such conditions will create a favorable environment for the active development of bacteria. A couple of other negative factors, such as eating spicy or fatty foods, drinking alcohol, will be enough to cause bulbitis;
- gastritis, one of the signs of which is a pathological increase in the secretion of hydrochloric acid. Getting into the duodenum, it provokes superficial bulbitis. Subsequently, a complex of these diseases often leads to gastritis taking on an erosive form;
- helminthic infections, the presence of giardiasis or Crohn's disease often cause a chronic form of bulbitis;
- mechanical or chemical traumatic factors: burns from too hot food or damage due to swallowed things, alcohol or drug exposure;
- a bacterial factor that affects the change in pH - acidity in the bulb. The pH may change due to Helicobacter pylori, a spiral-shaped gram-negative bacterium that is dangerous to both the intestines and stomach;
- long periods of fasting.
The situation can also be aggravated by the presence of a family history and an unhealthy diet.
Under the influence of the factors described above, the acidity in the duodenal bulb can change, which provokes the appearance of catarrhal bulbitis.
But, as stated above, there is no such disease officially. They indicate the degree of inflammatory processes.
The catarrhal form of bulbitis is a complex of pathological changes that manifest themselves in the form of:
- swelling of the intestinal folds;
- inflammation of the mucous membrane, which will have a “burnt” appearance;
- disturbances of intestinal motility;
- reflux;
- expansion of capillaries;
- accumulation of residual fluid in the stomach cavity.
The mildest type of bulbitis is superficial, followed by catarrhal, and then focal.
Symptoms of bulbitis
Take care of your health - save the VKontakte link
Often the disease is disguised as signs of gastritis and is asymptomatic for a person. For this reason, it is difficult to put forward a version of inflammation of the bulb in time. The most characteristic manifestations of bulboduodenitis can be considered hunger pain two hours after eating at night. The symptoms of gastritis and bulbitis in the early stages are very similar, so diagnosis is difficult. Stomach gulbit - what is it and its symptoms:
- cutting pain in the abdomen radiating to the navel;
- bad breath in the morning;
- spasms in left side;
- vomiting, nausea, dyspepsia.
All these symptoms should be cause for concern and undergo an examination to identify pathology. If induced hyperacid gastritis with gastroesophageal reflux develops, heartburn, a pulling sensation near the sternum, and belching of sour contents are added to the above symptoms. The symptoms subside after taking antacid medications, and the patient’s condition returns to normal. These symptoms appear in many people, but this does not mean that in 100% of cases a person develops bulboduodenitis.
Symptoms and development
For treatment to be effective, it is necessary to determine the form of the disease, understand its causes and differentiate the symptoms of possible accompanying diseases.
Any form of bulbitis is easy to diagnose.
The specialist is assigned to undergo a number of studies:
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy;
- X-ray of the stomach;
- analysis of stomach contents.
Sometimes probing may be necessary.
Catal bulbitis is similar in its manifestations to the chronic form of this disease and gastritis. At the catarrhal stage, the disease sometimes lingers for several years, after which it transforms into focal bulbitis.
The course of the focal form of the disease is much more severe and is associated with hormonal dysfunctions in the functioning of the duodenum.
Exacerbations and symptoms of catarrhal bulbitis appear seasonally. The pain, as a rule, is of an unexpressed dull, spastic nature.
In this case, painful sensations will mainly be localized in the area “under the stomach”, but can also radiate to the navel area or in the hypochondrium on the right side.
Patients with catarrhal bulbitis often experience belching, a strong odor and bitterness in the mouth.
This is due to the fact that the inflamed bulb interferes with the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, as a result of which the contents of the duodenum can be thrown back into the stomach.
Patients often complain of nausea, but at this stage it rarely reaches the point of actual vomiting.
The catarrhal form, unlike other types of bulbitis, is characterized by long asymptomatic periods when pathological processes proceed unnoticed.
Overeating or drinking alcohol and “junk” food can provoke painful sensations. And even in this case, the pain will be delayed. Most likely, it will appear only 2 hours after eating.
Taking medications that normalize acidity or eating the right foods should reduce pain. But this is not a substitute for full treatment.
Video:
https://youtu.be/oeCvrjd85Po
Diagnostic methods
Stomach bulbitis is usually discovered by chance during a routine examination, because the symptoms are disguised as gastritis. A blood test does not show anything until the pathology reaches a severe ulcerative form, the SOE is slightly increased. X-rays also do not provide a complete informative picture. The ability to diagnose the disease appeared only after the invention of endoscopic equipment.
Endoscopic examination has become the gold standard for detecting gastrointestinal diseases. It is recommended to carry it out in conjunction with esophagogastroscopy, which helps to obtain the most complete picture of the condition of the mucous membrane of the stomach, duodenum, and esophagus. These diagnostic methods will show:
- erosion;
- swelling;
- ulcers;
- inflamed areas;
- bleeding.
A flexible fiberscope opens up the opportunity not only to diagnose pathology, but also to begin therapy for the damaged area. To assess the possible factor in the development of gastritis, bulbitis, and the general acid-base state of the gastrointestinal tract, daily pH measurements are performed. If endoscopy fails for some reason, it can be replaced with antroduodenal manometry and electrogastroenterography.
Diagnosis of catarrhal bulbitis
Accurate diagnosis of catarrhal bulbitis is solely the result of a visual examination of the mucous membrane during fibrogastroduodenoscopy by introducing a special probe with a sensor containing a video camera.
External signs of acute inflammation:
- pronounced redness of the inflammation site - due to vasodilation and increased blood flow;
- swelling - due to changes in the physicochemical properties of proteins, their ability to attract and retain water increases.
The medical task is to establish how large the area of the affected area is, what its location is, whether there are surface defects of the mucous membrane or neoplasms. If during the examination deformations, diverticula, or anomalies of intestinal development are detected, additional studies are prescribed: radiography allows you to evaluate the “throughput” capacity of this section of the intestine.
In chronic cases, redness and swelling may be mild. The disease takes a chronic course when its cause is not eliminated for a long time or the action of an aggressive agent coincides with situational (or prolonged) weakening of the body.
Treatment of gastric bulbitis
Pathology is easier to cure if it is detected at an early stage. There are several directions on how to treat bulbitis. The maximum effect is achieved by taking an integrated approach to therapy, using the following methods:
- medicinal;
- folk recipes;
- diet therapy.
Medication
Treatment with medications can only be started after consultation with a gastroenterologist. The selection of medications is carried out based on the cause of bulbitis and the morphological form of the pathology. The following types of medications may be prescribed for therapy:
- Antacids. This group has proven to be effective when it comes to reducing acidity. As a rule, Gastal, Rennie, Almagel, Maalox are prescribed, which reduce the irritating effect that affects the gastric mucosa. Antisecretory agents such as Omeprazole and Ranitidine may also be prescribed.
- Painkillers. In the acute form of bulbitis, the doctor may prescribe No-shpa, Papaverine, Baralgin to reduce pain.
- In case of helminthic infestation, anthelmintic (anthelmintic) drugs will be prescribed: Suramin, Levamisole.
- When infected with bacteria, or when the hydrochloric acid barrier is weakened, antibacterial agents are prescribed. The appointment is based on microbiological and laboratory testing.
- Light sedatives help with the stress factor of gastric bulbitis.
Folk
Home medicine recipes have achieved high effectiveness in the treatment of gastrointestinal pathologies. Folk remedies are created only from their natural components, so they can be combined well with traditional medicines without the risk of causing unforeseen side effects. For example, milk has an enveloping effect, reducing inflammation and irritation of the gastric mucosa. Herbal infusions from:
- chamomile;
- plantain;
- St. John's wort;
- calendula flowers;
- Icelandic moss.
Freshly prepared carrot juice, which should be drunk 30 minutes before meals, has a positive effect in the treatment of pathology. A decoction of plantain helps to cope with the inflammatory process. All of these remedies for bulbitis have a real medicinal effect and are safe for humans, but it is worth consulting with a doctor so that the mutual influence of medications does not cancel the effectiveness of the treatment. It is not recommended to choose a course of therapy on your own.
Stomach bulbitis: signs, diagnosis, treatment, prevention and classification
Stomach bulbitis: signs, diagnosis, treatment, prevention and classification5 (100%) 5 vote[s]
The duodenum plays a special role in the digestion of food, which receives enzymes (pancreatic juice, bile) necessary for absorption in the walls of the small intestine.
With bulbitis, inflammation of the duodenal bulb adjacent to the stomach develops. This is why the disease is often confused with gastritis or duodenitis. Only differential diagnosis (fibrogastroduodenoscopy) will distinguish the disease from other gastrointestinal pathologies.
Based on the test results, the doctor will be able to establish an accurate diagnosis.
What is stomach gulbit?
Bulbit is a type of duodenitis in which the bulbus, a bulbous thickening located behind the sphincter of the stomach, is susceptible to inflammation. The disease is secondary. The reason is the impact of negative internal and external factors. More often it is gastritis, but when the inflammatory focus is localized somewhat lower than the stomach (along the digestive tract).
There are several types of bulbite:
- erosive;
- catarrhal;
- surface.
Each occurs with specific symptoms, on which the subsequent treatment plan will depend.
Causes
Inflammation of the bulb develops due to the entry of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori from the biliary tract or increased acidity due to unauthorized entry of contents from the stomach.
External causes of inflammation of the bulb:
- acute, chronic gastritis;
- low immunity;
- infection caused by Helicobacter pylori;
- hormonal imbalance, adrenal dysfunction;
- damage to the gastrointestinal tract by lamblia, helminths.
Internal reasons for the development of bulbitis:
- frequent stress and anxiety;
- prolonged fasting, staying on a diet for weight loss;
- abuse of smoking, alcohol, salty, smoked and fried foods;
- non-compliance with dosage during long-term use of anti-inflammatory, non-steroidal drugs.
Reference! Often the development of bulbitis is provoked by gastritis, when a large mass of hydrochloric acid begins to form and is released into the 12-gut.
The cause of the development of the acute phase of the disease can be the use of alcohol and medications, and gastrointestinal injuries. The chronic form of bulbitis develops against the background of Crohn's disease, giardiasis (infection with worms).
In a child, the pathology is associated with injuries to the digestive tract - a foreign object entering the stomach.
stomach gurgling
Classification
Bulbit (ICD-10 code) occurs in several forms:
- Focal – severe form, accompanied by complications.
- Catarrhal – mild, chronic with mild symptoms. During diagnosis, the mucous membrane resembles a burn. This form of the disease is highly treatable; it is enough to follow a special diet.
- Superficial with the involvement of exclusively the upper mucosal tissues in the inflammatory process, the appearance of diffuse pain in the navel area, nausea, heartburn, and rumbling in the abdomen in patients.
- Erosive occurs when erosion is localized, a defect on the surface of the mucous bulb of the duodenum. The main symptom is prolonged, burning pain in the epigastric region.
- Atrophic, chronic form, causing dysfunction and thinning of the intestinal mucosa. Patients experience constant malaise, intoxication, weakness, and drowsiness.
- Hyperplasticity develops when polyps settle on the mucous membrane of an organ, abnormal proliferation of OCD cells, and the appearance of painful symptoms before and after eating.
- Diffuse with transformation of fibrous tissue caused by inflammation affecting the walls of the small intestine and stomach. The form of the disease is severe. Lack of timely treatment can lead to cancer.
- The hemorrhagic form develops with the involvement of the mucous part of the bulb in the inflammatory process, the appearance of multiple bleeding wounds against the background of increased acidity. Patients experience pain in the stomach after eating, a disorder of the vegetative-vascular system, and increased fatigue.
- Follicular, caused by helminths with the appearance of small nodular follicles on the inner surface of the bulb.
In children, inflammation of the bulb often develops against the background of untreated gastritis, but responds quite well to drug treatment.
Why is bulbit dangerous?
There are several dangers of bulbit:
- Degeneration of mucous epithelium into oncology against the background of a prolonged inflammatory course.
- Tendency to malignancy during chronic course.
- Opening of bleeding inside the cavity in the erosive form.
- Development of adhesions in a complicated form in case of damage to the outer layer of the bulb, followed by intestinal obstruction and intestinal deformation.
- Mutation of cells with their degeneration into atypical ones in a progressive chronic form of the disease.
Symptoms and signs of bulbitis
The disease at an early stage manifests itself in the form of an outbreak of severe burning pain at the location of the duodenal bulb (usually after eating), then gradually begins to radiate to the hypochondrium. Characteristic symptoms may differ slightly depending on the form of the disease and the degree of its activation.
Signs of superficial bulbitis:
- irritation, weakness;
- rumbling in the stomach;
- pain before or after eating;
- swelling, hyperemia of the mucous membrane.
For follicular form:
- abdominal cramps;
- dizziness;
- belching, heartburn, nausea.
For erosive bulbitis:
- nausea;
- spasmodic pain in the stomach.
In the focal form:
- bloating;
- nausea;
- indigestion;
- belching;
- headache during exacerbations.
Reference! The signs of bulbitis are similar to ulcers, gastritis, duodenitis due to the close connection of the duodenum with the stomach and digestive tract.
At an early stage, there is a cramping, aching pain that gets worse at night, a yellow coating on the tongue, and rumbling in the stomach. As the disease progresses, the pain begins to radiate under the shoulder blade, into the navel, and right hypochondrium.
A sour taste appears in the mouth in the morning, heartburn, belching, nausea, diarrhea, constipation, bloating, increased gas formation.
With a complicated course of the disease, a febrile state, increased temperature, and intoxication of the body are possible.
Methods for diagnosing bulbitis
First of all, the attending physician palpates the abdominal cavity. Discomfort and painful symptoms can be so severe that patients are forced to go to a medical center for emergency care. Next, the medical history and duration of the exacerbation period are studied. A number of laboratory and instrumental studies are prescribed:
- Fecal analysis to determine the degree of digestion of food, assess the functions of the digestive system, and also to identify Giardia, roundworms or helminths.
- Blood test for the presence of antibodies to various external agents.
- PCR to detect the number of Helicobacter pylori bacteria, which provoke the development of gastritis and bulbitis.
Other research methods:
- X-ray – determination of pathological changes in the structure of the bulb.
- Esophagogastroscopy is carried out by collecting material from the affected area to obtain a complete picture and identify the level of acidity of gastric juice.
- An abdominal ultrasound is prescribed to assess the condition of the internal organs.
Treatment of the disease
A set of therapeutic measures is developed by a doctor after laboratory tests, identification of ailments, and visual examination of patients. The main treatment is medication:
- Antacids (Maalox, Gastal).
- Painkillers (No-shpa, Papaverine, Baralgin) to relax smooth muscle tone.
- Wound healing agents (Methyluracil) for erosive superficial bulbitis.
- Hydrochloric acid receptor blockers (ranitidine, omeprazole, metoclopramide).
In case of acute progressive form of bulbitis caused by Helicobacter pylori, emergency gastric lavage is necessary in a hospital setting. If food poisoning is suspected, a drip is installed with an infusion of saline solution to relieve signs of intoxication. If the cause of the development of the pathology is caused by worms, then emergency anthelmintic therapy is carried out.
Catarrhal and chronic forms of bullpitis are treated with antibiotics:
- Sumamed;
- De-nol;
- Vilprafen;
- Amoxicycline;
- Metronidazole.
Reference! Essentiale forte improves liver function during the inflammatory course of bulbitis. Wobenzym has a beneficial effect on the digestive system, takes an active part in metabolic processes, saturating it with active acids and enzymes.
The goal in the treatment of bulbitis is to restore the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, relieve unpleasant painful symptoms, and eliminate the impact of negative factors. Medicines are selected by the attending physician on an individual basis.
If the disease is caused by pathogenic microbes, then penicillin antibiotics (Amoxiclav, Amoxicillin) are prescribed. At an early stage of treatment, anthelmintics help if worms are detected.
To relieve spasms and calm the mucous membrane, sedatives are indicated - pharmaceutical tinctures (motherwort, valerian).
Most patients with bulbitis are often bothered by hungry stomach pains and heaviness in the abdomen, so enveloping drugs (Baralgin, Nurofen, Ketanov, Almagel, Maalox, Gaviscon, Phosphalugel) are prescribed to neutralize the effect of hydrochloric acid, eliminate the increased feeling of hunger and salivation.
With bulbitis, it is important to normalize the intestinal microflora and improve digestion. For this purpose the following may be prescribed:
- Mezim;
- Pancreatin;
- Turbiotic;
- Bifidumbacterin;
- Lactovit.
Using folk remedies, the disease (in consultation with the doctor) is treated with pharmaceutical herbal teas, tinctures, herbal decoctions (St. John's wort, linden, thyme, lemon balm, mint, chamomile, oats, flax seed, valerian root) with anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effects.
The note! Bulbit sells well in conservative therapy and allows patients to be completely cured. Surgical intervention is prescribed only in advanced cases.
Diet for illness
Proper nutrition for bulbitis is 50% success. During the period of treatment, patients are advised to exclude cold and hot foods from their diet. In the progressive acute form of the disease, avoid foods that irritate the mucous membranes:
- fresh bread;
- cabbage;
- spinach;
- mushrooms;
- legumes;
- rich broths.
Food should be easily digestible. It is worth giving up:
- strong tea;
- coffee;
- canned food
Food should be steamed or baked in the oven without adding spices or coarse oils. The main thing is that rough food does not get into the mucous membrane, so it is better for patients to take it pureed in small portions up to 8 times a day.
Diet for duodenal bulbitis
One of the main directions in the treatment of pathology is normalization of nutrition, eating only a certain type of food. It is very important to completely give up alcohol and smoking, which have a strong irritating effect on the gastric mucosa and gastrointestinal tract. Their influence can greatly aggravate duodenal bulbitis and cause a transition from mild to severe form.
In case of acute attacks of pathology, it is recommended to completely refuse food for a while to reduce inflammation, swelling, pain, then you are allowed to eat porridge with water or low-fat milk. The diet for duodenal bulbitis at the non-acute stage allows the following products for consumption:
- consumption of fermented milk products: yogurt, kefir, fermented baked milk, milk, low-fat cottage cheese, cheese;
- white bread crackers;
- vegetable broths;
- jelly.
If you have stomach pathology, you should permanently remove carbonated drinks, highly spicy foods, fried foods and smoked foods from your diet. Proper nutrition for bulbitis must be observed throughout the life of patients who have a predisposition to the development of gastrointestinal diseases. The patient’s body can fully recover, which will allow them to return to their normal diet. An approximate daily menu for the treatment of gastric bulbitis looks like this:
- The first breakfast is a steamed omelet with carrots.
- Snack – apple puree, rose hip decoction.
- Lunch – soup with meatballs or boiled rice, jelly.
- Afternoon snack – crackers, a glass of milk.
- Dinner – buckwheat porridge, fish soufflé, carrot salad.
- Snack – tea (not strong), cracker pudding with pear puree.
- Before bed - tea.
Diet and treatment for catarrhal bulbitis
If, based on the studies carried out, catarrhal bulbitis is confirmed, the doctor prescribes complex treatment.
It includes bed rest for several days, taking medications (if necessary), a strict diet for a month and eliminating unpleasant symptoms.
For gastric bulbitis, antacids are first prescribed. These may be Maalox, Rennie, Gastal and other drugs of a similar type of action that regulate the level of acidity in the gastrointestinal tract.
They bring relief, but are only a temporary measure. To defeat pathology, it is necessary to treat the true cause that caused it.
This is often caused by the bacteria Helicobacter pylori. As mentioned above, they affect the level of acidity in the gastrointestinal tract. In this case, antibiotics are necessary.
The doctor will select them taking into account the sensitivity of pathogenic microorganisms. The most commonly prescribed drugs are Amoxicillin, Vilprafen, Sumamed or Metronidazole.
Symptomatic treatment involves taking painkillers and antiemetics. To relieve spastic pain, No-shpa, Papaverine or Baralgin are used, which relieve the tone of the gastrointestinal tract muscles.
Video:
https://youtu.be/4I2qpNDP6MI
In the first days of the acute phase of catarrhal bulbitis of the stomach, it is necessary to endure a period of fasting and rest, so as not to provoke secretion and increased acidity in the stomach and intestines.
After this, for about another month you should strictly adhere to a special diet, similar to the diet used to treat gastritis:
- you need to eat only boiled or steamed dishes;
- You need about 6 meals a day, but the portions should be small;
- Spices and salt should be avoided;
- Alcoholic, carbonated drinks and coffee are prohibited.
- you need to quit smoking.
It is recommended to treat gastric bulbitis in a hospital under the supervision of specialists.
In a hospital setting, if necessary, the doctor will be able to administer an IV or conduct additional tests. In the hospital it is easier to comply with the necessary bed rest at first.
Timely contact with a specialist and competent treatment will help get rid of problems with the gastrointestinal tract and prevent further development of the disease.
Many people suffer from various diseases. The majority of diseases are diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Stomach gurgling, what is it? Bulbit is a chronic disease of the stomach. This disease is accompanied by inflammatory processes in the stomach, or more precisely in the part of the bulb adjacent to the stomach or, as it is called in medicine, the duodenum.
This disease causes quite severe pain in the stomach, as with the more familiar disease gastritis. These pains appear in attacks and can be triggered by overeating, alcohol or harmful components of the food eaten. Stomach bulbitis is accompanied by serious digestive problems.
Video
Many people have heard about diseases such as gastritis and duodenitis, but not everyone knows what gastric bulbitis is. In general, this name is not entirely correct, because bulbitis is one of the forms of duodenitis. This is an inflammation of the duodenal bulb (duodenum), into which the stomach directly opens.
But gastritis and bulbitis are often interrelated processes and have similar symptoms, which is why the term gastric bulbitis is used.
What is focal bulbitis
Focal bulbitis represents inflammation of the duodenum in a specific location (bulb section of the organ). With gradual progression of the disease, erosions form on the mucous membrane, and the general condition of the patient noticeably worsens.
Manifestations of the disease have no age restrictions, so inflammation occurs equally in adult men, women and children. Most often, inflammation progresses at a young age in the presence of a genetic predisposition factor.
According to statistics, focal bulbitis is most often diagnosed in young girls and middle-aged women. Men are less likely to get this disease. At the initial stage, the pathology develops asymptomatically, and with exacerbation, symptoms similar to other diseases of the digestive system appear.
Varieties of bulbit
There are several types of disease. According to the nature of the course, bulbitis can take acute and chronic forms. Depending on the extent, focal and diffuse inflammation of the bulb is distinguished, the latter affecting the entire mucous membrane of the anatomical formation.
According to gastroduodenoscopy and histological examination, bulbitis can be:
- erosive-ulcerative,
- catarrhal,
- follicular.
More common is catarrhal bulbitis of the stomach, which usually occurs in an acute form and, with proper treatment, ends favorably. With this type of disease, there is slight swelling of the mucous membrane, its hyperemia and irritation; the lumen of the bulb contains a lot of mucus. With erosive-ulcerative bulbitis, single or multiple erosions and ulcerations appear on the inner wall of the bulb. You can read more about this form of the disease in the article: Erosive-ulcerative bulbitis of the duodenum.
The morphological variant of bulbitis is determined using EGDS - fibrogastroduodenoscopy
Follicular bulbitis is especially distinguished. It is a consequence of an excessive reaction of the lymphoid tissue located in the wall of the duodenum. As a result of exposure to infection or other adverse factors, lymphatic follicles increase in size. During duodenoscopy, small nodules or bubbles up to 2-3 mm in diameter are visible on the pale pink mucosa.
Symptoms
The “reference” symptom of bulbitis, like gastritis, is a nagging pain that occurs on an empty stomach. It is explained by the release of digestive secretions - signs of the body’s readiness to eat food. Pancreatic juice and concentrated bile irritate the walls of the bulb. Due to inflammation of its walls, the secretion of alkaline secretion by special glands of the duodenum and the ability to withstand the action of an aggressive environment are reduced. Spasmodic contractions of the bulbus under such conditions lead to the reflux of bile into the stomach, nausea, and belching with a bitter taste.
While the destructive changes associated with bulbitis and tissue damage are weakly expressed, they remain practically unnoticed. Initially, the inflammatory process occurs in the area of action of the irritant and covers a small area. A so-called primary focus appears. The initial stage of the disease can be practically asymptomatic.
Acceleration of metabolic processes in the center of inflammation leads to the accumulation of under-oxidized metabolic products and “acidification” of the inflammation site - acidosis. The consequence is severe pain and dysfunction of the duodenum. With proper, timely treatment, the prognosis for bulbitis is favorable.
Exudation is the release of the liquid part of the blood (the so-called exudation) into the surrounding tissues or onto the surface of the wound through the vascular wall in case of advanced disease. Sometimes during its course one type of exudate transforms into another. The nature of the exudate depends on the type of irritant, the intensity and duration of its action, and the presence of complicating factors.
Depending on the quantity and properties of the released exudate, the nature of the flow, bulbitis is classified. The release of exudate, which has an alkaline reaction, is a protective measure by which the body normalizes the “local” acid-base balance.
Causes of inflammation of the duodenal bulb
As mentioned above, bulbitis is often associated with gastritis. Therefore, the causes of this disease in many cases are similar:
- Helicobacter pylori infection (especially for catarrhal bulbitis);
- unhealthy diet (overeating, dry food, spicy, smoked, fried foods);
- alcohol consumption;
- too hot food;
- taking certain medications, especially anti-inflammatory drugs, and chemicals (for example, acetic acid or alkalis).
Accidental or intentional ingestion of any objects can lead to focal bulbitis - what does this mean: a foreign body lingers in the bulb and compresses its wall, a local inflammatory reaction develops under and around it. Giardia and helminths can also cause inflammation of the bulb, especially in children.
Rarely, duodenal bulbitis becomes a manifestation of Crohn's disease. This pathology can affect any part of the digestive tract, from the oral cavity to the anus. In particular, Crohn's disease can begin to develop precisely in the duodenal bulb.
Reviews
Reviews about the treatment of focal bulbitis have different responses, since the recovery process depends on the severity of damage to the duodenal mucosa. In most cases, it is possible to achieve long-term remission without exacerbations.
It all started with the appearance of unpleasant sensations in the intestinal area. After a full examination, a diagnosis of focal bulbitis in a progressive form was established and treatment was prescribed with mandatory adherence to a therapeutic diet.
Regarding treatment, I want to say that if you adjust your diet in a timely manner and do not consume prohibited foods, then the negative symptoms quickly go away, and the general condition improves significantly. In general, at the moment I am continuing treatment, but in the future I will reconsider my own rhythm of life.
Sergey
I have been working in the field of gastroenterology for a long time and during this period I have encountered various manifestations of digestive tract disorders. Focal bulbitis is a type of duodenitis and, if not treated correctly, has serious complications. Therefore, if suspicious symptoms appear, it is best to consult a doctor and determine the exact cause of the discomfort.
In order to prevent the development of such diseases, it is necessary to carefully monitor your own diet and eliminate possible factors influencing the progression of inflammation. It is best to try to lead an active lifestyle and eliminate bad habits as much as possible. Treatment of the disease consists of preventing its development.
Gastroenterologist in Moscow
https://youtu.be/hFjX-jS65MY
Clinical signs of the disease
Duodenal bulbitis is manifested by rather nonspecific symptoms, such as:
- pain in the epigastric region, more on the left, which can radiate to the left hypochondrium or umbilical region;
- feeling of nausea, bloating in the stomach;
- bitter or metallic taste in the mouth;
- rarely - vomiting (in case of acute poisoning or toxic infections, it can be repeated);
- headache and malaise (also with acute inflammation);
- diarrhea or loose stools.
A characteristic symptom of bulbitis is the appearance of pain 1.5-2 hours after eating and at night. These are the so-called “hunger pains”, which decrease after taking milk or antacids. If bulbitis occurs as a manifestation of Crohn's disease, the severity of the symptoms evaluates the degree of activity of the inflammatory process. The following indicators are taken into account:
- frequency of diarrhea,
- intensity of abdominal pain,
- degree of weight loss, etc.
For example, with bulbitis of the 1st degree of activity, the patient’s well-being suffers little: diarrhea occurs 3-4 times a week, pain is minor and intermittent, and there is no weight loss.
Important: if these symptoms appear, you should contact a gastroenterologist.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies for the treatment of focal bulbitis are effective when prescribing complex therapy. It is preferable to agree on the chosen technique with your doctor. List of the most effective recipes:
- A combination of peppermint, plantain leaves, St. John's wort, and yarrow in equal proportions is brewed in boiling water and infused for 30–40 minutes. The finished product is taken warm, 60 ml three times a day before eating;
- Flax seeds in the amount of 1 tbsp. The spoon is brewed in 250 ml of boiling water and left for 1-2 hours. The prepared tincture is taken in the morning on an empty stomach 2 hours before breakfast. The duration of treatment is 30 days;
- Using prepared sea buckthorn oil. The product is taken in the morning on an empty stomach in the amount of 1 tbsp. Spoon. The course of treatment is 2–3 weeks;
- Making oatmeal jelly in combination with aloe juice. The proportion is 2 tbsp. Spoons per 1 liter of cold water. The combined ingredients are boiled and then unnecessary impurities are filtered out. Add juice to the finished product and take 125 ml three times a day before meals;
- Daily consumption of freshly squeezed carrot juice to restore damaged duodenal mucosa;
- Using alcohol tincture of propolis diluted with water in a ratio of 1:10. This substance is of natural origin and has a beneficial effect on the overall healing of the mucous membrane.
Currently reading: What is catarrhal bulbitis of the stomach - types, treatment and proper diet
Treatment methods
Treatment of the disease in most cases is conservative. When diagnosed with gastric bulbitis, treatment includes:
- use of medications,
- therapeutic nutrition,
- herbal medicine.
Surgery is very rarely required. It is mainly indicated for high activity of Crohn's disease or for chronic bulbitis with the development of complications, such as duodenal stenosis or bulb ulcer. If the cause of inflammation of the bulb is a foreign body, it can be removed during duodenoscopy or during surgery.
Drug treatment
If Helicobacter pylori is detected in the contents of the stomach and duodenum, combined antibacterial therapy in the form of 2-3 antibiotics is prescribed. Antacids, gastric H2-histamine receptor blockers and proton pump inhibitors can be used as symptomatic treatment for superficial bulbitis, both acute and chronic. They help reduce the acidity of gastric juice and reduce its negative impact on the duodenal mucosa.
Depending on the cause of inflammation, hormones (for Crohn's disease), anthelmintic drugs, and immunoregulatory agents (for follicular bulbitis) are also used.
Medical nutrition
Diet for duodenal bulbitis is the most important condition for recovery. You need to eat often and in small portions so as not to burden the stomach and duodenal bulb. From the diet you should exclude spicy, salty, smoked, fried foods, in short, everything that can irritate the gastrointestinal mucosa. It is very healthy to consume dairy products, including whole milk. Meat and fish should be chosen of low-fat varieties (chicken, beef, rabbit, hake, pink salmon).
During the period of exacerbation and acute inflammation, food should be warm and mushy. You should avoid alcohol, cigarettes, carbonated drinks, cold and hot foods.
The following products are allowed:
- cereals,
- pasta,
- White bread,
- vegetables and fruits,
- jelly, compotes, weak tea.
Food must be chewed thoroughly and slowly. Following a diet for superficial bulbitis often leads to recovery even without drug treatment.
How is the treatment carried out?
General treatment of bulbitis and stomach is usually prescribed. The plan must provide:
- diet and nutrition;
- use of medications;
- possible physiotherapeutic procedures;
- use of traditional herbal medicine techniques;
- Spa treatment.
Each patient requires an individual approach, studying the examination results, and taking into account concomitant diseases. Complex therapy helps cure the acute form and prevent exacerbations.
Features of the mode
In case of bulbitis and damage to neighboring organs, the patient will need to get rid of strong coffee, alcohol, soda, and smoking. Eliminating provoking factors helps improve immunity.
You will have to learn to relax and avoid stressful situations. The optimal diet includes frequent meals of heated food (5-6 times a day), avoidance of long breaks and feelings of hunger, good chewing (eating slowly).
Diet features
Maximum functional unloading of the duodenal bulb is achieved by using dietary table No. 1. Fatty and fried foods, rich soups, smoked meats and pickles, spicy seasonings, baked goods, raw vegetables and fruits, and fermented milk products are strictly prohibited.
For 2 weeks, the patient is recommended: low-fat chicken soup, baked vegetables (without mushrooms and cabbage), twisted minced meat dishes (steamed cutlets, meatballs), omelet, liquid milk porridge, dry white bread. Then they move to table No. 5.
There are exceptions for fried and fatty foods, smoked sausage. But the consumption of cottage cheese, kefir, milk noodles, and pasta is allowed.
The broth should not be greasy, the addition of boiled vegetables (potatoes, carrots), meatballs is allowed
Medications
Only a doctor can select the necessary medications. Tolerability, the presence of additional diseases, age, and stage of the disease are taken into account. Typically used:
- antibiotics and eradication agents to get rid of Helicobacter pylori infection;
- antispasmodics to relieve pain;
- drugs that reduce the acidity of gastric juice when its level is elevated;
- astringents and enveloping agents that protect the mucous membrane;
- drugs that promote the healing of erosions and ulcers;
- symptomatic agents (vitamins, immunocorrectors) with a general strengthening effect.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
If bleeding and the fact of metaplasia are excluded, physiotherapy methods have a good effect:
- galvanization;
- electrophoresis with novocaine on the epigastric zone;
- magnetotherapy.
They contribute to the reverse development of the inflammation process and the healing of damage. In sanatorium conditions, the patient consolidates the effect of medications, uses biological substances from natural mineral waters, and mud applications.
Folk remedies
Recommended after a period of acute symptoms. Can be combined with a maintenance dose of medications and diet. The selection of herbal remedies depends on the level of acidity. More often they use herbal tea with plantain, chamomile, and calendula flowers.
You can brew it in a thermos in the morning and drink it warm throughout the day before meals. It is recommended to add a spoonful of honey. Plantain and aloe tincture are contraindicated in case of high acidity. Oatmeal jelly and a decoction of oats have an analgesic and healing effect. This plant can be taken regardless of acidity.
Detection of bulbitis is no less significant than other diseases of the stomach and intestines, since the chain of digestive disorders continues and spreads to all organs. Timely initiation of treatment and compliance with the regimen and diet requirements help prevent more severe pathology.