What it is?
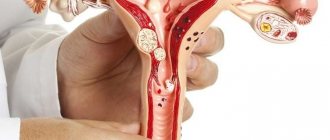
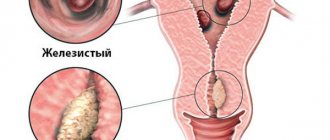
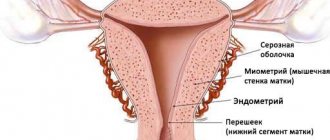
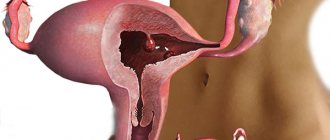
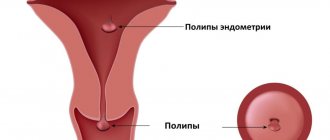
A glandular-fibrous endometrial polyp is a benign formation on the lining of the uterus. It is formed as a result of the growth of the inner layer of the uterus and most often appears in women of childbearing age or menopause.
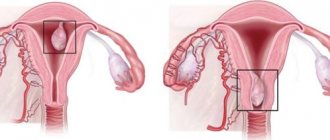
In appearance, a glandular fibrous polyp looks like a pink or burgundy formation located in the uterus. It consists of a body and legs with blood vessels. The polyp can have a variety of shapes: round, mushroom-shaped, on a thin stalk, or on a wide base.
The size and number of such formations can be very different. Processes of inflammation, circulatory disorders, as well as necrosis or necrosis can occur in polyps. If the endometrial glandular fibrous polyp becomes adenomatous, then it can actually be considered a sign of cancer. The same can be said if the tumor contains atypical cells. But malignancy of such formations occurs only in 2% of cases.
Causes
Several factors lead to the appearance of polyps:
- lack of the hormone progesterone and excess amount of estrogen, which leads to accelerated growth of the endometrium;
- obesity, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, as a result of which blood circulation in the capillaries is disrupted, oxygen starvation and increased cell division begin;
- abortions, which are traumatic medical procedures;
- use of an intrauterine device;
- decreased immunity;
- inflammatory diseases of the uterus and ovaries;
- constant stress;
- blockage and proliferation of blood vessels in the uterus;
- proliferation of the endometrium, which is often associated with diseases of the endocrine system;
- large body weight, which leads to metabolic disorders, excess estrogen and the formation of polyps;
- transmission of the disease by inheritance from mother to daughter;
- low physical activity, leading to stagnation of blood in the pelvic organs and increased division of endometrial cells;
- taking certain medications to treat cancer;
- clots of placenta that did not come out after childbirth later turn into connective tissue of the polyp.
Symptoms and diagnosis
An almost complete absence of symptoms is characteristic of the initial stage of the disease. Small polyps can only be detected during an ultrasound examination. The following signs of an endometrial polyp may gradually appear:
- spotting after sexual intercourse and pain during it;
- heavy menstruation and menstrual irregularities, especially in young women;
- leucorrhoea;
- spotting after exercise and stress;
- infertility;
- spotting without menstruation;
- heavy blood loss is accompanied by the development of anemia, pale skin, weakness and dizziness;
- cramping pain in the lower abdomen;
- premature birth and miscarriage.
Endometrioid polyps are usually discovered during a routine gynecological examination using a speculum. Also, the diagnosis of polyps requires an ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
Doctors note a thickening of the endometrial layer, proliferation of the mucous membrane, and expansion of the uterine cavity. But polyps with a glandular structure are not always noticeable on ultrasound, since their appearance resembles the endometrium. It is also difficult to distinguish between a polyp and a fibroid during this examination.
Hysteroscopy of the uterus makes it possible to clarify the diagnosis and increases the reliability of diagnosis to 97%. This technique allows you to see the entire uterine cavity and the formations in it. Hysteroscopy requires general anesthesia, since the uterus is examined using a hysteroscope, and after it the formation is removed.
The removed polyp is sent to the laboratory for further research. The location of the polyp is cauterized by electrocoagulation or laser, which reduces the risk of relapse of the disease.
In addition, metrography-radiography is often used, during which a special substance is introduced into the uterine cavity. As a result of the use of x-rays, all existing seals can be seen.
Before surgical removal of polyps, smears are made for oncocytological, microscopic and bacteriological examination. In this way, hidden sexually transmitted infections can be identified.
Treatment methods
A promising direction in the treatment of vascular polypous lesions is surgical intervention. Drug therapy is ineffective and is advisable for temporary relief of symptomatic manifestations and treatment of secondary infectious complications. Alternative methods of treatment are also ineffective, but can help reduce discomfort.
Surgical removal
Surgical intervention and the choice of method are determined by the localization and extent of the pathological process.
Uterus and endometrium
Most angiomatous polyps can be removed using the endoscopic method - hysteroscopy. The manipulation is carried out under local anesthesia, lasts only a few minutes, and does not require a stay in the clinic. During hysteroscopy, the tumors are removed along with the base, and the wound surface is sutured and coagulated with electric current or a laser beam.
In case of polyposis or large tumors, as well as in case of oncological transformation, laparoscopic surgery is performed. Several punctures are made under the peritoneum, through which the growth is exposed, pathological tissue is excised, and the wound surface is sutured. Rehabilitation depends on the extent of the intervention performed.
Removal of urethral polyps
Urethral polyps are removed using the following methods:
- TUR or transurethral resection . Removal is carried out with a regular scalpel under general anesthesia. After removal, the wound is sutured. The method is used for large polyps larger than 1-1.5 cm.
- Physical destruction . The impact on the tumor occurs through electric current, laser beam, and radio waves. All of these methods are suitable for removing small single polyps.
The rehabilitation period depends on the extent of the surgical intervention. If necessary, a catheterization procedure is performed to restore the outflow of urine and reduce the traumatic effect on a fresh wound.
Removal of laryngeal polyp
A laryngeal polyp can only be removed surgically. For this purpose, endoscopic methods of exposure are used: radio wave, laser and electrocoagulation.
For large tumors with signs of malignancy, an open method is used, when prompt access is provided through a skin incision in the larynx area and removal of the affected mucosa within healthy tissue.
Unfortunately, no operation guarantees a complete cure, since the risk of relapse reaches 3-19%. The risks of relapse are higher in patients who do not follow doctors’ recommendations after surgery and who abuse alcohol.
To minimize the likelihood of the emergence of new polyposis units, it is important to exclude all provoking factors.
Some people think that to get rid of urethral polyps using folk remedies. We offer our users a choice of methods, but insist on a professional approach to the treatment of this pathology.
How to treat?
Pharmacy medicines
If it is not possible to remove polyps through surgery, then drug treatment is prescribed. As a result, the formation may decrease in size or disappear completely. Such treatment is justified, in particular at a young age. The doctor selects all medications individually.
Up to 35 years of age, oral contraceptives, for example, Regulon or Yarina, are usually recommended. They need to be drunk according to a certain pattern over a long period of time. After 35 years of age, women are prescribed gestagens: Duphaston, Norkolut and others. When polyps form as a result of an inflammatory process, antibacterial drugs are prescribed: Monomycin, Gentamicin and others.
During menopause, doctors recommend taking Diferelin and Zoladex, which protect the uterus from the negative effects of estrogen. In symptomatic therapy, painkillers are used, in particular Diclofenac and Paracetamol, but for a short time, as they lead to the development of gastrointestinal diseases. With heavy menstruation, women are prescribed antiseptic solutions for washing: Septadine, Collargol for washing.
Folk remedies
Before starting treatment with folk remedies, it is necessary to conduct a histological examination of the tumor. For adenomatous polyps, traditional methods cannot be used. Any neoplasm can easily develop into cancer, even in young women, which will require its urgent removal.
After surgery, you can use various folk remedies on your doctor’s recommendation to maintain immunity and hormonal balance. But herbal preparations may have various side effects and contraindications, which also need to be taken into account. At the beginning of treatment, you should take hormonal tests and drink herbs according to the herbalist’s regimens.
Recipes:
- garlic in gauze in the form of a compress is inserted deep into the vagina at night. This procedure must be done for at least a month;
- hard-boiled yolks and fresh pumpkin seeds are mixed with vegetable oil and heated in a water bath. Take the remedy in the morning on an empty stomach until complete recovery.
- Propolis is a biologically active agent that can be prescribed even to pregnant women. Propolis is used to make medicinal tampons, which are inserted into the vagina at night.
Medicinal herbs:
- tincture of golden mustache with vodka is taken before meals;
- douching with celandine, but strictly on the recommendation of a doctor;
- An alcohol tincture of the sacred vitex plant is taken before meals;
- infusion of nettle, rose hips, and lingonberries is taken several times a day.
Operations
The most common treatment for polyps is surgical resection and curettage of the uterine lining.
To reduce the risk of complications, the polyp removal site is treated with liquid nitrogen.
For several days, a woman may experience cramping pain and spotting. To restore the menstrual cycle and prevent relapse of the disease, hormonal therapy is prescribed.
With the help of laser removal of polyps, there are no scars or scars left on the uterus. In addition, women fully retain their reproductive function. This procedure also does not require hospitalization, so you can go home after a few hours.
Laser treatment is characterized by the absence of bleeding, rapid tissue restoration and instant sealing of blood vessels. 6 months after the intervention, a woman can plan a pregnancy.
Every woman who has been diagnosed with this disease must maintain a healthy lifestyle and give up all bad habits. In addition, doctors recommend in this case to remain calm and eliminate all possible stress.
Treatment of adenomatous endometrial polyp after removal
Adenomatous polyp is a precancer of the endometrium. Therefore, it is treated in the same way as atypical endometrial hyperplasia, taking into account the patient’s age and reproductive plans.
During reproductive age, after removal of an adenomatous polyp, it is recommended:
- Anti-relapse hormonal therapy
Modern researchers advise postoperative treatment of adenomatous uterine polyp with progestins.
(consultation with the treating gynecologist is required)
| Drug name | Possible reception mode | Duration of treatment |
| Medroxyprogesterone acetate (Provera) | 10–12 mg continuously or cyclically | 6-9 months |
| Medroxyprogesterone depot (Depo-Provera) | 150 mg intramuscularly every 3 months | 9 months |
| Megestrol acetate (Megestrol) | 40–200 mg per day | 6-9 months |
| Hydroxyprogesterone caproate (HPC, OPK) | 500 mg, intramuscularly, 2 times a week | 6-9 months |
| Gestonorona caproate (Depostat) | 2 ml intramuscularly once a week | 6-9 months |
| Oral progestins | 100–200 mg continuously or cyclically | 6-9 months |
| Intrauterine progestins (LNG-IUD Mirena) if there are no contraindications | 1-5 years |
Monitoring the effectiveness of hormonal treatment is carried out 3 and 6 months from the start of the course using ultrasound and/or hysteroscopy with separate diagnostic curettage and subsequent histological examination of the removed tissues.
Treatment of recurrent adenomatous polyp in reproductive age:
- Removal of the uterus (hysterectomy) with revision of the ovaries
At any age, when an adenomatous polyp is combined with uterine fibroids, adenomyosis, ovarian pathology, metabolic and endocrine disorders, it is recommended:
- Removal of the uterus with a thorough revision or removal of the ovaries
In premenopause it is recommended:
- Removal of the uterus with a thorough revision or removal of appendages
In postmenopausal women it is recommended:
- Radical removal of the uterus and appendages
Laparoscopy. Radical hysterectomy
Angiomatous polyp can occur in almost any hollow organ. The features of the occurrence of tumor-like neoplasms do not differ from other types of tumors, but the symptoms and prognosis regarding cancer risks differ. If angiomatous neoplasms are detected, surgical removal is recommended.
Patient reviews
- I was treated with celandine, calendula and St. John's wort, which I took in equal proportions. I made an infusion from them and then used them for douching. Helps well with polyps in the uterus.
- Surgeons removed a large polyp from my uterus, and the anesthesia was selected taking into account the characteristics of my body.
- The doctor prescribed me to drink Lindinet for a whole year to restore hormonal levels. This is how I am undergoing treatment; I have no plans to remove polyps yet.
The glandular fibrous polyp of the endometrium is benign, but is recommended by many gynecologists for removal, as it is a precancerous condition. Therefore, for any treatment of polyps, you must undergo a mandatory medical examination and consult with a gynecologist.
Is it necessary to operate on an adenometasis polyp in the uterus?
The need for surgical treatment of a polyp: Firstly, conservative therapy for uterine polyps is ineffective. Treatment of any intrauterine tumor begins with its surgical removal under hysteroscopy control. Secondly, only histology can determine the shape of the polyp, and therefore make an accurate diagnosis. This study is possible after removal of suspicious tissue from the uterus, i.e. after operation.
A true adenomatous polyp of the uterus is a growing tumor. Any tumor is subject to surgical treatment; it cannot “resolve” under the influence of medications or other means.
https://youtu.be/onKDUIEGvP4