Thin stool
You already know from previous articles what a normal stool should look like and what a change in its color means.
Now I will tell you why it becomes thin, and what the consequences may be. If you notice that changes have occurred and the stool appears thin, listen to your condition and watch carefully to see if additional symptoms have appeared:
- Streaks of scarlet blood,
- Stool became more frequent.
The presence of such additional factors clearly indicates that it is time to see a doctor. These are symptoms of diseases such as:
- Rectal polyps,
- Haemorrhoids.
Most often, these diseases do not manifest themselves for a long time and do not bother the person in any way. The only indicator of their occurrence is a change in the shape of the stool (becoming, for example, thin).
It may be objected that these diseases are not dangerous and can be easily treated. It’s absolutely not difficult to get rid of both polyps and hemorrhoids if you don’t start the process.
Both of these diseases are harbingers of colorectal cancer, and this is already a very dangerous disease. Therefore, the sooner you notice that the stool is thin, pencil-shaped, and get checked by a gastroenterologist, you will save yourself from more serious troubles.
Tape feces
Very rarely, cancerous growths grow on their own; most often they are preceded by harmless small growths - polyps. They do not cause harm and do not bother a person until they develop into a malignant tumor.
Gradually, growing, the tumor blocks the lumen of the intestine, and the output is thin feces. If you ignore this fact, after a while you will feel:
- Mild pain radiating to the sacrum
- Frequent urge to defecate,
- Constipation.
Further development of cancer will result in ribbon-like stool, increased and spreading pain, as well as the sensation of a foreign body in the rectum.
Today's medicine successfully treats colorectal cancer, but why bring the situation to such a state?
I would like to dwell on one more point. Sometimes childhood illnesses pave the way for the development of serious illnesses in adulthood. For example, lamblia.
They live and develop in the small intestine and bile ducts. By attaching to the intestinal walls, they irritate the thin mucous membrane and cause inflammation.
Constantly inflamed intestinal walls, isn’t this an excellent environment for the growth of polyps or malignant tumors?
It is almost impossible to determine the presence of Giardia without analysis; they do not manifest themselves. Parents should be alerted to poor weight gain in the child, as well as frequent attacks of nausea for no particular reason.
Unhooking from their place, they are able to “travel” through the intestines in order to attach to a new place and become an adult lamblia. The presence of cysts or adult motile individuals in the stool is indicated by a stool analysis for Giardia.
For a more reliable result, you need fresh morning stool. It is collected in a special container with a preservative, received the day before at the clinic. In the laboratory, the presence of cysts is checked under a microscope. Visually detecting them is an indisputable result.
I hope I was able to convince even the most squeamish people that it is necessary to monitor the condition of your stool. If you find thin stool, do not put off visiting a doctor and check your health.
Currently, modern medicine identifies several types of clinical syndromes that have obvious and characteristic signs. One of the most common is the ribbon chair. This disease manifests itself in the form of feces and its porous texture. In order to determine (diagnose) the presence of this stool, it is not at all necessary to resort to the help of doctors, it is enough just to make sure that some symptoms are present (they can appear both simultaneously or separately).
Also, a disorder of the body may exhibit symptoms that are completely far from the classic ones. After all, it very often happens that a completely healthy person, due to some disruptive processes in the intestinal tract, becomes prone to the appearance of this disorder syndrome, but at the same time all tests and indicators refute this.
Preventive actions
To prevent the appearance of unusual stool shapes, it is recommended to follow certain rules.
In the daily diet:
- nutrition should be balanced;
- a prerequisite is the availability of liquid dishes;
- for variety, the menu contains vegetables and fruits;
- dry food should be excluded;
- drink the recommended amount of clean water per day;
- Tobacco products and alcoholic beverages should be abandoned;
- number of meals per day – from three to five times.
A few additional tips:
- avoid stress, be less nervous and worry;
- play sports;
- do not overdose on medications, take good quality medications at the prescribed dose;
- observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- In case of poisoning, consult a doctor promptly;
- visit the clinic for a preventive examination.
By following these rules, the possible risks of the formation of thin feces are minimized.
Why does ribbon stool appear?
People generally rarely pay attention to their stool, but changes in the nature of the feces can tell a lot.
If stool has a normal shape, color and consistency for a long time, then everything is in order with a person’s health.
These indicators may change for a short time depending on the diet. If a person’s feces have become thin, like a ribbon or a snake, then this is already a cause for alarm, since it indicates the presence of various diseases.
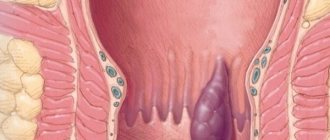
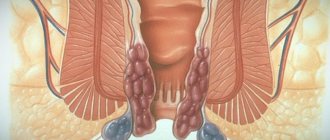
The most common cause of thin stool is hemorrhoids. If an adult constantly works physically, suffers from constipation or physical inactivity (deterioration of motor skills due to a sedentary lifestyle), then he may develop such a disease.
The disease develops due to the inflammatory process and further formation of blood clots in the veins of the colon.
As a result of thrombosis, nodes appear that protrude from the intestinal walls. Thus, the lumen in the colon decreases, which leads to the thinning of the feces passing through it.
In women, the appearance of thin stool may be associated with pregnancy. As the uterus expands, it begins to compress the intestines, reducing its width.
Such a process can lead not only to thinning of the stool, but also to constipation, which affects most expectant mothers.
In addition, a decrease in the lumen of the colon and a sedentary lifestyle during pregnancy can lead to hemorrhoids.
The appearance of thin feces is always associated with a decrease in the lumen in the large intestine. This pathology can occur due to the presence of polyps (growths on the mucous membrane) in the intestines.
Basically, such formations are not dangerous and do not cause discomfort at an early stage, but later they can cause pain and malignize (turn into malignant tumors).
In rare cases, banded feces can be a symptom of the presence of Giardia, a protozoan parasite, in the body. Living in the small intestine, they irritate the mucous membrane of the organ and lead to the development of an inflammatory process.
Carrying out diagnostics
We understand what ribbon-shaped feces look like. But in order to understand why feces come out of the body in the form of thin sausages, it is necessary to subject the body to a comprehensive diagnosis, which consists of:
- palpation of the rectum to detect hemorrhoids;
- analysis of feces to perform a coprogram, check for worms and perform a tank culture;
- X-ray and probing of the intestinal tract to detect tumors;
- checking stool for the presence of worm eggs, donating blood to determine the resistance of antibodies to Giardia.
The doctor, after conducting an examination and determining the symptoms of a particular disease, prescribes treatment. With the help of a therapeutic course, the cause of the disease and the main symptom – thin feces – are eliminated. Seeking help at the initial stage helps to get rid of the problem with the help of ointments, creams or rectal suppositories. Polyps in an advanced state are removed by surgery.
The most common causes of band-like stools
The cause of stool is nothing more than irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), which may not even manifest itself in a pronounced form. As a rule, about 15% of the total population of the planet suffers from this disease every year. These are mainly people of adolescence and adulthood.
The causes of ribbon-like stools can also lie in a violation of the physiological process of the body, in the consumption of foods that help induce the disease, in the use of medications that are aimed at combating diseases of the colon. In addition, numerous clinical studies have shown that the normal functionality of the body is also affected by overwork (chronic), stress, changes in intestinal microflora and hereditary predisposition of the body.
Scientists still cannot associate some of the causes of the disease with the appearance of ribbon-like stools, but the facts confirming this are undeniable. It is also undeniable that symptoms most often do not indicate a clear disease. They most often give a “call”, which should refer the patient to a doctor and undergo an examination.
Color
Types of stool vary in color. It can be brown (healthy color), red, green, yellow, white, black:
- Red color. This color may result from ingesting food coloring or beets. In other cases, the stool becomes red due to bleeding in the lower intestine. Everyone's biggest fear is cancer, but this can often be associated with diverticulitis or hemorrhoids.
- Green color. A sign of the presence of bile. Stool moving too quickly through the intestines does not have time to turn brown. A green tint is a consequence of taking iron supplements or antibiotics, eating large amounts of greens rich in chlorophyll, or supplements such as wheatgrass, chlorella, spirulina. Dangerous causes of green stool are Crohn's disease, celiac disease, or irritable bowel syndrome.
- Yellow. Yellow feces are a sign of infection. This also indicates gallbladder dysfunction, when there is not enough bile and excess fat appears.
- White stool is a sign of diseases such as hepatitis, bacterial infection, cirrhosis, pancreatitis, and cancer. The cause may be gallstones. Stool does not stain due to bile obstruction. The white color of feces can be considered harmless if the day before you took barium before an x-ray examination.
- Black or dark green indicates possible bleeding in the upper intestine. A sign is considered harmless if it is a consequence of consuming certain foods (lots of meat, dark vegetables) or iron.
Possible complications
A decrease in the lumen in the large intestine occurs as a result of various ailments - hemorrhoids, polyps, giardiasis.
All these diseases at an early stage do not create any discomfort for the patient, and they are quite easy to cure.
But if you let the disease take its course, the consequences in the future will be very sad.
Untreated hemorrhoids can lead to the development of paraproctitis - purulent inflammation of the rectum, which destroys organ tissue. With a long course of the disease, malignancy of the resulting fistulas is very likely.
Treatment of ribbon-like stools using innovative pharmacological drugs
Despite the fact that the disease, as a rule, does not belong to the group of dangerous diseases (in practice, some complications occur), it must be prevented or cured in order to restore normal functioning of the body. First of all, you need to adhere to a strict diet, which will be the first and decisive and effective step towards recovery, even if the reasons for the occurrence of stool are somewhat different.
To improve your general condition, you should include foods high in fiber in your daily diet. At the same time, it is necessary to consume at least 2-2.5 liters of water (daily norm; urination should occur every 4-5 hours). As for drug treatment, in this case drugs such as loperamide should be used.
In practice, drugs are also widely used that help inhibit and prevent the development of microorganisms that can cause this type of stool. No less important in treatment are the so-called pribiotics (beneficial bacteria that fight foreign bodies) and small doses of tricyclic antidepressants.
Right-sided colon cancer is primarily characterized by pain without pronounced signs of impaired movement of intestinal contents. Intestinal discomfort syndrome occurs quite early. Initially, this is a feeling of heaviness, fullness and rumbling in the intestines, which occurs 3-5 hours after eating;
later on, flatulence, belching, nausea, and then severe pain on the right and in the middle of the abdomen occur. Weakness increases relatively early, and anemia develops without any visible signs. intestinal blood loss. There is often an increase in body temperature, sometimes even with periodic chills. Cecal cancer with a tendency to ulceration is characterized by signs of general intoxication caused by the absorption of decay products.
In about a third of cases, it is possible to palpate the tumor “in the form of a lump of varying sizes with a dense consistency, usually not particularly sensitive, and in its outline not reminiscent of any organ” (V.P. Obraztsov). When localized in the right and left flexures of the colon (as well as in the area of the ascending and descending colon), the tumor is usually difficult to palpate.
In the blood, a decrease in red blood cells and hemoglobin is usually observed quite early, and when the tumor disintegrates, moderate leukocytosis and an increase in ESR are observed.
Left-sided colon cancer is characterized by a relatively long asymptomatic or, more precisely, low-symptomatic course and a lower frequency and degree of pain, although the latter in many cases can be intense. More often and more severely expressed is a violation of intestinal patency, up to the development of partial or complete obstruction, necessitating urgent surgical intervention. In approximately half of cases, constipation is noted, but constipation and diarrhea often alternate.
More than a quarter of patients have blood in their stool (on the surface of their stool). Often, in contrast to hemorrhoids, blood is released before the passage of feces, sometimes even outside the act of defecation in the form of “spitting” of bloody mucus, which is especially common with rectosigmoid cancer.
When localized in the sigmoid colon, the tumor is palpable relatively often, in the descending colon - less often, and in the left flexure of the colon - very rarely.
It should be remembered that it is possible to palpate the tuberosity in the sigmoid colon if there are fecal stones in it, and therefore, in doubtful cases, palpation should be repeated after a cleansing enema.
In case of rectal cancer, a violation of the act of defecation is very typical: constipation, pain, false urges. The stool is often released in small “nuts” (“sheep stool”) and in the form of a thin ribbon (ribbon stool). Blood, often mucus and pus are usually visible on its surface. In some cases, there is an alternation of diarrhea and constipation, as well as “constipated diarrhea.”
In some cases, there is a discharge of blood and mucus during the passage of gases and outside the act of defecation, and sometimes “bloody mucous spitting.” Digital examination is of decisive importance in the diagnosis of rectal cancer.
Laboratory studies indicate increasing anemia, a constant increase in ESR, and a positive reaction to the presence of occult blood in the stool.
All doctors have repeatedly emphasized that any disease is much easier to prevent than to treat. Diseases that cause thin feces in humans are no exception.
First of all, you should reduce the load on the intestines, that is, reduce to a minimum the amount of foods harmful to it.
Doctors do not recommend eating fast food, eating dry food, or chewing food in a hurry. It is advisable to drink as much fluid as possible, at least plain water.
A large amount of dry food leads to hardening of stool, which, in turn, can damage the intestinal walls and cause inflammatory processes.
The nature of the food you eat is of great importance - it is advisable to eat the first course (soup, borscht, broth) at least once a day. The frequency of food intake is also considered important - it is not recommended to eat either too often or very rarely.
In addition, you need to take a variety of medications with caution - do not exceed the dosage, and monitor for side effects.
Lifestyle is also of great importance. It is recommended to play sports, take walks in the fresh air, and sit less still. You should give up bad habits - smoking, drinking alcohol.
Question: What are the symptoms of colorectal cancer?
Lera asks:
What are the symptoms of colorectal cancer?
Colorectal cancer can be asymptomatic for a long time, especially if the tumor is small. However, colorectal cancer is accompanied by two types of symptoms - characteristic and nonspecific. Nonspecific symptoms include general weakness and lethargy, loss of appetite, aversion to food, perversion of taste and smell, as well as low-grade fever that does not rise above 37.0 o C.
Typical symptoms of colorectal cancer include the following:
- Pain in the lower abdomen. Pain may radiate to the sacrum, coccyx, lower back, or perineum;
- Intestinal dysfunction (flatulence, bloating, colic, etc.);
- Diarrhea or constipation lasting more than 4 weeks;
- A feeling of incomplete bowel movement after bowel movements;
- Sensation of a foreign body in the intestines;
- “Ribbon” or “pencil” chair (shape in the form of thin ribbons or a pencil);
- Any change in the usual shape of the stool;
- Frequent and painful false urge to defecate;
- Impurities of blood, mucus and pus in the stool. In this case, the blood can be black, semi-digested or fresh, red. But blood in colorectal cancer is always mixed with stool. Mucus is released from the anus not only during bowel movements, but also at rest. Pus may be absent and mixed with blood and mucus;
- Losing weight for no apparent reason;
- Iron deficiency.
In addition to the above general symptoms of colorectal cancer, there are some features of the clinical picture that depend on the exact location of the tumor. If the tumor is located in the right half of the colon, then it is characterized by the following clinical picture:
1.
Severe general weakness and malaise;
2.
Dull and sharp cramping pain localized in the right half of the abdomen and right hypochondrium;
3.
Severe iron deficiency anemia.
When the tumor is localized in the left half of the rectum, a person is bothered by periodic phenomena of incomplete obstruction, such as rumbling, flatulence, severe bloating, and cramping pain. Feces can be “ribbon” or “sheep”, with an admixture of mucus and blood.
If the cancerous tumor is localized in the rectum, then the following symptoms are most characteristic of it:
- Discharge of blood at the very beginning of defecation;
- An admixture of pus in the stool;
- False urge to defecate, after which pure blood or mixed with mucus is released from the rectum;
- Persistent constipation;
- Fecal incontinence due to tumor growth in the anal muscles.
In addition, depending on the leading symptoms, several characteristic clinical forms of colorectal cancer are distinguished. Let's consider the characteristic clinical forms of cancer:
1.
Dyspeptic form. With this form of colorectal cancer, the leading symptoms are disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, such as vomiting, heaviness in the abdomen, bloating, belching, loss of appetite, etc. Often all these symptoms are mistakenly taken for manifestations. The severity of symptoms varies, and it increases as the cancer progresses. Pain and discomfort in the intestines become more and more severe, up to the development of obstruction;
2.
Obstructive form. With this form of cancer, intestinal obstruction occurs early. At first, a person is bothered by constipation, diarrhea, bloating and rumbling in the abdomen, which gradually intensify and culminate in complete intestinal obstruction. Gradually, pain syndrome, combined with persistent constipation, becomes the leading one. The pain first appears in attacks and goes away on its own. Gradually, intestinal colic becomes prolonged and the pain becomes severe. An attack of pain is accompanied by bloating and strong peristalsis. Such an attack ends with the release of foul-smelling feces;
3.
Pseudo-inflammatory form. In the initial stage of cancer of this form, a person is bothered by abdominal pain, tension in the abdominal wall and fever. In addition, inflammatory infiltrates, abscesses or phlegmon can form in the abdominal organs. This form of cancer is similar to the clinical signs of appendicitis, stomach and duodenum, as well as diseases of the bladder and female genital organs;
4.
The toxic-anemic form is characterized by symptoms of general intoxication. At the initial stages of the pathological process, a person is worried about malaise, weakness, fatigue, loss of strength, a sharp decrease in performance, and an increase in temperature. In addition, the person has severe anemia, as a result of which the code takes on an earthy tint. Over time, nausea and abdominal pain develop;
5.
Enterocolitic form. With this form of cancer, a person is bothered by constipation, diarrhea and their alternation, a feeling of fullness and bloating, rumbling and other intestinal dysfunction. Any of the above symptoms is combined with abdominal pain, which can have varying intensity. In addition, during defecation there is bloody, bloody-mucous and mucopurulent discharge. Constipation in this form of cancer is very persistent, lasts several days or weeks and is resolved by passing large amounts of feces. Constipation is followed by diarrhea with the passage of watery, offensive stools;
6.
Tumor form. With this form of cancer, the tumor can be felt with your hands through the anterior abdominal wall, and all other possible symptoms of the disease are mild. Colon cancer of this type is usually discovered completely by chance against the background of complete well-being.
Find out more on this topic:
- Hiccups - why does it occur and how to quickly get rid of it at home? Causes of hiccups in adults, in newborns after feeding, in a pregnant woman and in the fetus. Remedies for hiccups. How to stop hiccups after drinking alcohol?
- Intestinal colic in adults and newborns - the essence of the phenomenon, symptoms, treatment, remedies for colic, massage, diet (foods that cause colic). What intestinal diseases cause colic?
- Tumor markers - interpretation of blood tests. Normal indicators. When there is an increased and decreased level of tumor markers secreted by cancer cells (CA 125, CA 15-3, CA 19-9, CA 72-4, CA 242, HE4, PSA, CEA). Combinations of tumor markers. Analysis price