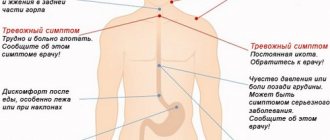
Pathological processes in the esophagus develop unnoticed. One of the signs of the disease is chest pain when swallowing. If you have a feeling of discomfort while swallowing food, then treat this with due attention. A timely visit to the doctor will help avoid the development of serious pathologies.
Pain when swallowing is called odynophagia. Dysphagia is the difficulty in moving food through the esophagus.
Unpleasant sensations when food passes through the esophagus are familiar to everyone - at least once everyone has unexpectedly swallowed a dry lump of poorly chewed food, which was pushed through the esophagus into the stomach with difficulty and pain. When this sensation occurs frequently or with every meal, it may be due to a disease of the esophagus.
Pain in the esophagus: causes
To determine whether pain behind the sternum has a relationship with the esophageal organ, one should monitor whether it is associated with swallowing or not.
- odynophagia – painful swallowing of food;
- dysphagia – difficulty passing a bolus of food (more about it).
If the pain is in no way related to swallowing food, such pain is called spontaneous. When chest pain is associated with swallowing, this indicates that the source is located directly in the esophagus and is accompanied by a violation of the internal walls.
Sometimes the esophagus hurts after vomiting. And when the esophagus hurts after drinking alcohol, it is caused by poisoning of the body.
Why does the esophagus hurt? The reasons may be the following:
- dysfunction of the esophageal tube;
- inflammatory reactions of the mucous membrane with reverse reflux of gastric contents (reflux esophagitis);
- malignant formations;
- hiatal hernia;
- wall diverticula (more details);
- esophageal achalasia ;
- narrowing of the tube lumen (stenosis);
- rupture of the esophageal wall due to injury or disease;
- developmental anomalies, etc.
Functional disorders
A disorder of the functions of the alimentary canal is a weakening of its motor abilities without visible inflammatory or tumor changes. The main function of the esophageal tube is to pass the eaten piece into the gastric region. Digestion of food does not occur in the esophagus.
Spasm
The movement of the food bolus into the stomach is disrupted when the esophagus is spastic. Spasm occurs as a result of contraction of muscle fibers; it can affect any part of the thoracic or cardiac region ( cardiospasm ).
Dysphagia during spasm either intensifies or weakens. This condition lasts for a long time. Pain in the esophagus occurs during eating, rarely associated with food.
Atony
The opposite condition is called atony - this is a weakening of the muscles of the organ, which also makes it difficult for food to pass through. With atony of the walls, peristalsis is weakened, the eaten food slowly moves along the canal, stops in some places, sticks to the walls, then slowly continues moving.
The causes of impaired functions are often associated with psycho-emotional problems: anxiety, depressed mood, persistent depression associated with psychological trauma in the service or at home. Under other circumstances, the reasons cannot be determined.
Pain in the esophagus during belching: why it occurs
Belching pain in the esophagus provokes:
- frequent smoking;
- eating fruit on an empty stomach;
- sleeping with a full stomach;
- hot bath immediately after eating;
- fast food;
- carbonated drinks.
The listed factors lead to inflammatory processes in the area of the larynx and esophageal canal, the epithelial layer changes, and pain occurs. Belching empty air occurs with reflux esophagitis (more about this disease). Now it’s clear why the esophagus hurts. Next, you need to find out what to do if your esophagus hurts after eating.
Esophagus hurts: what to do if functions are impaired?
This condition requires immediate consultation with a doctor: conduct an examination to rule out serious illnesses. When the disorder is severe, it is sometimes necessary to visit a psychotherapist or psychologist. The doctor will determine the psychological state and identify the internal conflict that caused functional changes in the organ. With the help of psychotherapeutic methods, correction of this condition is achieved.
Symptomatic treatment is carried out by a general practitioner or gastroenterologist . Patients will be advised to eat in a calm, quiet environment, eat slowly, and chew foods thoroughly. Among medications, long-acting nitrates are highly effective.
Types of esophageal spasm and their symptoms
The disease can manifest itself in several types, differing in symptoms and manifestations.
Diffuse
Manifests itself in uncoordinated prolonged muscle movements along the entire length of the esophageal tube. The x-ray shows an extended spasm of the wall.
Characteristic symptoms:
- severe pain behind the sternum or in the area of the transition of the esophageal tube into the stomach, which spreads up to the neck, radiating to the shoulders and lower jaw. An attack of pain occurs regardless of the act of swallowing;
- paradoxical difficulty in swallowing, so-called dysphagia, manifests itself more strongly when swallowing mushy food or drinks and less when trying to swallow solid food;
- At the end of the attack, regurgitation is possible.
Duration - from ten minutes to several hours.
Frequency - from several times while eating food or outside of this process to several attacks per month.
Development of diffuse spasm of the esophagus
Segmental
With this type of contraction, contractions occur in certain areas with great intensity. Deformation of the esophageal tube in the form of a “nutcracker esophagus” or in the form of a “rosary” is observed.
Symptoms:
- difficulty swallowing pureed foods (soft cottage cheese, liquid porridge, sour cream), as well as foods rich in fiber (fruits, vegetables, bread);
- frequent manifestations of dysphagia when consuming any liquids;
- the pain is moderate, manifesting itself in the lower part of the sternum; the spasm begins and ends gradually.
Duration from a few seconds to three to four hours.
Frequency - from two to four times with meals to several times a month.
Contraction of the esophageal muscles during spasm
Nervospastic (nervous spasms)
With this form, an involuntary, convulsive contraction of the muscles of the esophagus occurs. The cause of this condition is considered to be severe nervous shock, fear, prolonged stress, and depression.
An attack may occur:
- During meals, when the food bolus is retained when it is compressed by the muscles of the esophagus, it is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- occurs suddenly, acutely;
- food does not enter the stomach, getting stuck for a while in the esophagus, pushing through in the direction of the stomach with great difficulty;
- if it is impossible to get into the stomach, the food bolus is removed through involuntary vomiting movements;
- vomiting during esophagospasm of a neurotic nature differs from ordinary gastric vomiting - it occurs almost during meals, and the vomit consists of undigested food without hydrochloric acid and pepsin.
2. With severe neurological impairment, an attack develops suddenly, regardless of food consumption. Symptoms:
- pain resembles angina attacks, affecting the chest area;
- Pain sensations range from slight pressure to sharp pain, burning, squeezing, and a feeling of a foreign body getting stuck (“lump” in the throat). The sensation of “coma” occurs during contractions of the initial sections of the esophageal tube and is observed in neuroses and hysteria;
- feeling of suffocation;
- spasm and retching can occur with strong smells, sounds, or fear.
The pain in these cases lasts from a few seconds to many hours with varying degrees of intensity.
During the initial attack, which occurred while eating, the symptom of dysphagia can take hold subconsciously and subsequently arise reflexively when trying to swallow something.
Rough, spicy food increases pain, causing a person to refuse food.
It should be remembered that the patient may simultaneously exhibit different types of esophagospasm.
How does a person’s esophagus hurt: symptoms
The main clinical sign for various pathological conditions of the esophageal canal is dysphagia. Under some circumstances, it appears suddenly (with chemical burns) or grows gradually (esophageal cancer). Under other circumstances, dysphagia appears and disappears again (wall diverticula).
In acute inflammatory processes of the esophageal tract or ulcers in the canal, the passage of food along the esophagus causes pain. The narrowing of the canal causes retention of the food ball above the area of stenosis, and it is ejected back with a wave of peristalsis.
Esophagus hurts: additional symptoms
A condition where the esophagus and throat hurt can also have the following manifestations:
- difficulty swallowing forces patients to chew food for a long time; bulky pieces have to be chewed vigorously and washed down with water;
- over time, it becomes impossible to swallow dense food, the patient eats only pureed food and drinks liquids;
- subsequently, the passage of fluid also becomes difficult or stops, constant dysphagia develops with cancer, the process is irreversible;
- in other situations, pain along the esophageal canal is observed due to ailments of nearby organs: the aorta, mediastinum. The aneurysm and tumor compress the walls of the esophagus from the outside, causing a feeling of heaviness and squeezing;
- if canal stenosis exists for a long time, swallowed food, having spent a short time inside the esophagus, comes out in the form of vomit;
- the food is not digested, but only swollen. If the process of putrefaction has begun, the vomit emits a putrid, fermented odor (with achalasia);
- with inflammatory foci in the esophagus, vomit contains mucus and/or streaks of blood.
Esophagus hurts after drinking alcohol
Ethyl alcohol is a toxic substance for the body. Systematic intake depresses all organs, the esophagus in particular, since it is the first to receive alcohol damage. The chemical formula of alcohol has a detrimental effect on epithelial cells, this is accompanied by painful cutting sensations that appear even after a small portion of alcohol.
- pain can be periodic or constant;
- regularly taken alcohol causes constant pain;
- the normal functioning of the organ is disrupted, and a burn to the mucous membrane is possible.
Burn lesions often develop in the cardiac part of the esophagus, causing pain in the esophagus and stomach. Regeneration takes time, but repeated drinking of alcohol leads to a second burn. As a result, the healing process is slowed down, and the pain in the esophagus does not go away.
Diagnostic tests for esophageal pain
Numerous additional tests are helpful in diagnosing esophageal pain. Three main research methods are used as a standard:
- X-ray of the esophagus after administration of a contrast agent.
- Endoscopic examination.
- Esophagomanometry of the esophagus.
An X-ray contrast agent allows you to visualize narrowing or stretching of the esophagus, the presence of a tumor in the esophagus or diverticulum, or simply scan the esophageal passage. During an endoscopic examination, changes located inside the wall of the esophagus can be detected, and above all, a developing tumor can be identified.
How is esophageal manometry done?
During endoscopy, biomaterial is collected from the walls of the mucous membrane for histopathological examination. In turn, esophageal manometry measures the muscle tone of the organ of the digestive system. It is useful in diagnosing achalasia and esophageal spasticity. When diagnosing gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), a 24-hour pH measurement and the so-called esophageal impedance are prescribed, which provides information about the volume and type of contents, gas or liquid in the cavity environment. In addition, if cancer is suspected and severity is assessed, ultrasound, CT and MRI of the esophagus are prescribed.
Pain in the larynx and esophagus after vomiting
Often, a frequently repeated gag reflex causes a sore throat, and the entire food canal hurts. Vomit damages the mucous membrane of the larynx and esophagus, an inflammatory process begins, the epithelium of the mucous membrane swells, as a result, swallowing is impaired and becomes painful.
If the esophagus is severely injured, the patient experiences a sensation of a stuck object. A lump in the throat occurs after severe vomiting. To ease the symptom, you should drink a small amount of warm liquid.
Common diseases of the esophagus: treatment
If the esophagus in the chest hurts and heartburn causes a lot of inconvenience, it is necessary to undergo a medical examination, since this is a sign of the development of the disease. Gastric erosion is one of the most common diseases of the digestive system. To cure the pathology, you need to eat right and take the medications prescribed by the doctor. You can restore the esophageal mucosa using the following drugs:
- “Almagel”;
- "Motilium";
- "Drotaverine".
How to eliminate the unpleasant symptoms of this pathology? With the help of alginates, you can temporarily improve the patient's well-being. The active substances of the drugs interact with gastric juice and suppress its acidic environment. Under such conditions, a protective film is formed on the surface of the esophagus. Thanks to this, the unpleasant symptoms of the disease are eliminated - heartburn, burning sensation, soreness. With the help of prokinetics, you can eliminate gag reflexes and stimulate gastric motility. If the esophagus hurts in the chest and a lump in the throat appears due to erosion of the esophagus, then you need to take Motilium tablets. With the help of this medication, erosion of the esophagus, flatulence, bloating, and heartburn are treated. The duration of therapy should be determined by the doctor, depending on the severity of the pathology and the severity of the manifestation of unpleasant symptoms.
How does the esophagus hurt?
Symptoms vary. Pain in the esophageal canal occurs right at the table or after eating. The patient feels strong pressure, a burning sensation behind the sternum, or a dull, aching pain radiating to the neck, back, and upper limbs.
Soreness is often combined with heartburn . It intensifies when a person leans forward, lies horizontally, or during physical activity. The symptom decreases when swallowing saliva or after drinking warm water or antacids.
If the esophagus hurts in the chest? Atypical chest pain associated with the esophagus sometimes appears spontaneously and is not dependent on food intake. Intense, debilitating pain may indicate the presence of ulcerative processes or oncology. Practice shows that atypical pain has various clinical manifestations; patients have difficulty describing their sensations. Often this condition is combined with psychosomatic disorders.
After FGS, the esophagus and stomach hurt
Fibrogastroscopy is considered a safe procedure; side effects after it are extremely rare. However, some patients complain of pain in the esophagus and stomach after the examination.
In general, this is normal, since the tissues are stretched by the gastroscope during manipulation for better examination of the walls. A sore throat may persist for up to 2 days.
If after this period the pain does not go away, becomes more intense, a feverish state develops, it becomes difficult to breathe, vomiting with blood appears, you should contact a medical facility, since injuries to the esophagus with a micro-tear are possible.
If the patient follows all the recommendations of the gastroenterologist, such injuries are excluded. In addition, the esophagus may hurt after FGDS if it has undergone a puncture biopsy.
Diseases that cause similar symptoms
Post-infarction pain is not always associated with esophageal disease, however, the pain symptoms are very similar. The source of pain can also be all anatomical structures located in the abdominal cavity, with the exception of the lung parenchyma. Any inflammation in the abdominal cavity can cause pain that the patient will find in the chest. Naturally, the diagnosis presupposes the presence of symptoms. During exercise or emotional stress, patients suffering from coronary artery disease will also hold their chest in an attempt to relieve symptomatic chest pain. A person may experience similar symptoms with the aforementioned myocardial infarction.
Fatty foods can cause pain in the esophagus
Pain that occurs after eating a rich, fatty meal is likely caused by the presence of gallstones in the gallbladder. In addition, stomach ulcers can cause similar symptoms. We should also not forget about neurotic pain caused by inflammation of tendon joints, as well as injuries to the musculoskeletal system. Take care of yourself and always be healthy!
Diagnosis of pain along the esophagus
If there is pain in the esophagus, treatment begins with diagnosis. In order to make a correct diagnosis, you need to collect a thorough history. The patient should be asked when the pain in the esophageal canal began, whether it is associated with food intake or occurs suddenly. With dysphagia, it is important to clarify whether it appeared acutely or developed over a long period of time. It is necessary to find out the duration of existence of dysphagia, whether it progresses, or disappears and returns again.
It is necessary to ask the patient what kind of food is more difficult for him to swallow: dense or any food is difficult to pass and the pain does not depend on its consistency. It is also necessary to identify the role of the psycho-emotional factor, ask whether vomiting occurs after stress, or whether sudden weight loss has occurred.
If you have a pain syndrome, you should clarify how the esophagus hurts, where the pain goes when it appears. The esophagus itself is not directly accessible for examination, so various diagnostic techniques are used.
Fluoroscopy and radiography
X-ray examination of the esophagus, as well as other parts of the gastrointestinal tract, is carried out using a contrast agent, which is barium sulfate. It is given to the PER OSS as a solution in jelly, or added to liquid semolina porridge.
Rg-scopy and Rg-graphy of the esophagus are performed while standing; at the beginning, images are taken without a contrast suspension in order to exclude the influence of external conditions on the canal. After this, the patient drinks the mixture, and contrast is observed to pass through the digestive tract. The examination is performed semi-sideways on both sides, the patient is slowly turned from one position to another in order to see the entire canal from all sides.
Probing
The method is used to determine the patency of the esophageal canal. In case of stenosis, the probe makes it possible to determine the degree and nature of the narrowing and determine the location. The narrowed area is determined by the obstacle found, the distance is measured from the teeth. The nature of the stenosis is revealed by an uneven wall; with neoplasms, an obstacle is felt; with a spasm, the obstacle is easily overcome.
The degree of narrowing is calculated by the diameter of the probe tube or by the circumference of the olive, which passes through the stenotic gap.
Useful video
As you can see, when the esophagus hurts, the symptoms are different. What should the treatment be? Pain in the esophagus can be eliminated with the right approach. Important tips in this video.
Contraindications for probing:
- aortic aneurysm;
- thermal and chemical acute esophagitis;
- heart defects and angina pectoris;
- hypertonic disease;
- phlegmonous inflammatory processes in the mediastinum.
Semi-solid probes with a diameter of 6-15 mm are used for the study The probe is inserted while the patient is sitting on a chair or lying down if the patient is too weak. The insertion of the probe should not be accompanied by force to avoid damage to neighboring areas and the food canal itself.
The person must breathe calmly; in case of a gag reflex or convulsive cough, the umbrella is removed. Contraindications and the danger of probing reduce the value of the method. If possible, the study is replaced by other advanced techniques.
Esophagoscopy
This is a diagnostic research method that is used to determine diseases of the esophagus. It applies:
- with varicose veins along the esophageal canal;
- with cicatricial changes in the esophagus;
- to identify tumors and neoplasms;
- for inflammatory diseases of the mucous membrane;
- for esophageal injuries;
- with diverticula, achalasia;
- when foreign objects enter;
- for painful sensations of unknown etiology and other conditions.
Before the examination, an X-ray with contrast of the larynx, esophagus, and stomach is required to identify contraindications for the examination.
It should be remembered that the patient at the time of the manipulation has individual characteristics and diseases. If the probable risk in such a situation is higher than the benefit, then it is better to abandon the study and use other alternative examination methods.
How to carry out treatment?
When the esophagus in the thoracic part hurts severely, what should you do and what drug will help eliminate the pain? Based on the diagnostic results obtained, the doctor will diagnose the patient and prescribe drug therapy, which includes taking the following medications:
- With the help of “Papaverine”, “No-Shpa”, “Atropine”, spasms can be eliminated. The dosage will be determined by your doctor. The tablets should be taken before meals.
- With the help of “Trazodone” and “Novo-Passit” you can get rid of feelings of anxiety, neurosis and depression. It is recommended to visit a psychologist and psychotherapist; this will help speed up the patient’s recovery process.
- If the patient has severe pain that interferes with leading a full and normal lifestyle, then you need to take an anesthetic drug. Thanks to Novocaine and Anestezin, you can temporarily improve your health if the esophagus in the chest hurts when swallowing. You should know that painkillers do not affect the development of the disease, so it is not recommended to use them systematically. The dosage of Novocaine will be determined by the doctor. This drug should not be used other than as prescribed by a doctor.
- An enveloping medication should be taken if the esophagus in the thoracic part hurts. Burning and discomfort can be eliminated with the help of Phosphalugel. To reduce pain, it is necessary to treat with coating medications that will help protect the esophageal mucosa. “Almagel” is the most effective and safe drug.
- If there is a reflux of acid from the stomach, the doctor prescribes physiotherapeutic treatment for the patient - chloride electrophoresis on the area of the cervical nerve nodes.
You should know that during therapy it is important to eat a healthy and balanced diet. It is not recommended to abuse spicy and fatty foods, this will only delay the patient’s recovery process. You can check the detailed menu with your doctor.
The real reasons
The causes of pain in the esophagus can be very diverse:
- esophagitis – inflammation of the esophagus;
- reflux esophagitis - a disease in which the contents of the stomach are thrown into the esophagus;
- esophageal rupture;
- presence of foreign objects;
- neoplasm;
- blunt injuries to the neck, abdomen and chest;
- hiatal hernia;
- burn;
- a painful outbreak may appear after vomiting;
- diaphragmatic hernia;
- pregnancy;
- neuromuscular diseases.
Treatment methods
Complex therapy, including taking medications, following a special diet, and using folk remedies, helps relieve pain in the area of the esophageal tube. The duration of treatment depends on the cause of the disease, the nature, degree of intensity, and location of the spasms.
Medications
Medicines prescribed for attacks of pain are aimed at enveloping the walls of the esophagus, protecting against the aggressive effects of hydrochloric acid, as well as for the natural regeneration of damaged, inflamed internal walls.
The main medications are:
- prokinetics;
- antacids;
- alginates;
- proton pump blockers;
- antispasmodics, painkillers.
Prokinetics help improve the digestion process and normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Antacids neutralize hydrochloric acid through a chemical reaction of magnesium and aluminum with caustic enzymes. Alginates have an enveloping, protective effect that promotes rapid restoration of damaged epithelium.
Proton pump blockers reduce the active production of gastric juice. Painkillers are aimed at eliminating the sensation caused by the spasm. For severe intensity syndrome, intravenous infusions and intramuscular injections are prescribed. Treatment of the throat involves taking antiseptics.
Symptoms
Symptoms of pain in the esophagus differ depending on the underlying disease:
- painful to swallow. The symptom occurs unexpectedly, without apparent reason. At first, discomfort in the larynx occurs after excitement or rapid chewing of food. Problems when swallowing food are usually selective in nature. For example, drinking water may not cause any discomfort, while swallowing dairy products may cause pain. After eating, there is a pressing feeling in the upper part of the sternum, tachycardia, as well as difficulty breathing;
- belching. Occurs immediately after eating or after some time. Bends or physical activity can provoke an unpleasant symptom;
- pain. The esophagus can hurt due to stretching of the walls of the esophagus or involuntary contractions. The attack can last up to several minutes. Often pain in the esophagus radiates to the back, jaw, neck, ear;
- heartburn.
How to take painkillers correctly?
Many patients experience increased pain in the stomach after taking painkillers. The problem is that many people do not study the instructions for use of medications and do not consult with their doctor. To avoid this problem, you need to remember the following recommendations from experts:
- Take the drug “Gastal” 3 tablets per day, which should be divided into several doses - 2 or 4. Take the medicine 20 minutes before meals or before bed.
- If severe pain occurs in the esophagus, then you need to take Maalox - two tablets after meals. The pills should be completely dissolved.
- “Controloc” is suitable for long-term treatment. The duration of the course of therapy is 1-3 weeks. Depending on the severity of the disease and the specific clinical picture of the patient, the doctor will determine the dosage. The recommended dose is 1-2 pills per day.
- “No-Spa” is an effective antispasmodic that eliminates pain in the stomach area. You should take 1-2 tablets (three times a day). If after using the drug your overall health does not improve, you should call an ambulance or consult a doctor: this may indicate that a serious illness is developing.
The esophagus hurts in the chest and there is a lump in the throat, what should I do? Stomach pain is a symptom of the development of a dangerous pathology. Gastritis, ulcers, reflux esophagitis are common causes of pain. There is no need to take painkillers regularly. This only masks the underlying disease, but does not affect its development. You should definitely visit a doctor.
Diseases that cause pain
A painful outbreak indicates a deviation in the functioning of the organ. Let's consider the main diseases that cause the appearance of an unpleasant symptom.
Esophagitis
Esophagitis is a disease in which the lining of the esophagus becomes inflamed. A characteristic sign of the disease is a burning sensation in the area behind the sternum and discomfort during swallowing. The pain intensifies while eating and bending the body. If you walk around a little after eating, the discomfort will certainly decrease.
Also, with esophagitis, heartburn, belching of air, vomiting with mucus or even blood may appear. Some patients even experience an increase in body temperature. An inflammatory reaction can be caused by infections, burns, injuries, gastroesophageal reflux, malnutrition, and allergies. People whose work involves inhaling chemical vapors are at risk.
What to do if esophagitis occurs? The fight against inflammation directly depends on the root cause. So, in case of a chemical burn, gastric lavage is indicated. If there is an ulcerative lesion, then gastric lavage is strictly contraindicated.
In acute processes, fasting is indicated during the first days. In the future, foods that irritate the mucous membrane and activate the active production of gastric juice are excluded from the diet:
- hot, spicy, rough food;
- alcoholic drinks;
- coffee;
- chocolate;
- fatty food.
Esophageal spasm
The pathological process causes dysfunction of smooth muscles. During an attack, the patient simply cannot swallow food, which is aggravated by severe pain in the chest.
When exerting, a compressive pain occurs behind the sternum. Even liquid foods can cause difficulty swallowing.
The disease can be caused by spicy food, alcoholic drinks, stressful situations, infectious diseases, or a foreign body. Antispasmodics will help relieve the symptoms of esophageal spasm. The manifestations of the disease will help reduce sedatives. They relieve anxiety and fear.
Reflux esophagitis
The essence of the pathological process is the ingress of gastric juice onto the surface of the mucous membrane of the esophagus. The disease provokes the appearance of pain, heartburn, belching of air, vomiting with milk and other digestive disorders.
The pathological process can cause symptoms that are not related to the digestive system: hoarseness, persistent cough, dental disease. The acute process can cause hyperthermia, burning and pain in the neck, as well as profuse salivation.
The following diseases can be provoking causes of reflux of stomach contents: gastritis, ulcers, gastroduodenitis, neurosis. Treatment involves eliminating the underlying cause. Diet plays an important role. Spicy, fatty foods, citrus fruits, and tomatoes should be excluded from the diet. Along with this, medications are prescribed that reduce stomach acidity.
Esophageal carcinoma
A malignant formation in the esophagus is clinically manifested in the form of swallowing disorders, deterioration of appetite, and loss of body weight. The earlier the pathological process was identified, the greater the chance of curing cancer. If the tumor was detected at the third or fourth stage, it is simply impossible to completely cure the disease.
Experts identify a number of provoking factors for esophageal cancer in humans:
- eating too hot or, conversely, cold food;
- smoking;
- alcoholism;
- burns;
- contaminated air;
- obesity;
- poor nutrition;
- reflux esophagitis.
When the tumor reaches a size that makes it difficult for food to pass through, clinical symptoms appear. The main symptom is difficulty swallowing. Solid food simply gets stuck in the esophageal tube, which is why patients try to take liquid food. There is a feeling as if there is a lump in the throat.
As the tumor grows, pain appears behind the sternum and in the throat. Difficulty in passing food causes vomiting. Cancer is often accompanied by a dry cough and hoarseness. Therapeutic tactics largely depend on the location of the tumor, its size and the presence of metastases. The main treatment method is surgery.
Diaphragmatic hernia
A hernia is an opening or protrusion through which peritoneal organs penetrate into the chest cavity. The pathological process may be the result of traumatic injury, relaxation of the diaphragm muscles, or genetic abnormalities.
Experts also identify a number of provoking factors in the occurrence of diaphragmatic hernia:
- age over fifty years;
- pregnancy;
- frequent constipation;
- lifting weights;
- overweight;
- intense cough;
- chronic processes of the digestive tract.
https://youtu.be/d80rMA7nlPU
A diaphragmatic hernia can cause pain in the esophagus. The disease causes difficulty swallowing, vomiting of eaten food, bloating, belching, heartburn, as well as shortness of breath and tachycardia after eating. Surgery is performed when a hernia is strangulated, which causes the following symptoms: nausea, vomiting, bloating, intense chest pain.
Conservative treatment includes the following recommendations:
- eat food in small portions;
- sleep in a semi-sitting position;
- last meal three to four hours before going to bed;
- taking antispasmodics and antacids to reduce acidity.
Esophagus burn
Most often, an organ burn occurs due to the consumption of hot food or exposure to chemicals - acids, alkalis. Severe pain occurs in the neck, behind the sternum and upper abdominal cavity. Chemicals attack the vocal folds, causing hoarseness.
The vomit may contain mucus, blood, as well as pieces of the affected mucous membrane of the esophageal tube and stomach. Intoxication of the body causes weakness, nausea, hyperthermia. The first thing to do in case of a burn is to rinse the stomach. In case of alkali poisoning, washing is carried out with acetic or citric acid. If the burn was caused by acids, then a soda solution is used for washing.
Etiology
Severe pain in the esophagus indicates a dysfunction of this organ. Assessing its intensity and the nature of its course allows the clinician to suspect a particular ailment before starting a comprehensive examination.
The most common causes of pain are:
- consuming excessively hot or hard foods;
- penetration of a foreign object leading to microtrauma of the esophagus. Often such foreign bodies are fish bones;
- abuse of alcoholic beverages, which cause burns to the mucous layer of this organ;
- the course of the inflammatory process in the internal organs, which are anatomically close to the esophagus;
- achalasia cardia;
- esophagitis is a disease that causes inflammation of the lining of the esophagus. A feature of the disease is that it can affect the deep layers of such a food organ;
- GERD is a pathology that causes the backflow of contents into the stomach. The pathology can be completely asymptomatic or accompanied by severe pain;
- the formation of a malignant or benign neoplasm on the walls of the esophagus. Often it is oncology that becomes the source of pain. The main characteristic feature is that it occurs when food comes in and during the process of swallowing;
- spontaneous rupture of the esophageal wall;
- a wide range of injuries, which are divided into closed and open. The first category includes internal damage to the mucous membrane by various irritants. The second group involves wounding a person in the chest or neck area;
- ulcerative lesions of the duodenum or stomach;
- formation of stones in the gallbladder or bile ducts;
- development of a diaphragmatic hernia - in this case, the digestive organs are displaced into the sternum, which in turn causes the development of an inflammatory process.
Causes of pain in the esophagus
In addition to the above predisposing factors that lead to unpleasant sensations in the esophagus, there are several provocateurs of such a symptom that are not directly related to the gastrointestinal tract. Rare causes of severe pain may include:
- prolonged exposure to stressful situations;
- incorrectly selected dentures - in this case, a person does not chew food thoroughly enough, which leads to injury to the esophagus;
- the course of illnesses of an infectious nature, for example, measles, scarlet fever, herpes or influenza;
- inflammatory damage to the intercostal nerve, which takes part in the functioning of the esophagus;
- meningoencephalitis - with this disease, the inflammatory process is localized in the lining of the brain;
- uncontrolled use of medications, an overdose of which negatively affects all internal organs and the gastrointestinal tract in particular.
It is also worth highlighting such a predisposing factor as the period of bearing a child - female representatives during pregnancy quite often encounter such manifestations as pain in the esophagus. This situation often does not become a cause for concern, since the symptom is provoked by active intrauterine growth of the fetus. However, one should also not exclude the negative impact of the above pathologies and negative conditions. In any case, you should seek qualified help.
Pain in the esophagus during pregnancy
A change in the position of the stomach, which is raised by the growing uterus, often provokes esophagitis and reflux esophagitis. Most often, damage to the esophagus appears in women who have given birth repeatedly, especially in a short period of time. In many women, after childbirth, the inflammatory process gradually goes away on its own.
Changes in hormonal levels are another cause of pain in the esophagus in pregnant women. This leads to changes in the motor activity of the esophagus and gastric motility. Pregnant women complain of the following symptoms:
- belching sour;
- heartburn;
- pain when swallowing;
- discomfort in the upper abdomen and chest.
Heartburn and inflammation of the esophagus do not affect the development of the fetus and do not cause premature birth. Still, this negatively affects the mother’s condition. As a result, scars may appear on the mucous membrane of the organ and stenosis may develop - a narrowing of the lumen of the esophagus.
It is extremely important for pregnant women to monitor their diet. It is important to exclude carbonated drinks, fatty foods, and fried foods. It is better to take food more often, but in small portions. Immediately after eating, it is not recommended to take a horizontal position; it is better to take a walk in the fresh air. Also be careful when choosing clothes; they should not be tight.
Pain in the esophagus is a common symptom with which patients consult a doctor. The disease can be caused by a variety of reasons: gastritis, reflux esophagitis, cancer, diaphragmatic hernia, hormonal changes in pregnant women, and more.
The symptom will go away on its own as the underlying cause is eliminated. A doctor will be able to make a diagnosis after conducting a diagnostic examination. By self-medicating, you can seriously harm yourself and waste valuable time.
How to treat
If there is a sharp pain when swallowing, which spreads to the esophagus, you need to drink a glass of slightly warmed water. It shouldn't be carbonated. Then you should slowly inhale and exhale.
Important! To eliminate unpleasant symptoms, you can drink a sedative (you can use herbal tea based on lemon balm or mint). After this, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Treatment of pathology largely depends on what causes it. Naturally, you cannot do without medications, but they should not cause any more harm. Treatment may be as follows:
| Causes | Therapy |
| Injuries or hernias | This will require surgical intervention if the situation has gone too far and drug treatment does not work. After surgery, the patient will need to undergo a recovery period. |
| Burn | It is necessary to neutralize the effect of the substance that causes injury to the organ. Next, the patient will need diet and drug therapy. In rare cases, surgery is required. |
| Pregnancy | The main treatment will be a diet that involves eating very small portions. After childbirth, the stomach pain will disappear. |
| Esophagitis | In this case, a strict diet and drug treatment are necessary until the end of the acute period. |
| Tumor | Radiation or chemical therapy, as well as surgery, will be required. |
Interesting! Blowing (swelling) stomach in men - possible causes
Treatment with medications is necessary in almost all cases. The patient may be prescribed the following medications:
- Antispasmodics: No-shpa, Atropine.
- Sedatives: Novo-passit.
- Painkillers: Nifidipine.
- Local anesthetics (for severe pain that can radiate to other parts of the body): Novocaine.
- Special enveloping agents that protect the mucous membrane: Almagel.
- Antacids (if reflux is present). If the esophagus hurts when swallowing and more.
Physiotherapy is no less useful. Electrophoresis will be useful. It helps relieve pain when swallowing food. It is important to pay attention to your diet. Perhaps its revision will eliminate many problems. It is better to give up heavy and junk food, alcohol, and processed foods. You should diversify your diet with plant foods and juices. It is worth consulting with a gastroenterologist and nutritionist.
Esophagus hurts: causes
The esophagus can hurt for the following main reasons:
1. Development of esophagitis. This disease is characterized by severe inflammation of the mucous membrane of the alimentary canal, which develops due to exposure to gastric juice. Most often, esophagitis manifests itself in the form of a burning sensation and severe heartburn, so a person’s esophagus hurts when swallowing.
2. Pain in the esophagus can develop as a result of its damage, which in turn can be internal or external (open), which penetrates through the neck.
3. Often severe pain in this area of the esophagus occurs when various foreign bodies enter it. This could be a fish bone, a small grain, dentures, buttons, nails, paper clips, etc. Also, a feeling of pressure can occur from a long stay in the area of the esophagus of the tracheotomy tube.
The reason for the accidental use of such foreign objects may be:
• negligence (inattentiveness) when preparing food;
• eating on the run;
• poor chewing of food, due to which a person simply cannot feel a foreign object in the mouth;
• the habit of some people to hold various small objects (toothpicks, etc.) in their mouths while cooking.
It is important to know that foreign objects can easily cut the esophagus, so if they are detected, you need to remove them from the body as quickly as possible.
4. Perforation of the walls of the esophagus can develop in the presence of cancer, chemical burns and ulcers. The main symptom of esophageal perforation is considered to be very acute pain behind the chest area, which has a paroxysmal increasing character.
This condition is very dangerous because at any moment a person’s esophagus can simply rupture, causing terrible pain, coughing and difficulty breathing. Severe vomiting of blood and loss of consciousness may also occur.
5. A burn is often the reason why the esophagus hurts when swallowing. It occurs when accidentally ingesting various chemical compounds, acids, etc. In this condition, the mucous membrane of the esophagus and mouth is subject to severe damage.
6. Esophageal cancer primarily develops in people who:
• eat excessively spicy or hot food;
• smoke;
• drink a lot of alcoholic beverages;
• inhale harmful chemical fumes.
When oncological pathologies form in the esophagus, a person suffers from malaise, weakness, chest pain and increased salivation. If at least two of these symptoms occur, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible, because the success of treatment largely depends on the early diagnosis of the disease.
7. A functional disorder of the esophagus is a violation of the motor function of this organ without visible changes. As a rule, this condition is accompanied by severe spasms, which causes pain in the esophagus.
The causes of esophageal disorders are mental factors (emotional instability, stress, depression, etc.).
Cancers
Cancers of the esophagus most often appear in those people who lead an unhealthy lifestyle - they smoke a lot and drink alcohol excessively, and regularly inhale harmful chemical fumes. To reduce the risk of developing pathology, it is important to lead a healthy lifestyle. Do not overuse spicy or hot foods. Warm food is the best option. If a person develops cancer, the following symptoms occur:
- weakness;
- the esophagus hurts in the chest, it hurts to swallow;
- increased salivation;
- fast fatiguability.
If one of the symptoms appears, you need to visit a doctor. At the initial stage of disease development, therapy is carried out much faster and more effectively. If you do not contact medical personnel in a timely manner, therapy will be carried out using the surgical method in a hospital setting.
Esophagus hurts: causes (additional)
1. A hiatal hernia is a chronic pathological condition in which the esophagus is displaced through a hole in the diaphragm.
2. This condition provokes inflammation of the esophagus (esophagitis). A symptom of a hernia is pain in the left side of the chest, which intensifies after exercise, coughing, burping or eating.
3. Esophageal diverticula are a process of protrusion of the walls of this organ. There may be one or more diverticula in one esophagus. They appear in those people who have greater flexibility of the walls of the esophagus to pressure.
Symptoms of diverticula include nighttime cough, foreign body sensation in the throat, and regurgitation.
4. Esophageal achalasia is a disease in which the esophagus becomes dilated. The reasons for its appearance are considered:
• eating cold food;
• acute deficiency of vitamin B1;
• stress.
With achalasia, a person will be bothered by dull pain behind the chest that radiates to the back, as well as frequent nausea.
5. Sometimes the esophagus hurts due to disruption of the nervous system. This is due to the fact that several cranial nerves are responsible for the functionality of this organ, which cause its relaxation. With strong emotional outbursts, this balance is disrupted, which provokes spasms and pain in the esophagus.
It is also important to know that an unstable psycho-emotional state of a person can provoke various diseases of the digestive system (ulcers, pancreatitis) and the cardiovascular system (heart attack, hypertension, tachycardia, arrhythmia, etc.).
Symptom after illness
This symptom may be due to infectious abnormalities. The main ones are ARVI, which are the result of infection with viruses. Most often, this condition is accompanied by pain in the chest and throat. Lymph nodes often become enlarged.
Such symptoms may be the result of infectious abnormalities:
- Allergy. In addition to pain, it causes swelling and coughing.
- Cardiopsychoneurosis. Causes spasms in the throat and muscle tissue. In addition, there is pain.
- Penetration of a foreign object into the throat. It provokes not only pain, but also a cough.
- Unfavorable environmental conditions. These signs may be associated with chemicals. All this provokes irritation of the throat and respiratory organs.
Esophagus hurts: what to do
Sometimes it happens that pain in the esophagus occurs spontaneously. First of all, in this case there is no need to panic, because this will not help. It is better to follow this scheme of actions:
1. If pain occurs while eating, then you need to drink a glass of warm water (still).
2. Inhale and exhale slowly. Hold your breath for a second and then restore it.
3. Drink a sedative (Persen).
4. It is also recommended to drink chamomile tea or lemon balm drink.
5. If there is no sedative nearby, you can replace it with mint candy.
If such attacks of pain often bother you, you need to consult a doctor.
Diagnostics
Diagnostics is necessary to establish the exact cause of the disease, since the further treatment plan depends on this. The diagnostic complex includes various procedures:
- differential blood test (counting the number of immune cells, red blood cells, platelets);
- qualitative blood and urine analysis;
- Ultrasound of the chest;
- examination of the esophagus;
- chest x-ray;
- CT scan.
The attending physician may prescribe additional diagnostic procedures if those listed above could not create a complete picture of the patient’s condition.
If problems arise, you need to contact a therapist, neurologist and pulmonologist. If the causes of pain cannot be identified, it is necessary to conduct a number of studies:
- general blood analysis;
- X-ray of the lungs;
- tuberculin test;
- sputum culture.
To exclude
tumor lesions of the lungs
a puncture of the organ tissue is performed and a histological examination is carried out. If there is a suspicion of bronchitis, tracheitis, pharyngitis, there is a need for chest X-ray. Sputum analysis is also performed.