Metronidazole for pancreatitis
Popular articles on the topic: metronidazole for pancreatitis
Modern doctors often have to deal with such a difficult clinical situation when a patient is diagnosed with both diabetes mellitus and chronic pancreatitis.
We continue to publish materials prepared based on one of the most interesting medical events of the year - the VII Winter School of Internists, organized with the support of the famous pharmaceutical company.
Acute pancreatitis continues to be a pressing problem both in surgery and in intensive care medicine. In Ukraine, the incidence of AP is 5.2 cases per 10 thousand population.
Antibacterial therapy occupies an important place in the treatment of acute and chronic pancreatitis, so a practicing physician should know its positive and negative aspects, the features of choice and treatment with antibiotics in pancreatology.
Adequate treatment of surgical infection involves solving two diagnostic problems: differential diagnosis of local and generalized forms of infection.
Gallstone disease is a disease caused by impaired metabolism of cholesterol and/or bilirubin and characterized by the formation of stones in the gall bladder (cholecystolithiasis) and/or in the bile ducts (choledocholithiasis).
Nonspecific ulcerative colitis is a serious problem in gastroenterology, since its etiology remains unknown and there is currently no specific treatment.
Over the past two decades, clinical medicine has been renewing its ideology and direction of development everywhere. There are a number of important prerequisites for this, among them the emergence and understanding of the principles of evidence-based medicine and the introduction of the latest methods.
Functional dyspepsia is a symptom complex of functional disorders, including pain or discomfort in the epigastric region.
Sources used: www.health-ua.org
Features of the use of Metronidazole for pancreatitis
Metronidazole for pancreatitis is prescribed by the attending physician as an effective treatment for this disease. Metronidazole is a popular broad-spectrum drug that can be taken for a number of diseases caused by various types of microorganisms and protozoa.
Action for pancreatitis
What properties does Metronidazole have? This medicine is a reliable and effective therapeutic agent that has the following effects:
- antibacterial;
- antimicrobial;
- trichomonacid;
- antiprotozoal;
- antiulcer.
The active component of the therapeutic agent is a 5-nitroimidazole derivative, the effect of which is aimed at destroying the DNA of anaerobic microorganisms and protozoa, which deprives them of the ability to develop and live.
What are the indications for using Metronidazole? Metronidazole is prescribed for infectious diseases; it is also used in the complex treatment of diseases associated with the digestive system, such as:
- abscesses of the abdominal cavity and liver;
- inflammatory processes occurring in the colon;
- duodenal ulcer;
- stomach ulcer;
- acute and chronic pancreatitis.
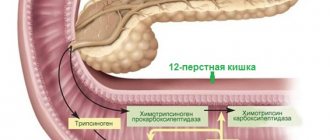
Pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas. When overeating, a tendency to fatty foods and alcohol, an increased amount of enzymes is produced in the pancreas, which causes the inflammatory process.
With the development of pancreatitis, the patient experiences congestion in the pancreas, which provokes its swelling. As a result, the so-called effusion condenses in the abdominal cavity, that is, a secretion filled with biologically active substances that cause inflammation.
When inflammation spreads to the connective tissue of the abdominal cavity, the development of peritonitis begins, namely, necrosis of the connective tissue. Peritonitis is facilitated by the fact that the effusion contains constantly multiplying microflora, since for it it is an excellent nutrient medium.
Peritonitis is a severe complication of pancreatitis, which may well result in the death of the patient.
Treatment of pancreatitis and its complications is carried out with Metronidazole. To treat and prevent an inflammatory process in the abdominal cavity, a patient suffering from acute or chronic pancreatitis needs broad-spectrum antimicrobial agents—antibiotics.
Metronidazole is prescribed as part of complex antibacterial treatment for acute or chronic pancreatitis.
How to take Metronidazole?
This drug for pancreatitis in adults should only be prescribed by the attending physician in cases where tissue death inside the abdominal cavity is approximately 30%. However, in some cases, Metronidazole is taken as prescribed by a doctor and to prevent tissue necrosis in acute pancreatitis, when the attending physician has every reason to suspect the possibility of infection in the pancreatic tissue.
The therapeutic effect of Metronidazole largely depends on the timeliness of treatment of the disease. As a rule, treatment of pancreatitis with antibiotics, including Metronidazole, lasts up to 2 weeks, and in cases of infection spreading - up to a month.
The use and dosage of Metronidazole in the treatment of pancreatitis is individual for each patient. It must be remembered that dosages and treatment regimens can only be used as prescribed by the attending physician. All recommendations presented are for informational purposes only and cannot be taken as a guide to self-medication.
This drug is used in the treatment of pancreatitis in adults as one of the components of complex antibacterial treatment. As a rule, Metronidazole should be taken together with the drugs Pefloxacin, Kanamycin, Carbenicillin or their analogues.
Courses of antibacterial treatment of pancreatitis and prevention of complications are usually carried out on an inpatient basis, under the supervision of medical staff to avoid re-infection.
The course, regimen and dosage of antibiotics are prescribed depending on the severity of the disease, as well as based on factors of individual drug tolerance. For example, if a patient has liver dysfunction, then Metronidazole should be taken with constant monitoring of its concentration in the blood.
There are also certain contraindications when taking Metronidazole. Metronidazole should be used with caution, taking into account the following contraindications:
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding. Metronidazole is dangerous in the first 1st pregnancy, and it can be taken in the 2nd and 3rd trimesters only on the recommendation of doctors.
- In cases of urgent need to take Metronidazole for pancreatitis during breastfeeding, lactation is stopped.
- If you are hypersensitive to the drug or other nitroimidazole derivatives, you should not take the drug.
Side effects of the drug:
- Nausea, vomiting, pain and other digestive system disorders.
- Headache, insomnia, tinnitus, fainting and other manifestations associated with the central nervous system.
- Skin itching, redness and other allergic reactions.
Metronidazole is an effective component in the treatment of pancreatitis in adults, which must be carried out only as prescribed and under the supervision of a doctor.
Sources used: ozheludke.ru
Average prices
The average price of antibiotics may differ depending on the type of drug. The difference in price is also affected by the location of the pharmacy, since in the capital the same drug will cost more than in smaller cities.
When purchasing, you should consider the following circumstances. The fact is that the same drug belonging to the same general group may have different names and differ in price. These differences primarily depend on the country where the medicine is produced and the company where it is directly manufactured. Differences in price arise due to the fact that original drugs are several times more expensive than generics, although the active substance in them is the same. Moreover, this does not mean that a copy of a branded drug will be much weaker in effectiveness.
Currently reading: Is it possible to eat mashed potatoes with pancreatitis - recipes and reviews
For comparison, you can look at the existing differences in the price of the drug, which is often prescribed for pancreatitis:
- Pancreatin in Russia can be purchased at a price starting from 30 rubles for one package of 60 tablets;
- Mezim Forte (the same pancreatin, but under a different brand) will cost an average of 245 rubles for 80 tablets.
In general, drugs in the form of antibiotics are quite accessible and inexpensive, their price depends on the type of drug, since in case of severe exacerbation it is necessary to use the latest generation of antibiotics, their average price will be slightly higher than others. If the prescription is made simply to eliminate the symptoms of inflammation, then they turn to simpler drugs, which will not cost much.
Antibiotics for pancreatitis of the pancreas
Pancreatitis is a disease of the pancreas that is inflammatory in nature. It is based on a change in the exocrine part of the organ, atrophy of its cells, and their replacement with connective tissue. With the disease, disturbances in the duct system of the gland, the formation of cysts and stones that disrupt its activity, can be observed. It must be treated comprehensively - not only by relieving pain and replacing enzymes, but also by preventing complications.
Antibiotics for pancreatitis can be prescribed as a preventive measure or as therapy at the first symptoms of bacterial damage (fever, intoxication).
Over the past three decades, the incidence of pancreatitis has more than doubled. It can have either a simple edematous (reversible) form or progress to pancreatic necrosis (organ death), which ends in the death of the patient. It should be noted that recently the disease has become significantly “younger”, and began to develop already at the age of 38–40 years.
Which drugs are better
Treatment of pancreatitis with antibiotics should be carried out taking into account the following parameters:
- the ability of the drug to pass through the hematopancreatic barrier into the pancreas and nearby tissues;
- sensitivity of microflora to the selected type of antibacterial agent;
- possible side effects associated with taking an antimicrobial drug.
In severe attacks of the disease, the incidence of bacterial complications reaches a third of all cases of the disease. Infection due to inflammation of the pancreas can occur in several ways:
- hematogenous, that is, by spreading the infection through the blood;
- lymphogenous – infection of an organ through plasma;
- ascending – infection from nearby neighboring organs: duodenum, biliary tract, portal vein system.
The question of which antibiotics to use for pancreatitis is always decided individually.
Preventive antimicrobial therapy for the edematous form is unjustified, since their effectiveness in this case has not been established. Antibacterial drugs are immediately prescribed only when the first symptoms of infection appear: nausea, vomiting, fever.
Considering that conducting a study of the flora of the pancreas using a non-invasive (bloodless) method is impossible due to the deep location of the organ, the choice of antimicrobial drugs should be made in favor of representatives with a wide spectrum of action. In addition, the resistance of known bacterial strains to them should be minimal.
Special cases of antibacterial prophylaxis
As a preventive measure, antibacterial agents can be prescribed if the patient has:
- HIV infections,
- viral hepatitis,
- diabetes mellitus,
- tuberculosis,
- oncopathology,
- other serious diseases.
The most common indication for the prescription of antibiotics is the biliary-related origin of the disease, which is associated with diseases of the liver and gallbladder. This form is observed in 35–56% of cases of pancreatitis in adults. It occurs because the bile and pancreatic ducts enter the duodenum through the same opening or very close. Therefore, when it is blocked, bile is released into the pancreas. Due to the influence of bile acids and enzymes, organ damage occurs. Most often, biliary pancreatitis develops against the background of:
- cholangitis – inflammation of the bile ducts;
- chlamydial or lamblia cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder);
- papillitis - inflammation of the mouth of the large nipple of the duodenum;
- bacterial contamination of the small intestine;
- bacterial overgrowth syndrome.
The most prescribed antibiotics for pancreatitis and cholecystitis are macrolides, namely clarithromycin (Clabax, Klacid, Fromilid and others). Its antimicrobial activity includes intracellular agents: mycoplasma, legionella, chlamydia, ureaplasma, gram-positive streptococci and staphylococci, as well as many gram-negative microorganisms and some anaerobes.
The choice of this group of antibiotics for cholecystitis is due to their wide range of action with the predominant excretion of clarithromycin in bile, due to which high concentrations are created in it, and a pronounced antimicrobial effect is observed.
When inflammation of the pancreas develops against the background of microbial contamination of the digestive tract, the drugs of choice will be non-absorbable antiseptics - rifaximin (Alfa Normix), and tablets based on bismuth compounds (Vitridinol, De-nol, Novobismol, Ulcavis, Escape).
Modern antimicrobial agents
The choice of antibacterial agent depends on the form of inflammation of the organ, which is complicated by infection, as well as on the degree of microbial spread. The minimum effective concentration in pancreatic tissue is created after taking an antibiotic from the following groups:
- Protected broad-spectrum penicillins: ticarcillin with clavulanic acid (Timentin).
- 3rd generation cephalosporins: cefoperazone (Medocef, Cephobid, Cefpar), cefotaxime (Intrataxime, Rezibelacta, Talcef).
- 4th generation cephalosporins: cefepime (Cefsepim, Movisar, Cefomax).
For effective treatment of edematous pancreatitis, it is recommended to drink or inject antibiotics, which provide high concentrations and have a reliable therapeutic effect. These include:
- Fluoroquinolones: ciprofloxacin (Quintor, Tsiprinol, Tsiprolet), pefloxacin (Abaktal, Pefloxabol, Unikpef).
- Carbapenems: meropenem (Genem, Mepenem, Penemera), imipenem with cilastatin (Aquapenem, Grimipenem, Tienam).
- Metronidazole (Tricho-PIN, Trichopol, Efloran).
- Combination of the latest generation cephalosporins with metronidazole.
For pancreatitis, it is not recommended to take drugs from the group of aminoglycosides (amikacin, gentamicin, neomycin and others), aminopenicillins (ampicillin, amoxicillin, talampicillin, bacampicillin, pivampicillin), 1st generation cephalosporins (cephalexin, cefazolin, cefadoxil), since their concentration in the pancreas gland does not reach therapeutic values.
All antibiotics used to treat pancreatitis have a broad spectrum. Therefore, when treating it, it is necessary to take into account that a person taking antibiotics eliminates not only pathogenic, but also beneficial microflora. After taking antimicrobial agents, it is recommended to use probiotics containing lacto- and bifidobacteria.
Sources used: gastrolekar.ru
How does taking antibiotics affect the digestive system?
In all cases, inflammatory disease of the pancreas is a severe pathology that is difficult to correct. Pancreatitis cannot be completely cured due to the rapid death of cells during an acute process or their replacement with connective or adipose tissue. In addition, any inflammation can be complicated by life-threatening conditions, which develop in 20% of cases of existing pancreatitis.
In order to treat the inflammatory process in the diseased pancreas and other digestive organs affected by its destruction, antibiotic therapy is prescribed. Sometimes this therapy is used if there is a threat of infection spreading to neighboring digestive organs. Treatment with these drugs is used to prevent severe complications of pancreatitis:
- abscess;
- retroperitoneal phlegmon;
- peritonitis;
- sepsis.
Indications also include:
- rupture of the common pancreatic duct;
- bile stasis.
But today, the use of antimicrobial drugs for prophylactic purposes is considered inappropriate, since in these cases their effectiveness has not been proven: they do not reduce mortality when used prophylactically, despite a decrease in the incidence of infection, but the toxic effect on the body is significant. For the edematous form of pancreatitis, antibacterial agents are also not used. They are prescribed when the first signs of infection appear: fever, nausea, diarrhea, and sometimes vomiting.
When prescribing antibiotics, it is necessary to consider:
- the ability of the drug to penetrate the blood-brain barrier into the pancreas and neighboring organs;
- sensitivity of the suspected pathogenic agent to the selected drug;
- side effects that a certain medicine may cause.
In each specific case, antibiotics are prescribed individually.
Of the digestive organs, the pancreas and stomach are most sensitive to the effects of antibiotics. Violation of their functions develops due to a sharp decrease in normal microflora and a significant increase in pathogenic microbes.
Objective indicators of pathological changes in the gastrointestinal tract after taking antibiotics include the occurrence of abdominal pain of various types and locations, bloating, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. To reduce the risk of their occurrence, probiotics are prescribed.
The liver is also susceptible to antibacterial agents. In a healthy person, it does not react to medications, neutralizing toxic substances. But with impaired functions, the clinical manifestations of its damage are in the mouth, heaviness in the right hypochondrium, and nausea. To prevent the toxic effect of medications on liver tissue, hepatoprotectors are additionally prescribed.
Treatment of pancreatitis with Metronidazole
To treat inflammatory processes of the pancreas, in some cases it is necessary to use antibiotics. Most often, Metronidazole for pancreatitis is prescribed by doctors as part of complex therapy for the disease or to prevent possible bacterial complications. Timely use of the drug greatly increases the effectiveness of treatment.
The use of antibiotics for pancreatitis
Metronidazole and other antibacterial agents are prescribed for the treatment of acute and chronic pancreatitis in the following cases:
- with the development of infectious complications, in particular with necrosis, parapancreatitis, cyst formation, cholangitis, etc.;
- to prevent inflammation caused by bacteria;
- when predicting severe bacterial complications of pancreatitis.
It should be noted that in the latter case, Metronidazole is prescribed in cases of severe pancreatitis, when the volume of necrotic tissue is more than 30% of the size of the pancreas.
Pharmacological properties
Metronidazole is an antibacterial agent that exhibits active antimicrobial and antiprotozoal effects. In the process of interaction with deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) found in bacterial cells, Metronidazole blocks the production of their nucleic acids, which causes the death of harmful microbes.
Purpose
Treatment of pancreatitis with Metronidazole is carried out only in severe cases of the disease . In mild forms of the inflammatory process, the use of antibiotics is not advisable.
For the preventive treatment of severe complications of purulent pancreatitis, the following combination of drugs is most often used:
- Metronidazole + fluoroquinolones (peptofloxacin);
- Metronidazole + third generation cephalosporins (ceftriaxone or cefoperazone);
- Metronidazole + fourth generation cephalosporins (cefepime or cefoperazone-sulbactam).
If necessary, Metronidazole can be replaced with Trichopolum, since both drugs have the same active substance, a similar mechanism of action and indications for use.
Before starting treatment for pancreatitis, it is necessary to conduct an appropriate examination and consult with a doctor who will prescribe an individual treatment regimen. And also make sure that there are no contraindications for using the antibiotic.
The standard dose of Metronidazole for pancreatitis for adult patients is as follows: one tablet of the drug (250 mg) is taken three times a day. Metronidazole must be taken for 5 to 7 days. However, the doctor may prescribe a different duration of therapy.
If necessary, treatment can be repeated, but at intervals of at least 3 to 6 weeks. When conducting a repeat course, studies of the leukocyte level in the patient’s blood are necessary.
Contraindications
Before starting complex treatment of pancreatitis, which includes Metronidazole, you must ensure that the following contraindications are absent:
- lack of coordination;
- reduced concentration of leukocytes in the patient’s blood (anemia);
- organic pathologies of the central nervous system;
- disturbances in the activity of liver functions;
- the first three months of pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- the presence of hypersensitivity to the components included in Metronidazole.
If at least one of the contraindications described above is identified, the use of the antibacterial drug is prohibited.
Side effect
With pancreatitis, Metronidazole can cause side effects from various body systems:
- dysfunctions of the digestive system: nausea, vomiting, lack of appetite, discomfort in the epigastric region, intestinal colic, constipation;
- dysfunctions of the nervous system: headaches, encephalopathy, convulsive manifestations, hyperexcitability, irritability and hallucinations, general weakness;
- dysfunctions of the immune system: allergic manifestations;
- pathologies of the urinary system.
If the effects described above or any other discomfort develop, you should consult a doctor for advice. After determining the cause, the doctor will change the treatment regimen for pancreatitis or replace the drug with its analogue.
Overdose
During treatment of pancreatitis, it is very important to prevent an overdose of the drug.
Because if the permissible therapeutic dose is exceeded, the following negative effects are possible:
- convulsions;
- dysfunction of peripheral nerves (peripheral neuropathy);
- development of a feeling of nausea;
- gagging;
- coordination disorders.
To treat an overdose of Metronidazole, symptomatic therapy is carried out, which may include hemodialysis.
Conclusion
Currently, many patients are concerned about the question: is it possible to take Metronidazole for pancreatitis? We found out that the antibiotic is used for severe forms of the disease, as well as for the prevention of bacterial complications in pancreatitis.
Before starting treatment, you must make sure that there are no contraindications to the drug, and also undergo an appropriate examination by a specialist doctor.
If it is not possible to buy Metronidazole at the pharmacy, it can be replaced with Trichopolum, since the products are analogues.
Found a mistake? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter
Sources used: pillsman.org
Acute form
Previously, antibiotics were prescribed to patients diagnosed with acute pancreatitis. It was believed that the tablets had a good preventive effect, protecting the body from the occurrence of parallel diseases. Clinical studies have provided optimistic data stating that after taking such drugs, the number of deaths among patients with pancreatitis decreased. This meant that the risk of an inflammatory infection while taking medications was sharply reduced, which means that the disease progressed more calmly.
Common medications for acute illness:
- Cefotaxime;
- Abaktal;
- Ceftriaxone;
- Vancocin;
- Tienam;
- Amoxiclav.
Later it was confirmed: the tablets do indeed reduce the risk of infection (antibiotics of different spectrums are used), but the tablets do not affect the lethality. Even after the end of an attack of acute pancreatitis, drugs are not prescribed, allowing the pancreas to rest. Re-appointment occurs if any of the internal organs experience failure, which indicates the possibility of infection and the need to fight.
The earlier the anti-infective medicine is prescribed, the more pronounced the effect of the drugs. There are situations when antibiotics are mandatory: suppose peritonitis develops in parallel with acute pancreatitis. Then prescribing antibiotics is vital.
Several principles for prescribing antibiotics
The prescription of antibiotics is preceded by many factors; the drug is not prescribed by a doctor unless necessary. You should also be aware of the accompanying symptoms:
- excessively acute pain that is difficult to bear and impossible to relieve with other medications;
- the maximum effect is achieved by administering the medicine by injection;
- the maximum course of injections is 2 weeks, 2-4 times a day;
- when peripancreatitis develops, the patient is prescribed Pefloxacin and Azithromycin;
- when there are potential signs that the disease will be severe (possibly based on the severity of symptoms or other signs - genetics, medical history). Antibiotics will need to be prescribed sooner.
Self-medication should not be carried out; a doctor's advice is necessary. Unreasonable use of antibiotics leads to the opposite effect: due to the complete destruction of intestinal microflora bacteria by the drug, the beneficial ones are also destroyed, which worsens the already undermined health of the patient.
An honest selection of antibiotics for acute and chronic pancreatitis in adults
Pancreatitis is a group of diseases of the digestive system in which there is inflammation of the pancreas. This organ secretes digestive enzymes and produces insulin, a hormone responsible for carbohydrate metabolism in the body. With pancreatitis, enzymes do not enter the duodenum and begin to destroy the pancreas. At the same time, the released toxins enter the bloodstream, damaging vital organs: lungs, kidneys and even the brain. In medicine, the following forms of the disease are distinguished:
- acute form;
- relapse of acute pancreatitis;
- chronic form;
- exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis.
When are antibiotics prescribed?
In 20% of patients suffering from pancreatitis, the disease is severe. The situation is aggravated by incorrect diagnosis, errors in nutrition and delays in seeking medical help.
For inflammation of the pancreas, therapy consists of prescribing antispasmodic, analgesic and anticholinergic therapy. Fasting for two days and drinking plenty of fluids are also recommended; forced diuresis is effective. Infusion therapy is used to eliminate water-electrolyte imbalance.
In addition to the basic complex, in severe cases of the disease, antisecretory and antienzyme therapy is prescribed. Antihypoxants and antioxidants are also used. If the pain process is severe, prolonged epidural analgesia is performed.
In mild cases, early administration of antimicrobial agents is not advisable, since it cannot reduce the risk of septic complications.
Antibiotic therapy is prescribed for severe disease, with a risk of infection (attachment of a bacterial component) due to the activation of opportunistic flora.
In this case, the use of antibiotics that have affinity for pancreatic tissue is indicated.
To prevent purulent complications, combinations with metronidazole are most effective:
- fluoroquinolones (peptofloxacin);
- third generation cephalosporins. Preference is given to ceftriaxone or cefoperazone;
- 4th generation (cefepime or cefoperazone-sulbactam);
Carbapenems may be prescribed.
The duration of treatment is from 7 to 14 days.
Effective and commonly prescribed antimicrobial agents
In acute cases of the disease, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed: fluoroquinolones, synthetic penicillin derivatives and cephalosporins. Let's look at each drug in detail.
Cefoperazone is administered intravenously. Highly effective against a wide range of microorganisms, has a pronounced bactericidal effect. Used for seven to 10 days. It is also used as an antibacterial cover in the surgical treatment of pancreatitis and its complications.
Ceftriaxone is a 3rd generation cephalosporin antibiotic that has a bactericidal effect. The course of treatment for pancreatitis using Cefriaxon is about a week. The drug is administered intravenously twice a day.
Amoxiclav is a combination drug produced in tablet form. It contains amoxicillin and clavulanic acid. For effective therapy, it is enough to drink one tablet once a day. The duration of the course is approximately 7 days.
Pefloxacin, or abactal, is a broad-spectrum antibiotic belonging to the class of fluoroquinolones. It has a high affinity for pancreatic tissues. The most effective is infusion administration (intravenous drip, over an hour) twice a day.
Vancocin is an antibiotic, an antibiotic belonging to the group of glycopeptides. Used for sepsis, in case of ineffectiveness of beta-lactams. The drug is specially designed to treat infections. The active ingredient is vancomycin hydrochloride. One bottle contains 0.5 or 1 gram of this substance. The antibiotic is available in powder form.
Doxycycline is administered intravenously or intramuscularly. When taken orally, Doxycycline is almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. The course of treatment lasts no more than 10 days.
Antibiotics for acute pancreatitis
The dosage and duration of the course of antimicrobial therapy depend on the severity of the disease and associated complications. Stagnation in the glandular tissue and edema are fraught with the development of autolysis, in which the cells and tissues of the pancreas disintegrate under the influence of their own enzymes.
Exudate often occurs - a pathological condition characterized by the accumulation of biological fluid. The latter, together with proteolytic enzymes, comes into contact with the peritoneal membrane. This leads to inflammation of the parietal and visceral layers of the peritoneum, i.e. peritonitis.
Peritonitis poses a threat to the patient's life and requires prompt medical intervention. The prognosis in case of untimely or inadequate treatment is unfavorable, even death. With the rapid progression of the disease, mortality reaches 60-80%.
Broad-spectrum antibiotics will help prevent the development of septic complications: Amoxicillin, Tsiprolet, Chloromycetin.
Amoxicillin is a semisynthetic antibiotic belonging to the penicillin group. It is well absorbed by the body and is not destroyed by gastric juice. Amoxicillin in acute pancreatitis is used to prevent relapse. The medicine is actively used in pediatrics.
Tsiprolet is an antibacterial drug from the group of fluoroquinolones. In medicine, the oral method of administration of Tsiprolet is practiced. Gram-positive, gram-negative bacteria and anaerobic microorganisms are sensitive to the drug.
Chloromycetin, or Levomycetin. Has a wide spectrum of action. Colorless, bitter-tasting crystals are practically insoluble in water. Prescribed for shigellosis, or dysentery and typhoid fever. Chloromycetin is highly active and toxic. Due to severe side effects, it is prescribed only for serious infectious lesions.
Basically, drugs are administered intravenously and into the abdominal cavity. To relieve pain, the patient is prescribed tricyclic antidepressants, which have a sedative-hypnotic effect.
Taking antibiotics is a preventive measure to avoid life-threatening pathological conditions. A favorable rehabilitation prognosis is observed if the patient goes to a specialized medical institution in a timely manner.
Antibiotics for exacerbations of chronic pancreatitis
Taking antibacterial medications for pancreatitis is impractical and even dangerous, since the inflammation is of non-infectious origin. Potent medications enter the intestinal lumen and destroy beneficial microflora.
A gastroenterologist prescribes antibiotics if there is a risk of developing parapancreatitis. This localized complication leads to inflammation of the retroperitoneal tissue layer. In case of relapses, doctors prescribe patients a course of treatment with Ampiox, Augmentin, Cefuroxime, Cefixime and Cefoperazone.
To destroy the infection in pregnant women, antibiotic drugs of the penicillin series or its synthetic analogues, for example, ampicillin, are prescribed. In severe cases of the disease, the prescription of Carbenicillin.
Antibiotics for pancreatitis in adults are not suitable for treating inflammation in children. For adolescents over 12 years of age, the drug Bactrim , available in the form of tablets and suspensions, is suitable. It is taken orally and washed down with plenty of water. Pregnancy and breastfeeding are not contraindications, but it is better to consult with your doctor.
Rules and features of taking antibiotics
Therapy with potent antibiotic drugs requires compliance with a number of recommendations:
- the maximum effect can be achieved by intravenous or intramuscular administration of the drug;
- course of treatment from seven days to two weeks. Exceeding 14 days of antibiotic therapy is not recommended;
- It is recommended to take medications only with clean still water;
- Under no circumstances should you adjust the dosage yourself;
- lack of improvement within three days indicates that the pathogen is resistant to this type of antibiotic, so the medicine should be replaced;
- You should not stop taking the drug as soon as the condition improves.
- to consolidate the result, therapy should continue for another 2-3 days;
- Equal periods of time must be maintained between doses of the medication to maintain a constant concentration of the drug in the blood.
- Antibiotics for pancreatitis and cholecystitis are prescribed only by a doctor.
When is it necessary to take antibiotics?
In most patients, pancreatitis is severe. Most often, this is due to an incorrect diagnosis or late contact with a specialist. Nutrition also plays an important role. If you do not follow the diet prescribed by your doctor, exacerbations of the disease often occur, which are accompanied by severe pain and an increased risk of serious complications.
As a rule, in case of exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis or development of acute pancreatitis, antispasmodics are prescribed, which eliminate spasms and improve the passage of pancreatic juice through the ducts of the gland, painkillers and anticholinergic therapy are used