The pathological degeneration of healthy cells of the intestinal dermis into malignant cells provokes a disease called rectal cancer in humans. The exact causes of anal canal cancer have not yet been fully established, but predisposing risk factors have been identified. The initial symptoms of colon cancer do not appear immediately; they often bother the patient already in the third stage, when the risk of metastases spreading is high. Therefore, it is important to treat the disease in a timely manner and prevent the possibility of cancer recurrence.
Rectal cancer is a fatal disease that is very dangerous due to its asymptomatic course in the early stages.
Causes of rectal cancer
There are still no exact causes for any cancer, but we will try to explain some of the factors that contribute to the development of colon carcinoma.
- Alcohol.
- Smoking.
- Excess body weight.
- Poor diet - red meat, fast food, etc.
- Intestinal diseases.
- Sedentary work and sedentary lifestyle.
What does colon cancer look like?
Causes of neoplasms
In oncology, when considering the causes of cancer, some risk factors are identified that can trigger the development of a malignant neoplasm. First of all, the appearance of colon cancer is influenced by the papilloma virus. It can cause the appearance of genital warts around the anus, which sometimes transform into cancer. The disease often affects people with HIV infection, after organ transplantation, with chronic diseases of the anus, anal sex, and STDs. A high risk of developing pathology occurs with regular smoking. The use of radiation therapy as a treatment for other types of cancer also has a negative impact on the body.
Please note! Anal canal cancer often appears as a result of constant irritation of the anus due to various diseases and injuries.
Poor nutrition, a sedentary lifestyle, hereditary predisposition, and bad habits can also cause anal cancer.
https://youtu.be/KwcB2SokVPk
Classification and types of colon cancer
Usually, before starting treatment, you need to fully understand how exactly the tumor is developed at this stage? How far is the intestine itself damaged? Is there damage to muscle tissue and lymph nodes, and how far is it located from the anus?
Tumor location
| Name of intestinal section | Affected area |
| Rectosigmoid region | The distance from the anus to the tumor is more than 12 cm |
| Superior ampullary section | The distance is already from 7 to 12 cm. |
| Midampullary section | Distance from 4 to 7 cm |
| Inferior ampullary section | Up to 4 cm |
| Oncology of the anus | The tumor is located directly in the anus (near the anus) |
Types of cancer
| Type name | Description |
| Infiltrative | The tumor very quickly grows into all tissues of the intestine. |
| Endophytic | The tumor can grow throughout the entire wall of the organ and have a rounded shape on the other side. |
| Exophytic | The tumor has the appearance of a nodular coma. |
Classification by metastases
- Nearby lymph nodes are affected.
- Spread of metastases in the pelvic tissue.
- Damage to the para-aortic and inguinal lymphatic collectors.
- Metastasis to the lungs, liver and other distant organs.
By aggressiveness
- Highly differentiated - the tumor grows rather slowly and is not aggressive.
- Poorly differentiated - fast-growing malignant tissues quickly metastasize.
- Moderately differentiated - Has a moderate rate of growth and development.
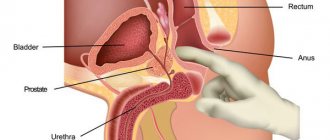
Hemorrhoids or tumor: how to recognize during rectal digital examination?
In the first stages, pain begins to bother you only during bowel movements. It does not last long and is variable in nature. Soon the pain becomes constant. You should also be aware that the pain may be located in the lower abdomen or genitals. It should be taken into account that the presence of severe pain syndromes does not mean that the tumor is no longer operable and cannot be cured.
Anal cancer has the main symptoms:
- Severe itching in the anus;
- The appearance of neoplasms in the form of small swellings and wounds near the anus;
- The presence of various discharges (bloody or accompanied by an unpleasant and pungent odor);
- history of HPV;
- Painful sensations when pressing on the anus;
- Severe fatigue and fatigue;
- If shortness of breath occurs even with little physical activity;
- There is a feeling of fullness in the intestines after visiting the toilet;
- Nausea.
Pain will accompany you at all stages of the disease. Most people suffering from anal cancer, as the first signs of the disease gain momentum, complain of severe pain in the pelvic area, some cannot even sit.
Additionally, the disease may be accompanied by constipation, but most often they are caused by worries and stress resulting from the disease. It would be more advisable to adhere to a special diet to avoid stool retention.
All patients who have an appointment with a proctologist or surgeon who express complaints from the colon must undergo a rectal digital examination.
During this examination, the doctor can palpate the inner surface of the initial part of the rectal canal (about 10 cm), determining the presence of a tumor. Also, during a digital inspection of the rectum, the difference between cancer and hemorrhoids will be in shape, consistency and extent.
Symptoms of colorectal cancer
Like many cancers, rectal carcinoma in the first stages is practically invisible and does not manifest itself in any way. In this case, the tumor can already reach the second stage - it can grow deeply and already have an impressive size before the very first symptoms.
Typically, patients present with more characteristic symptoms in the later stages, when the tumor metastasizes to nearby organs, tissues and lymph nodes. Let's look at all the signs of colorectal cancer.
Rectal cancer - first symptoms
Usually the very first sign is blood in the stool. Then you should notice small blood clots, or darkening of the stool itself. This is due to the fact that as the tumor grows it begins to damage the blood vessels.
In addition, unexplained fatigue, shortness of breath, and a constant feeling of fullness in the intestines may appear, even after bowel movements. Later, nausea and headaches appear, which are associated with severe intoxication of the body.
General symptoms
How does adenocarcinoma manifest at an early stage? Unfortunately, the first symptoms usually appear in the later stages of tumor development, then there is a sharp deterioration in the patient’s condition, severe weakness and fatigue - even after a small load the patient feels very tired.
He loses weight quickly - while he also eats normally. Later, you lose your appetite and don’t feel like eating at all. Dry skin and mucous membranes, general pallor. All this occurs due to severe intoxication from the vital activity of the tumor, as well as from heavy bleeding.
Symptoms of anal cancer
- In the stool you can find scarlet blood, which may indicate the presence of hemorrhoids, but subsequently there may be mucous and purulent discharge from the anus, and this is cancer.
- The tumor also spreads to the nearest nerve endings, which is why pain initially occurs during the act of defecation. Then subsequently the pain intensifies and the lower abdomen begins to hurt.
- Constipation is a fairly common cause that occurs due to an increase in tumors inside the intestines, which makes stool passability worse. If the tumor grows even larger, it can lead to complete blockage and fecal peritonitis.
- The patient constantly feels like he wants to go to the toilet, but after defecation nothing happens except a few purulent and bloody discharges. At the same time, the patient experiences constant stress due to dissatisfaction - it constantly seems to him that there is some kind of foreign body inside.
- Anal itching with discharge.
- If the tumor affects the nearest muscle tissue, then incontinence of gases and feces occurs - insufficiency of the anal sphincter.
- In the later stages, intestinal obstruction occurs and intoxication increases due to the abundance of stool.
Symptoms of ampullary cancer
- There are strange impurities in the stool.
- Fecal incontinence.
- Constipation and diarrhea.
- If the tumor grows into the bladder, there may be a false urge to urinate.
- In women, with the development of a vesico-rectal fistula, feces may be discharged from the vagina.
- Intestinal obstruction develops quite rarely.
Symptoms of rectosigmoid cancer
- Mucous discharge during defecation.
- Constipation.
- Bloating of the left abdomen.
- Vomit.
- Intestinal obstruction - due to tumor enlargement.
- Abdominal pain.
Among women
The cancerous tumor will first begin to affect the lymph nodes, and then attack the nearest organs. Very often, cancer spreads to the bladder and uterus. In this case, when a rectovaginal fistula develops, gases and fecal clots will begin to be released from the vagina.
In men
Pelonephritis can develop when the tumor affects the bladder, and gases and feces from the intestines can enter there. One of the symptoms is that you constantly want to go to the toilet, and subsequently, if the lesion is severe, an infection develops.
How to distinguish from hemorrhoids?
With cancer, of course, scarlet blood can be released, just like with hemorrhoids, but you must take into account that blood gets into the stool during the act of defecation, with hemorrhoids, and with a tumor it itself becomes darker in color, and the clots are in the stool itself even before excreta.
With hemorrhoids there is no clay discharge or mucus. With hemorrhoids, the stool has the same shape as during a healthy bowel movement, but with a tumor, due to the enlargement of the neoplasm itself, the stool has a ribbon-like shape. Also, with intestinal cancer, the temperature periodically rises.
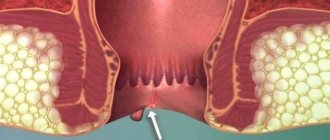
Description of anal cancer
Anal cancer is a malignant tumor of the anus, which is localized in the area between the area of the transition of the anus to the perinal skin and the upper edge of the anorectal ring. This pathology is rare and is characterized by abnormal growth of cancer cells inside and outside the anal canal. If left untreated, the cancer spreads into the tissue of the anus and rectum, filling its entire space with pathological cells. Cancer often affects the scrotum or vagina. In oncology, this type of oncology is usually classified as one of the types of skin cancer.
The disease occurs in 2% of cases among malignant neoplasms of the colon. Most often, the disease affects people over fifty years of age. Anal cancer is twice as common in people with HIV infection. With timely diagnosis, the pathology can be successfully treated.
Note! A particularly common cause of pathology among men is homosexual intercourse, in which case the risk of developing cancer increases thirty-five times.
At the initial stage, anal cancer looks like hemorrhoids, which sometimes bleed and cause pain. There are several types of pathology:
- Cloacogenic or basoloid anal cancer, in which the tumor occurs closer to the center of the anus, where the border of the transition of columnar epithelium to squamous epithelium passes. Pathology is observed in 30% of cases.
- A squamous cell tumor develops further from the center of the anal line from the outer tissues of the anus; it can ulcerate. The disease is observed in 55% of cases.
- Adenogenic cancer or adenocarcinoma of the anus, which is formed from the glandular epithelium of the anal gland.
- Glandular squamous cell carcinoma. The tumor may have a dark color due to the development of pathology from epithelial cells and mucous membranes.
Bowel cancer stages and prognosis
The malignant tumor itself takes a long time to develop, and the disease drags on for several years. At the same time, the malignant cells themselves begin to develop and grow up and down. Only after identifying the stage of the tumor can we talk about prognosis and therapy.
Stage 1
The cancer itself in the early stages is small in size - up to 2 cm. Cancer cells have a clear shape and do not extend beyond the mucous membrane of the rectum. The disease detected at this stage is treated in 80% of cases. Everything also depends on the degree of differentiation of the tumor.
Stage 2
At the second stage, metastases may already appear in the nearest lymph nodes. The tumor itself is 5 cm in size and occupies half of the inner intestine. If there are metastases, then the survival rate is 70%, if not - 75%.
Stage 3
Most pathology is detected at this stage. Metastases can spread to both the nearest lymph nodes and internal organs: bladder, uterus, prostate gland. The survival rate is 40-50%.
Stage 4
As the tumor grows, blood vessels are damaged and constant internal bleeding occurs. Plus, due to metastases, all nearby lymph nodes and organs are affected. Subsequently, it spreads to all human organs. The 5-year survival rate for patients with this diagnosis has not been reported. In the final stage, it can spread and become colon cancer.
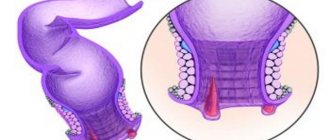
Polyposis
It is determined by chance during examination of other gastrointestinal diseases. The tumors resemble a small ball or fungus on a stalk. Polyps are harbingers of cancer of this organ, since at a late stage of development they become malignant, forming adenocarcinoma. In this case, the intestinal lumen is blocked, causing obstruction and bloating. Small neoplasias are easily removed during colonoscopy. Symptoms of polyposis include:
- pain in the groin and anal canal;
- flatulence;
- itching in the anal area;
- the appearance of mucous discharge;
- moderate but constant bleeding;
- increased frequency of stools.
Diagnosis of rectal cancer
In fact, at the moment it is possible to detect cancer at any stage, but the problem is that patients come mainly in phases 2 and 3, when the tumor is already fully developed. Let's look at all the diagnostic methods that can detect malignant cancer:
- To begin with, the doctor listens to the patient and writes down a list of complaints. He also takes into account: how the patient lives, his bad habits, nutrition and type of activity.
- Next comes the examination of the patient with palpation of the abdomen.
- The doctor conducts an examination of the rectum.
- Submission of urine and feces, as well as blood for general analysis and biochemistry.
- Colonoscopy procedure. If a tumor is found, the doctor takes a sample of cancer tissue for a biopsy.
- Next, the patient is sent for an x-ray.
- If the presence of cancer is confirmed, additional blood tests are performed for tumor markers.
- MRI, CT and ultrasound of the abdominal cavity.
Diagnosis of the disease
Let's consider ways to determine the presence of a tumor in the rectum. This diagnosis establishes the location and stage of development of the tumor.
- Palpation. Determines the presence of a tumor near the anus. Examined by inserting a finger.
- Irrigoscopy. The method involves performing radiography using a contrast agent.
- Computed tomography (CT). Used to study tumor size.
- Laparoscopy. Determines the presence and location of metastases. The optical device is inserted through the outer walls of the peritoneum.
- Ultrasound examination. It also determines the presence and location of metastases.
- Blood test for the presence of tumor markers.
- Fibercolonoscopy. A special device is used to examine the length of the colon. Allows you to obtain damaged tissue for biopsy and remove insignificant benign tumors.
- Sigmoidoscopy. This test examines up to 50 centimeters of the rectum. Allows tissue to be taken for biopsy.
Based on the data obtained as a result of the diagnosis and the general condition of the patient, the doctor will be able to build the most appropriate treatment plan.
At the first visit to the doctor, data on the presence of complaints, medical history, hereditary characteristics is collected, and a rectal examination is performed.
Next, a full blood test is performed to determine anemia. A test for tumor markers of rectal cancer and a stool test for the presence of red blood cells are prescribed.
What the study shows
- irrigoscopy;
- fibrocolonoscopy - visualize the tumor, if it is small and benign in nature - it is removed, it is also possible to perform a biopsy
- Ultrasound - determines the presence of metastases and parts of the tumor in nearby organs;
- CT scan determines the diameter of rectal cancer and the stage of the disease.
- laparoscopy.
Digital rectal examination is the main and simplest diagnostic method in the arsenal of a coloproctologist, which does not require the use of special equipment. During this manipulation, the specialist examines the rectum by inserting the index finger into the intestine. When performing a digital rectal examination, it is possible to determine the presence of intra- and extraintestinal formations at a height of up to 10 cm from the edge of the anus, assess the nature of the formation (benign or malignant), and the involvement of neighboring organs and tissues in the tumor process.
Treatment of rectal cancer
In general, when treating cancer, complex treatment using several methods is used at once. Surgical intervention is mainly used, and chemotherapy and radiotherapy are used for auxiliary therapy.
Typically, surgery is performed to remove the tumor along with nearby tissues and lymph nodes. For intestinal patency, a primary anastomosis is performed. Of course, everything depends on the degree of damage by the tumor itself. Surgery is not used at stage 4, when metastases have already spread throughout the body.
Chemotherapy is usually used as an additional treatment after surgery to remove part of the rectum. Then chemicals are introduced into the human body, which are aimed at destroying the remaining cancer cells and to control relapse.
Radiotherapy can also be used before surgery to reduce the size of the tumor itself and reduce its growth rate. Sometimes used for hopeless patients to reduce their suffering.
Is it possible to do without surgery? Actually, probably not, since this is the main type of treatment. You must understand that chemotherapy and radiotherapy do not give 100% results and do not destroy all cancer cells - that is why it is necessary to remove the tumor with all damaged tissues in a timely manner.
What is the life expectancy of patients with colorectal cancer? It all depends on when exactly the cancer was discovered and how the treatment went.
Classification
The disease in question is a set of malignant cells of different nature (histological structure of the neoplasm). In some cases, the tumor grows slowly and practically does not manifest itself, in others it quickly increases in size and is characterized by an aggressive course. For adequate treatment of rectal cancer, it is necessary to conduct a series of examinations to determine the type of tumor.
Based on the characteristics of the cellular structure, this pathology is divided into several types.
- Adenocarcinoma
It is often diagnosed in people who have crossed the 50-year mark. The basis of its structure is glandular tissue. There are several degrees of differentiation of adenocarcinoma (lower differentiation means worse prognosis). This type of tumor is most popular among rectal cancers.
- Signet ring cell carcinoma
When examining the structure of this tumor microscopically, you can see a narrow rim (similar to a powerful ring), in the center of which there is a lumen. It is not detected as often (3%) as adenocarcinoma, but it is characterized by an unfavorable outcome. The average life expectancy of patients with this type of rectal cancer often does not exceed 3 years.
- Squamous cell carcinoma
It is less common (2%) than the two previous types of rectal cancer. Characterized by a tendency to rapid metastasis. The main location of this type of tumor is the anal canal area. There is an opinion that squamous cell carcinoma of the rectum occurs due to exposure to human papillomavirus infection.
- Solid cancer
Formed as a result of the fusion of poorly differentiated cells, which are glandular. Determining the exact nature of solid cancer cells is problematic: the sheet-like arrangement of these components of a malignant neoplasm is characteristic.
- Scyrous cancer
The main component of neoplasms of this pathology is the intercellular substance. The number of malignant cells here is limited.
- Melanoma
Localized in the anal canal area. Predisposed to early appearance of metastases. Represented by pigment cells (melanocytes).
The direction of rectal tumor growth may vary.
- A malignant tumor can grow into the rectal cavity ( exophytic cancer ).
- The tumor can be localized in the walls of the rectum without extending beyond them ( endophytic cancer ).
- Cancer cells can be fixed in the lumen and walls of the rectum. In such cases, a mixed form of rectal cancer .
Prevention
https://youtu.be/Z62NL-2zRzc
- Some diseases of the rectum give rise to further development of a cancerous tumor. That is why you should not delay treatment: hemorrhoids, fistula, anal fissures, etc.
- Prevent constipation and consult a doctor if it occurs frequently.
- Eat less red meat and junk food. Try to eat more plant foods.
- Try to give up alcohol and smoking, as well as exposure to chemicals.
- Try to move more and lead an active lifestyle.
- Be sure to be examined by a doctor once a year and take a general and biochemical blood test.
( 2 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)