Gastritis affects older and younger people. In the first stage of the disease, the antrum of the stomach is damaged. If the disease is not treated, it develops into chronic gastritis. The disease manifests itself in “hunger pains,” usually occurring in the morning. I suffer from heartburn. Often the symptoms and treatment of gastritis are similar to peptic ulcers. With gastritis, belching appears with a sour taste, and constipation begins.
For a long time it was believed that gastritis begins from poor nutrition or is inherited. It later turned out that the bacterium Helicobacter Pylori was to blame. One of the factors that helps fight the disease is a special diet. But you can’t help with just proper nutrition; you will need to be treated with medications.
Bacteria Helicobacter pylori
When scientists discovered that Helicobacter causes type B gastritis and gastric and duodenal ulcers, a new stage in the treatment of diseases began. Researchers have developed new therapies based on getting rid of Helicobacter pylori using a combination of different drugs. The technique includes therapy with antibiotics and medications that reduce the secretion of stomach acid and create poor conditions for the life of Helicobacter. Not all people who are carriers of Helicobacter develop gastritis. In each individual case, if Helicobacter is detected in the body, consultation with different doctors is necessary to determine the degree of need for treatment. World medicine uses standards that determine what conditions a person will need to be treated for.
Antibiotics for gastritis caused by Helicobacter are used:
- if gastritis is accompanied by a stomach or duodenal ulcer;
- for cancer, in a precancerous condition of the stomach;
- for MALT lymphoma.
Doctors consider it mandatory to treat gastritis caused by Helicobacter pylori if functional dyspepsia and gastroesophageal reflux are present. Or if the patient is additionally treated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Modern schemes for combating Helicobacter are quite effective. In 80% of cases, it is possible to completely recover from helicobacteriosis. The therapy is safe for patients. Up to 15% of those treated experience side effects. The duration of taking the drugs is short. After 10 days, it is possible to completely get rid of Helicobacter. If the chosen antibiotic is not suitable for the patient for a certain reason, the drug is replaced with other medications.
What type of gastritis is called Helicobacter pylori?
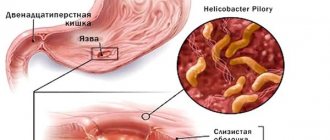
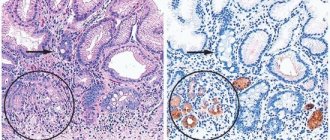
Helicobacter are gram-negative bacteria with a spiral shape. Their size is 3 microns. The multiplication of the microorganism does not require a lot of air, which makes the human digestive organs a good environment for their life. Bacteria are capable of secreting urease. This is a crystalline substance that inhibits the action of gastric enzymes, which over time provokes the development of inflammation. Helicobacter also secretes mucinase, which affects the protein produced in the stomach, causing the mucus to become more liquid, which helps the proliferation of pathological cells in the stomach and the formation of inflammation. Additionally, Helicobacter pylori is capable of producing cytotoxins, which can destroy organ walls at the cellular level; if the substance is not produced, a person faces a disease such as chronic Helicobacter pylori gastritis.
The disease is characterized by an inflammatory process in the stomach, which develops as a result of bacteria such as Helicobacter pylori entering the body. This can happen through food, dirty hands, and a host of other ways. The pathology is called B-type gastric inflammation. Not all Helicobacter bacteria cause inflammation. The development of the disease is directly related to the state of the immune system, which is why many of us are carriers of microorganisms.
Helicobacter pylori
The bacterium Helicobacter pylori is one of the most common human infections. In the world, at least 50% of the population is infected with Helicobacter pylori. In Russia, this microorganism is detected in 80% of people over 18 years of age [1, 2].
The discovery of Helicobacter pylori infection in 1983 caused revolutionary changes in ideas about the causes of the development of many common diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. The authors of this discovery, Australian scientists Robin Warren and Barry Marshall, were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2005 [3].
The image is artistic. Prepared based on the description of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori given in sources 4, 5.
Helicobacter pylori is a spirally curved rod with flagella at one end. The habitat of Helicobacter pylori in the human body is the stomach and duodenum. The bacterium either moves freely in the mucus layer using flagella, or attaches to the epithelial cells of the mucous membrane. Helicobacter pylori is one of the few microbes that have adapted to living in conditions of high acidity of gastric juice [4, 5].
Forms of gastric damage
There are several forms of damage to h. bacteria:
- latent - a person is a carrier of a pathological microorganism, but there are no external signs of the disease, so its presence can be diagnosed only by examining the mucous membranes;
- acute gastritis - the symptoms of the disease are hard to miss;
- chronic gastroduodenitis - inflammatory processes develop not only in the stomach, but also in the duodenum, which is externally manifested by swelling, erosion and pronounced inflammation;
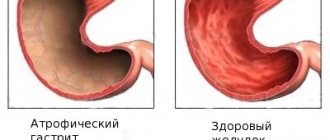
- chronic atrophic gastritis - pathological processes begin to develop in the antrum, spreading to the entire stomach;
- peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum - the disease develops due to the chronic form of Helicobacter gastritis.
Diet
The importance of dietary nutrition in the treatment of gastritis can hardly be overestimated, since if dietary requirements are neglected, the recovery processes will slow down. All products that are included in the daily menu of a patient with Helicobacter pylori gastritis should not irritate the gastric mucosa, but contribute to its restoration. Food entering the stomach must be properly prepared by boiling it or using the steaming method. Dishes should not be fried, smoked, contain hot seasonings or sauces, have no solid particles, or cause difficulty in digestion.
You need to take food at least five to six times a day, using small portions at a temperature comfortable for the stomach. Alcohol, strong brewed tea and coffee are completely avoided. During the period of exacerbation, it is important to follow a strict diet, and after eliminating the painful symptoms, it includes some relaxations. The patient’s menu is compiled individually based on his state of health and the stage of the disease, as well as the presence of concomitant diseases and the possibility of exacerbations.
Causes of the disease
The Helicobacter type of gastritis spreads quite easily between people, since the infection can be transmitted from one patient to another (drinking from the same mug), due to poor hygiene (poor dishwashing).
The pathogenesis of the disease is as follows:
- Helicobacter settles in the body and inhibits the aggressiveness of the gastric environment;
- pathogenic organisms multiply;
- with the help of antennae, the bacterium “screws” into the mucous membranes (usually the antrum is the first to be affected);
- the bacterium that causes stomach ulcers secretes certain substances that destroy the walls of the organ, which is accompanied by an inflammatory process;
- Helicobacter pylori destroys organ tissue at the cellular level, causing hp-associated gastritis;
- Damaged tissues erode over time, which can lead to peptic ulcers.
Helicobacter pylori
The bacterium Helicobacter pylori is one of the most common human infections. In the world, at least 50% of the population is infected with Helicobacter pylori. In Russia, this microorganism is detected in 80% of people over 18 years of age [1, 2].
The discovery of Helicobacter pylori infection in 1983 caused revolutionary changes in ideas about the causes of the development of many common diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. The authors of this discovery, Australian scientists Robin Warren and Barry Marshall, were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2005 [3].
The image is artistic. Prepared based on the description of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori given in sources 4, 5.
Helicobacter pylori is a spirally curved rod with flagella at one end. The habitat of Helicobacter pylori in the human body is the stomach and duodenum. The bacterium either moves freely in the mucus layer using flagella, or attaches to the epithelial cells of the mucous membrane. Helicobacter pylori is one of the few microbes that have adapted to living in conditions of high acidity of gastric juice [4, 5].
Typical symptoms
Typical symptoms are constipation.
which alternate with diarrhea. The clinical manifestation of hp gastritis does not differ from other types of pathology:
- severe pain in the epigastrium, especially after a meal;
- the stomach hurts when food does not enter it for a long time;
- burning in the esophagus;
- belching with a sour or bitter taste;
- constipation alternates with diarrhea;
- a dense white coating (plaque) forms on the tongue;
- when an infectious infection expands localization, spreads to the entire organ, the desire to eat disappears;
- nausea;
- constantly thirsty;
- after a small amount of food, heaviness appears in the organ;
- flatulence;
- metallic taste in the mouth;
- rash on the body;
- stomach growls;
- unpleasant odor from the mouth.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing hp infection can be quite simple. After collecting an anamnesis, visual examination and palpation of the abdominal cavity, the doctor can assume the presence of gastritis and send the patient to undergo diagnostic procedures, which will help determine the type of disease and determine adequate therapy. If the disease has responded to therapeutic procedures, finding Helicobacter pylori is much more difficult.
During treatment
Breath test for Helicobacter.
Scheme of instrumental diagnosis of hp gastritis:
- breath test;
- X-ray examination;
- analysis of secretory function;
- biopsy;
- fibrogastroscopy;
- histological analysis of tissues;
- serological study.
Laboratory tests for HP infection:
- enzyme immunoassay blood test;
- analysis of stool for the presence of antigen.
After therapy
After therapy for Helicobacter pylori gastritis, the cause of the development of the pathological process is more difficult to diagnose using histological analysis, since the bacterial background of the disease can change the morphological structure (cocci predominate). In addition, pharmaceutical therapy destroys a significant portion of bacteria, making their diagnosis difficult.
Prevention
If a person does not have gastritis and does not want to get sick, he will need, first of all, to lead a healthy lifestyle, eat right and remain careful while taking any medications. If symptoms of gastritis appear, it is recommended to consult a doctor as soon as possible in order to correctly diagnose the disease and prescribe appropriate treatment.
To prevent Helicobacter pylori infection, you can drink 1 teaspoon of rosehip syrup daily. The effective remedy is used for a month. After a month of taking the syrup, take a break for two weeks. And if there is a need to resume taking it for preventive purposes, the course is repeated.
It is imperative to observe the rules of personal hygiene. Before eating - wash your hands, after using the toilet - wash your hands, never use dirty dishes and towels. Do not use other people's personal hygiene items. If a family member has been diagnosed with Helicobacter pylori infection, the rest of the family members also need to undergo a medical examination to detect Helicobacter pylori.
Treatment
If HP gastritis has been detected, the patient is recommended for complex treatment, the regimen of which includes the simultaneous use of:
- medicines;
- diets;
- folk ways.
Medicines
There are several drug therapy regimens. First of all, they are aimed at relieving the symptoms of the disease and eliminating helicobacter pylori. Usually the patient is prescribed:
- antibiotics that belong to macrolides (destroy h. bacteria), for example, Amoxicillin tablets;
- drugs that inhibit the secretion of hydrochloric acid;
- antimicrobial agents (“Metronidazole”);
- bismuth preparations (“De-nol”, “Vicair”);
- proton pump inhibitors (inhibit the secretion of gastric juice), for example, Omeprazole tablets.
The treatment regimen with antibiotics and auxiliary drugs involves their use for 1-2 weeks. If the drugs do not help and the patient’s health does not improve, others are prescribed that have similar properties or the dosage of the drugs already used is changed. Such manipulations should be performed exclusively by a doctor.
Traditional medicine recipes
For cholecystitis, the use of flax seeds is prohibited.
Healers are sure that h. Gastritis can be cured using folk remedies. Grandmother's recipes cannot be used as the only therapy for this type of pathology, since it is impossible to get rid of HP bacteria without antibacterial medications. Before using this method as an auxiliary one, you should consult a doctor. There are many recipes using a variety of herbs and botanicals. The most popular method of folk therapy is the use of honey and propolis or flaxseed.
- Honey with propolis. These products are derived from the activities of bees. They are considered a safe and effective remedy for almost all existing diseases, including h. gastritis. There is a positive trend in the use of these substances in conjunction with basic drug therapy. It is noticed that patients become healthy faster. This is explained by the fact that honey and propolis are active immunostimulants. Their use helps the immune system quickly cope with pathology.
- Flax-seed. An infusion of flaxseed is a good herbal analogue of inhibitors, since the product envelops the stomach, thereby protecting it from the effects of bacteria. In addition, it has anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. The drug relieves the symptoms of the disease, including pain. It should be remembered that patients who suffer from cholecystitis are prohibited from using flax seeds.
Diet
Nutrition plays an important role in the treatment of gastritis. It should be aimed at eliminating additional irritants. The patient should eat at least 6 times a day. It is necessary to limit the amount of salt in the diet. The diet requires drinking plenty of fluids (at least 2500 ml per day). Food should not be cold or hot. The menu should be selected individually for each patient.
Allowed dishes:
- weak meat broth;
- jelly;
- slimy porridge on water;
- vegetable puree;
- stale bread, etc.
Therapy
For gastritis with high acidity, a whole range of treatment procedures is prescribed, which includes medications, diet and decoctions of medicinal herbs. Here is an approximate composition of the course:
- antibiotics that destroy bacteria;
- antispasmodics that relieve pain;
- remedies for flatulence and bloating;
- antiemetics;
- enzymes that help the stomach digest food;
- probiotics that normalize microflora, for example, Bifidumbacterin.
The specific names of the drugs may change because there are different drugs that work the same way.
Bifidumbacterin is indispensable for gastritis with high acidity - it reduces the aggressiveness of the environment and helps regulate stool. It can also be taken for other types of gastrointestinal disorders, especially if antibiotics are prescribed.
The bacterium, which causes gastritis due to its own waste products, can increase or decrease acidity in the body. To normalize it and reduce discomfort, you can drink decoctions of medicinal herbs.
With high acidity, it is best to take infusions from plants such as calendula, chamomile, yarrow, and with low acidity, knotweed, plantain, and trifoliate.
How to prepare a decoction (infusion)
If you buy dried mass at a pharmacy, the preparation method is usually indicated on the packaging. But decoctions of freshly picked and dried herbs are many times more effective: they are more concentrated and give a rich color. To prepare a medicinal drink, you need to take herbs in a ratio of 1:10. For a hundred gram glass of decoction you will need 1 tbsp. spoon of chopped plants. The grass is poured with boiling water and covered with a lid or plate. The decoction should not be drunk hot; it must be cooled until barely warm. It is advisable not to store it for more than 8 hours.