The hepatitis C genotype is represented by a specific set of genetic information of the pathogen. Under the general name of the disease there are several types of viruses. They are classified into types and quasitypes.
Modern medicine knows 11 genotypes of viral hepatitis C, but WHO recognizes only 6 main varieties. Conventionally, they are designated by numbers and have many subtypes.
Types of viral agents, which genotype of hepatitis C is the most dangerous, why genotyping is carried out, how much research costs - we will consider in detail.
What is a phenotype in biology
This is the totality of hereditary information in the body. In other words, it is the sum of genes that forms a single system.
Unlike the gene pool, it describes not the entire species, but an individual.
A phenotype in biology is a set of characteristics formed on the basis of a genotype. However, under the influence of the environment, the set of properties can change, which is why individual differences appear.
Based on the properties of an organism, it is not always possible to understand what genotype an individual has. Organisms can have the same set of properties even with a different set of genes. For example, a red flower can have both “AA” and “Aa” genotypes. In this case, analytical crossing is used to determine the set of genes.
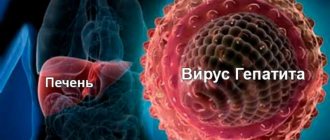
Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) is dangerous not only because of its hidden symptoms. The pathology can destroy a person’s liver for years without causing significant clinical manifestations. Based on the differences in the order of amino acid residues, experts identify several varieties of the viral pathogen.
Hepatitis C genotypes vary in symptoms, rate of progression of necrotic liver lesions, and likelihood of complications. It is the genotype that is the fundamental factor in the selection of effective therapy.
From time to time, information appears in the medical literature about the discovery of a new type of viral infection. As a result, data on how many genotypes hepatitis C has varies.
Some experts call the number 11 (excluding quasi-types).
But practicing hepatologists are guided by the recommendations of the World Health Organization (WHO), according to which 6 genotypes of the HCV virus are distinguished.
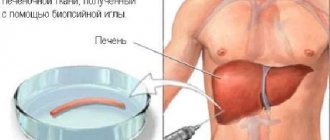
Molecular diagnostic methods make it possible to accurately study the structure of a pathogen found in a patient’s blood plasma or liver tissue biopsy. In this way, specialists can accurately determine the type of pathogen, and based on the results obtained, the doctor prescribes appropriate therapy.
Hepatitis C virus is a single-chain virus from the genus Hepacivirus, with a diameter of 50 nm. It has a high rate of spread.
HCV genotypes represent genetically different groups of the virus that arose during its evolution. Genotyping is a way to place the hepatitis C virus into categories based on similar genes.
- The hepatitis C virus has eleven genotypes, labeled 1 to 11. There are also subtypes, designated by letters, such as genotypes 1a and 1b;
- According to the World Health Organization (WHO) classification, there are 6 main genotypes of the virus that are of clinical importance;
- Most people have one dominant genotype of the hepatitis C virus, but it is possible to have more than one at the same time. This condition is called mixed infection.
The genotype of the virus usually remains unchanged. Genetic changes or mutations can occur randomly or in response to environmental influences. Some mutations are harmless, but others can affect how well a patient responds to treatment.
New treatments for hepatitis C include two or more drugs to prevent drug resistance by targeting more than one step in the virus's life cycle. However, if patients miss doses of medication, this can lead to genetic mutations that cause resistance to HCV treatment.
Knowing the genotype of hepatitis C is important information that can help patients and doctors find the most effective treatment, predict its course and duration.
Because of the geographic location of individual hepatitis C virus genotypes, genotyping them can be a useful tool for tracing the source of an outbreak. For example, genotyping and molecular characterization of HCV isolates have provided evidence for the possibility of transmission of hepatitis C virus during colonoscopy.
All hepatitis C genotypes cause approximately the same liver damage. However, people infected with genotype 1, especially subtype 1b, may be more likely to develop cirrhosis or severe liver scarring than those with other genotypes. And genotypes 1b and 3 may increase the risk of developing liver cancer.
Hepatitis C genotypes are important epidemiological markers. Differences between genotypes in pathogenicity are unclear and unproven. In combination with other markers, such as quantification of HCV RNA, genotyping may be useful in the management of chronic hepatitis C and in the selection of candidates for interferon treatment.
A person of any racial or ethnic group may have some genotype or subtype of hepatitis. However, some hepatitis C genotypes may be more common in certain countries or ethnic groups.
People who travel between regions where different genotypes are more common may be exposed to different HCV genotypes, resulting in mixed infection.
Although hepatitis C genotypes 1, 2 and 3 have spread throughout the world, its relative prevalence varies from one geographic area to another. The most common genotypes in Russia, Europe and the United States are subtypes 1a and 1b.
Treatment regimen
The treatment protocol is selected individually. In this case, the doctor takes into account the presence of cirrhosis and its form (compensated or decompensated), coinfections (for example, antiretroviral drugs are not combined with some antiviral drugs).
Also, treatment tactics differ depending on whether hepatitis C is diagnosed for the first time or the patient repeatedly consults a doctor with a similar problem.
Antiviral course
| Medicines used | Duration of treatment and dosage features |
| Asunaprevir (0.1 g) + Daclatasvir (0.06 g) | Indicated for genotype 1b, standard dosages (1 tablet per day) for 12 or 24 weeks |
| Asunaprevir + PEG-IFN + Ribavirin | Asunaprevir is used in a dose of 0.1 g, interferons and ribavirin are dosed depending on weight, the duration of therapy is 12 or 24 weeks |
| Sofosbuvir (0.4 g) + Daclatasvir (0.06 g) | 1 tablet of each drug for 12 or 24 weeks (if liver cirrhosis is present) |
| Sofosbuvir and Ledipasvir (0.4 g) + (0.09 g) | Dosages are also standard. The usual duration of therapy is 12 weeks, with aggravating factors - 24 weeks |
| Sofosbuvir (0.4 g) + Velpatasvir (0.1 g) | Treatment tactics are the same - 12 or 24 weeks |
| Viqueira PAK | 12 weeks |
| Maviret | From 8 to 16 weeks depending on the condition of the liver |
Viral load control
Throughout the course of therapy, the attending physician issues referrals for tests to assess how effective the treatment is. The main criterion for a positive result and sustained virological response (SVR) is negative indicators of qualitative and quantitative PCR.
These studies are carried out several times: at week 4 of taking medication, at week 12, and additionally at week 24 if the patient is prescribed a longer course of therapy.
Some doctors recommend additional quantitative PCR testing in the second week of treatment. A predictor of effectiveness is a decrease in viral load. But such research is not mandatory.
If the result is negative at 4 weeks, they speak of a rapid virological response, which increases the chances of a full recovery. But PCR must also be taken after the end of therapy - at 24 and 48 weeks. At the same time, I recommend doing a qualitative study, since it is more sensitive than quantitative. Maintaining a negative result means that the person is completely cured.
At the same time, liver function tests must be checked. Normalization of physiological parameters indicates restoration of organ functions.
Diet
Patients with the first type of HCV are advised to strictly adhere to diet No. 5 with a complete abstinence from alcohol. All foods containing solid, indigestible fats, snacks, fast food, etc. are also excluded.
It is recommended to eat small meals, consume low-fat fermented milk products, cereals, vegetables and fruits (with the exception of too acidic varieties and legumes). They advise you to drink more. Compotes, juices, tea are allowed. Coffee should be limited.
Subsequently, it is possible to expand the diet, but the timing of abandoning a specialized diet depends on the results of treatment and the condition of the patient’s liver. It is prohibited to switch to the previous diet on your own. Adding new dishes and products to the menu is possible only after consulting a doctor.
Types of hepatitis C virus genotype
There are currently 11 varieties, and the disease is considered extremely mutagenic. The first 5 types are important for diagnosis. In particular, subtypes: 1a, 1b, 2a, 2b, 3a.
The first genotype is considered the most dangerous of the species. The probability of cure in this case is no more than 50%. This is a low figure. It also has the longest duration of therapy, which is at least 48 weeks. Patients whose bodies contain this type of virus must carefully follow medical recommendations and closely monitor their health.
The most effective fight is observed by doctors in the case of genotypes 2 and 3. They are easier to treat than others. The probability of recovery is 80%. The treatment period is halved compared to genotype 1.
The first three species are widely distributed throughout the world. In Eastern and Western Europe, cases of hepatitis with viruses of genotypes 1 and 2 are recorded more often than others. In America, species 1a and 1b are common. Residents of African countries suffer from hepatitis with genotype 4.
Residents of the Russian Federation have remarkable statistics. In the blood of about 50% of patients, virus 1b is detected, 20% - 3a, 10% - 1a, 5% - 2.
Why is genotyping needed?
Since the course of various forms of the disease often leads to fatal complications (liver failure, cirrhosis, cancer), and its early detection due to the absence of symptoms is impossible, timely accurate diagnosis is necessary.
Due to constant mutations of the hepatovirus, the human body cannot develop stable immunity to it.
If antibodies to the virus are detected in the blood, hepatitis C genotyping is required using the PCR method, which allows:
- choose the right treatment regimen and dosage of drugs;
- determine the timing of therapy;
- evaluate its effectiveness;
- If there are complications, determine the need for surgical intervention.
In some cases, in the presence of antibodies and high liver tests, determination of the genotype gives a negative result. This indicates the presence of a rare type of virus - many laboratories in the Russian Federation do not have drugs for genotypes C5 and C6. In this case, the blood is delivered to a specialized medical center.
Hepatitis C genotypes
Every year, the hepatitis C virus, discovered in 1989, takes the lives of millions of people on our planet. Today, this extremely insidious and dangerous virus is put on a par with diseases such as AIDS, syphilis and cancer.
And although modern medicine has made significant strides in the study of the virus, its etymology and modes of transmission, a vaccine against hepatitis C has not been developed to date, and treatment of the disease is very difficult and expensive.
Despite the fact that modern medicine has already discovered 11 genotypes of hepatitis C, the World Health Organization recognizes only 6 main strains.
Viral hepatitis C is a serious disease that requires timely diagnosis and proper treatment. Otherwise, complications arise that worsen the patient’s standard of living. The main factor in effectively combating the disease is a well-designed treatment plan.
To do this, it is necessary to determine the genotype of the hepatitis C virus. As a rule, a person is a carrier of only one type. However, in practice there are cases when an organism contains two genotypes. In this case, the doctor will prescribe treatment, which will contain an individual scheme.
Human phenotypes are characteristics inherent to an individual at a given point in time. In other words, it is a set of properties of an organism.
| View | Subspecies | Characteristic |
| 1 | 1a | Most common in all territories |
| 1b | Makes up 40% of all genotypes | |
| 1c | More often affects young people | |
| Most dangerous | ||
| 2 | 2a | Has a favorable prognosis |
| 2b | Rarely becomes chronic | |
| 2c | Treats well | |
| 2d | Is 1/20 | |
| 3 | 3a | The most common third genotype of hepatitis C liver |
| 3b | Has high contagiousness | |
| 3c | More often diagnosed in injection drug addicts | |
| 3d | ||
| 3e | ||
| 3f | ||
| 4 | 4a | Rarely detected |
| 4b | ||
| 4c | ||
| 4d | ||
| 4e | ||
| 4f | Characteristic of Western populations | |
| 4h | ||
| 4i | ||
| 4j | ||
| 5 | 5a | Isolated cases recorded |
| 6 | 6a | Rarely seen |
Genotypes are types of viruses that differ from each other in their set of genes. They may have their own subtypes (quasi-types), which, due to their unstable genetic material, constantly mutate and change.
Hepatitis C genotypes are conventionally designated by numbers from 1 to 6, are unevenly distributed throughout the world and have a large number of subtypes.
Distribution of HCV genotypes in the world
According to statistical data obtained by WHO from around the world, genotypes 1-3 have been recorded in all corners of our planet, while genotype 4 is most widespread in North America, and genotype 6 in South Africa.
If we talk about the age distribution, scientists note that quasi-type 1b is predominantly found in adults (52%), while in children it is diagnosed only in 25% of cases. At the same time, genotypes 5 and 6 were not identified at all in the child population.
Interestingly, in recent years there has been a tendency towards an increase in the prevalence of genotype 2 and a decrease in the level of quasi-type 1b.
In approximately 9% of cases, more than one type of HCV virus is diagnosed in the blood of patients. In this case, they speak of a mixed genotype of hepatitis C.
Features of hepatitis C genotypes
The hepatitis C virus is characterized by high variability in its genetic structure. It is the ability to mutate that makes treating the disease difficult. Essentially, the hepatitis C virus is a collection of viruses classified into genotypes and subtypes. Hepatitis C virus genotypes include 11 subspecies. But WHO identifies only 6 main ones, which are found everywhere.
Is it possible to cure genotype 1 hepatitis C?
The disease can be cured if it does not develop over a long period of time and is detected in the early stages. The virus causes serious complications that cannot be cured:
- cirrhosis;
- fibrosis;
- malignant tumors;
- diseases of the gallbladder and ducts;
- hepatic coma.
The treatment regimen for hepatitis C genotype 1 is selected taking into account the damage to the organ in order to reduce and stop the multiplication of the viral infection.
After confirming the diagnosis, the main question that worries the patient is: “Is it possible to cure the pathology?”
Complex forms of pathology, for which “classical” therapy with sofosbuvir in combination with other antiviral agents is ineffective, can be cured with modern medications containing fixed dosages of active ingredients, for example, Maviret or Viqueira Pak.
Considering the high cost of original drugs, treatment of genotype 1 hepatitis C with Indian drugs (generics), completely similar in composition, is becoming increasingly popular. For comparison, a course of taking original medications registered in Russia will cost almost $100,000, and using generics will cost up to $1,000–2,000. But the final decision on how to treat the disease must be made by the doctor, taking into account the financial capabilities of the patient.
Which types have the most favorable prognosis?
The second type of viral infection is easier to treat, but it is practically not diagnosed in Russia. Therefore, when asked which genotype of hepatitis C is best treated, domestic infectious disease specialists usually name the third type. Although this group of pathologies is often accompanied by various kinds of complications, there is a high probability of complete recovery provided that timely diagnosis is made.
The third subtype of the disease is not the easiest, but with the use of modern antiviral drugs, recovery is possible without a significant impact on the patient’s life expectancy. To reduce the likelihood of a severe course of the pathology, it is necessary to follow all the doctor’s recommendations and strictly adhere to the diet prescribed by the doctor.
After recovery, you should continue taking medications that have hepatoprotective activity. The rules regarding diet and avoidance of alcoholic beverages also remain.
HCV infection is not accompanied by the formation of specific immunity. Therefore, the previous illness does not exclude the need to comply with all preventive measures in the future.
Prevalence and possibility of infection
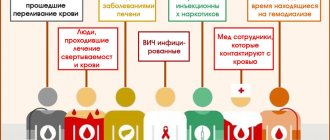
There is a risk of infection due to blood transfusion.
Genotype 1b is diagnosed in patients who have undergone blood transfusions. This is a common route of transmission. It is possible that 1b may be associated with genotype 3, subtype a, which is called “mixed infection,” and this negatively affects the clinical picture and sensitivity to therapy. Genotype 2 is better treated than all other types of the disease. This is due to the typical structure of the genetic material, which is destroyed under the influence of small doses of interferons.
Genotype 3a of the hepatitis C virus is diagnosed in patients who abuse drugs that are administered intravenously. The use of unsterile needles leads to the rapid spread of this disease among this part of the population and accounts for 1/5 of all patients. Types 4-6 were discovered relatively recently, so this infection is recorded. According to research published in the journal Pharmacist Practice, these types of hepatitis C will soon spread throughout the population.
Varieties 4, 5, 6
Genotype 4, as well as 5 and 6 varieties of HCV, are the least diagnosed. Most domestic laboratories do not even provide for the determination of such types of virus. A test for these groups of hepatitis C is prescribed only if the result is negative for the determination of types 1–3. Due to their low prevalence, these types of pathologies have not been sufficiently studied.
It has been established that they are characterized by:
- predominantly acute course;
- high probability of an effective immune response and self-healing;
- long latent course without increasing the parameters of viremia;
- low risk of complications (there are practically no cases of liver cancer in patients with types 4, 5 or 6).
The fourth genotype is divided into 10 quasi-types. As for the fifth and sixth, today only one subgroup is known - a. Therapy for these types of HCV is not difficult. A standard course of pangenotypic antiviral agents is sufficient. But the likelihood of complications during the infection increases if the infection occurs against the background of liver tissue damage.