The mucous membrane of a woman’s vagina must be constantly moisturized. This process is supported by the regular secretion of mucus by epithelial cells under the influence of sex hormones. The secretion protects the genital tract from pathogens, as well as injuries during sexual intercourse. Normally, the amount of vaginal discharge should not be significant, have an unpleasant odor or irritate the skin and mucous membranes. A healthy woman experiences virtually no discomfort. If a large amount of secretion appears, causing itching, burning, redness, or having a strong and unpleasant odor, you should immediately consult a gynecologist. Such signs most often indicate an infectious-inflammatory process that requires adequate treatment. Leucorrhoea can differ in its nature, cyclicity, color, quantity, and effect on surrounding tissues. This depends on the type of microflora actively reproducing in the genital tract. As a rule, a large number of leukocytes (purulent inflammation) gives the green color to the discharge. This is often observed with STDs (chlamydia, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, mycoplasmosis), bakvaginosis, acute endometritis and salpingoophoritis.
Trichomoniasis
This is a protozoal infection with sexual transmission. Statistics show that every tenth sexually active person on the planet suffers from it.
Trichomonas vaginalis is a unicellular microorganism with flagella, thanks to which its movement occurs. After infection, symptoms of the disease appear early, after 3-5 days.
Trichomoniasis in women is characterized by the following symptoms:
- 1 Copious, purulent, often foaming gray-yellow or green discharge with an unpleasant, pungent odor.
- 2Irritation, redness of the walls of the vagina, its vestibule, labia, urethral opening.
- 3Itching and burning.
- 4Frequent painful urination.
- 5Dyspareunia (pain during sex).
- 6Nagging pain in the lower or lateral abdomen.
In the postpartum period, postmenstrual days, and the first week after an abortion, the chances of infection with Trichomonas are increased.
Drugs of choice for treatment: Metronidazole, Tinidazole (in tablet form, course 5-7 days); Additionally, metronidazole vaginal tablets can be prescribed once a night for 6 days.
https://youtu.be/qqBR_7hVDnI
Medicines
The treatment regimen for green discharge consists of the personal characteristics of the body and the infectious cause that provoked the pathological changes.
In most situations, the following medications are prescribed:
- For sexually transmitted infections and inflammation therapy, more than 200 drugs from the penicillin category can be used - Bicillin, Tetracycline, Ceftriaxone, etc.
- Vaginosis is treated with Metranidazole in the form of suppositories, gels, and tablets. Initially, vaginal sanitation is carried out with etiotropic treatment with individual selection of the course and dose of Metranidazole.
- When treating candidiasis with green discharge of a cheesy, odorless consistency, the administration of intravaginal capsules, which include a combination of the antibiotics Neomycin and Polymyxin, will be effective. It is possible to use both vaginal tablets and Clotrimazole and Fluconazole cream.
As symptomatic therapy to eliminate itchy signs that accompany many pathogenic processes, the following are prescribed:
- Vaginal suppositories are good at eliminating itching and unpleasant odor - suppositories Fluomizin, Clindacin. Antifungal suppositories – Terzhinan, Klion.
- Cooling compresses and baths using medicinal herbs - chamomile, string, horsetail, burdock, oak bark.
- Antiallergic drugs – Suprastin.
Vaginal disorders should not be left unattended, since their prolonged course becomes chronic, causing complex consequences that are difficult to treat.
Bacterial vaginosis
Gardnerella vaginalis (gardnerella) is a representative of the normal microflora of the vagina, therefore, under optimal conditions (microflora balance), it does not cause disease.
When the number of lactobacilli begins to decrease (pregnancy, vitamin deficiency, dysbacteriosis, severe somatic pathologies, violation of intimate hygiene rules, uncontrolled use of antibiotics, menopause, frequent douching), gardnerella actively multiply and lead to inflammation of the vaginal mucosa in women and girls.
In addition to Gardnerella, other microorganisms are also important; their number in a woman is assessed using the Femoflor test system.
The main symptom of bacterial vaginosis can be considered the appearance of yellowish, white-gray, white-green, greenish leucorrhoea with the smell of rotten fish and herring. They are often abundant and liquid, but can also be viscous and thick. In addition, itching and burning in the vagina and discomfort may occur.
The following drugs are used for treatment:
- 1Metronidazole in the form of tablets or 0.75% vaginal gel. The duration of the course is at least 7 days.
- 2 Clindamycin, vaginal cream 2% - at least 7 days.
- 3 Local treatment of bacterial vaginosis: combined suppositories (Hexicon, Terzhinan, Neo-Penotran), douching with Chlorhexidine or Miramistin.
Treatment at home
You can cure discharge at home. However, it is important to use complex therapy, which will include medications and traditional medicine methods. It is important to approach this issue responsibly and follow the recommendations of a specialist. How to treat the disease?
- Proper nutrition. High-quality nutrition and a light diet will restore all functions in the body. It is necessary to exclude fried, salty and canned foods. It is important to include fresh juices based on spinach, celery and parsley in your daily diet. Strawberries, lingonberries, barberries, blueberries and viburnum will complement your daily nutrition.
- High-quality intimate hygiene. Proper personal hygiene will help you avoid many problems with women's health. It is important to maintain the natural microflora of the vagina, which itself is capable of protecting the body from many infections. You are allowed to wash yourself no more than 2 times a day, using special hygiene products. You need to dry yourself with an individual towel made from natural fabrics.
- Douching. The procedure is beneficial if performed only when necessary. Initially, you need to prepare a decoction. For this purpose, mistletoe leaves, oak bark, eucalyptus, calendula, and St. John's wort are used. To prepare the medicine, take 1 tbsp. spoon of dry raw materials and pour 0.5 liters of boiling water. The decoction should steep for 30 minutes. After which everything is filtered and given time to cool.
Use of tablets
Medications are prescribed comprehensively, that is, for local use (suppositories or vaginal tablets), and in advanced cases, drugs with extensive action are recommended. As a rule, gynecologists recommend the following medications:
- Fluconazole has many analogues, which contain the same active ingredient (Mikosist, Flucostat, Mikoflucan, Diflucan, Diflazon, Ciskan);
- Orunit, the drug has many analogues (Itraconazole, Itrazol, Irunin);
- Ketoconazole (Mycozoral, Nizoral);
- Pimafucin.
All these drugs are aimed at eliminating a variety of infections. Each disease requires an individual dosage, which can only be set by a doctor. During therapy, it is recommended to take vitamins; they will strengthen the body and increase immunity.
It is important to take the treatment of gynecological problems seriously and not self-medicate. At the first unpleasant symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor, he will tell you what to do if the diagnosis is established.
Gonorrhea
It belongs to sexually transmitted diseases, although a household method of transmission of infection is not excluded (through clothing, underwear, personal hygiene items, a wet towel, a sauna), as well as from mother to child during childbirth.
The causative agent of the disease is gonococci, which have a high affinity for the epithelium of the genitourinary tract (cases of damage to the mucous membrane of the rectum, conjunctiva and pharynx have been recorded).
The infection manifests itself on the 3-6th day after infection and is expressed in acute purulent inflammation of the woman’s genitourinary organs (urethritis, vaginitis, cervicitis, salpingitis, proctitis, bartholinitis). Clinical picture:
- 1Burning, itching, tingling sensation in the urethra.
- 2Frequent painful urination.
- 3 Copious or scanty vaginal discharge of yellow, bright green color with a characteristic odor.
- 4Irritation and maceration of the skin in the perineum, labia, swelling and redness.
- 5 Enlargement and pain of regional lymph nodes (groin area).
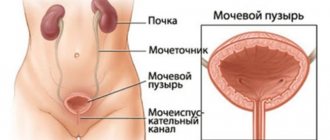
An ascending infection with the development of gonococcal cystitis, damage to the kidneys (pyelonephritis), uterus (endometritis or parametritis), and appendages (purulent salpingoophoritis) is possible.
Gonorrhea can be acute, asymptomatic (with isolated complaints, a small amount of leucorrhoea) or asymptomatic (a fairly common option). In the latter case, the woman is a carrier of the infection and poses a great danger to others.
The asymptomatic course of gonorrhea can lead to irreversible changes in the internal genital organs (adhesions in the fallopian tubes), which can cause infertility.
It is recommended to treat uncomplicated gonorrhea of the lower genitourinary tract with intramuscular administration of 500 mg of Ceftriaxone or Cefixime tablets at a dose of 400 mg once. Spectinomycin is an alternative drug. The course of therapy can be extended to 14 days if the infection spreads to the overlying parts of the genitourinary system.
In addition, douching with antiseptics and vaginal suppositories (Hexicon, Betadine) can be prescribed for a course of 7-10 days.
Recommendations for women, hygiene rules
To protect yourself from green discharge, you must adhere to the following personal hygiene rules:
- After all trips to the toilet, you should wash yourself, preferably with a solution of chamomile or calendula;
- Change panty liners more often, as well as on critical days, not forgetting to wash yourself;
- Do not use personal hygiene products that contain fragrances, fragrances, or dyes. It is better to use baby soap;
- Practice safe sex practices.
https://youtu.be/1Nplef0vfHY
Chlamydia
Chlamydia (the simplest intracellular microorganisms) can cause inflammation in many organs and tissues of the human body.
Damage to the female genital area often occurs latently (in 30% of cases) or with scant symptoms, which leads to late consultation with a doctor and the appearance of complications.
Chlamydia is transmitted sexually from an infected person, as well as from mother to child during childbirth. The incubation period of chlamydia is about a month (usually two weeks), then symptoms of the disease appear:
- 1 Cervicitis (light, cloudy, light green, light green odorless discharge, discomfort in the vagina, irritation, cervix is swollen, hyperemic).
- 2 Colpitis (burning, itching, discharge, pain during sexual intercourse).
- 3Adnexitis, endometritis (lower abdominal pain, intermenstrual bleeding, dyspareunia). Inflammation of the uterus, tubes and ovaries as a complication of untreated chlamydia leads to serious consequences, such as infertility.
The drugs of choice for the treatment of chlamydial colpitis and cervicitis are Doxycycline 100 mg orally 2 times a day (course - one week) or Azithromycin 1 gram orally once. In addition, vaginal suppositories (Polygynax, Neo-Penotran, Hexicon) are prescribed for a course of 7-14 days.
Prevention of discharge
There are certain rules that, if followed, can significantly reduce the likelihood of green discharge. These include the following:
- Visit a gynecologist once a year. If there were intimate problems, then it is best to do it 2 times a year.
- Observe personal hygiene rules.
- Engage in sexual contact only with a regular partner and avoid casual sex.
- Engage in physical activity without overloading the body.
- Do not be in a humid environment or in low temperature conditions wearing inappropriate clothing.
- During sexual intercourse, use contraception to protect against infection.
- Include more fresh vegetables and fruits in your diet and maintain a drinking regime. Try to consume to a minimum or completely eliminate fried, fatty, salty, smoked and spicy foods from your diet.
Following simple measures will help maintain sexual health and strengthen the body's immune system as a whole.
Nonspecific purulent salpingoophoritis
This is an acute or chronic purulent inflammation of the fallopian tubes and ovaries (on one side or both). It is most often provoked by nonspecific coccal flora: staphylococci, E. coli (Escherichia coli), enterococcus and others.
Ways of infection entering the tubes and ovaries:
- 1Hematogenous or lymphogenous route (with the flow of lymph and blood through the vessels).
- 2 Descending route (through the peritoneum from the large intestine).
- 3The ascending route (from the vagina) is the most common.
Acute adnexitis is characterized by a clear clinical picture, manifested by local and general symptoms:
- 1General clinical symptoms: increased body temperature, fever, headache, nausea, weakness.
- 2 Locally: mucous or purulent greenish-yellow discharge from the female genital tract, severe abdominal pain radiating to the perineum, rectum, lower back, bloating, pain, stool upset.
When the infection spreads to the pelvic peritoneum, symptoms of its irritation (pelvioperitonitis) appear, the condition worsens, temperature and intoxication increase. In this case, immediate hospitalization of the woman in a hospital and intensive care is required.
In the chronic form of adnexitis, abdominal pain and discharge appear periodically, the symptoms are scanty and mild, possible disruption of the monthly cycle, prolonged low-grade fever, pain during sexual intercourse.
Treatment is carried out with antibacterial drugs of the macrolide group, tetracycline or fluoroquinolones, depending on the type of pathogen. Additionally, antiseptics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and multivitamins are prescribed.
Acute endometritis
Acute purulent inflammation of the inner lining of the uterus, caused by specific (gonococcus, chlamydia, trichomonas) or nonspecific mixed microflora (enterobacteria, klebsiella, gardnerella, etc.).
As a rule, purulent inflammation of the endometrium occurs after childbirth (including cesarean section), abortion, diagnostic curettage, hysteroscopy, intrauterine manipulation to remove the remains of the fertilized egg, IUD.
The development of infection is facilitated by weakened immunity, hormonal fluctuations, and concomitant sexually transmitted infections.
Symptoms of acute endometritis:
- Discharge of varying intensity depending on the microflora and the severity of inflammation (leucorrhoea, cloudy, grayish, green, mixed with blood).
- Pain in the lower abdomen, groin, rectum, perineum.
- Pain when urinating.
- The general condition suffers significantly: chills, palpitations, fever, fatigue, weakness, and other signs of intoxication.
Green mucus in pregnancy discharge
Changes in the amount, consistency and color of secreted mucus depend to a large extent on the variability of hormonal levels, provoked by certain unfavorable or special circumstances. Depending on which hormones predominate in the blood at this time, the vaginal secretion changes - it can be abundant, or scanty, liquefied or thick, discolored, or with a green tint.
During pregnancy, mucus secreted can be anything. This may be due to both hormonal changes, weakened immunity, and “dormant” infections that awaken during this period. It is also possible that new ones will be added, such as those described above.
Scanty discharge of greenish mucus may indicate the initial stage of infection, which is grounds for urgent examination. But not always, infections and inflammatory processes can cause a change in the normal color of the secreted secretion to a green tint. The reason for this may be:
- Incorrect hygienic manipulations, for example - douching;
- Injury during a gynecological examination;
- Uncomfortable underwear.
In these cases, when the provoking factor is eliminated, the pathological changes go away on their own. Particular attention should be paid during pregnancy to light green discharge. This sign may indicate:
- About inflammatory processes in the amniotic membranes of the uterus, which can lead to infection of the fetus;
- Leakage of amniotic fluid (amniotic fluid) due to microcracks and thinning of the amniotic sac membrane. With these disorders, the consequences are unpredictable, since the fetus develops a chronic form of hypoxia, and the risk of intrauterine infection is high. After childbirth, the child may be subject to frequent inflammatory processes.
If any changes in health occur, self-medication of expectant mothers is unacceptable. It is always safer to consult a doctor and determine whether the green color of mucus in your case is normal or pathological. After all, the child’s life depends on the correct solution to the problem. In the arsenal of modern medicine there are many medications that can quickly eliminate pathology without causing harm to the baby.
Pathological discharge in girls
Girls may also experience uncharacteristic green discharge from the genital tract. Most often, the cause of this is vulvovaginitis, caused by mixed microflora or caused by pinworm infection (enterobiasis).
7.1. Nonspecific vulvovaginitis
Inflammation of the vaginal mucosa in girls occurs due to the penetration of bacterial flora (enterococcus, staphylococcus, E. coli).
This can be facilitated by a low level of the hormone estrogen in the blood, a neutral vaginal environment, as well as the following factors:
- Lack of intimate hygiene, improper care.
- Rare change of girl's underwear.
- Masturbation in children, foreign objects in the vagina.
- Vitamin deficiencies, decreased general and local immunity, frequent infections.
- Uncontrolled use of antibiotics.
- Frequent use of synthetic detergents for bathing, washing clothes, and caring for plumbing fixtures.
Vaginitis in girls manifests itself as discharge from the genital tract (profuse yellow, mucous or yellow-green), redness of the vulva, itching, pain when urinating, general irritability and tearfulness of the child, deterioration of sleep and anxiety.
Treatment for vaginitis is prescribed by a gynecologist after receiving the results of smears. Local therapy is most often prescribed, but sometimes general treatment is also required:
- 1 Topical: Polygynax Virgo emulsion, use 1 capsule before bedtime - 6 days; sitz baths with anti-inflammatory herbs, potassium permanganate, furatsilin, antiseptic solutions.
- 2General treatment: multivitamins (A, E, group B), antihistamines (Zyrtec, Fenistil), oral antibiotics, as a rule, are not indicated.
7.2. Enterobiasis
When infected with pinworms, girls can scratch the anus and perineum area, which contributes to the infection.
At night, pinworms, crawling out of the anus, often move to the vulva area, causing severe itching, burning, the mucous membrane becomes inflamed, swollen and red, and pathological discharge of varying intensity appears.
Treatment of enterobiasis consists of taking anthelmintic drugs: Nemozol, Vermox, Pyrantel (tablets, suspension) once in an appropriate dose (the dosage depends on the weight and age of the child).
If, a week after curing enterobiasis, the symptoms of vaginitis have not disappeared, you should contact a gynecologist to clarify the state of the microflora of the genital tract and carry out additional therapy.
Diagnosis of the disease
Even if a woman has yellow-green, odorless discharge and other pathological abnormalities, self-medication is unacceptable. Only after examination and research will a qualified specialist determine the causes of a suspicious symptom and prescribe effective treatment. A significant role is given to the following diagnostic measures:
- gynecological examination (in a chair);
- collection of secretions for bacteriological analysis (smear);
- Ultrasound of the pelvis;
- assessment of fallopian tube patency (if necessary);
- detection of pathogen DNA using PCR.
Treatment depends on the diagnosis, the phase of the pathology, the patient’s condition, and the characteristics of her body. The therapeutic regimen, consisting of drug treatment, douching and a special diet, is selected individually for each case. In mild cases, vaginal suppositories are prescribed; in more severe cases, antibiotics may be required. If the smear contains a fungus, antifungal drugs are prescribed.
If green secretion is not a consequence of an illness, a woman simply needs to reconsider her lifestyle, eliminate provoking factors, drink more fluids, and switch to a balanced diet.