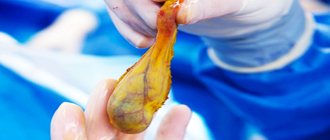
In the last decade, laparoscopic operations account for the largest share of the number of surgical procedures performed in the abdominal cavity and pelvis. The method is recognized as gentle, safe and extremely effective. The postoperative rehabilitation period for the patient is significantly reduced.
Laparoscopy is a surgical procedure performed using a laparoscope. The device contains a video camera equipped with a lighting device and trocars that help in performing the operation. The mechanism is placed into the patient’s abdominal cavity using a 2 cm long puncture. The image from the laparoscope is reflected on special screens, allowing the surgeon to observe the operated organs and effectively perform laparoscopy. When conservative treatment of gallstone disease is impossible, a decision is made to perform laparoscopy. There are two types of laparoscopic interventions on the gallbladder: removal of the gallbladder or removal of stones from the organ.
Indications for laparoscopy
Gallbladder diseases are considered common. Poor ecology, stress, an abundance of low-quality fatty foods lead to pathological changes in the organ. The result is cholelithiasis. If the disease does not affect the functioning of the human body, conservative treatment is possible.
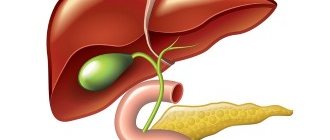
Laparoscopy of the gallbladder
When pain that is difficult to bear or malfunctions in the body appear, the issue of surgical intervention is decided. When choosing, the following symptoms deserve special attention:
- the volume of stone formations makes up more than a third of the organ space;
- Severe pain is often recorded;
- stone formations are found simultaneously in the organ and ducts;
- loss or noticeable impairment of gallbladder contraction function;
- pancreatitis, which arose in connection with cholelithiasis, is in remission;
- destruction of the walls of the organ;
- obstruction of the hepatic duct.
According to international standards, symptoms accompanying cholelithiasis are assigned certain scores. Based on the total score, the doctor determines the need for surgery or whether conservative treatment methods can be used. Mostly, if surgery is necessary, organ removal is prescribed. Especially if the gallstones are large. Extraction of stones with preservation of the organ is prescribed extremely rarely, in the presence of a chance to preserve natural functions.
What it is?
Laparoscopy is a highly effective, safe and low-traumatic method of surgical intervention on internal organs. For this reason, treating gallstone disease with this method has long become a common daily operation.
What is this treatment? In everyday life, this means surgical therapy, during which the severed gallbladder is removed from a person along with the stones formed in it, using an important device - a laparoscope.
Today, practically no operations are carried out so that the organ can be preserved and only numerous gallstones can be removed. If the stones are single, then other methods of removing them are used, such as:
- Dissolution using medications;
- Crushing using laser equipment;
- Shock wave litholripsia.
During these treatments, the dissolved stones are eliminated from the body naturally.
To better understand what laparoscopic treatment of the gallbladder is, you should first become familiar with how this therapy differs from laparotomy. Let's get acquainted with the basic principles.
Contraindications to laparoscopic intervention
Laparoscopy is not performed on women in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy. Surgical intervention is prohibited in the presence of diseases of the respiratory tract and cardiovascular system in the acute severe stage. Contraindications for laparoscopy are:
- the presence of abscesses in the organ;
- difficulties in determining the location of organs inside the abdominal cavity;
- abdominal operations previously performed in the abdominal cavity;
- the gallbladder is located inside the liver;
- state of acute stage of inflammation of the pancreas;
- jaundice formed due to a failure of the bile ducts;
- development of a cancerous tumor in the gallbladder or suspicion of cancer;
- gangrenous and porcelain cholecystitis in the acute stage;
- the presence of significant scars in the intestines, liver or neck of the gallbladder.
Surgical intervention is impossible if there are malfunctions in the blood clotting mechanism, the presence of fistulas in the biliary tract, or the presence of a pacemaker in the patient.
Preparation period
Preparation for laparoscopy and abdominal surgery is practically no different. The patient must undergo laboratory and instrumental examination. A few days before the intervention, laxatives are prescribed, and nutritional adjustments are made (avoiding foods that contribute to gas formation in the intestines). This is necessary to cleanse the intestinal tract. The evening before the operation you need to have dinner; in the morning you can no longer eat or drink. In exceptional cases, you can take the medicine with a sip of water (with your doctor's permission).
Proper preparation for surgery is the key to its success
Surgeons should know what medications, vitamins, or dietary supplements the patient is taking, and whether the patient has any allergic reactions to any medications or substances. Also, before cholecystectomy you need to take a shower, and if necessary, remove hair from the surgical field (applies to men).
Principles of laparoscopy
Removal of stones from the gallbladder or this organ is carried out using general anesthesia. A special tube is inserted into the patient's stomach to remove any remaining fluids and gases. The probe remains until the end of the procedure. Then the patient is connected to an artificial lung ventilation system; due to the nature of the operation, there is no possibility of spontaneous breathing.
A small semicircular puncture is performed in the navel area. The laparoscope is lowered there using a trocar. Having the opportunity to operate, sterile gas, usually carbon dioxide, is injected inside to expand the volume of the abdominal cavity and straighten the internal organs. Then, an additional 2–3 trocars of the manipulator are lowered under the ribs on the right side.
Removing gallstones
After carrying out these actions, the gallbladder is opened, the edge of the suction is inserted into the organ, removing stones and foreign formations from the inside of the organ. Using a laparoscope, the complete absence of stones in the organ is checked. Then the incision site is sutured, and the abdominal cavity is disinfected using antiseptic drugs.
Gallbladder removal
It is performed when it is impossible to restore the functions of an organ or when the resulting stone is too large. In such a case, the organ is cut out using trocars and placed in a special sterile container. The container is pulled out through a small incision.
At the end of the operation, stitches are placed on the punctures. If complications arise during laparoscopy, the doctor has the right to decide to perform abdominal surgery. The duration of the procedure depends on the complexity of the operation and the qualifications of the doctor. Usually takes from 40 minutes to one and a half hours. The cost of laparoscopy in different medical institutions ranges from 9 to 100 thousand rubles.
Application of anesthesia
Anesthesiologist performs endotracheal anesthesia
The main method of pain relief during endoscopic operations on the abdominal organs is endotracheal anesthesia. This type of anesthesia makes the operation as safe as possible for the patient, and also creates comfortable working conditions for the operating team:
- The patient feels absolutely no pain and retains no memory of the operation. The surgeon does not have any time restrictions and knows that the anesthesia cannot suddenly disappear.
- Carrying out artificial ventilation facilitates abdominal operations due to the ability to control breathing.
- The drugs used allow achieving good results with a low risk of side effects. It is most optimal to use the latest generation of inhalation drugs - Isoflurane, Sevoflurane, etc.
Such features of the use of general anesthesia during operations make the procedure safe and highly effective, which certainly has a positive effect on the patient’s health.
When performing laparoscopy, inhalation techniques are used for short operations
Thus, anesthesia is most often used during laparoscopy for the purpose of pain relief. Carried out by intravenous administration of drugs, using a mask or tracheal intubation, it allows you to achieve high safety and optimal conditions for pain relief.
Recovery after surgery
When the operation to remove stones from the gallbladder or the organ itself is completed, the patient is no longer given sedatives, promoting awakening. You must remain in bed for 4-6 hours from the end of the intervention. Then you are allowed to drink water and perform simple actions: stand, sit, roll over, etc.
Postoperative period
On the second day, fractional meals are possible in the form of small portions of light foods. You need to take a lot of water. Starting from day 3, follow diet No. 5.
Initially, the patient may experience pain at the puncture sites, on the right side under the rib and above the collarbone. The condition is associated with skin damage and goes away in 3-4 days. If after the specified period the pain remains, this indicates postoperative complications.
Laparoscopic stone removal has a postoperative period of approximately a week and a half. At this time, physical activity and heavy lifting are prohibited. You should use underwear made from soft natural fabrics. After a week and a half, the surgical sutures on the abdomen are removed.
Rehabilitation after laparoscopy
After one and a half to two weeks after laparoscopy, it is allowed to perform work that is not accompanied by physical stress. In order to achieve better results, the following recommendations are prescribed:
- observe sexual abstinence for a month;
- It is prohibited to lift weights exceeding 3 kg;
- nutrition is aimed at eliminating constipation;
- sports and heavy physical labor can be started gradually after at least a month;
- following the rules of diet No. 5 for 3-4 months.
A month after laparoscopy to remove gallstones, physiotherapeutic procedures begin to quickly heal wounds and tissue regeneration. To maintain the body and speed up rehabilitation, it is necessary to take vitamins. If you follow the diet and doctor’s recommendations, final rehabilitation occurs within six months.
Diet No. 5 after laparoscopy of the gallbladder
If the gallbladder is preserved during surgery, the organ is unable to immediately fully perform its functions; time is required until complete recovery. The patient is prescribed a special diet after surgery that does not provoke the production of bile.
Diet No. 5 is optimal, which is recommended to start 3-4 days after surgery. The regimen is based on fractional meals; food and drink are taken warm. Food may be boiled, steamed, baked or stewed. An acceptable diet includes the following products:
- soups with vegetable broth, based on cereals;
- chopped lean meat, fish;
- porridge;
- butter or vegetable oil;
- compotes, jelly and weak tea;
- a small amount of white bread, at least the next day after production;
- cooked vegetables;
- low-fat fermented milk products;
- non-acidic fruits;
- sweets in the form of jam, preserves or honey.
These restrictions are adhered to for 3-4 months, then it is possible to add raw vegetables. Meat and fish products are not allowed to be chopped. The restrictions must be implemented within two years.
Reviews about the operation
Reviews from patients who have undergone laparoscopy are usually positive. Patients often write that the procedure was quick, and the postoperative period is short compared to abdominal surgery. After the intervention, 2-3 small stitches remain, which heal quickly. The post-operative pain did not last long.
Reviews note the cost of removing an organ or stones laparoscopically. They express the opinion that the amount is quite acceptable to endure the more severe consequences of abdominal surgery.
The negative aspects most often found in reviews are the difficulty of individual patients with breathing due to the injected gas for half a week. Abdominal pain remains for a couple of days. These side effects are not particularly critical for patients.
Based on the above, gallstone disease is well treated with laparoscopic intervention. The operation is less traumatic compared to abdominal surgery. The recovery period is noticeably easier, allowing the patient to quickly return to normal life.