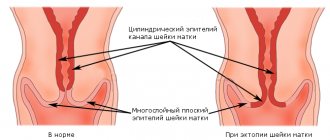
The essence of the method
Radiation therapy for cervical cancer is effective in the first and second stages of the disease. If we talk about a more advanced form, then radiotherapy is combined with chemotherapy.
The essence of the technique is this: having encountered a cancer cell, the radio beam helps to destroy its base, as a result of which it can no longer develop. Healthy cells can withstand the flow of radiation, but those affected by cancer cannot, because they spent a lot of energy dividing. So, they die and stop dividing.
What is radiation therapy?
Radiation or radiotherapy is carried out by ionizing radiation affecting the affected tissue. Thanks to this, the growth and spread of atypical cells throughout the body is suppressed. A beam of elementary particles is created by medical accelerators.
Radiotherapy equipment
During irradiation, the affected tissue does not disintegrate, but its DNA is changed and the division of cancer cells is inhibited. In atypical structures, molecular bonds are broken as a result of radiation therapy. Only malignant cells undergo changes, while healthy tissues remain unaffected.
The direction of radiation changes regularly during the procedure. This ensures the maximum dose of radiation at the lesion site. Radiation therapy is considered as an independent way to combat the disease, but can be supplemented with surgery. Radiotherapy is of particular importance in the fight against metastases in cancer.
The method is widely used to eliminate bone growths and hypertrophied sweating.
Types of irradiation and how they are carried out
For cervical cancer, doctors may use:
- gamma therapy;
- X-ray therapy.
If we talk about the position of the device in relation to the patient, the following can be used:
- intracavitary irradiation;
- remote influence on the tumor;
- contact method;
- interstitial RT.
There are external and internal LT:
- external – the affected area is directly irradiated with a special apparatus (linear catalyst). The procedures are performed on weekdays, the duration of the sessions depends on the stage of the disease. The patient has virtually no pain, and there is also no risk for those with whom the patient comes into contact;
- internal radiation therapy - the action is carried out in relation to the cervix and areas that are nearby. Sources that emit radiation are introduced into applicators, and they are placed close to the site of the disease. If a woman is irradiated after her uterus has been removed, then the applicator is inserted into the vagina without anesthesia; if the uterus has not been removed, the applicator is inserted intrauterinely, with anesthesia.
Radiotherapy is carried out as follows: the patient undergoes a CT scan. After taking several pictures, the doctor can, based on the structure and size of the tumor, select the correct direction of the radio rays to ensure maximum penetration into the tumor. The computer itself controls the process of placing and rotating the patient and the emitter, and also adjusts the localization of protective devices. If the contours of the tumor are clearly visible on the CT scan, the laser will illuminate only the point it should affect.
How long does a LT session last? The maximum duration of one such session is five minutes. The woman must lie still during the procedure. If for any reason the procedure was missed, the doctor may perform two in one day, but with an interval of eight hours.
Intracavitary gamma therapy according to the generally accepted option
When carrying out RT, three stages are conventionally distinguished:
- pre-radial;
- ray;
- post-radiation.
Each of these stages has its own characteristics that determine the rules of your behavior. Compliance with them will improve treatment results and reduce the incidence of side effects.
Problems with swallowing during and after radiotherapy
Radiation for breast cancer can cause swelling and tenderness in the throat area. There are difficulties swallowing solid food. To solve this problem, use a soft, simple diet. Avoid foods that irritate the throat (crackers, spicy foods, hot drinks, alcohol, etc.).
Nausea after radiation therapy
Radiation therapy can cause nausea, and the radiation affects areas close to the stomach. Mostly, nausea manifests itself in a mild form and can last several weeks after the end of treatment.
Currently, intracavitary irradiation is carried out using three different options: 1) conventional technique; 2) a method based on the principle of manual sequential introduction of applicators and radionuclides of low dose rate and 3) a method based on the principle of automated introduction of high activity radionuclides using hose gamma therapeutic devices.
Intracavitary gamma therapy has undergone significant evolution, which is reflected in the classical methods: “Parisian”, “Manchester”, “Stockholm”. In the 60-70s they were improved by V.P.
We previously presented a detailed description of these methods and treatment results in the monograph “Clinic and Treatment of Cervical Cancer” [Bohman Ya. V., 1976]. The generally accepted options for intracavitary gamma therapy involve the introduction into the uterine cavity and vagina of radionuclide sources of the linear form 60Co, the total activity of which is 0.91-1.82 MBq. The duration of an irradiation session with this method is 24-48 hours.
For uniform distribution of radiant energy in the pelvis, various models of colpostats have been proposed (G. Fletcher, V. P. Tobilevich, etc.). Their purpose is to fix radionuclides in a certain position.
The intervals between intracavitary irradiation sessions are usually 5-7 days. Single absorbed doses at points A, depending on the stage of cervical cancer, are 10-15 Gy, at points B - 3-5 Gy, total at points A - 60-80 Gy, at points B - 12-18 Gy.
Indications and contraindications for
Cases when radiotherapy is indicated:
- cervical cancer of the first and second degrees (before removal of the uterus);
- the tumor has metastasized to nearby organs and/or regional lymph nodes;
- a measure that temporarily improves the patient’s condition (for inoperable cancer);
- prevention of possible relapse of the disease.
At the third stage of cancer, radiation therapy is carried out in combination with chemotherapy.
Contraindications:
- fever;
- low number of leukocytes and platelets in the blood;
- anemia;
- radiation sickness;
- last stage of cancer (stage of uterine cancer);
- renal failure;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- diabetes;
- other individual contraindications.
Preparation for the procedure
First of all, physicists and the doctor calculate the correct radiation dose. Then a mark is made on the skin with a marker, and a laser will be directed along its contour.
A couple of days before the start of the sessions, you need to apply iodine. If you have diaper rash, it is better to warn your doctor. Sunbathing is strictly prohibited.
During the course of treatment (and 7-8 days before it starts), you must follow the doctor’s recommendations:
- eat well and drink plenty of fluids;
- do not smoke or drink alcohol;
- clothing should not fit tightly to the irradiation area;
- You can’t wear synthetics and wool;
- You cannot use cosmetics, soaps, creams, deodorants, etc. on the irradiated area;
- It is forbidden to rub, cool, or heat the irradiation area.
After each session you need to eat high-calorie food, so it is better to take something sweet with you.
The process of irradiation for cervical cancer
Before conducting a course of radiological treatment, the oncologist performs the following actions:
- calculates the radiation dose in accordance with the individual characteristics of the patient;
- determines the size of the tumor and its exact location;
- Applies markers to the patient’s skin according to the projection of the contours of the tumor.
Preparation for radiation exposure is carried out a week before the start of therapy and consists of the following:
- You must drink at least 2 liters of water per day;
- to eat well;
- give up bad habits, including smoking.
After starting the procedures, you must follow these recommendations:
- do not wear woolen or synthetic clothing;
- It is unacceptable to thermally influence the irradiation area (cool, warm);
- The irradiated area must not be rubbed, or cosmetics, deodorants or soap solutions applied to it.
It is recommended to eat high-calorie foods after the session. Sweet dishes are good for this.
The specialist describes the treatment plan in detail, calculating the radiation dose for the full course of therapy and separately for each session. The doctor determines the duration of the course of treatment and the duration of one procedure. Before starting radiation therapy, the following preparatory procedures are performed:
- At the hospital, the patient is offered disposable clothing. If a woman wants to stay in her clothes, then she should take care of some nuances:
- things should not fit the body or restrict movement;
- the jacket must have an open collar.
- If necessary, the patient is fixed to the table using belts, mattresses and other fasteners. These measures are necessary in order to completely limit the patient’s movements during the intervention.
- Healthy tissues and organs are covered with special protective blocks to protect them from radiation exposure.
- Before the procedure, the doctor can take a control photo to assess the correct positioning of the woman relative to the medical device.
Patients should adhere to several basic rules before treatment:
- do not dry your hair with a hairdryer;
- hide irradiated areas under clothing when leaving home;
- stop using cosmetics and sunscreen for a while;
- minimize physical activity;
- try to go outside after sunset;
- consume enough fluid.
10 days before treatment, the patient needs to adjust her diet. At this time, pickled foods, carbonated and alcoholic drinks, spices, and spicy dishes are completely excluded. A week before radiation therapy, doctors recommend that a woman do breathing exercises and increase rest time.
Recovery period
Recovery from radiation therapy for cervical cancer is a long process. To avoid complications, after irradiation you must adhere to several rules:
- rejection of bad habits;
- frequent walks in the fresh air;
- minimize the consumption of tea and coffee;
- play sports (physical activity should be moderate).
In addition, a diet during radiation therapy is indicated. The following should be excluded from the diet:
- fat;
- smoked;
- flour;
- sweet.
You need to eat less meat, and it should be stewed or steamed. Don't forget to eat fruits, vegetables and dairy products as often as possible.
Consequences
After radiation sessions for cervical cancer, complications often arise. Much depends on the method of radiotherapy, the general condition of the woman’s body, and the dosage of radiation. After completing the course of treatment, minor bleeding may occur. If this phenomenon is prolonged and accompanied by pain, then you should tell your doctor about it.
Chronic fatigue is another side effect. Organizing the right regime can cope with this. Thinning of the walls of the vessels of the intestines and bladder often occurs, as a result of which bloody inclusions appear in the urine and feces. Another consequence of radiation therapy is the absence of menstruation. Narrowing of the vagina is also not uncommon.
How does life change after cervical cancer?
In the modern world, there is a disease that is not so easy to defeat, especially if it is not detected at an early stage - it is cancer.
It is treated in different ways, one of which is surgery. And just when it seems that the disease has gone away and everything is behind us, it unexpectedly returns.
Why cancer relapses after surgery, what are the symptoms and how to prevent the disease from returning, we will talk further.
Oncological relapse is the return of a malignant disease after a period of remission.
It is customary to distinguish between a recurrence of an entire cancer and a tumor.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yAtvJa8OIhg
The cause of tumor relapse may be the activation of cancer cells that remained after treatment and surgery and have been dormant for some time. This can be quite a long period of time.
No one can guarantee that a relapse will not happen after recovery. But there are factors that can help the doctor determine the likelihood of the disease returning and inform the patient about this.
Let us highlight several factors on which the occurrence of a recurrent malignant process will depend:
- Where is the tumor located? If this is skin cancer at the first stage, then a recurrence of the disease is practically excluded, but a recurrence of breast cancer of the inner quadrant or rectal cancer is more likely. What stage is the disease at? Thus, in the early stages of the disease, when malignant cells have not penetrated the tissue barrier and have not spread through the circulatory and lymphatic systems, a complete cure is possible without relapse of the disease. What is the histological structure of the neoplasm. Superficial tumors, as a rule, do not form a second malignant formation. And infiltrative cancer often recurs even after surgery. What method and extent of treatment were used. A combination therapy method is considered the most effective. It gives a higher cure rate. What is the patient's age? It is known that cancer recurrence at a young age is a very rare phenomenon, which cannot be said about people in an older age category. It is also known that secondary cancerous tumors grow very quickly and aggressively.
One of the methods of treating cancer is surgical removal of the malignant tumor. However, even after such intervention and a course of chemotherapy, relapse of the pathology is possible. The reasons for the return of the disease can be listed as follows:
- One of the reasons is that cancer cells are not completely removed during surgery. This is possible due to the fact that they began to form not in one, but in several places of the affected organ. Carrying out inadequate treatment or using ineffective methods. Heavy physical activity. Injuries to the operated part of the body. Drug use, smoking and addiction to strong alcoholic drinks. Chronic pathologies. Infectious diseases. Malfunctions of the endocrine system.
Relapse at the initial stage is practically asymptomatic, but one of the manifestations is the identification of nodular formations of pathological tissue at the site of surgical intervention. Therefore, it is necessary to undergo regular examinations, as symptoms in the early stage are minimal.
In order to determine how much the pathological formations have increased, doctors may order the following tests:
- X-ray examination. Ultrasound examination. Lab tests. Biopsy of pathological tissues.
Recurrence of a malignant neoplasm does not always occur in the place where it was first identified and removed.
Where is tumor recurrence most often found:
- Local relapse. Cancer appears in the same tissues or very close to them. However, the process did not spread to nearby organs and tissues. Regional relapse. Malignant cells are found in lymph nodes and tissues near the site where the cancer was removed. Distant relapse. Pathological changes were found in distant areas from the main primary cancer.
Let's look at the symptoms of cancer relapse for some diseases.
Even a 100% cure does not guarantee that the disease will not return. If you have undergone surgery for ovarian cancer, there is some chance that your ovarian cancer may recur.
For timely detection, you should pay attention to the following symptoms:
- Malaise and weakness appear more and more often. There is a feeling of pain and heaviness in the lower abdomen. Quick fatigue. There is a disturbance in the menstrual cycle. Malfunctions in the functioning of the pelvic organs appear. Disorders of urination and defecation. Metastatic pleurisy or ascites appears.
As mentioned earlier, the first symptoms of the recurrence of the disease are so insignificant that you may not even pay attention to it. However, you need to know what the symptoms may be if it is a recurrence of uterine cancer:
- Loss of strength, apathy. Dizziness. Dyspeptic disorders. Increase in body temperature to 38 degrees and above. Periodic pain in the lower back and pelvis, worsening at night. Bloody or watery discharge.
Let us highlight several common signs that are characteristic of relapse of cancer:
- Constant feeling of fatigue. Headaches, dizziness. Disorder of the digestive system. Impaired bowel and bladder functions. Lumps or growths in any part of the body. Unusual discharge or bleeding. Frequent pain. Changes in the size and nature of moles and birthmarks. Persistent cough or hoarseness of voice.
I would like to note once again that most often, cancer relapses in the initial stages are not very noticeable for patients. Therefore, it is necessary to regularly see specialists and get tested for cancer cells.
Currently, medicine is successfully fighting cancer in the early stages, and treating a relapse at an early stage can give a person a better chance of recovery.
Recurrence after cancer removal can be early or late. Early relapse occurs 2-4 months after surgery, and late relapse occurs 2-4 years or more later.
Scientists have found that after surgery, cancer cells begin to actively progress after 4-6 months, so it is advisable to carry out specific therapy as soon as primary signs of oncology are detected in the operated organ.
What is anticancer therapy?
- Surgical intervention. Excision of a malignant tumor if the tumor cells have not penetrated into other tissues. Radiation therapy. Chemotherapy. Treatment using immunotherapy. Taking into account the type and stage of cancer, radiofrequency ablation, cryodestruction or hormonal therapy are performed.
As a rule, not one treatment method is used, but several, which gives good results. Chemotherapy is often used together with radiation therapy.
I would like to note that cancer relapses, as a rule, cannot be treated using the same methods and drugs that were used in the treatment of the primary tumor. Malignant cells may be resistant to chemotherapy, so it can no longer be used in case of relapse.
Radiation therapy is used if the tumor cannot be removed surgically and metastases have already formed. This type of treatment is also complementary to chemotherapy.
To prevent relapse after cancer, you must follow several recommendations:
- Constantly be monitored by an oncologist. Pass a medical examination at least 2 times a year. Conduct laboratory tests, monitor the condition of the lymph nodes, and also conduct an examination for the presence of compactions and neoplasms. Adhere to a healthy lifestyle. Do not smoke, do not abuse strong alcoholic drinks. Maintain proper nutrition. The diet should be rich and balanced. Taking vitamins and nutritional supplements is recommended, but only after consulting your doctor. Moderate physical activity and sports are recommended. Proper alternation of work and rest, active lifestyle.
As is known, cancer relapses occur in a more aggressive and fleeting form. To prevent this, you need to follow the advice of doctors, lead a healthy lifestyle, and if you are still afraid of the disease returning, seek psychological help.
An unfavorable outcome from treatment for cervical cancer is often associated with relapse of the disease and the development of metastasis. Recurrence of cervical cancer occurs in the same place where the primary tumor was originally detected.
To make a diagnosis of relapse, the primary neoplasm must be completely eliminated and a prosperous period without progression of pathology must be maintained for some period of time.
If a favorable condition has not been identified within several months, the disease is in the progress stage.
Reasons for relapse
Spread of metastases beyond the primary localization of the formation
the operation was not performed radically enough; the formation had spread beyond the limits of possible tissue removal even before the operation.
The first reason is common, since during surgery cancer cells can disseminate, that is, spread to neighboring tissues and at the same time remain unnoticed by doctors, but grow as a result of an ordinary tumor. Relapse after cervical cancer when using combined treatment in the form of surgery and radiation therapy occurs quite often, in 30% of cases.
Note! The recurrence rate in late stages is much higher than when the tumor is detected at the initial stage.
Recurrence of cervical cancer is the resumption of the oncological process in the area of the primary lesion after completion of radical treatment and subsequent well-being.
Forecast
Prognosis depends largely on the stage at which the disease was diagnosed. At the first stage, a positive result is achieved in 97% of cases, at the second stage – 75%, at the third stage, survival rate is more than 60%. At the last stage, radical surgery cannot be performed; radiotherapy is a palliative method. Not much more than 10% of patients survive.
To avoid recurrence of cervical cancer, be sure to have a routine examination with a doctor every three months.