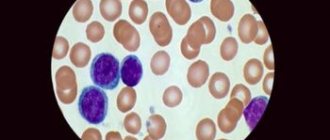
Leukocytosis is an increase in the level of white blood cells (leukocytes) in the blood. When does leukocytosis occur, what causes it and how to treat it? Of course, each person has his own indicator of the norm of leukocytes in the blood, but it ranges on average from 4 to 10/ μl in an adult. In children this number is higher and depends on age.
Leukocytosis is not a disease in the full sense of the word. An increase in the number of leukocytes, or white blood cells, is a symptom of the disease and is not treated, but diagnosed. Having determined the cause of leukocytosis, appropriate treatment is carried out.
Kinds
Neutrophilia
It is neutrophilia that occurs most often. This condition is usually caused by a specific disease. In medicine, it is also called true or absolute leukocytosis. Neutrophilic leukocytosis is characterized by rapid growth of neutrophils. Later, these cells are noted in the urine.
True neutrophilic leukocytosis occurs as a result of various pathological processes. Not only transitional or mature forms of cells appear in the blood, but also young and even blast cells.
Lymphocytic leukocytosis
Lymphocytic leukocytosis is characterized by rapid growth of lymphocytes (due to acute or chronic inflammatory process). This condition is observed in viral hepatitis, tuberculosis, whooping cough, mononucleosis and other acute and chronic infections. The symptoms are quite pronounced.
Eosinophilia
In medicine, this type is also called eosinophilic leukocytosis. The level of eosinophils increases due to the presence of certain diseases in the body:
- Loeffler's syndrome;
- dermatoses;
- periarteritis nodosa;
- lymphogranulomatosis;
- pulmonary infiltrates;
- myeloid leukemia;
- Quincke's edema.
General blood analysis
Eosinophilic leukocytosis in some clinical cases can be caused by allergic reactions, taking synthetic medications, or vaccines.
Eosinophilic leukocytosis can be suspected, but it can only be accurately confirmed after a general blood test. It will show an increased content of eosinophils. This form of the disease can develop in both children and adults. Moreover, its symptoms are symptoms of the disease that caused the development of leukocytosis. Treatment is carried out only after establishing the true cause of the increase in the number of eosinophils in the blood.
Monocytosis
The level of monocytes increases in the presence of septic processes, breast or ovarian cancer, typhus, and ulcerative colitis.
Basophilia
Basophils in the blood increase in very rare cases. Their growth is observed during pregnancy, as well as with myxedema and myeloid leukemia.
The role of leukocytes and blood norms
Leukocytes (white blood cells) are produced in the bone marrow and perform a protective function. When foreign objects, pathogens, enter the body's structures, active production of white cells occurs.
They ensure reliable destruction of bacterial, viral structures or fungi and are integral components of the human immune system.
Leukocytes themselves are heterogeneous, represented by a large group of varieties: neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, lymphocytes and monocytes.
Such heterogeneity ensures the most effective fight against different types of pathogens, be they fungal structures, viruses, bacteria.
Sometimes abnormalities occur when the immune system is overactive. Allergy is considered a particular and well-studied case of this kind. When the body begins to attack generally harmless structures that have entered the bloodstream. Mistaking them for dangerous intruders.
The normal concentration of leukocytes, as already mentioned, is up to 9000 units per μl of blood. This is the limit. Top bar.
The biomaterial should be collected 10-12 hours after the last meal. Otherwise, the result will be false positive. Blood from a vein or capillary is suitable. Deviations will be insignificant.
Causes
The process of growth of leukocytes in the blood can be pathological or physiological in nature.
Physiological leukocytosis in most clinical situations occurs in absolutely healthy people. The level of white cells is slightly increased. There are practically no symptoms. Typically, no treatment is required. An increase in the level of leukocytes can be noted in the blood, but they will not be in the urine.
Main reasons:
- increased physical activity. This leukocytosis is called myogenic. The level of white blood cells increases due to the intense production of lactic acid by the body. Myogenic leukocytosis often develops in athletes;
- birth of a child. The number of leukocytes increases in women giving birth. A widespread condition in women after childbirth. Typically occurs in the first few weeks and then goes away. A moderate increase in white blood cells in women after childbirth can be considered a normal condition. But if the level is significantly elevated, then this will indicate the presence of a pathological process in the body (it is necessary to choose the right treatment plan);
- leukocytes in the blood can increase due to food intake, in particular protein (dietary leukocytosis). This condition is not dangerous. As a rule, food leukocytosis completely disappears after a few hours. It is precisely because food leukocytosis can develop that it is recommended to donate blood on an empty stomach in order to obtain more accurate readings. Nutritional leukocytosis occurs in both adults and children. No treatment is required;
- pregnancy. As a rule, the growth of leukocytes during pregnancy is observed at 3–6 months. It is associated with hormonal changes, but it may also be of unknown origin. Also, an increase in the number of white cells can be observed in women after childbirth;
- the level of leukocytes may increase in women before menstruation;
- stress and psycho-emotional stress;
- sudden changes in temperature;
- the level of leukocytes increases in newborns (noted immediately after birth). But this is a completely normal reaction of the body.
Physiological leukocytosis is divided into long-term (observed in pregnant women and women after childbirth) and short-term (reactive).
Pathological leukocytosis and the reasons for its development:
- uremia (with this disease, white blood cells are excreted in the urine);
- inflammatory diseases of an infectious nature (including chronic);
- organ infarctions;
- allergies;
- severe burns;
- blood loss;
- splenectomy.
Leukocytosis: causes of the disease
Leukocytosis, the causes of which everyone should know, is a dangerous disease. If a person has a significant increase in white blood cells, this indicates the presence of a serious blood disease called leukemia. When a person’s leukocytes increase to several tens of thousands, then acute and inflammatory leukocytosis begins.
The most important thing is that childhood leukocytosis is not as dangerous as adult leukocytosis. In childhood, the blood formula changes quite quickly. For this reason, white blood cells can return to normal in a short period of time. But it is necessary to consult a doctor to avoid complications and further consequences. Leukocytosis, the symptoms of which are not immediately identified, can lead to death.
Leukocytosis in children is detected quite quickly, and it is much easier to cure than in adults.
The main and most important causes of leukocytosis:
- Various types of infections transmitted both sexually and by airborne droplets. This could be chicken pox, pneumonia and other types.
- The cause of leukocytosis is inflammatory processes occurring in the body. In some cases, they can be chronic: the level of leukocytes is constantly elevated.
- Any (significant or less serious) damage to the skin. It could be a burn, a scratch, or cancer.
- Wrong diet.
- Various types of disorders that are directly related to the bone marrow. After all, it is in this organ that leukocytes are stably produced.
- An immune reaction that occurs in people with allergies or asthma.
- Stress or severe emotional stress that accompanies a person for a long period of time.
- Heredity.
Leukocytosis in children can occur in the following cases: stress, intense and irrational physical activity, infections or unbalanced nutrition.
Symptoms
This process does not have its own symptoms, since it is not a disease. Its symptoms are signs of diseases that provoked an increase in the level of leukocytes. Therefore, here are the general symptoms of inflammatory diseases:
- increase in body temperature to high numbers (one of the most important symptoms);
- fainting;
- cardiopalmus;
- dizziness;
- sweating;
- blurred vision;
- loss of appetite;
- fast fatiguability;
- weakness;
- malaise;
- shortness of breath or difficulty breathing.
Increased body temperature is the most important symptom of leukocytosis
It is especially necessary to carefully monitor the condition of pregnant women, as well as women after childbirth who have an increase in the number of white cells, since this process can negatively affect the condition of the baby and the woman herself. Symptoms may not appear immediately, which is where the greatest danger lies.
Elimination of causes
As already mentioned, this ailment is not a disease in itself, unless it is leukemia, popularly called blood cancer. Leukocytosis is the body's immune system's response to an invading infection. And it is necessary to eliminate the reasons that provoked it.
When diagnosing and identifying the causes of leukocytosis, appropriate treatment is carried out. By analyzing changes in the number of white cells in the blood, you can understand how effective this treatment is. Moderate leukocytosis indicates that the patient is close to recovery, while persistently elevated leukocytosis may indicate that this treatment is ineffective and should be changed.
If this disease is not diagnosed and the disease that caused it is not treated properly, then after a while the number of white blood cells in the blood drops as the disease becomes chronic. Such a chronic disease becomes difficult to diagnose.
https://youtu.be/MuefjcJl6Lo
Treatment
Leukocytosis can be treated only after the cause of its occurrence has been established (it is especially difficult to prescribe treatment for leukocytosis of unknown origin). Treatment depends on the underlying disease. The following methods are most often used in medicine:
- in case of uremia, detoxification is indicated;
- if the cause of the development of eosinophilic or other types of leukocytosis lies in the development of the inflammatory process, then antibacterial or antiviral therapy is prescribed. The same technique is sometimes used for leukocytosis of unknown origin;
- In case of burns and infarctions of organs, the damaged areas are restored. In this case, only such treatment is effective;
- for leukemia, chemotherapy is indicated;
- if blood loss leads to an increase in the number of leukocytes, then a plasma transfusion is prescribed.
In some cases, leukocytosis can be treated with folk remedies, but only after consulting a specialist and after an examination (blood test and urine test).
Classification
- absolute or true (leukocytes from the bone marrow supply increase);
- relative or redistributive (leukocytes increase against the background of blood thickening, as well as redistribution of leukocytes in the vessels).
- acute (symptoms of acute leukocytosis are not always possible to determine);
- physiological (diagnosed in healthy patients);
- pathological (positioned as a manifestation of a particular disease of the body).
Main types:
Pathological is divided into several types:
- neutrophilic (develops against the background of an increase in neutrophils, diagnosed with chronic inflammation of organs and systems);
- basophilic (develops against the background of an increase in the rate of basophil formation, diagnosed during pregnancy);
- lymphocytic (develops against the background of the production of a large number of lymphocytes during acute infectious diseases);
- eosinophilic (observed against the background of the production of a large number of eosinophils, often diagnosed in the presence of protozoa in the intestine);
- monocytic (occurs in malignant tumors, as well as bacterial infection).
There is also a so-called short-term form, in which leukocytes are sharply produced in large quantities, but their numbers decrease after the elimination of the causative agent of the inflammatory process. This occurs against the background of diphtheria, scarlet fever, sepsis, typhoid and other diseases. Only an experienced doctor can determine the exact type of leukocytosis based on a comprehensive diagnosis.
What to do
When the number of leukocytes in the blood of an adult is slightly higher than normal, there is no cause for alarm and immediate measures, but in the future you need to monitor the indicator. If white blood cells in adults are very high during a blood test, you will need to take a number of additional tests and conduct a thorough examination. It is impossible to make a correct conclusion about the disease based on WBC analysis alone. In addition, a detailed examination is needed to determine the degree of pathology.
Important information: What does it mean to have elevated eosinophilic cationic protein (protein) in a blood test?
Based on the results of all tests, studies, and anamnesis, a clinical picture is drawn up, and a specialist will be able to make an accurate diagnosis. By comparing the indicators of all types of leukocytes with the norm, the doctor can predict the course of the pathology, draw conclusions about the chances of recovery (for cancer), and possible complications. The data from all examinations will help you choose the right treatment method and select medications that correspond to the identified disorder.
https://youtu.be/UEvkVOovRC4
If the child’s leukocytes are elevated, the examination needs to be carried out even more thoroughly. It is possible that a repeat WBC test will be required to accurately determine the pathology. In consultation with the doctor, basic drug treatment can be combined with the remedies offered by traditional medicine.
You should carefully monitor the child’s condition and ensure his psychological comfort. Excessive physical activity and hypothermia should not be allowed. A high level of white blood cells in the child’s blood obliges parents to constantly monitor the indicators. All measures will help to promptly stop the development of the disease and its transition to a chronic form.
Patients with leukocytosis need to adjust their daily routine, devoting enough time to walks in the fresh air and night sleep (its duration should be at least 8 hours). You should give up bad habits; smoking and alcoholic drinks have a negative effect on white blood cell counts. It is necessary to maintain a drinking regime, consuming a sufficient amount of liquid (clean water without gases).
Medicines
Drug treatment of leukocytosis depends on the pathology. It is aimed at eliminating the cause of high white blood cell counts, and not at destroying the white cells themselves. If a malignant tumor is detected, the selection of drugs is influenced by its location, stage of development, and the presence of metastases.
Bacterial infections are treated with antibiotics, which are also selected strictly individually.
Leukocytosis can be a side effect of taking medications. Then it is necessary to abandon the medication that led to this result and choose a new treatment. To eliminate allergies, antihistamines and sorbents are prescribed that bind and remove aggressive components from the body.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are also used to treat inflammation:
- Ibuprofen;
- Analgin;
- Paracetamol;
- Naproxen;
- Diclofenac;
- Piroxicam.
They have analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties, and reduce fever. Medicines in this group reduce blood viscosity, increasing the amount of plasma and decreasing the number of formed elements. If necessary, antiviral drugs are prescribed depending on the strain of the virus. In case of mechanical damage to soft tissues, the doctor may prescribe antimicrobial drugs to treat local inflammation.
Nutrition
An increased content of leukocytes requires a revision of the list of foods consumed. You need to remove fried and smoked foods, foods containing preservatives, dyes, and other food additives from your diet. You should not consume instant food products, because... it contains a minimum of useful substances. All dishes should be prepared using technologies that conserve vitamins.
Food should not contain excess amounts of fat, both vegetable and animal origin. You need to stop using hot spices, marinades, and synthetic sauces. The diet should include a sufficient amount of fresh vegetables, fruits and berries. It should include:
- dairy products, preferably with live lactic acid bacteria;
- lean meats (rabbit, young lamb, chicken breast, veal);
- sea fish and other seafood;
- various greens;
- porridge, preferably whole grain;
- legumes
A good addition to your diet if you have an increased number of leukocytes in the blood are nuts and unroasted sunflower seeds. Freshly squeezed juices can enrich the menu, but they should not be consumed in their pure form. Drinks should be diluted with water. You need to reduce the amount of protein foods in your child’s diet to reduce the load on the body. If your doctor allows, you can include infusions and decoctions of medicinal plants in the list of products, which reduce the level of leukocytes and stimulate the body's defenses.
Treatment of leukocytosis
Treatment of leukocytosis consists of therapy characterized by the elimination of the disease that caused it. Therefore, when resorting to different treatment methods, the doctor must take this ailment into account. Usually the patient is prescribed:
- Antibiotics, the purpose of which is to prevent the spread of infection, as well as to destroy it.
- Drugs that destroy viruses and also combat allergies.
- Chemotherapy and bone marrow transplantation – when a patient is diagnosed with leukemia.
- Detoxification if the disease is caused by uremia.
- Steroid drugs. They relieve and reduce inflammation.
- Leukopheresis. This special procedure removes white blood cells from the blood, after which the “purified” blood is infused back.
If leukocytosis is detected in the blood of a child, woman or man, it can be treated with traditional medicine. There are recipes that will help normalize the level of leukocytes:
- 15 gr. horsetail pour 1 tbsp. boiling water and cover, then let sit overnight. Before taking, strain and drink 20 ml. 3 times a day. The therapy lasts for a month.
- 1 kg. Blackthorn berries are poured into 400 ml. water and then crushed. A masher is suitable for this. The mixture should sit for a day, then boil for about 10 minutes. When the product is at room temperature, filter it and add honey or sugar. You need to take 50 ml of the medicine. 3 times a day before meals. The course of therapy is 2-3 weeks.
- You need to brew linden leaves twice a day. Honey and sugar can be used as a sweetener.
- Take strawberries, lingonberries and birch blossoms, all 1 tsp each. The ingredients are poured into 250 ml. boiling water and boil for 7 minutes. The drink is infused for 15 minutes, and then divided into three servings. You need to drink the decoction before meals.
- 3 tbsp. l. pour 600 ml of chopped wormwood. boiling water, let it brew for an hour and only then consume it before a meal, adding 15 drops of propolis tincture to the drink.
Diet
It is important that nutrients enter the body.
- You should consume foods rich in vitamins B1, B9, B12, B19. These include lean meat without fat, various cheeses, dairy products, seaweed, black bread, red caviar, fish and other seafood.
- Another important component is folic acid. Therefore, patients need to consume fresh vegetables and fruits. Also, foods containing folic acid include legumes, white cabbage, lettuce, green onions, parsley, and dill.
- An important trace element is iron. Products containing this component are recommended to be consumed along with an increase in hemoglobin. These products include all types of mushrooms, peas, beans, beans, dried fruits, as well as fresh apples.
- The component that lowers the number of white blood cells is copper. It is found in large quantities in seafood, white bread, nuts, liver and buckwheat.
Absolute and relative indicators of the norm
In the results of the general blood test, there are two results with the designation “LYM”: one of them is presented in numerical form (LYM#, LY#), and the other is presented in percentage form (LYM%, LY%). The first is used directly to diagnose deviations in the number of lymphocytes from normal values, and the second is used for comparison with the total number of white blood cells.
Absolute lymphocytosis is a condition that is observed when the normal quantitative value of LYM# is exceeded, which is 3.7-3.9*106/ml (3.7-3.9*109/l).
Relative lymphocytosis is a deviation to a greater extent from the normal ratio with other types of immune cells. The proportion of lymphocytes in the leukocyte mass in a healthy person ranges from 18-19 to 37-40%.
Normal indicators for children are calculated by age: in a 2-month-old child, the number of lymphocytes can reach 18*109/l, which corresponds to 70% of the leukocyte mass of their body. This is due to the active formation of immunity to pathogenic microflora of the environment and the growth of the infant.
Absolute and relative lymphocytosis do not necessarily correlate: against the background of neutropenia (decrease in the number of segmented and rod neutrophils), the normal value of the number of lymphocytes will correspond to an increased relative one. In severe infections (eg, tuberculosis), even a low lymphocyte count will show a high LYM% result due to leukopenia.
The opposite situation - an increased absolute indicator with a normal relative indicator - is observed less frequently and is usually a more formidable symptom.
https://youtu.be/4TrcMCSvQuc
Diagnostics
To identify this disease it is necessary:
- take a general blood test;
- take a complete blood test;
- perform a bone marrow biopsy;
- perform a lymph node biopsy;
- do a biopsy of the liver and spleen;
- give a peripheral blood smear.
The analysis should be deciphered by an experienced therapist who, based on the results, can confirm or refute the diagnosis. If alarming symptoms are observed in a child, diagnosis and examination must be done by a pediatrician.
Symptoms of leukocytosis
As a rule, leukocytosis indicates acute diseases; less commonly, it can be observed in chronic pathologies. This is always a secondary syndrome caused by a causative disease. Depending on the type of the latter, the clinical picture will be formed.
There are no specific manifestations for leukocytosis. However, the symptoms of leukocytosis are directly dependent on the cellular characteristics. Therefore, it is important for the doctor to identify which cells exceed the standard values - neutrophils, lymphocytes, eosinophils or others.
Thus, neutrophilic leukocytosis indicates:
- Bacterial infections with a tendency to purulent inflammation (most often their causative agents are staphylococci, streptococci and meningococci).
- Suffered blood loss.
- Acute hemolysis (acute destruction of red blood cells).
- Malignant tumors.
- Hypoxia (lack of oxygen saturation in the body).
- Intoxication that develops when the functioning of internal organs is impaired (for example, uremic intoxication in kidney disease).
- Painful injury.
An important diagnostic symptom is a shift to the left with leukocytosis. It allows you to evaluate its degree. This criterion is the ratio of the number of all segmented neutrophils (functionally mature cells) to non-segmented ones (young forms that practically do not perform immune functions). The normal value of this index is 0.06 – 0.08.
Based on this indicator, it is possible to determine the prognosis of the course of the causative disease. If the index is 0.25 - 0.45, then this corresponds to the regenerative type of changes, for which the prognosis is favorable.
In this case, a large number of band neutrophils appear in the blood. Severe infections with a tendency to generalize and develop purulent-septic complications correspond to a hyperregenerative index (1.0-2.0). The prognosis in this case is unfavorable. Young forms and their precursors (metamyelocytes) appear in the blood, which cannot perform immune functions.
A serious symptom is the presence of myeloblasts against the background of a high level of leukocytes. This may indicate acute leukemia (tumor of the hematopoietic system). Less commonly, it can be a sign of a severe purulent-septic condition, in which a leukemoid reaction develops.
Laboratory symptoms of neutrophilic leukocytosis include not only counting the number of white blood cells, but also determining their morphology. Its change in the form of degenerative signs is observed in the case of a strong influence of infectious and toxic factors. Degeneration is indicated by signs such as:
- the presence of granularity inside the cell (in the cytoplasm);
- core fragmentation;
- the appearance of vacuoles;
- change in cell shape (neutrophils with spikes appear, “bitten”, etc.).
The laboratory technician indicates all these changes on the blood test form if he detects them. For a doctor, such signs greatly facilitate the development of a diagnostic search program.
Another variant of leukocytosis is an increase in the level of eosinophils by more than 5% (eosinophilia). Most often it is regarded as a sign of an allergic process. Therefore, clinical symptoms include manifestations of one of the following diseases:
- bronchial asthma;
- allergic dermatitis;
- hay fever;
- Quincke's edema;
- allergic drug intolerance.
The main symptoms of allergies that a person can independently detect are:
- itchy skin rash;
- suffocation;
- redness of the eyes;
- sneezing;
- mucous discharge from the nose, etc.
In some cases, eosinophilic leukocytosis indicates helminthic infestation (helminthiasis). Therefore, along with the laboratory sign, characteristic clinical manifestations are also present: poor appetite, itching in the perianal area, weight loss and skin rashes, etc.
Sometimes with eosinophilia there may be symptoms of rarer diseases:
- autoimmune (they are characterized by the fact that leukocytes begin to damage the body’s own cells);
- lymphogranulomatosis;
- myeloid leukemia with a chronic course.
An increase in basophils in the blood in most cases is a rarely diagnosed condition, because the proportion of these cells in the leukocyte formula is insignificant (from 0.5% to 1%). Basophilia can occur with diseases such as:
- myxedema – tissue swelling associated with a deficiency of thyroid hormones;
- nonspecific ulcerative lesions of the intestine;
- allergic reactions;
- erythremia (tumor, the source of which is the precursors of red blood cells);
- chronic myeloid ycosis.
Monocytosis is a condition in which the number of monocytes in the blood is more than 8%. Monocytic leukocytosis may indicate some specific infections and cancers:
- bacterial infections – septic endocarditis, tuberculosis;
- Infectious mononucleosis;
- sarcoidosis;
- systemic inflammatory diseases of connective tissue;
- tumors of the ovaries and mammary glands during the beginning of recovery in women who previously lacked granulocytic leukocytes (neutrophils, basophils and eosinophils), i.e. in this case, monocytosis is a prognostically favorable factor.
The detection of lymphocytosis (more than 35%) in peripheral blood is accompanied by a variety of clinical symptoms, because The list of causative diseases is huge. Most often this is:
- Some chronic and acute infections - whooping cough, hepatitis, infectious mononucleosis, tuberculosis
- Malignant tumors – lymphosarcoma, lymphocytic leukemia
- Endocrine diseases – adrenal insufficiency, increased functional activity of the thyroid gland
- Lack of vitamin B12 and folic acid. Unlike inflammatory diseases, this causative condition does not have an increased ESR. Leukocytosis (lymphocytic) is combined with neutropenia (decreased number of neutrophils).
Symptoms
Most often, at the initial stage, the disease is not accompanied by specific symptoms and is diagnosed after a blood test.
The main symptoms of leukocytosis are the following:
- weakness of the body;
- increased fatigue;
- general malaise;
- acute periodic headaches;
- increased sweating;
- tingling sensation in the limbs and stomach;
- increased liver size;
- spleen extending beyond the edge;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- sudden fainting;
- bleeding in the mucous membranes;
- difficulty breathing;
- streaks of blood in various parts of the body;
- increased body temperature;
- lack of weight;
- lack of appetite;
- visual impairment, etc.
As is known, leukocytosis is not an isolated disease. As a rule, such a pathology is considered a signal of the presence of serious diseases of the body (most often blood diseases).
What are lymphocytes?
Lymphocytes in the blood
Lymphocytes are one of the subtypes of leukocytes - cells responsible for the body's immunity. They belong to the group of agranulocytes (non-granular leukocytes). Lymphocytes are considered the main immune cells because... provide humoral and cellular immunity (production of antibodies and contact with pathogenic cells), and also regulate the interaction and activity of other types of immune cells.
By functionality, lymphocytes are classified into:
- T lymphocytes. T-killers are directly involved in the destruction of foreign cells, T-helpers support the main reaction, stimulating the production of antibodies, and T-suppressors inhibit the process and do not allow it to spread to one’s own blood cells. The proportion of T-type cells ranges from 65 to 80% of the total number of lymphocytes.
- B lymphocytes. The function of B cells is to “memorize” pathogenic agents. They recognize foreign structures and produce specific antibodies, the action of which is directed against a specific agent. Their effect is noticeable in the results of vaccination, when a once-experienced attack by a weakened pathogen allows one to develop immunity to the disease. The proportion of B-type cells is up to 15%.
- NK lymphocytes. NK cells, the proportion of which is the smallest, control the compliance of body cells with normal values. Their task is to destroy atypical (cancerous) cells and cells that are infected with a virus.
Lymphocytes are directly involved in the body's immune reactions, so their number and ratio with other types of leukocytes is sometimes an important indicator for further diagnosis.
Types of leukocytes
Prevention
It is also necessary to exclude harmful foods and fast food from the diet. It is necessary to give up bad habits - smoking and drinking alcohol. You need to spend more time outdoors.
To quickly reduce the level of leukocytes before analysis, you should take medications or a decoction of folk remedies. The results of the examination are also affected by the consumption of food taken shortly before the procedure.
Leukocytosis is a sign of pathology or severe inflammatory process. Therefore, in order to reduce the number of snow-white particles in the blood, you need to find the reason. To do this, it is necessary to undergo a complete diagnosis of the body and pass a clinical analysis.
To prevent leukocytosis, drugs that enhance immunity are used. Maintaining a normal level of leukocytes is facilitated by a healthy lifestyle and monitoring your health.
How to downgrade?
An increase in leukocytes does not cause the disease, but accompanies it. In this way, the body tries to apply its protective functions. To understand how to reduce elevated leukocytes in the blood, you need to identify the disease that caused the increase and begin to treat it.
In case of a bacterial infectious disease, the use of antibiotics is mandatory if the body cannot cope on its own for a long time. Viral infections are treated with antiviral drugs. In the event of an allergic reaction, you can quickly lower your white blood cells by identifying the allergen and stopping contact with it (if possible). The doctor will prescribe tablets suitable for a particular case.
What does this mean for an adult?
The main function of leukocytes in the body is to protect against foreign pathogenic microorganisms, absorb dead particles, fungi, and parasitic infections. In the process of life, immune elements can freely move into the intercellular environment and die, with increased absorption of foreign organisms. An example of dead leukocytes is wound suppuration.
An increased number of white blood cells is called leukocytosis. It is not an autonomous disease, but serves as a marker when taking a blood test for the presence of pathologies in the human body. The source of renewal of the circulatory system is the human bone marrow.
The standard norm for adult men and women is: (4 – 9) x 109/l. If there are a lot of leukocytes, this means that the human body is fighting infection.
All elements of the immune system are divided into types that perform their protective functions and are present in a certain percentage of the total amount for an adult:
- 25 – 40% lymphocytes – cells with a smooth (not granular) structure that produce antibodies that control the quality of other cells, destroy them in the presence of pathologies (tumor cells), and regulate immune processes;
- 3 - 11% are monocytes - the largest elements of the immune system with a size of about 19 microns, migrating throughout the body in search of foci of inflammation, absorbing foreign organisms (phagocytosis);
- 0.5 - 1% are occupied by basophilic granular cells, capable of penetrating beyond the circulatory system and releasing substances contained in the granules when an allergenic cell is found, as well as accelerating the arrival of other immune elements, controlling blood clotting;
- 47 – 71% (most common) – granular bodies neutrophils with the main function of absorbing small structures, after which they die;
- 0.5 - 5% of the leukocyte niche is occupied by eosinophils - systems with a double nucleus that provide protection against parasitic infections and have the ability to phagocytose, coursing throughout the body.
If the level of leukocytes in an adult is increased, this means that the percentage of a certain group of cells or the total number of white blood elements, which accompanies certain diseases, increases. What are leukocytes and leukocyte formula?
Types of leukocytes
Why are white cells elevated?
The reasons for elevated white blood cells may be different. The amount of these blood elements can increase due to emotional stress, poor functional state of any organ system, or physical stress. The concentration of these elements in the blood varies depending on the quality of food consumed. A large number of white cells in the plasma is recorded if poisoning has occurred with phenol or its derivatives, such as aniline.
White blood cells may be higher than normal with extensive bleeding. Exceeding cell indicators occurs when the development of a malignant formation begins. Most often, an increase indicates the onset of an inflammatory process of an infectious or aseptic nature. When leukocytes in the blood are elevated, the causes in women may be associated with changed hormonal levels.
Eosinophils
Allergic reactions are a side effect of many medications or result from individual intolerance to a particular product. In this case, leukocytes increase, and eosinophils reach the highest values in the leukocyte formula.
A high level of these blood cells, indicating the presence of foreign agents, serves as an impetus for the activation of the body's defenses. These cells in the blood plasma sensitize proteins on the surface of macrophage cells in the immune system and activate powerful cytotoxic mechanisms.
The action of eosinophils is aimed at neutralizing and binding histamine (or other allergic mediators) - an indicator of the inflammatory process and allergies. Therefore, the level of eosinophils increases greatly during allergic manifestations. This type of leukocyte also takes part in antiparasitic immunity.
Important information: What does it mean to shift the leukocyte formula to the left and to the right?
Reasons why eosinophil counts are increased include:
- seasonal or drug allergies;
- asthma;
- bronchitis;
- infection with worms (roundworms, echinococci, trichinella, opisthorchiasis, lamblia, hookworms);
- damage to the connective tissue of the heart vessels and small joints.
Neutrophils
If there are pathological processes in the body, the WBC analysis detects elevated leukocytes in the blood; What does this mean, a specialist will tell you. The doctor is most often interested in the level of neutrophils, because a jump in the indicators of these elements is associated with the onset of a local or extensive inflammatory process, up to sepsis. A change in the number of such leukocyte cells may be associated with the following pathologies:
- bacterial, fungal, viral infection;
- injuries;
- inflammation after surgery, blood loss, blood poisoning;
- parasitic infestations;
- tumors;
- diabetes mellitus;
- poisoning;
- functional kidney failure;
- arthrosis and arthritis.
Excessive physical activity also causes an increase in the number of white uniform elements. It requires the mobilization of all the body's resources, which changes the composition of the blood and sharply increases the number of neutrophils.
Lymphocytes
Their increase is a sign of the appearance and growth of a malignant neoplasm. It can also be caused by the onset of “childhood” diseases of both a viral and bacterial nature (rubella, chickenpox, mumps, measles, whooping cough). The reasons for the increase in this group of blood cells include:
- drug allergies;
- autoimmune diseases;
- hyperfunction of the thyroid gland;
- rheumatoid diseases.
An increase in lymphocytes can be caused by poor nutrition, for example, a strict diet or a mono-diet (based on one product), hunger, or removal of the spleen.
Basophils
Many leukocytes of the basophil group indicate that the development of a cancerous tumor begins in the body, because their number increases in the initial stages of the disease. Diseases of the circulatory system are also one of the reasons that increases the number of basophils. The levels of these cells increase during the premenstrual period and during an allergic reaction to medications. The growth of basophils is caused by:
- irradiation;
- asthma;
- infectious diseases of the digestive system (intestines and liver);
- viral infections;
- pathology of the thyroid gland.
An increase in basophils can occur due to an acute inflammatory process in the postoperative period.
Monocytes
The number of these formed elements in plasma increases in cancer. Some helminthic infestations also lead to an increase in the number of monocytes. There are a lot of them in the blood during the recovery period after surgery, acute bacterial or viral infection (tuberculosis, hepatitis, syphilis, influenza, childhood diseases). A lot of monocytes in a blood test may be due to a foreign body entering the respiratory system, which is often used to diagnose this pathology.
By increasing monocytes, the body responds to intestinal infections and diseases of rheumatoid origin. Autoimmune disorders and diabetes mellitus can also cause an increase in the number of this group of leukocytes.
Answers to frequently asked questions from patients
Leukocytes are cells of the immune system. While the baby is in the mother's body, it does not need its own immune system. But, as soon as the child gets rid of the umbilical cord and breaks the close connection with the mother, his immune system begins to develop. While the mother feeds him with breast milk, she actively replaces the baby’s immunity, supplying antibodies and necessary substances.
| Child's age | newborn | 0-7 days | 7-30 days | 1-6 months | 6-12 months |
| White blood cell count | 8,5-24,5 | 7,2-18,5 | 6,5-13,8 | 5,5-12,5 | 6-12 |
It has been established that pregnancy and elevated leukocytes in the blood are normal, but only in the second half of pregnancy (exactly in your case)
The mother’s body (yours in this case) tries to protect itself and the child from infection. This is a kind of “general mobilization of military forces to the country’s borders,” if it’s easier that way. The immune status becomes aggressive towards any possible pathogenic agents.
Another case is when the number of leukocytes exceeds 9 in the first half of pregnancy. In this case, you need to look for the cause of its occurrence. These can be either inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system or other diseases. In any case, your doctor will tell you what to do.
A general blood test is a simple procedure, but very responsible for the patient. First, you should follow all the recommendations that your doctor gives you:
- The analysis is taken on an empty stomach
- Avoid overheating and hypothermia before analysis
- Avoid alcohol 2 days before the test and do not smoke for several hours before the procedure
As you can see, even a hot bath an hour before a general blood test can ruin the whole picture of what is happening in your body. Rule out all these factors next time and get tested again as soon as possible.
In this case, we should talk about blood cancer (leukemia, leukemia). The leukocyte is exposed to mutagenic effects of various extreme factors (radiation, genetically modified substances), after which it loses its immune activity, but begins to divide uncontrollably.
At various stages of leukemia, a complete blood count will show 100 billion or more leukocytes per liter of blood. With microscopy, a doctor in a clinical diagnostic laboratory will see a clear cytological picture of cancer cells.
Thus, leukocytosis is characteristic only of leukemia. In other oncological processes, leukocytes in the blood are not always elevated.
Leukocytosis is characteristic of all diseases in which the immune system is involved. This means that if a person does not have a serious immunodeficiency, when the production of their own leukocytes becomes impossible, then leukocytosis can be detected in any infection, autoimmune disease, etc.
https://youtu.be/Yirvmv9ZKBA
How does leukocytosis manifest?
Leukocytosis is often accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Malaise, fatigue
- Moderate and high hyperthermia
- Excessive sweating, dizziness, loss of appetite
- Decreased vision, sleep disturbance
- Weight loss and joint and muscle pain
All signs associated with leukocytosis are also due to the phenomena that accompany this leukocytosis. As can be seen from the list above, some of the symptoms accompany an increase in temperature and the onset of an infectious process.
Sometimes leukocytosis can be detected only during the next general blood test. There are a number of little-studied human conditions in which ESR, leukocytes, and temperature may increase. As a rule, time passes and all indicators return to normal. These deviations from the norm do not have any manifestations.
Leukocytosis during pregnancy
Leukocytosis during pregnancy in the blood, developing in the second half, is a normal variant. Its appearance is explained by 2 main mechanisms:
- Redistribution of blood in the body;
- Activation of the process of formation of leukocytes (leukopoiesis) in the bone marrow.
This feature must be taken into account by doctors of different specialties so as not to prescribe unreasonable examinations that supposedly should reveal the cause of this condition.
If a woman feels well and the pregnancy is more than 20 weeks old, and elevated levels of leukocytes are found in the blood, then further diagnostics are not indicated.
What condition is considered leukocytosis?
This disease is commonly called a pathological condition during which a change in the cellular composition of the blood occurs, namely an increase in the number of leukocytes. Normally, they should be 4-8.8X10⁹/liter. This indicator applies to adults; for children it is as follows:
- Newborns - 9.4-32.2.
- 1 month - 9.2-13.8.
- 1-3 years – 6-17.5.
- 4-10 – 6-11,4.
- Up to 20 years - 4.5-10.
Many people are interested in what leukocytosis is in an adult. This condition is described by an increase in the rate of 10X10⁹/liter.
https://youtu.be/1zFMpZ8SwSc
Symptoms of the disease
The smaller the child, the more likely the manifestation of leukocytosis. This is due to heredity, stress, changes in body temperature, and poor nutrition. In children, the composition of the blood changes rapidly and the leukocyte imbalance of the formula can be normalized in a short period.
For pregnant women, a blood test is required before registration. The presence of leukocytosis during this period is a physiological norm for expectant mothers. However, a greatly exceeded indicator indicates infectious pathologies, usually of the urinary tract (thrush, colpitis, cystitis).