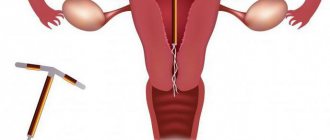
What is an intrauterine device and how does it work?
Intrauterine devices are contraceptives, a means of controlling the onset of pregnancy.
Their effectiveness is very high: when used correctly, they protect Birth Control Methods: How Well Do They Work? from pregnancy by 99%. They are even used for emergency contraception after unprotected sex. Externally, most of the spirals that are now used resemble the letter T with different tails. But there are intrauterine implants of other forms.
Spirals are divided into two large types:
Copper intrauterine device
healthinfi.com
The principle of operation is this: copper supports aseptic inflammation in the uterus. Aseptic means that it does not happen due to microbes and does not threaten anything. But the action of copper changes the composition of cervical mucus, making it more difficult for sperm to penetrate the uterine cavity. In addition, copper prevents the egg from attaching to the wall of the uterus Intrauterine device (IUD).
Intrauterine device with a hormonal component
healthtalk.org
These are plastic coils that contain progesterone, an analogue of the human hormone that prevents pregnancy. They also interfere with sperm and egg implantation, and at the same time also suppress ovulation in some women Intrauterine system (IUS).
What are the features of installation after childbirth and abortion?
Women who have recently given birth or had an abortion, as a rule, do not want another pregnancy. In order to preserve sensations during sexual intercourse, but at the same time prevent unwanted conception, they strive to install an IUD.
After childbirth, the IUD cannot be placed immediately, but after some time.
When the procedure can be performed after childbirth or a medical abortion, and whether it is possible to insert an IUD without menstruation - these are questions that often interest women. The menstrual cycle in this case does not play a big role if there are no contraindications. Regarding the past pregnancy, each case should be considered separately.
The IUD can be installed after childbirth no earlier than 1.5 months later, when the discharge ends and the organs are fully restored. Moreover, after a caesarean section, the drug can be installed no earlier than 6 months later. After an abortion (regardless of its type), the IUD can be inserted into the uterine cavity after 7 days, if there are no complications. The procedure itself is no different.
Women who have given birth, according to their reviews, experience less pain and discomfort, since the uterine os is expanded and the cervical canal is easily accessible.
How to install a spiral
Only a doctor can install any type of spiral, and the same can remove it. Therefore, you cannot do without consulting a specialist who will help you choose a product (with copper or hormones) and decide on the installation.
This is usually a simple procedure, but an extremely rare complication is uterine perforation INTRAUTERINE DEVICES. Sometimes the spiral may fall out. Therefore, in the first three months you need to regularly visit the gynecologist; the doctor himself will prescribe a schedule.
fancy.tapis.gmail.com/Depositphotos.com
After installation, the spiral is not felt, only two short antennae are released from the cervical canal (from the cervix). These are Intrauterine Device (IUD) threads that help make sure the IUD is in place. Subsequently, they will help the gynecologist remove the IUD.
These same mustaches do not interfere in everyday life, including during sex.
Sometimes after installation a woman may feel discomfort and dizziness, but they pass quite quickly. The procedure itself is not very pleasant, but not much worse than a regular examination by a gynecologist.
Signs of an ingrown helix. Methods and methods for removing an IUD
Most often, IUD removal is performed on an outpatient basis in the middle of the menstrual cycle. The standard IUD removal procedure does not require pain relief.
Removal of the IUD is carried out by pulling with a forceps (a special surgical instrument) or tweezers by the antennae, which normally should hang from the cervical canal.
This method of removing the intrauterine device is the simplest, safest and least expensive.
If the IUD antennae are missing, the intrauterine contraceptive can be removed instrumentally during hysteroscopy or using an extractor. Instrumental removal of the IUD is carried out under local or intravenous anesthesia.
After mechanical expansion of the cervical canal, a hysteroscope is inserted into the uterine cavity. If the intrauterine device lies freely in the uterine cavity, it is grabbed with special forceps and then pulled out.
In severe cases, the instrumental method of removing the IUD may be accompanied by damage to the walls of the canal, uterus and bleeding.
If the reason for the removal of the intrauterine contraceptive is the presence of inflammatory, infectious or tumor processes in the uterine cavity, after removal of the IUD, smears in the form of fingerprints are taken from it for further histological examination.
Often, during a preliminary gynecological examination, the doctor can identify an IUD that has grown into the uterine walls.
In such a case, removal of the intrauterine contraceptive is performed by curettage of the uterine cavity, followed by histological diagnosis of the resulting biomaterial.
If part of the IUD is located near large vessels, the ureter and bladder, or has grown into the abdominal cavity, removal of the spiral is carried out through laparotomy or laparoscopy.
In any case, removal of the IUD should only be performed by a qualified gynecologist. Removing the intrauterine device yourself at home is contraindicated.
Such actions can cause mechanical damage to the mucous membranes of the genital organs and their infection.
When removing an IUD, the doctor can determine the possible consequences of using the IUD and, if necessary, develop an individual course of therapeutic action.
What are the advantages of an intrauterine device?
The main advantage is the reliability of contraception. Nothing here depends on the woman, her partner or a host of external factors. Condoms break, you can forget about the pill, but the coil stays in place and doesn’t go away.
In addition, the IUD can be used by breastfeeding women who cannot afford, for example, hormonal contraceptives.
In most cases, women do not notice the spiral at all.
Contrary to popular belief, the IUD can be installed in women who have never given birth or become pregnant before (but it is better to use the IUD after 20 years, when the internal organs are fully formed). IUDs have a reversible effect, and you can get pregnant literally in the first month after removing the IUD.
In addition, IUDs do not increase the risk of cancer and can be combined with any medications Your contraception guide.
How and where is an IUD installed?
When a woman decides to use a contraceptive method such as an intrauterine device, she must first undergo a comprehensive medical examination. The installation procedure is carried out in stationary conditions.
You might be interested in: Toxicosis during early pregnancy: when does it start?
If we consider the question of how long a session lasts, it should be noted that the entire process takes no more than half an hour.
When should you not insert an intrauterine device?
There are not many contraindications for Birth Control and the IUD (Intrauterine Device):
- Pregnancy. If you want to use the IUD as emergency contraception, you need to hurry.
- Infectious diseases of the pelvic organs (including sexually transmitted diseases or those associated with complications after termination of pregnancy). That is, we first treat infections, then introduce the IUD.
- Oncological diseases of the uterus or cervix.
- Vaginal bleeding of unknown origin.
- There are additional restrictions for the IUD with hormones, just like for taking hormonal contraceptives.
What to do if pain and discharge appear after insertion of the IUD
- If pain occurs during installation of the IUD (usually sudden and severe), then perforation (puncture) of the uterus can be suspected. This is a fairly rare complication, but very serious and may require surgery. To exclude such a dangerous complication, an ultrasound is performed.
- If pain occurs a few days after the procedure, or periodically occurs during sexual intercourse, then displacement of the coil should be excluded. Check the length of the antennae yourself. If they become longer or absent, consult a doctor.
- Minor bleeding from the genital tract during the first few days after installation of the IUD is allowed.
If you have heavy, bloody, continuous discharge or menstruation, consult a doctor immediately!
If, while using intrauterine contraception, purulent discharge or discharge with an unpleasant odor is noted, especially in combination with pain in the lower abdomen, a visit to the doctor is inevitable. This is how inflammation of the uterus can begin. In this case, it is important to start treatment on time and decide on the removal of the IUD.
What side effects may there be
Apart from complications when installing the IUD, the most common side effect is changes in the menstrual cycle. As a rule, periods become heavier and last longer. This is especially noticeable in the first months after the installation of the spirals.
Sometimes bleeding becomes too heavy and long, bleeding appears between cycles - in any case, this should be discussed with your doctor. Sometimes you have to abandon this method of contraception.
IUDs do not protect against sexually transmitted infections, and in some cases increase the risk of an ascending genital tract infection. Therefore, with a new partner you need to use additional methods of contraception.
Indications for use
It should be remembered that the introduction of an IUD does not protect a woman from sexually transmitted diseases and does not provide a 100% guarantee of protection against unwanted pregnancy. But still, IUDs have a number of advantages and indications for use:
Diseases for which pregnancy is contraindicated.
- Reluctance to have children.
- The presence of severe gene diseases in a woman or her sexual partner.
- Frequency of unwanted pregnancies.
- Indications for hormonal IUDs include some gynecological diseases (endometriosis, uterine fibroids, bleeding, and others).
The effect of the IUD on the menstrual cycle
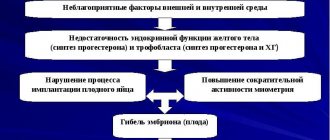
The nature of the influence of the spiral on the cycle depends on the type of product. Modern contraceptives are made of plastic and metal in the shape of the letters “T”, “S”. The protection effect is achieved due to the following factors:
- thickening of the secretion of the cervical canal, which makes it difficult for sperm to move;
- prevention of endometrial proliferation and implantation of a fertilized female germ cell;
- increased contractile activity of the tubes, ensuring the passage of the immature fertilized egg.
The spiral has a direct effect on the organs of the reproductive system. The influence of the product on the cycle differs from individual to individual. Many women note a decrease in the intensity of bleeding during menstruation. During the adaptation period, acyclic spotting may appear.
Complications with intrauterine contraception
With proper preparation and compliance with all the doctor’s requirements, the intrauterine device has disadvantages, but should not provoke the occurrence of a side pathological condition or disease. Sometimes the following complications occur:
- constant pain syndrome;
- ingrowth of the spiral into the tissue of the uterus;
- uterine bleeding (in 24% of cases);
- the onset of tubal pregnancy (especially dangerous for women who have not given birth, because it can result in infertility);
- infection of the genital organs (up to 4% of cases).
Loading...
Share with friends!
Treatment
If the fact of pregnancy with an IUD installed is confirmed, then you should not rejoice at this, since such a condition may not always end favorably for both the mother and the child. If the implantation of the embryo is correct, and it is possible to remove the drug without injury, then this will be an ideal outcome, however, in most clinical cases, there is a need for artificial termination.
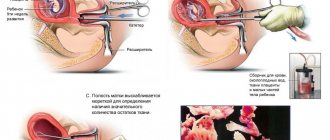
Laparoscopic removal of ectopic pregnancy. Source: fb.ru
In situations where an ectopic pregnancy with an IUD is diagnosed, a laparoscopic operation to remove the embryo is necessarily performed. This technique is not associated with serious consequences, and patients rarely develop complications after the procedure.
If the embryo has reached a large size, then it is removed by laparotomy. In this case, not three small punctures will be performed, but a significant incision on the anterior abdominal wall. If the pathology is detected in a timely manner, medical termination of pregnancy is also possible, which is the best option for solving the problem.
To prevent ectopic implantation of the ovum, if a woman uses the IUD as the main means of contraception, it is necessary to take a responsible approach to its choice. This is best done after consulting a gynecologist. In turn, doctors almost always recommend giving preference to installing Mirena. Although its cost is high, the quality is not low, so you don’t have to worry about the development of negative consequences and unplanned pregnancy.
Who can use this method
IUDs can be installed in patients with the following conditions:
- Women who have already given birth.
- Girls who have had an abortion that is not accompanied by inflammatory processes.
- Women over 35 years of age and patients who have given birth, if they have contraindications to other types of contraceptives.
- For patients who do not have pathologies in the cervical area.
Before the procedure, all acute and chronic diseases of the genitourinary system must be cured. Otherwise, various complications may arise.
What does the price depend on?
Different gynecological departments set different prices for the installation of an intrauterine device. The cost of this procedure depends on a number of factors:
- The woman's health status.
- Type of Navy.
- Price of intrauterine barrier.
- Qualification level of the doctor, his experience.
- Pricing policy and prestige of a medical institution.
- Cost of examination.
Examination before removal
| № | Research | Price |
| 1 | Vaginal smears | according to the price list |
| 2 | General blood analysis | according to the price list |
| 3 | General urine analysis | according to the price list |
| 4 | Ultrasound of the pelvic organs | according to the price list |
| 5 | Blood for HIV, hepatitis C, hepatitis B, RW, blood type and Rh factor | according to the price list |
Types of spirals (IUD)
In the world, intrauterine contraception ranks second among methods of birth control.
Currently, the most commonly used copper intrauterine devices are the third generation, with a duration of use of up to 5 years.
Multiload Cu 375 – available in 2 types: standard and mini type. The IUD has the shape of a semi-oval with spike-like protrusions, which, by fixing the contraceptive in the highest possible position, reduce the percentage of expulsions.
T Cu 380 A is the “gold standard” of contraception. One of the most effective contraceptives ever developed. This is a T-shaped contraceptive with a high copper content. Its period of use is no more than 6 years.
Nova - T is an IUD similar to a T-shaped one, but with soft, flexible horizontal arms that are easy to insert.
T de Plata 380 NOVAPLUS is an IUD made of copper and silver. In addition to a fairly high contraceptive effect, it also has an anti-inflammatory effect due to the content of silver ions.
T de Oro 375 Gold is an intrauterine device containing a 99/000 gold core. WITH
The Mirena intrauterine device is an intrauterine hormonal system. The IUD contains a vertical reservoir rod containing levonorgestrel, which is released daily into the uterine cavity in a dose of 20 mcg. within 5 years.
Currently, Spanish-made spirals (silver and gold) are available.
Intrauterine devices
The ideological fathers of this method of contraception, the intrauterine device, can be considered the Arab nomadic camel drivers. They took into account that a pregnant animal is not able to withstand all the difficulties of crossing the desert, so they introduced smooth stones into the uterus of females, thereby preventing pregnancy.
In the 20s of the last century, a German doctor invented a contraceptive device, which was a structure made of goat intestine and silver wire, the convenience and reliability of preventing pregnancy was highly appreciated by his patients.
But nevertheless, intrauterine devices gained truly wide popularity in the 80s of the last century. This is explained primarily by the fact that intrauterine devices satisfy the requirements of most women who are looking for a reliable and highly effective method of contraception that does not require regular active actions on their part.
Today, the two most common types of intrauterine devices are those with copper and progesterone.
Intrauterine devices cause local inflammation of the uterine wall at the point where the device's antennae come into contact with it. As a result of this inflammation, an acidic environment and an increased number of leukocytes are formed, which kill sperm that have entered the uterus as foreign bodies. And even if the sperm survives and fertilizes the egg, the latter will not be able to attach to the wall of the uterus and comes out. Often, the installation of such intrauterine devices is prescribed for those women for whom oral contraceptives are contraindicated.
In addition to this, progesterone-containing intrauterine devices have the same effect as oral contraceptives due to the same active ingredient.
Insertion of an intrauterine device has traditionally been considered a reliable method of contraception, despite the fact that the devices sometimes fall out. According to statistics, this occurs in approximately 7% of cases, with the vast majority of them occurring in the first 3 months after installation of the intrauterine contraceptive device.
For copper-containing intrauterine devices, the reliability of birth control exceeds 99%, and for progesterone-containing devices, this is even higher. But arguments in favor of the first type of intrauterine contraception can be served by the fact that the intrauterine device with copper serves without the need for replacement for 4 years, while the second requires annual replacement due to depletion of progesterone concentration.
The greatest danger to women's health is the installation of the intrauterine device itself - during this process there is a risk of perforation of the uterine wall. Therefore, you should be concerned about finding an experienced and qualified gynecologist who performs a similar procedure. Removal of the intrauterine device is possible at any time at the request of the woman.
Also, when using intrauterine devices, a number of other unpleasant phenomena are observed. In particular, when using contraceptive devices containing copper, menstruation may occur with pain that was not previously observed, and bleeding becomes more abundant. Also, spotting may appear in the intervals between menstruation - if such phenomena occur for more than 3 months, you should abandon the intrauterine device and choose another type of contraception.
In addition, the intrauterine device almost quadruples the risk of inflammation of the genitourinary system, so its use requires strict adherence to all rules of sexual hygiene.
And the last disadvantage that intrauterine devices have compared to some other methods of contraception is that they not only do not protect against the risk of contracting AIDS and other sexually transmitted diseases, but even increase this likelihood. Therefore, women who have several sexual partners or often change them, as well as have repeatedly suffered from sexually transmitted diseases, should abandon the intrauterine device and choose another method of contraception.
Intrauterine devices are not recommended for use in case of infectious diseases of the genitourinary system and chronic inflammatory diseases, heavy bleeding during menstruation and immunosuppression.
The IUD as a method of contraception
What examinations need to be done before inserting a fallopian device?
- A conversation with the patient allows the doctor to identify any chronic gynecological diseases she has.
- Bacteriological analysis of smears from the vagina and cervix.
- General blood and urine analysis.
- Thorough examination for sexually transmitted infections: syphilis, HIV, hepatitis B and C.
- Conducting colposcopy (instrumental examination of the vaginal cavity and cervical mucosa).
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
Indications for removal of intrauterine contraceptives
- A woman's desire.
- Expiration date.
- Menopause (one year after the last menstruation).
- Medical indications:
- Pregnancy.
- Pain.
- Bleeding that threatens the woman's life.
- Inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs are acute or exacerbation of chronic ones.
- Oncology of the uterine body or cervix.
When and how is the IUD inserted?
The introduction of the spiral is unlimited by a strictly defined period of the cycle. However, it is recommended to insert it on the 4-8th day of the menstrual cycle, during this period the uterine mucosa is less vulnerable, the cervical canal is slightly open - all this makes the insertion of the IUD less traumatic and safe. Also, menstrual flow is a reliable sign of absence of pregnancy. Bloody discharge, characteristic of the early period after implantation of an intrauterine contraceptive device (IUD), does not cause psychological discomfort in a woman, since menstruation is still ongoing.
The IUD can be inserted immediately after or within 4 days after an artificial termination of pregnancy or miscarriage (spontaneous termination of pregnancy), provided there are no signs of inflammation or bleeding. If an IUD is not implanted during this period, then it must be inserted at the onset of the next menstruation.
Simultaneous termination of pregnancy and implantation of an IUD into the uterine cavity are practiced. Insertion of an IUD immediately after childbirth or in the postpartum period (within 48 hours after birth) greatly increases the risk of contraceptive expulsion (loss). If the IUD is not inserted during the specified period, then the procedure can be performed 4-6 weeks after birth.
The structure of the intrauterine device and location in the uterine cavity:
1 — horizontal flexible hangers, 2 — spiral leg with copper wire, 3 — threads for removing the spiral,
4 - uterus.
- Before administration, a vaginal examination and probing of the uterine cavity are mandatory.
- The installation of the IUD is carried out in a special room under aseptic conditions. As a rule, insertion of an IUD is painless and does not require pain relief.
- Insertion of the IUD is possible only with grades I and II of vaginal cleanliness. If an infectious-inflammatory disease of the internal genital organs is detected or the cleanliness of the vagina corresponds to grade III or IV, then an in-depth gynecological examination is necessary, followed by antimicrobial treatment. Upon completion of treatment, a control examination of its effectiveness is necessary. After effective antimicrobial treatment of an infectious-inflammatory disease of the pelvic organs, subject to complete recovery, a 6-10 month break is required for complete recovery and to prevent the disease from becoming chronic before introducing an IUD.
Is monitoring necessary for patients using intrauterine contraceptives?
- During the first week after insertion of the IUD, it is recommended to abstain from sexual activity and intense physical activity.
- The first control examination should be carried out by a gynecologist after 7-10 days. During the examination, the doctor is interested in the presence of threads in the vaginal cavity - this is necessary to make sure that the IUD is installed correctly. Now, after the first gynecological examination, sexual activity is allowed without the use of an additional method of contraception. An ultrasound of the pelvic organs is also performed to clarify the location of the IUD in the uterine cavity.
- The next examination is carried out after one month, during the first year - at least once every 6 months, then - annually with a bacterioscopic examination of the cervical discharge. Ultrasound is recommended to be performed according to indications.
- It is necessary to train a woman to palpate the presence of IUD threads after each menstruation in order to detect the IUD loss in time. If there are no threads in the vaginal cavity, a gynecological examination and ultrasound of the pelvic organs are necessary to clarify the location of the spiral.
Possible adverse reactions and complications when using intrauterine contraceptives
Complications associated with IUD implantation are more often observed in patients with menstrual irregularities in the past, chronic pelvic inflammatory diseases (PID) in remission, and when the doctor ignores contraindications to IUD insertion. Complications arising from intrauterine contraception are usually divided into 3 groups: complications caused by the introduction of the IUD while the device is in the uterine cavity and those arising during or after removal of the contraceptive. The following complications are most often observed: pain, prolapse of the IUD, inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs and bleeding.
Reviews
Marina
I myself have not installed such devices, but my colleague regularly does. She currently has Mirena due to endometriosis. The periods are coming drop by drop. But overall she is happy.
Anna
I have a negative experience - an ectopic pregnancy. Now I live with one pipe. I protected myself on my own!
Lavender
The spiral itself stood and worked. But when the time came to take it out, I had to clean it. The doctor couldn’t do anything – neither with a crochet hook nor with other tools. I won't put it on again.
Preparing to install the spiral
After the decision has been made to install the IUD, the woman needs to prepare for the procedure as follows:
- consult with a gynecologist to prevent possible contraindications to the installation of the IUD;
- test blood for HIV and TORCH infections, hepatitis;
- submit urine for analysis;
- take a smear to check the microflora and the degree of vaginal cleanliness;
- undergo an ultrasound examination of the reproductive system;
- undergo an examination of the vagina and cervix with a colposcope.
A few days before the procedure, you must refrain from sexual intercourse, the use of vaginal medications, and rinsing the vagina with medicinal solutions. During this period, it is necessary to especially carefully observe personal hygiene and pay attention to the composition of the products that are used for washing in order to avoid an allergic reaction.