Vitamins and minerals are primarily involved in regulating metabolic processes in the body. Depending on age, gender, health status, weight, height, physical activity, and physiological needs, a person needs different amounts of these substances. Therefore, there are standards that help prevent vitamin deficiency and its consequences associated with the development of diseases. Prevention of vitamin D deficiency is one of the important public health goals. Among the vitamins valuable for a woman’s health, of course, vitamin D (calciferol) plays a special role, existing in two forms - D2 and D3, the activation of which occurs in the liver and kidneys.
Varieties D2 and D3
- D3 (cholecalciferol) is called “solar” because it is formed in the skin due to exposure to ultraviolet radiation. To do this, children and adults should be in the sun for about 15-30 minutes several times a week. However, intensive production of vitamin D occurs during hours that are harmful to health - from 11.00 to 14.00, when the skin needs protection.
In addition, the natural absorption of the vitamin decreases over time, and people with dark skin absorb it more slowly. Negative factors for the perception of beneficial sunlight are sunscreens and unfavorable ecology, such as air pollution. Therefore, even in the summer months, not always and not everyone can stock up on cholecalciferol.
- D2 (ergocalciferol) enters the body along with the usual food. However, not many foods of animal origin are known fortified with vitamin D: fatty fish (herring, sardines, salmon, mackerel, tuna, halibut), lamb, eggs (yolk), butter, cream, sour cream, hard cheese, beef liver , seafood, cod liver, red caviar, fish oil. The vitamin is present in limited quantities in plant foods: chanterelle mushrooms, oatmeal, potatoes, oranges, parsley, broccoli, nuts, vegetable oils.
It is important to follow the cooking rules so that the beneficial vitamin is not destroyed. It has also been proven that food cannot provide the body with a sufficient dose of D2, since this requires eating too many foods rich in it, some of which also contain cholesterol. In addition, this list contains things that are advised to be consumed with caution or are not allowed at all for pregnant women and in the first 6 months of lactation.
What is the danger of an overdose of vitamin D3?
The substance accumulates in the liver and fatty tissues. High doses can be harmful to health.
Overdose causes:
- Increased calcium levels in the blood (hypercalcemia). The main symptoms are vomiting, nausea, abdominal pain, dizziness, excessive thirst, and frequent urination.
- Indigestion. Overdose is indicated by constipation and diarrhea.
- Kidney failure. In this case, the amount of urine excreted decreases.
Calciferol begins to have a toxic effect on the body when taken for more than 6 months. In this case, the dosage should be many times higher than the recommended values. Intoxication occurs if vitamin D levels in the blood increase to 150 ng/ml or more.
What is vitamin D for?
Calciferol is considered a women's health vitamin. Indeed, it is of great importance for women. After all, its consumption, like other vitamins in general, is much higher than in the body of men. This is due to the characteristics of the female body and its functions: the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, childbirth, breastfeeding, menopause. Therefore, at different periods of life, the need for D3 and D2 may increase. But the most important thing is that women need to maintain an adequate amount of calciferol, avoiding its shortage or excess. Thus, vitamin D is extremely necessary because:
- is responsible for the level in the blood of minerals such as calcium and phosphorus, which contribute to the preservation and strengthening of musculoskeletal tissue (bones, joints, muscles, teeth); important for the musculoskeletal system, including correct posture, which is formed before the age of 20;
- controls the functioning of the immune, cardiovascular, endocrine, hormonal, and nervous systems. In particular, it supports the level of innate immunity; acts as a hormone (D-hormone) that regulates carbohydrate metabolism, that is, it is directly related to weight loss issues. This means it is needed for proper metabolism and maintaining optimal body weight; regulates more than 200 genes;
- has anti-inflammatory, antitumor, immunomodulatory effectiveness; slows down the aging process, fills with energy; promotes conception, maintenance of pregnancy and normal gestation; is extremely necessary during pregnancy, as it affects the formation of the immunity of the fetus and its bone tissue;
- restores a woman’s body after childbirth; corrects the condition of PMS;
- has a good effect on vision, concentration and memory.
Daily norm
What is the daily requirement of vitamin D for women?
The requirement for calciferol per day is 5 mcg.
We get cholecalciferol from food, and ergocalciferol from sunlight. The daily intake of this component for people living in the north can be increased to 10 mcg.
It is recommended to increase the daily dose of vitamin D3 to 10 mcg for women who rarely spend time outdoors, are mainly nocturnal, or live in poor environmental conditions.
Girls aged 11 to 20 years need to increase the amount of calciferol to 10 mcg, since this period is the final stage of the formation of bones and teeth, the development of the female reproductive system, high activity, and muscle growth.
The need increases for both pregnant and lactating women. It will be 10 mcg per day. This dose is necessary for the normal development of the child and the prevention of rickets.
The program “Live Healthy” in this video highlights the required daily dose of vitamin D:
Lack of vitamin D in a woman’s body
Vitamin D deficiency occurs in 75% of the world's population, the majority of whom are women and children. The reasons why a woman’s body lacks this substance can be:
- insufficient production of D3 under sun exposure;
- winter-spring period of the year (from October to March);
- mono-diets, protein diets, unbalanced nutrition, vegetarianism; pregnancy;
- breastfeeding: in the first 6 months of feeding, the mother’s vitamin D level drops sharply, which provokes a loss of calcium 4 times more than during pregnancy;
- mature age (after 50 years);
- the presence of diseases of the liver and kidneys, gall bladder, small intestine; excess weight;
- lack of physical activity;
- taking antacids (which reduce high levels of acidity in the stomach) and cholesterol medications; chronic diseases of the endocrine system, gall bladder, pancreatitis, etc.
The consequences of this condition lead to serious problems - the development of various pathologies of organs and systems:
- immunity suffers;
- there is a metabolic disorder;
- malfunctions may occur in the functioning of organs such as the thyroid, parathyroid, pancreas, adrenal glands, kidneys, lungs, heart, intestines, stomach, pituitary gland, hypothalamus, etc.;
- possible complications during pregnancy;
- menstrual irregularities may occur;
- changes in bone tissue begin, which leads to osteomalacia (leaching of minerals from the bones), and then osteoporosis, which is fraught with fractures and injuries;
- postural deformation, weakness and muscle pain are observed;
- problems with the ovaries and uterus are noted: endometriosis, fibroids, etc.
- disrupts hormonal balance: the production of testosterone and estrogen may increase, which leads to early menopause;
- the condition of the skin worsens (vitamin D is involved in the process of renewal of skin cells), hair, teeth (caries). Manifestations of skin diseases may occur;
- excess weight gain occurs;
- there is a feeling of anxiety, insomnia, depression;
- chronic fatigue and headaches are felt;
- hypertension, diabetes, arthritis, multiple sclerosis may occur; ARVI and acute respiratory infections become frequent.
Monitoring
- Serum calcium concentrations should be checked regularly over a period of weeks after initiation of therapy. Then, after 3-4 months of treatment, the levels of vitamin D, PTH and calcium are determined to assess the effectiveness and implementation of therapy. Vitamin D and calcium levels should be monitored every six months to a year.
- In kidney disease, 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol is monitored until alkaline phosphatase levels return to normal. Then treatment is reduced to maintenance therapy. Alfacalcidol can be used for vitamin D deficiency due to kidney disease.
- Hypocalcemic tetany requires urgent treatment with intravenous calcium gluconate (initially 10 mmol of a 10% solution).
Further prevention is needed to prevent a possible relapse. It includes eliminating any underlying cause, lifestyle recommendations (diet, sun exposure) and often long-term use of dietary supplements:
- Infants up to one year: 200 IU per day.
- Children over one year old: 280-400 IU daily.
- Adults: 400 IU per day. To a greater extent, this recommendation is for certain groups: those who do not receive sunlight; old people; taking anticonvulsant medications; for kidney or liver diseases.
Excess vitamin D for women
During pregnancy or with the onset of menopause, women begin to take vitamin complexes, synthesized D3 in the form of dietary supplements and medications. However, it is worth knowing that it is fat-soluble and is difficult to eliminate from the body. Due to prolonged overdose of more than 10,000 IU over many days, vitamin D easily reaches the point of toxicity. So its elevated level is also very dangerous. Hypersensitivity to this substance can also provoke an overabundance. Interestingly, the sun is usually not the cause of too much vitamin D. There are two stages to the problem of hypervitaminosis. Initially, the consequences of intoxication include symptoms such as nausea, thirst, headaches, lack of appetite, weight loss, constipation or diarrhea, frequent urination, dehydration, weakness, fever, cramps, irritability, muscle and joint pain. Then calcium deposits occur in soft tissues, and atherosclerosis may develop. Severe cases include loss of consciousness and coma. It is also worth mentioning that an increased content of calciferol is fraught with infertility and the onset of early menopause, frequent colds, arrhythmia, hypertension, liver enlargement, etc. Therefore, the dosage of the vitamin should be prescribed by a doctor after receiving the results of a blood test. In case of long-term use, regular testing is necessary.
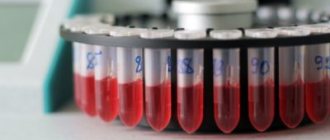
Contents in blood test
A blood test helps show the level of Vitamin D in the body, its deficiency or excess. Usually the test is prescribed by an endocrinologist, but in order to drink any complex, it is better not to neglect this analysis.
Blood collection is performed on an empty stomach ; you cannot eat for 8-10 hours before it. As for drinks, you can only drink pure water, since coffee, tea, and especially sweet juices and sodas can interfere with the veracity of the readings.
The cost of the analysis usually ranges from 1.5 to 3 thousand rubles, depending on the place of residence and the medical center itself.
A scale indicating low, very low, normal or excessive levels of vitamin D in women’s blood: if the reading is less than 10 ng/ml, there is a deficiency of calciferol, 60-100 ng/ml is a normal concentration, more than 100 ng/ml is an excess.
A video about vitamin D will tell you in detail in what cases it is prescribed:
How to find out about your vitamin D level?
You can get information about how saturated your body is with vitamin D by doing a 25OND blood test. Typically, this laboratory test is carried out if osteoporosis is suspected, during pregnancy, if the woman spends very little time in the sun, lives in the northern regions, is a vegetarian, has chronic diseases or hereditary disorders of the metabolism of this vitamin.
Vitamin D correction
Taking D3 is the prevention of diseases, the treatment of pathologies of internal organs, a recipe for good health and longevity. However, its absorption directly depends on physical activity, such as fitness classes and walking. Interestingly, swimming does not produce vitamin D, since water reduces body weight, relieving stress on it. Vitamin D can only be prescribed by a doctor - his recommendations must be strictly followed. The maximum dose for adult women, as well as pregnant and breastfeeding women, is 4000 IU per day (100 mg). At the same time, women should pay attention to calcium, magnesium, vitamins A, C, E, B6, which improve the absorption of vitamin D, zinc, phosphorus, and calcium. That is why a vitamin complex is often prescribed for preventive purposes. A nursing young mother or postmenopausal woman can drink special complexes. One of the most popular is the Amway product - Calcium, magnesium, vitamin D complex NUTRILITE, containing the daily requirement of vitamin D. It is recommended to take 1 tablet 3 times a day with meals for 1 month. It is convenient to purchase and arrange delivery in Moscow or other cities of the country on the official Amway website. When taking such complexes or vitamin D on its own, you should avoid iron, which impairs its absorption. To achieve a more effective effect and give the body everything it needs, you need to make changes to your diet. In addition, it should be remembered that the absorption of vitamin D is greatly harmed by drinking alcohol and smoking.
Daily requirement
The need for calciferol and its norm are associated with many factors and depend on body weight, area of residence, skin tone, time of year, and chronic diseases. Vitamin deficiency increases significantly in older people. Its need is great for people living in the northern regions, where the sun does not spoil them.
To prevent calciferol deficiency, doctors recommend drinking fish oil obtained from cod liver. Fish oil can be taken from the fourth month of a child’s life. The duration of D-therapy is 2-3 months, then a break is required. You can continue taking it after consulting your doctor. The daily dosage for different age categories is prescribed in the instructions for the drug.
It is recommended to take from 200 to 600 IU (international units) per day. If you look at this dose in food products, then 85 g of salmon contains 800 IU, in a glass of milk - up to 100 IU, the vitamin is artificially introduced into some products, for example, corn flakes.
Children and the “sunshine” vitamin
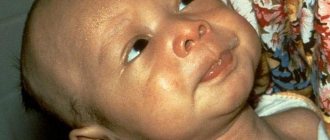
The history of the discovery of vitamin D, which occurred about a century ago, was connected precisely with the search for a treatment for childhood rickets. It was found that this disease is a sign of calciferol deficiency. The level of this substance begins to affect the baby in the womb, then during breastfeeding. Therefore, prevention of calciferol deficiency in pregnant and lactating mothers is so necessary. A deficiency can result in significant problems associated with the formation of the skeletal system and the baby’s susceptibility to diseases after birth, which often manifests itself after some time, including in adulthood. There is also a risk of having low birth weight babies. Prematurity, untimely cessation of breastfeeding, lack of sun, and poor nutrition deprive the baby of the necessary vitamin. But it is necessary not only to increase bone strength, growth, but also general development, because vitamin D interacts with the level of cognitive potential and affects the child’s performance at school. Learn more about the symptoms of vitamin D deficiency in children.
Symptoms
What are the symptoms of vitamin D deficiency in women? They do not exist, since the only reliable way to determine the level of this substance is a special analysis. People at risk are definitely:
- with dark skin color;
- over 50 years old;
- prone to depression, melancholy and bad mood;
- overweight;
- those suffering from joint pain;
- who have increased fatigue syndrome;
- with excessive sweating in the head area;
- those who do not observe results from daily care procedures (hand baths, masks, etc.), since a lack of vitamin D leads to deterioration of the condition of the skin, hair and nails;
- dramatically lost weight due to lack of appetite;
- frequently using sunscreen;
- living in northern latitudes, where there are too few sunny days.
If a woman does not replenish the lack of vitamin D for a long time, then she experiences the following possible symptoms of deficiency of this element:
- tachycardia;
- nervous breakdowns and depression;
- dental problems;
- insomnia;
- complete apathy;
- hair loss;
- bags under the eyes;
- brittleness, thinning and slow growth of nails;
- slow healing of cuts and wounds;
- excess weight;
- increased fatigue and reluctance to move;
- tearfulness;
- attacks of nausea;
- bruises, hemorrhages and bleeding for no obvious reason;
- pallor, peeling and flabbiness of the skin;
- joint pain;
- muscle cramps, back pain;
- intestinal dysfunction (constipation followed by diarrhea).
If these symptoms occur, you should immediately begin treating vitamin deficiency with medications prescribed by a specialist. Only a doctor can prescribe a patient’s dosage and schedule for taking medications.
Vitamin D and men's health
A man’s life is connected with physical activity, so the importance of the vitamin, on which the strength of the musculoskeletal system depends, is quite great. In addition, D3 and calcium, which are normal, maintain high levels of testosterone, which is responsible for male strength, sperm quality, emotional state, muscles, and also reduce its antagonist, the female hormone estrogen. Consequently, a lack of this vitamin causes a risk of fatigue, male infertility, prostate diseases, loss of muscle mass, obesity, and decreased stamina. An active and healthy lifestyle, exercise, sun exposure (although the production of vitamin D3 also decreases with age), proper nutrition, and vitamin D intake helps men maintain vitamin D.
Calciferols and aging
Doctors note a steady decrease in the amount of calcium in the body of women over 30 years of age. This phenomenon is associated with the course of physiological cycles, including the leaching of microelements or caused by a deficiency of group D biologically active substances in the body.
After 40-45
Health problems are especially acute during menopause and the postmenopausal period. Women aged 40-45 years are recommended to take calciferol in the form of vitamin and mineral supplements.
After 50-55 years
After 50 years, the usual dosage of the drug can be increased to one and a half and two and a half times. At this time, there is a process of decreasing the production of hormones and reducing the concentration of minerals in bone tissue. These changes are reminiscent of the processes that occur during pregnancy and breastfeeding. The recommended dosage of calciferol is 30-60 mcg/day.
We will tell you in detail everything you wanted to know about it.
All photos pixabay.com
Drinking vitamins and numerous dietary supplements has become extremely fashionable in recent years, they are advertised, they are prescribed by many doctors in many cases, in general - a new trend. We propose to understand one of the most studied, important and popular vitamins for the body - vitamin D, why do men need it?
We warn you that the material is for informational purposes only and is not at all a recommendation to start taking certain vitamins. Remember that you should take any vitamins only on the recommendation of a doctor, based on the results of your tests, otherwise it can cause serious harm to your health.
Treatment
If symptoms of overdose appear, all vitamin complexes are immediately canceled, foods high in calcium are removed from the diet, and the patient’s time in the sun is reduced.
The patient is given a large amount of fluid, and a doctor is called to determine whether hospitalization is necessary. Infants and children under one year of age are required to be hospitalized.
The harm that an overdose of vitamin D3 causes to a child’s health is difficult to exaggerate:
- for 3 years the baby has been registered at a dispensary, where the composition of urine, blood pressure, and heart function are systematically monitored;
- The immunity of such children remains weakened throughout their lives.
A low calcium content in the diet is necessary to compensate for the high concentration of this macronutrient in the blood caused by its leaching from bone tissue.
Additionally prescribed:
- glucocorticosteroid hormonal drugs to reduce inflammation in the body caused by calcinosis;
- ammonium chloride – against the formation of calcium kidney stones;
- vitamins B and C, which help restore metabolism.
Clinical symptoms of vitamin D overdose, if treated in a timely manner, begin to disappear when the drug is discontinued, and with appropriate treatment under the supervision of a physician, they disappear within a short time.
Treatment
The symptoms of a calciferol overdose are not so obvious, so diagnosing this particular disease is extremely difficult. But if a blood test for vitamin D and urine showed that the cause of the ailment lies precisely in an excess of this substance, it is necessary to begin treatment immediately.
First of all, the doctor prescribes the exclusion of foods containing calcium and vitamin D from the diet. At the same time, other vitamin complexes are prescribed: with ascorbic acid and B vitamins. Ammonium chloride also comes to the rescue, preventing the deposition of kidney stones. In some cases, hormonal drugs are prescribed. A special diet containing foods rich in tocopherol (vitamin E) and retinol (vitamin A) is recommended.
If acute symptoms worsen within a few hours, you should call a doctor. In this case, the patient must be provided with plenty of fluids. Children under one year of age are required to be hospitalized. After hospitalization, visits to doctors do not end for the baby: the child must be observed for another three years. Under the supervision of physicians, the little patient’s heart function, urine and blood composition will be regularly checked.
However, as a rule, to eliminate the signs of hypervitaminosis, it is enough to simply stop taking the vitamin complex.
What is calciferol
Vitamin D belongs to the category of fat-soluble provitamins. The substance is officially called calciferol. It first became known almost 100 years ago. This is a great merit of the famous biochemist Elmer Werner McCollum, who spent a significant part of his life on research in this field and achieved significant results.
Calciferol is divided into several types:
- Cholecalciferol (D3). Formed as a result of ultraviolet radiation.
- Ergocalciferol (D2). Enters the body with food.
The substance promotes the absorption of magnesium and calcium, stimulates the growth of normal cells and prevents the formation of malignant ones, improves the functioning of the immune system, normalizes hematopoietic function, has a positive effect on the thyroid gland, etc.
Hypovitaminosis D: consequences
To allow such a state to happen and do nothing is at least frivolous. This means exposing yourself to the risk of many unpleasant diseases.
Due to the lack of this important component, a variety of pathologies can occur:
- arterial hypertension;
- osteoporosis, which threatens the destruction of bone tissue, which also leads to loss of vision, migraines, and muscle weakness;
- diseases of the musculoskeletal system - arthrosis, arthritis;
- metabolic disorders, and, as a fact, diabetes mellitus;
- in women – ailments of the genitourinary organs and the inability to conceive a child normally;
- development of bronchial asthma;
- atherosclerosis with all the ensuing consequences in the form of heart attack and acute cerebrovascular accident.
In the future, this situation can lead to problems with the heart, intestinal disorders, malignant tumors, not to mention the fact that the patient develops persistent depression and mental disorders.
In addition, the immune system also suffers an irreparable loss, which is why the body is more susceptible than ever to colds and infections.
Causes of calciferol overdose
Excess vitamin D occurs due to an overdose of drugs containing calciferol. Occurs when a high dose is taken once or continuously exceeded for a long time. Hypervitaminosis in the body of vitamin D is caused by:
- if drugs are taken during long walks with high solar activity, an overdose occurs;
- if calcium sources are consumed at the same time;
- if taking calciferol is accompanied by a seafood diet;
- acute overdose is possible when drinking an alcohol solution in a dosage of 20 drops for a month;
- chronic excess occurs when taking alcohol drops in a dosage of 5 drops for two months;
- An overdose is possible due to individual sensitivity, even if the normalization is observed.
The video talks about the causes and dangers of overdose:
Diseases that develop due to vitamin D deficiency
Lack of vitamin D “washes out” bones
- Osteopenia and osteoporosis,
- Rickets,
- Cardiovascular pathologies,
- Neuromuscular diseases,
- Cancer,
- Diabetes,
- Multiple sclerosis,
- Psoriasis,
- Autoimmune diseases,
- Granulomatous diseases.