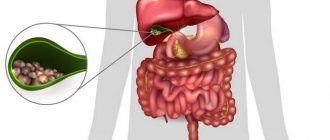
Biliary dyskinesia (BD) in children is a dysfunction of the biliary system. The process of bile formation and separation itself suffers, which contributes to stagnation of bile and interferes with the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
One of the first to occur is reactive pancreatitis, due to an interruption in the absorption of nutrients, including fats, which are crushed by bile into smaller particles. Due to improper functioning of the gallbladder, the pancreas begins to suffer.
Reasons: where to expect a catch?
The basis of biliary dyskinesia in children is a violation of the regulation of sequential contraction and relaxation of the gallbladder and sphincters on the part of the nervous and paracrine systems.
As a result of discoordination of the activity of the biliary system, the passage of bile into the intestine is disrupted, which is accompanied by a complex of clinical manifestations. In infants, biliary dyskinesia, like other functional disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, are most often a consequence of perinatal lesions of the central nervous system (hypoxia, birth trauma, asphyxia, etc.). The development of biliary dyskinesia in children is facilitated by abnormalities of the bile ducts and kinks of the gallbladder, which impede the normal outflow of bile; disorders of the sphincter apparatus; cytogenic or hepatogenic dyscholia.
In pediatrics, there is an association between the occurrence of biliary dyskinesia and infectious diseases suffered by the child - hepatitis A, salmonellosis, dysentery. A certain role in a number of causes of biliary dyskinesia in children belongs to chronic diseases (sinusitis, chronic tonsillitis, etc.), giardiasis, ascariasis, and neuro-arthritic diathesis.
In older children, the role of vegetative-vascular dystonia, neuroses, psycho-emotional disorders, physical inactivity, and nutritional errors in the development of biliary dyskinesia increases. Since contraction and relaxation of the gallbladder occurs under the influence of peptide hormones (cholecystokinin, gastrin, secretin, glucagon, etc.), disruption of their production during gastritis, gastroduodenitis, pancreatitis, enterocolitis can also lead to biliary dyskinesia in children.
The entry of bile into the duodenum is ensured by rhythmic contractions of the sphincters and muscles of the gallbladder. This occurs as a result of regulation of the process with the help of digestive hormones (gastrin, secretin, cholecystokinin). However, if there is a mismatch between the contractile activity of the organs and the action of the stimulus in the stomach, children develop gallbladder dyskinesia.
Reasons for the development of PVD in children:
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT): enterocolitis, gastritis, pancreatitis and inflammatory processes in the duodenum;
- chronic diseases: uric acid diathesis, tonsillitis, parasitic infestations, sinusitis;
- signs of biliary dyskinesia in infants appear when there are disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system caused by damage received during childbirth, hypoxia during intrauterine development of the fetus, asphyxia;
- dyscholia - changes in the structural composition of bile;
- congenital structural anomalies: the presence of narrowings and constrictions, underdevelopment of sphincters, valves, ducts or gall bladder;
- damage to the body by pathogenic microflora pathogens: hepatitis A, dysentery and salmonellosis;
- unhealthy diet: overeating, abuse of high-fat foods, eating low-quality foods containing large amounts of preservatives and chemical additives;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia, prolonged stay in a state of neurosis, stressful situations, psycho-emotional stress, characteristic of children aged 10 - 12 years.
In addition, among the factors causing the appearance of dyskinesia in children, experts include food allergies (for example, chocolate or lactose), low physical activity and genetic predisposition.
Under the influence of various factors, the gallbladder and its ducts can contract excessively or, on the contrary, insufficiently.
The organs of the digestive system function normally and are healthy, but certain factors can interfere with the coordinated contraction and relaxation of the biliary tract.
* Dietary disorders: snacking, poor chewing, overeating, eating fatty spicy foods, etc.
* Psychogenic factors (stress, neuroses, negative emotions) and damage to the nervous system (consequences of hypoxia, convulsive syndrome, etc.).
* Allergies: allergic skin lesions (rash, itching, etc.), food allergies (very common), bronchial asthma, etc.
They occur when there are initially some diseases or changes in the organ.
* Anatomical features (septum/kink of the gallbladder) become the causes of bile stagnation.
* Worms (giardiasis, opisthorchiasis). While in the gallbladder, parasites disrupt the flow of bile and irritate the nerve endings.
* Intestinal infections and lesions of the digestive system: (pancreatitis, cholecystitis, gastritis, hepatitis, ulcers, etc.). May disrupt the formation of intestinal hormones.
Causes of dyskinesia
Dyskinesia of the gallbladder and biliary tract can occur for the following reasons:
- Chronic stress. Children who are overloaded with schoolwork and extracurricular activities are at risk for many diseases. It is believed that dysfunction of dopamine receptors may lead to ADHD.
- Cholecystitis. The inflammatory process in the wall of the gallbladder damages the receptors responsible for its contraction.
- Vegetovascular dystonia. The autonomic nervous system is responsible for the proper functioning of internal organs. An imbalance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems leads to incoordination of muscle contractions of the gallbladder.
- Hypothyroidism. Thyroid hormones, namely thyroxine, relax the sphincter of Oddi, which is responsible for the release of bile into the duodenum. With hypothyroidism, the amount of this hormone in the blood decreases, which leads to a decrease in the excretion of bile.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. In addition to enzymes, the intestinal mucosa synthesizes hormones that affect the digestion process. When it is inflamed, the amount of local intestinal hormones decreases, and the regulation of bile excretion is disrupted.
All these reasons lead to ineffective contraction of the gallbladder and the development of dyskinesia.
Norma: how is everything arranged and how it works?
Knowledge will help you understand what is happening.
Produced by liver cells. It is a liquid containing special substances that are involved in many processes. Without bile, it is impossible to digest fats and move food through the intestines. Bile also helps destroy pathogens.
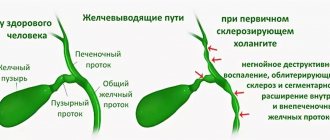
Provide transport of bile from the liver to the duodenum. They consist of a system of ducts (elastic tubes) and the gallbladder. The walls of the ducts and bladder have a muscle layer, due to which they can contract. In some places, the walls of the ducts are thickened - these are muscle valves (sphincters).
Bile promotion
When we start to eat, the bladder and its ducts contract, and the sphincters relax and open - bile pours into the duodenum. Then, before the next meal, the gallbladder and its ducts relax and the valves close. A coordinated process is controlled by intestinal hormones and the nervous system.
JVP of the hypotonic type: treatment
Treatment of hypokinetic type VVP is based on three principles.
- Treatment of the underlying disease. This may be gastritis, cholecystitis, disorders of the autonomic nervous system, etc.
- Treatment of cholestasis and its consequences. It is carried out with antispasmodics, antibacterial drugs, and enzymatic agents.
- Restoring normal function of the gallbladder and preventing GIB. Long-term adherence to a strict diet and daily routine. Water therapy. Spa treatment.
Do not forget about traditional medicine, which is quite effective in the treatment of ADHD. Rosehip decoction and grapefruit juice have a very good choleretic effect.
How are CVDs classified?
When studying their child’s medical record, mothers are faced with many incomprehensible terms and abbreviations. One of these may be VHD - this is a common pathology in children. This abbreviation refers to biliary dyskinesia. The disease is characterized by a violation of the normal outflow of bile into the initial part of the small intestine.
It has been established that the proper functioning of the gallbladder and its ducts depends on the coordinated activity of all structures of the biliary system. This is determined by neurohumoral regulatory mechanisms. Disruption of the innervation of the splanchnic and legal phrenic nerves has a direct impact on the development of pathology.
The basis of the pathological mechanisms of GIB is a violation of the humoral and autonomic regulation of the tone of the sphincters of the gallbladder and its motility. Excitation of the sympathetic parts of the nervous system leads to inhibition of gallbladder motility, provoking a spasm of its sphincters. In most cases, secondary biliary dyskinesia in children occurs for this reason. If there is a predominance of the vagus nerve, hyperkinesia of the gallbladder and a decrease in the tone of the sphincter apparatus are observed.
It is worth noting that biliary dyskinesia in children occurs against the background of the appearance of provoking factors, which are:
- stressful situations, psycho-emotional overload;
- improper diet and eating disorder;
- the presence of a large amount of fatty foods on the menu;
- binge eating;
- physical inactivity;
- infections of the gastrointestinal tract;
- hereditary predisposition.
VA in a child requires correction. Digestive disorders can negatively affect the development of the baby: infants with this pathology do not gain weight well, and their physical development indicators differ from their peers. Impaired bile passage, left untreated for a long time, leads to the development of pathologies of the biliary system. In patients with this diagnosis, the following organs are involved in the pathological process:
- liver;
- pancreas;
- duodenum.
The diagnosis of the disease is carried out by a pediatrician and a gastroenterologist. It is more difficult to determine the hypotonic type of DVT in children. To make a diagnosis and confirm it, doctors actively study the child’s complaints, medical history, and collect a thorough anamnesis. To assess the size of the gallbladder, its shape, contractile activity, and check the condition of the sphincters, an ultrasound is prescribed. Also on the list of mandatory examinations for suspected biliary dyskinesia in children:
- Duodenal intubation (portions of bile are measured, microscopy and biochemistry are performed).
- Cholecystography (study of the size of the gallbladder, its shape).
- Retrograde cholangiopancreatography (studies of the gallbladder and pancreas).
- Gastroscopy (examination of the stomach).
- Coprogram (laboratory stool analysis).
The disease requires mandatory adjustment of the diet. For biliary dyskinesia in children, it is necessary to exclude fatty, fried foods, broths, smoked meats and pickles from the menu. A whole list of products is prohibited:
- nuts;
- mushrooms;
- black bread;
- legumes;
- chocolate;
- cocoa;
- ice cream.
The menu of a child with ADHD should consist of:
- vegetable purees;
- light soups;
- porridge
In the hypokinetic form of the disease, the diet should contain foods that increase the motility of the biliary tract:
- eggs;
- sour cream;
- vegetable oil;
- mild cheeses;
- fresh vegetables;
- fruits and vegetables (strawberries, apples, apricots, plums, pears, cucumbers, cabbage, beets).
JVP differs in the nature of the disease and the age at which the disease manifests itself.
- Hyperkinetic dyskinesia. It occurs as a result of increased tone of the walls of the bladder, as a result of which the sphincters are compressed and bile does not enter the duodenum. Rhythmic compression of the walls of the bladder leads to frequent and rapid secretion. The sphincter muscles are in spasm and work according to the hypertonic type. Hyperkinetic dyskinesia is caused by an increase in the tone of the parasympathetic nervous system and is observed in children of younger age groups.
- Hypokinetic dyskinesia. In this case, the bile ducts and bladder walls are in a relaxed state. As a result, the pathology of the bile duct develops, proceeding according to the hypotonic type and leading to a slow outflow of bile. A type of pathology of the hypomotor type is observed in children who have a dominant influence of the sympathetic region of the autonomic nervous system, and is observed in children of older age categories.
The symptoms of dyskinesia in children are determined by the type of pathology; therefore, for successful therapy, it is critical for the doctor to correctly determine the type of disorder.
Reasons for the development of PVD in childhood
In children, there are primary (approximately 10% of cases) and secondary dyskinesias. The first type of biliary diarrhea is caused by congenital physiological abnormalities in the structure of the organs of the biliary system. Secondary bile ducts are more common, when the function of contraction of the biliary tract is impaired in the normal structure of the organs. Dyskinesia is not considered an independent disease, but a consequence of another disease. Factors contributing to the development of ADHD:
- genetic predisposition;
- unhealthy diet (eating large quantities of fried and fatty foods);
- inflammation of the digestive system;
- helminthiases;
- giardiasis;
- viral hepatitis;
- hormonal imbalances;
- nervous system disorders;
- psychological and physical stress.
In childhood, secondary PVD is most often a temporary phenomenon and occurs during the period of active growth of the musculoskeletal system. At this time, it often happens that the child’s internal organs do not have time to grow as quickly as muscles and bones. This phenomenon is especially typical for teenagers.
Symptoms in children
Depending on the nature of the observed symptoms, the following clinical forms of ADHD in children are distinguished:
- hyperkinetic;
- hypokinetic.
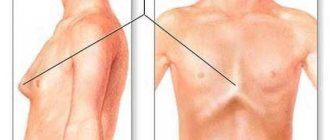
The first type is characterized by increased, sometimes excessive contraction of the gallbladder. This causes the appearance of severe, paroxysmal pain of an acute nature, which can radiate to the right shoulder blade or shoulder. When the speed of bile movement through the ducts decreases, patients are bothered by an aching, dull pain that is constantly present and is not associated with meals. Among the additional symptoms of the disease, experts identify the following possible signs of biliary dyskinesia:
- staining the patient's skin and mucous membranes yellow;
- stool lightening;
- liver enlargement;
- dryness and bitterness in the mouth;
- attacks of vomiting and nausea after eating.
Biliary dyskinesia of the hypokinetic type is accompanied by a decrease in the tone of the gallbladder muscles. As a result, the organ contracts weakly and increases in volume. This may also be accompanied by spasm of the biliary sphincters. These changes are accompanied by the appearance of specific symptoms:
- dull aching pain in the right hypochondrium, in the navel area;
- general weakness;
- fatigue;
- fatigue.
When examining the motor and contractile function of the gallbladder, the child is given a choleretic breakfast. After an ultrasound, doctors record a contraction of the gallbladder of less than 50%. This fact is always taken into account when diagnosing the disease and making a diagnosis, but additional examinations are carried out.
Hyperkinetic dyskinesia is manifested by increased activity of the muscular apparatus of the biliary tract. This is manifested by short-term attacks of pain. The baby points to the right hypochondrium, the navel area. In rare cases, nausea occurs. Based on these signs, it is possible to identify ADHD, the symptoms of which in children may be subtle.
Dyskinesia in children differs in the manifestation of symptoms.
- With the hypokinetic variety: dull and aching pain in the right hypochondrium, caused by stretching of the bladder or violation of the diet recommended by the doctor. With this type of pathology, there is a decrease in appetite, a feeling of bitterness in the mouth, bloating, abnormal bowel movements, nausea and the urge to vomit.
- With the hyperkinetic type of the disease, symptoms and treatment will depend on the stage of dyskinesia. Painful sensations of a stabbing type in the area of the right side, hypochondrium or colic in the umbilical area are caused by psycho-emotional, physical stress or excessive consumption of fatty foods.
The development of pathology in infants can occur according to one of the listed types or have mixed symptoms. Detection of symptoms should lead to immediate diagnosis, determination of the type of disorder, and prescribing adequate therapy. The progression of the disease leads to digestive disorders and carries a high risk of complications.
Signs of hyperkinetic dyskinesia are sudden attacks of colic in the right side, lasting no more than 20 minutes. The hyperkinetic form of the disease is also characterized by:
- loss of appetite;
- thinness;
- diarrhea;
- tachycardia;
- fatigue.
Treatment of dyskinesia in adults is necessary depending on the type of disease - hyper- or hypodyskinesia. For hypertonicity of the gallbladder, drugs that reduce it are used - antispasmodics (Drotaverine, No-Shpa, Papaverine), as well as sedatives and restoratives. Nifedipine is used to reduce muscle tone and the sphincter of Oddi (responsible for the release of bile).
The consumption of fats and irritating foods is limited. Choleretic and bile production stimulating agents are not used for hypertonicity.
Treatment of hyperkinetic type JVP in children involves taking drugs that strengthen the nervous system and reduce excitability, as well as to relieve pain and spasms. The dosage of drugs for children is less than for adults, it is determined by the doctor. Herbal infusions are useful for the nervous system - ginseng, eleutherococcus.
The main manifestations of biliary dyskinesia in children are pain, dyspeptic syndrome and positive cystic symptoms. The nature of the manifestations depends on the form of dysfunction.
The course of hypertensive-hyperkinetic biliary dyskinesia in children is characterized by paroxysmal (cramping, stabbing, cutting) pain in the right hypochondrium, which is short-term (5-15 minutes). On palpation, the area of the gallbladder is painful, positive bladder syndromes are determined. With the hypertensive form of biliary dyskinesia, the child often experiences loose stools, nausea, loss of appetite, vomiting, bitterness in the mouth, general weakness, and headache. Provoking factors for pain and dyspeptic syndrome, as a rule, are physical activity, consumption of fried or fatty foods, and negative emotions. During the periods between attacks, the children’s well-being is satisfactory; sometimes they may be bothered by short-term cramping pain in the abdomen.
The hypotonic form of biliary dyskinesia in children is rare. In this case, the pain in the hypochondrium is constant, aching, dull; sometimes there is only bloating and heaviness in this area. Dyspeptic disorders may occur: alternating constipation and diarrhea, decreased appetite, belching of air, flatulence. Due to cholestasis and overstretching of the gallbladder, palpation reveals an enlarged and painless liver.
Classification and general signs of the disease
Depending on the characteristics of motor impairment, the nature of the tone of these organs, as well as accompanying clinical manifestations, the following are distinguished:
- JVP of the hypotonic type in children (also known as hypokinetic or hypomotor dyskinesia) is characterized by excessive relaxation of the bladder muscles and an associated disturbance in the outflow of bile. Children often complain of a feeling of heaviness or periodic aching pain in the right hypochondrium. Hypomotor-type dysplasia in children is often accompanied by loss of appetite, fatigue, bitterness in the mouth, nausea or vomiting, a tendency to constipation, increased gas formation, and swelling. During the acute stage, the baby’s temperature may rise to 37-37.5°C.
- Hypertensive (hyperkinetic) dyskinesia of the biliary tract in children is a dysfunction in which the release of bile into the intestines occurs too often and rapidly, as a result of which the bladder and sphincter are constantly in a spastic state. At a young age, this form is more common than the hypotonic form. Symptoms of hyperkinetic dyskinesia are short-term (from 5 to 15 minutes) painful spasms on the right side of the peritoneum and under the ribs, nausea, vomiting, unformed stool, diarrhea. Among the indirect signs of ADHD in children are headache, excessive fatigue, causeless weakness, and loss of appetite.
Complications and danger of the disease
The development of the disease leads to diseases and disorders:
- changes in secretion circulation leading to stagnation;
- the formation of stones, in which the presence of stones is detected in the area of the bladder;
- decreased antibacterial characteristics of the intestine;
- pathologies in the gastrointestinal tract and changes in metabolism;
- secondary infection of the area where the disorder is located, increasing the risk of developing chronic inflammatory diseases (cholecystitis or cholangitis).
Dysfunction of the gallbladder in children disrupts the digestive processes, provokes a disruption of the body's cleansing system, and reduces the antimicrobial effect of secretions in the intestines.
Despite the unpleasant symptoms, studies usually do not reveal any abnormalities. Such conditions are called functional: when the organ is healthy (there is no inflammation or other changes), but it does not work correctly.
The disease is not dangerous. However, due to prolonged disruption of the outflow of bile, diseases of the digestive system may develop: cholecystitis, pancreatitis, gallstones, etc.
Diagnostics
Conventional methods (ultrasound, blood tests) do not help to identify the disease, since with bile ducts, the bile ducts work normally at rest.
In children, ultrasound with stress is of diagnostic value. The first study is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach, but most often it is not informative. The second is after breakfast (for example, you can take a sandwich with you). Then an ultrasound reveals a violation of the motor activity of the biliary tract.
Methods for diagnosing dyskinesia
Diagnosis of suspected biliary dyskinesia in children is carried out in several stages. At the first stage, the doctor conducts a visual examination and records the characteristic symptoms of the disorder. Using palpation, checks for the presence of pain symptoms in the epigastric zone and the area where the bladder is located.
The doctor prescribes studies to determine the stage, type of disease and select a course of individual therapy. Among the common diagnostic methods, experts call:
- conducting a clinical, biochemical or general blood test designed to determine the content of lipids in plasma and the presence of antibodies to viral hepatitis;
- stool testing to determine the presence of oviworms;
- bacteriological culture to exclude the diagnosis of dysbacteriosis;
- coprogram;
- magnetic resonance cholangiography;
- endoscopy of the duodenum, esophagus and stomach;
- duodenal intubation, necessary to determine the volume of secreted secretion, assess its composition and the existing risks of complications;
- intravenous or oral cholecystography;
- cholescintigraphy using radionuclides;
- gastroscopy.
To assess the tone, contractile potential of the organ and the state of the sphincter of Oddi, it is practiced to eat breakfast, which acts as an irritant, after which an ultrasound examination is performed.
Diagnostic measures
For biliary dyskinesia in children, the doctor first examines the patient and collects an anamnesis, which will allow him to tentatively make a diagnosis. In order to confirm the clinical diagnosis and determine the type of dyskinesia, it is recommended to use instrumental and laboratory tests.
To determine the pathological process, it is recommended to conduct an ultrasound examination. It provides the opportunity to assess the shape, size and deformation of the organ. This diagnostic technique determines the condition of the ducts and stones in the organ. The child is recommended to take a provocative breakfast and undergo a repeat ultrasound examination. This will determine the contractility of the gallbladder, as well as the performance of the sphincter of Oddi.
To assess portions of bile, its biochemical and microscopic composition, duodenal intubation is recommended. This diagnostic technique provides the opportunity to assess signs of an inflammatory process and the possibility of stone formation in the gall bladder. If there is a need to determine the morphology and functioning of the biliary system, then oral or intravenous cholecystography is performed. Patients are also prescribed retrograde cholangiopancreatography and radionuclide cholescintiography.
In order to exclude other pathological processes in the digestive system, it is recommended to perform gastroscopy. Some patients are advised to have a stool test for helminths. If a pathological process is suspected, a coprogram is performed. In order to determine dysbacteriosis, it is necessary to carry out bacterial culture. The doctor may prescribe a biochemical blood test.
In case of biliary dyskinesia in a child, a comprehensive diagnosis is recommended. This will allow the doctor to determine the type and severity of the pathology and develop an effective therapeutic regimen.
Signs of biliary dysfunction: what to look for?
Based on the type of violation, there are three possible course options.
Hypertensive type
The tone of the ducts and bladder is increased, bile quickly and often enters the intestines.
How it manifests itself
Severe pain, usually in the form of colic, occurs on the right side of the upper abdomen. In young children, pain may occur around the navel or throughout the abdomen. The appearance of pain is caused by stress (most often), physical activity or dietary errors. An attack of colic usually lasts up to half an hour, then the pain subsides and reappears after a while.
Bitterness in the mouth in the morning or after eating is a common companion to dyskinesia.
During an attack, children often feel sick or vomit. After an attack or eating, loose stools are possible.
Hypotonic type
The tone of the bladder and ducts is reduced (pathways are relaxed). Bile enters the intestines rarely, slowly and in insufficient quantities.
How it manifests itself
The pain is located in the right hypochondrium. It is aching or bursting in nature, but often children cannot describe what they feel. The pain persists constantly, intensifying during or immediately after eating.
Sometimes a child complains of nausea or vomiting after eating or if there is a malnutrition. There may be a bitter taste in the mouth. Constipation is common.
Mixed form
There are signs of both hypertensive and hypotonic types of dyskinesia.
Treatment
Since the symptoms of biliary dyskinesia in children, as well as the cause of the development of pathology, vary, there is no identical treatment regimen for all patients. The primary task of the doctor is to determine the root cause and eliminate it with the help of antibacterial, antiviral, anthelmintic and other special drugs. To combat clinical manifestations, depending on the form and symptoms of dyskinesia, the patient may be prescribed the following:
- Choleretics and choleretic drugs – Cholenzyma, Cholagol. Such drugs or their analogues are indicated in the treatment of hypotonic type VA in children. Combining these medicinal groups not only increases the production and accelerates the excretion of bile, but also improves its chemical composition;
- Medicines containing bile acids - Lyobil, Allohol. Such drugs enhance the synthesis of bile, activate the intestines and prevent the development of putrefactive processes in it;
- Medicines that have a tonic effect on the ducts - Magnesium sulfate, Xylitol, Sorbitol;
- Medicines that relax the biliary tract - Eufillin;
- Decoctions of medicinal plants - rose hips, St. John's wort, nettle, chamomile.
Physiotherapy is used as additional therapy:
- Applications with paraffin;
- Electrophoresis is a method in which the body is exposed to a constant current in parallel with certain medications absorbed through the skin;
- Inductothermy is a procedure based on the application of a high-frequency magnetic field. This manipulation stimulates the functioning of organs, as well as the endocrine glands;
- Galvanization – continuous exposure to low-power electrical impulses, improving blood circulation, eliminating inflammation and pain;
- Bernard currents - the procedure activates the contraction of smooth and skeletal muscles through dynamic current delivery. It has a positive effect on the body, improving blood circulation and providing an analgesic effect.
It is important to remember that in the acute period of pathology, of all the above methods, only electrophoresis is allowed, and other manipulations are carried out already at the rehabilitation stage.
Diagnosis of diarrhea in children
For effective therapy, the doctor gives recommendations on the nutrition of children regarding permitted and prohibited menu items. If dyskinesia is detected, exclude:
- strong coffee, cocoa, tea;
- nuts;
- legumes;
- fried, fatty and spicy foods;
- vegetables with a strong taste, such as radishes or garlic;
- meat broths;
- canned food;
- smoked and pickled foods;
- carbonated drinks;
- freshly prepared baked goods.
Among the foods recommended for consumption, on the basis of which the diet of a child with dyskinesia is compiled, experts name:
- dried rye bread;
- low-fat cheeses, cottage cheese and omelets made from chicken egg whites;
- vegetables (beets, potatoes, cabbage, carrots);
- herbs and seasonings (vanillin, dill, cinnamon, parsley);
- fruits (apples, pomegranates, bananas), in the absence of individual allergic reactions;
- porridges cooked with milk;
- lean soups;
- fruit juices diluted with water before consumption in a 1:1 ratio, fresh vegetable juices and compotes;
- low-fat varieties of meat and fish, cooked in a boiled manner;
- teas based on herbs and infusions recommended by the therapist, rosehip decoction.
Compliance with the diet requires the mandatory inclusion of fiber products in the diet, thermal processing of food only by boiling (or stewing), frequent consumption of small portions - splitting the daily amount of food into 5-7 meals.
Prevention of biliary dyskinesia
Prevention of the disease comes down to maintaining a rational and proper diet for the child. It is worth reducing the consumption of unhealthy foods, such as: chips, soda, snacks, fried, fatty, smoked, spicy and salty foods. The diet should contain more vegetables, fruits, and dietary meat. It is also better to exclude sweet confectionery products with a lot of cream.
The diet should be frequent, but in small portions. It is better to feed the child at the same hours, so the body will quickly adjust to eating at the same time. It is necessary to strictly ensure that the child does not overeat, as this is one of the common causes of dyskinesia.
Particular attention should be paid to the psycho-emotional state. When the brain is working hard, it is worth taking frequent breaks, which can be occupied with any of the child’s hobbies. The same applies to the physical training of the child. Sports should definitely be a part of a child’s life, not only for the purpose of preventing illness. Sport helps the physical development of the body, helps burn extra calories, strengthens the immune system, cardiovascular and respiratory systems of the body. But sport should not cause fatigue, tension and irritation. You can attract him to it with the help of various games, then the loads will be not only useful, but also enjoyable.
It is also necessary that in the child’s life there are:
- regular adequate sleep of at least 8 hours,
- the child falls asleep no later than 11 pm,
- frequent walks outdoors, cycling,
- routine examination of the body.
Biliary dyskinesia in a child is much easier to prevent than to treat. Close attention to the child, his nutrition, emotional state and complaints will help diagnose the disease at the primary stage. And it will save you from possible future complications.
How to distinguish dyskinesia from poisoning and intestinal infection?
Some dangerous diseases can masquerade as symptoms of ADHD. Let's figure out how these conditions differ.
| Symptom | JVP | Food poisoning/intestinal infection |
| First signs | Usually they increase gradually or there is a light interval between attacks. | They appear in a healthy child and within a few hours his condition worsens. There is often a relationship with the consumption of poor-quality food or the presence of patients with intestinal infection in the child’s environment. |
| Stomach ache | Paroxysmal and strong - with the hypertensive type. Dull and aching, worse after eating - with the hypotonic type. | The entire abdomen or upper part (stomach area) hurts. Small children show pain around the navel. |
| Nausea/ vomit | Appear during or immediately after eating. | Nausea almost constantly. Vomiting is repeated and profuse. They occur regardless of food intake, but may intensify after eating and drinking. |
| Appetite | Reduced or normal. | The child is bad or refuses to eat at all. |
| Chair | Hypotonic type - constipation. Hypertensive type - diarrhea that occurs immediately after eating or during an attack. | Frequent, does not depend on food intake. It can be watery or foamy. May contain particles of undigested food, mucus or blood (rarely). The color changes: it can be yellow, greenish. |
| Loss of consciousness | No. | Possibly in serious condition. |
| Body temperature | Normal. | It increases from the first hours of illness. |
| Dehydration (dry skin, baby losing weight) | No. | Due to vomiting and diarrhea it increases rapidly. |
Why is JVP dangerous?
In itself, gallbladder dyskinesia in children is not dangerous, but its consequences in the future entail unpleasant consequences:
- Deficiency of vitamins and nutrients that develops from indigestion;
- Metabolic disease;
- Chronic dyspeptic disorders - constant nausea, periodic vomiting, constipation or diarrhea;
- Excessive accumulation of bile leads to its thickening and hardening, which is fraught with an increased risk of stone formation in the gallbladder or its ducts.
Preventive measures include organizing proper nutrition, optimizing a balanced daily regimen for children, systematic medical monitoring, as well as immediate visits to specialized specialists at the first atypical symptoms.
Timely diagnostic measures, as well as strict adherence to all medical recommendations, will help normalize the flow of bile, put digestion in order and protect your child from the development of adverse consequences of dyskinesia.
Prevention measures
In addition to performing medical procedures, clinical recommendations include instructions for preventing biliary dyskinesia in children, including:
- excluding the child from eating cold food;
- creating conditions that protect the child from physical overload, stress and emotional experiences;
- periodic scheduled examinations by a local doctor;
- adherence to the diet recommended by the therapist.
After the discovery of VHD, children are registered with a gastroenterologist, pediatrician, neurologist and local therapist. Periodic (once every six months) choleretic treatment and ultrasound are prescribed to monitor the child’s condition.
Timely diagnosis and adequate treatment of dyskinesia, taking into account its type, makes it possible to normalize the processes of bile drainage and digestion, prevent inflammation and early stone formation in the biliary tract in children. Long-term disruption of the biliary system can lead to the development of cholecystitis, cholangitis, cholelithiasis, and intestinal dysbiosis.
Children with biliary dyskinesia need clinical observation by a pediatrician, pediatric neurologist and gastroenterologist, ultrasound monitoring, courses of choleretic therapy twice a year, and recreational holidays in specialized sanatoriums. It is necessary to monitor the child’s diet and routine, as well as his emotional state.
Classification
A condition such as biliary dyskinesia will be indicated by the presence of one of the following features:
- relaxation of the sphincter or sphincters located in the bile ducts occurs at the wrong time;
- lack of relaxation of the sphincters, even during the act of consuming food;
- intense contraction of the bladder;
- slow rate of bile secretion, slow contraction of the organ.
The following types of dyskinesia are distinguished:
- hypertensive form – the sphincters have increased tone;
- hypotonic - constantly reduced tone;
- hypokinetic - the release of bile occurs at a slow pace;
- hyperkinetic - there is an active outflow of bile due to sudden emissions.
Hypertonic and hyperkinetic types of dyskinesia can be combined into a hypertonic-hyperkinetic form. The same can be observed with the hypotonic and hypokinetic species. This is how mixed types of biliary dyskinesia are formed. In the first case we are talking about a spastic form, in the second - about an atonic one. The first condition develops when the parasympathetic part of the nervous system predominates, the second when the sympathetic part predominates.
Treatment of gallbladder dyskinesia
Therapy for gallbladder dyskinesia is aimed at improving the outflow of bile from it. For this purpose it is recommended:
- normalization of work and rest regimes;
- drinking mineral waters;
- diet;
- drug treatment (choleretic, antispasmodics, enzymes, tranquilizers);
- carrying out tubing tests;
- physiotherapy (paraffin baths, diadynamic currents, electrophoresis);
- massage;
- Spa treatment.
Diet for gallbladder dyskinesia
Diet therapy plays a primary role in the complex treatment of gallbladder dyskinesia. Patients are prescribed diet table No. 5 according to Pevzner (the modification is determined by the form of the pathology and the characteristics of its clinical course). Food should be taken frequently, at least 5 times a day in small portions. All food and drinks should be warm, as too hot or cold food temperature can trigger a painful attack. When preparing dishes, dietary heat treatment methods are used: baking, boiling, steaming. Exclude from the diet:
- fried, fatty and spicy foods;
- pickles and marinades;
- fatty meats and fish;
- cocoa and chocolate;
- confectionery, baked goods;
- alcohol;
- strong tea and coffee, carbonated drinks;
- vegetables that irritate the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract (sorrel, radishes, onions, garlic);
- products that stimulate gas formation in the intestines (rye bread, cabbage, legumes);
- fresh milk.
Probeless tubing is indicated only for hypokinetic forms of gallbladder dyskinesia in remission.
The diet for biliary dyskinesia allows the consumption of the following products:
- dried bread made from second grade flour;
- lean varieties of meat, poultry, fish;
- fermented milk products (cottage cheese, kefir, yogurt, natural yogurt, fermented baked milk);
- boiled or fresh vegetables, except those included in the list of prohibited foods;
- any cereals in the form of a dressing for soup or porridge;
- vegetable oil;
- butter (no more than 20 g per day);
- weak broths;
- coffee or tea with milk;
- honey.
The diet must be followed for a long time, at least 6 months, which allows you to achieve stable remission. It is advisable for patients suffering from gallbladder dyskinesia to adhere to the stated principles of dietary nutrition throughout their lives.
Treatment of gallbladder dyskinesia with mineral water
For gallbladder dyskinesia, it is recommended to drink one glass of mineral water warm 3 times a day half an hour before meals. For the hypokinetic form, mineral water with a high degree of mineralization is indicated (Mashuk, Borjomi, Batalinskaya, Essentuki No. 17). For hypokinetic, on the contrary, water with low mineralization is prescribed (Smirnovskaya, Narzan, Lipetskaya, Karachinskaya, Darasun). The duration of therapy with mineral waters is 3-6 months.
Drug treatment of gallbladder dyskinesia
Medicines for the treatment of biliary dyskinesia are prescribed by a gastroenterologist depending on the form of the disease. In the treatment of hyperkinetic dyskinesia of the gallbladder, the following is used:
- choleretic drugs belonging to the group of cholekinetics (Gepabene, Holosas, Flamin, Mannitol, Sorbitol, Oxafenamide) - improve the flow of bile;
- Cholespasmolytics (Drotaverine, Papaverine, No-shpa) – relieve pain;
- sedatives (Novopassit, motherwort or valerian tincture).
Dyskinesia of the gallbladder in almost all patients is accompanied by the development of asthenovegetative syndrome.
Source: myslide.ru
For the hypokinetic form of gallbladder dyskinesia, the following are prescribed:
- choleretic drugs belonging to the group of choleretics (Allohol, Cholenzym, Tanacechol, Liobil);
- myotropic antispasmodics (Odeston, Duspatalin);
- enzyme preparations (Penzital, Creon, Mezim) - used for severe dyspeptic syndrome (flatulence, constipation or diarrhea, bitterness in the mouth);
- tonics (tincture of eleutherococcus, ginseng).
Tubazhi for dyskinesia of the gallbladder
Probeless tubing is indicated only for hypokinetic forms of gallbladder dyskinesia in remission. Before performing the procedure, the patient drinks 200 ml of a 10% solution of magnesium sulfate, 2 lightly beaten egg yolks, a glass of freshly squeezed beet juice or still mineral water, for example, Essentuki No. 17, and then lies down on the right side, placing a heating pad under it. The procedure lasts 30-40 minutes. Tubages are repeated 6-8 times with a frequency of once every 7-10 days.
Physiotherapy for biliary dyskinesia
Physiotherapy is actively used in the complex treatment of gallbladder dyskinesia and promotes rapid relief of the main symptoms of the disease. For the hyperkinetic form of pathology, the following are used:
- Microwave therapy;
- inductothermy;
- electrophoresis with 0.1% solution of papaverine hydrochloride, 10% solution of magnesia or 5% solution of novocaine;
- applications of ozokerite or paraffin;
- Charcot's shower.
For patients with hypokinetic dyskinesia of the gallbladder, the following are recommended:
- faradization of the gallbladder;
- UHF;
- diadynamic currents.
Treatment of children for dyskinesia
If chronic inflammation is detected, children are prescribed antibiotics. If intestinal parasites are the culprits, treatment is carried out with anthelmintic drugs. Doctors develop specific therapy measures taking into account the type of dyskinesia.
For hypokinetic disease, drug treatment is selected from drugs of different groups. To stimulate gastrointestinal motility, prokinetics are prescribed - Metoclopramide or Domperidone. Choleretics stimulate the process of bile production (Allohol, Flamin, Febichol). In order to relax the sphincters of the vital fluid and improve the bile flow, babies are given Mannitol, Xylitol, Sorbitol, and magnesium sulfate. Essentiale is prescribed to support the liver. Enzyme deficiency is corrected with Festal or Mezim.
To receive physical therapy, pediatrician Komarovsky recommends sending children for galvanization and electrophoresis with Prozerin, calcium chloride, and magnesium sulfate. Sinusoidal modulated currents and diadynamic Bernard currents will be useful for children.
Conservative treatment of hyperkinetic type JVP is carried out with different drugs:
- hepatoprotectors;
- enzyme substances;
- sedatives;
- Cholespasmolytics;
- hydrocholeretics.
Physiotherapy for hyperkinetic dyskinesia includes microwave procedures, paraffin baths, inductothermy, antispasmodic electrophoresis, radon and pine baths. Surgical intervention is not included in the treatment of VVP.
Symptoms of the disease
Pain in the right hypochondrium is the main symptom. Character allows you to determine the type of dyskinesia:
- Hypertensive-hyperkinetic type. Short-term pain, similar to a sharp spasm. They become stronger from rich fatty or spicy foods. Strengthening occurs when playing sports (fast walking and running). The duration of the attack is about an hour. The reason is a disturbance of peace. Since the tone is increased, the caustic liquid does not have time to be released in the required quantity due to sudden strong contractions. As a result, it is missing. There are more patients with dyskinesia due to hypertonicity among men.
- Hypotonic-hypokinetic type. The pain lasts longer. Dumb. Exhausting. Also present with dyskinesia: belching or vomiting reactions, a feeling of nausea occurs. Attacks appear after eating fatty and sweet foods. Asthenics, sedentary people and people after forty years are prone to the disease due to hypotension. Provocateurs are long breaks in eating. Women get sick more often.
Additional signs:
- heartbeat;
- paleness of the skin;
- pain (headache);
- an increase in the amount of sweat produced;
- pain in the heart, right shoulder and shoulder blade;
- but a soft belly.
How should a child with dyskinesia eat?
When the first signs of illness appear, parents should make sure that the child’s diet is correct and in accordance with the doctor’s recommendations. Treatment of the disease with medications may not give the expected result, so you will need to pay sufficient attention to diet. Experts recommend adhering to the following rules:
- Preservatives and flavorings with dyes should not be allowed on a child’s menu.
- Food should be varied, but the main emphasis is on foods that are rich in fiber and magnesium.
- The diet for intestinal dyskinesia in children is based on a large consumption of vegetables and fruits; fresh and natural juices are also welcome.
- It is strictly forbidden to eat fatty and smoked foods; it is advisable to steam or boil all dishes.
- The diet includes the consumption of fermented milk products, for example, sour cream, cottage cheese or kefir.
- Porridge should be boiled in water, and bread should be specially dried.
Parents should ensure that the baby chews food thoroughly and eats in small portions, but often, at least six times a day.
Prognosis for recovery
Intestinal dyskinesia is a non-fatal disease that has a fairly favorable prognosis for recovery. It should be noted that with age the risk of getting sick decreases. In particularly difficult cases, it will not be possible to completely recover from the pathology, but it is still possible to achieve long-term remission, but only if the patient adheres to the doctor’s recommendations. The prognosis may worsen if the child is constantly under stress or has mental disorders.
Diet food
From the moment dyskinesia is detected, the patient is prescribed a special diet, the purpose of which is to improve the functioning of the liver and biliary tract. It is necessary to exclude fatty, spicy, salty, sour foods and rich broths from the patient’s daily diet.
Gastroenterologists categorically do not recommend onions and garlic, or various seasonings containing them. If you have problems with the gallbladder, fatty fish, milk and cream will harm you. You cannot consume canned food, store-bought or homemade marinades, alcoholic beverages and carbonated drinks, strong coffee and tea, and any kind of baked goods.
Portions should be small. During periods of exacerbation, viscous porridges and pureed vegetable soups are prepared for the patient. You should eat up to 6 times a day. In addition, you need to limit the amount of salt consumed so as not to provoke fluid stagnation. When the period of exacerbation is over, stewed, boiled or steamed dishes are introduced into the patient’s diet.
Soups based on vegetable broth, cereals, pasta, vegetables, low-fat meat and poultry, and day-old bread are allowed for consumption. You can consume butter, juices, honey, and marmalade in limited quantities.
For hypertensive biliary dyskinesia, exclude sugar, caramel, veal, pork, fresh berries, fruits, and yolk.
How to treat a child with dyskinesia?
Treatment of biliary dyskinesia requires an integrated approach and patience. Children are usually treated on an outpatient basis under the supervision of a gastroenterologist. In case of severe pain, it is necessary to call an ambulance, since even if the diagnosis is clarified, there remains the possibility of the simultaneous occurrence of cholecystitis, appendicitis and other diseases.
A child of any age needs attention to his complaints. Neurological symptoms such as increased irritability, crying, poor sleep are caused by a malfunction of the digestive process and a neurosis-like state. Quiet games, walks together, the belief that everything can be corrected with treatment have a significant impact on the fragile psyche.
Diet
Organizing dietary nutrition for a child with biliary dyskinesia requires:
Diet for liver and gallbladder diseases
- categorical refusal of dry snacks, consumption of nuts, chips, carbonated water;
- feeding every 4 hours;
- exclusion of any fried, fatty foods, hot sauces, sweets, carbonated water;
- serving only warm dishes (hot dishes and ice cream are prohibited);
- meat and fish are cooked in a double boiler or boiled; if tolerated, stewing is allowed;
- the food should have enough plant fiber and vitamins (porridge, fruits, vegetable salads);
- Vegetable oil (olive, sunflower, soybean) is added to prepared dishes; butter is used less frequently;
- To maintain the balance of intestinal flora, yoghurts, Rastishka, and fermented milk mixtures with bifidobacteria and lactobacilli are recommended.
There is no doubt that this baby will face all possible digestive disorders due to the negligence of his parents
Drug and physiotherapeutic treatment
For children, doctors try to select the least severe herbal preparations; the dose of tablets is calculated according to weight and age. For hypertensive type of dyskinesia, soothing mixtures with valerian and motherwort are recommended.
Pain is relieved with antispasmodics (Papaverine, No-shpa, Drotaverine), cholespasmolytics (dry bile, Flamin). Children are willing to be treated with physiotherapy methods. Applications of warm paraffin, diathermy, electrophoresis, and inductothermy are effective. Massage of the cervical-collar area is prescribed for severe neurological symptoms.
With a rare hypokinetic form of dyskinesia, stimulating procedures and medications are necessary. Exercise therapy and massage are recommended. Choleretic drugs are selected that can enhance the “pushing” of bile and the contractility of the tract. Cholinokinetics (Xylitol, magnesia solution, Sorbitol, magnesium sulfate) have a similar effect.
Herbal remedies include decoctions of rose hips, corn silk, and calendula. To prevent stagnation and cleanse the gallbladder, it is recommended to do tubage (blind probing) with mineral water, Xylitol, magnesium, and vegetable oil once a week.
Stimulation using physiotherapeutic methods is carried out by galvanization, Bernard currents, electrophoresis with magnesium sulfate. It is very useful for a child to drink natural mineral waters once a year at the resorts of Pyatigorsk, Kislovodsk, Essentuki. You can buy bottled water, but it is devoid of biological active substances that are not preserved, and its origin is questionable.
Sample menu for every day
The menu for children suffering from dyskinesia of the intestines and gallbladder ducts should be developed taking into account several requirements. The total daily calorie content of food for children 5-8 years old is about 2000-2400 kcal. In addition, the menu should be compiled according to the following rules:
- daily amount of fat should not exceed 90 g;
- a child should eat about 300 g of carbohydrates per day;
- The protein norm is 90 g, of which most should be of animal origin.
You need to eat according to the dietary system every day. The duration of such therapy depends on the characteristics of the disease - you can stick to the diet for up to 5 weeks. An approximate menu for the week is presented in the table.
| Day of the week | Breakfast | Dinner | Afternoon snack | Dinner | Snacks |
| Monday | Pancakes with jam | Vegetable soup, bread | Cottage cheese casserole | Chicken meatballs, spaghetti | Fruit jelly |
| Tuesday | Syrniki | Fish soup, meatloaf | Oatmeal pancakes, yogurt | Steamed vegetables, boiled beef | Baked apple with curd filling and honey |
| Wednesday | Oatmeal, bread and butter | Vegetable soup with noodles | Fruit jelly | Fish cutlets, mashed potatoes | Rice porridge with apple and raisins |
| Thursday | Milk soup with noodles | Buckwheat soup | Kefir with banana cake | Vinaigrette, stewed rabbit with sour cream | Sandwich made from bread and suluguni |
| Friday | Steam omelette, sandwich with low-fat cheese | Borscht with vegetable broth, buckwheat porridge | Apple pie | Steamed fish with vegetables | Milk pudding |
| Saturday | Cottage cheese casserole | Potato soup with meatballs | Rice and pumpkin porridge with milk | Buckwheat, veal cutlets | Banana milk muffins |
| Sunday | Oatmeal pancake with low-fat cheese | Chicken and rice meatballs | Bread with butter and jam | Boiled beet salad, chicken chop | Zucchini pancakes |
Clinical manifestations
Symptoms with the development of biliary dyskinesia manifest themselves in different ways, it all depends on age, the degree of neglect of the disease, and the number of concomitant pathologies, but the doctor will make an accurate diagnosis after a thorough examination.
General symptoms:
- The main symptom of any type of disease is pain. In the hypokinetic type, it is dull and does not have precise localization. With the hyperkinetic type, sharp spasms are felt, acute and very painful on the right, but extending to the left side and back.
- Nausea is almost always present when there is a malfunction of the gallbladder ducts, but most often it occurs simultaneously with colic. A feeling of nausea occurs after eating, when there is a feeling of heaviness from overeating or when there is a dietary disorder.
- The problem of biliary dyskinesia can be identified by the lack of appetite, and bile is its direct stimulator.
- Loss of extra pounds due to disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, when vitamins and beneficial microelements are not absorbed in the intestines.
- Feeling of a bitter taste in the mouth.
- Chronic constipation occurs due to poor breakdown of food, which moves slowly through the intestines.
- Diarrhea occurs when the diet is not followed, immediately after eating.
- Dyskinesia is accompanied by obesity when the disease is in an advanced stage. The process of breaking down food in the intestines occurs faster, which provokes the growth of adipose tissue.
- Belching and bloating.
- Sweating.
- Sleep disturbances and irritability.
Some of the listed symptoms are characteristic only of a certain type of bile duct dyskinesia. For example, the hypertensive type is characterized by rapid heartbeat, fatigue, and headaches.
What not to eat if you have diarrhea
People with gastrointestinal disorders often believe that they will have to radically change their eating habits. In addition, there is always the fear that the diet will become extremely meager and undiversified. However, when it comes to JVP, this is not entirely true. Here is the list of allowed products:
- milk or vegetable soups;
- lean fish and meat, poultry;
- group A pasta (durum wheat);
- cereals, bran;
- milk porridge;
- stale bread, crackers;
- milk, soft-boiled eggs, omelet, low-fat cheeses;
- kefir, yogurt;
- butter and vegetable oils in small doses;
- baked or boiled vegetables (fresh ones are best chopped very finely);
- fresh fruits, finely chopped;
- tea with lemon, berry infusions, juices diluted half with water;
- marshmallows and marshmallows in small quantities;
- honey (if there is no allergy).