A feeling of pressure and a feeling of heaviness in the right hypochondrium, as well as discomfort after eating, soreness are clear symptoms of problems with the hepatobiliary system in the body. If you ignore these kinds of symptoms, they will cause an increase in the size of the liver. If the organ increases significantly in size, then the situation can be considered very critical. For this reason, it is important to track bloating, stopping the problem at the initial stage of development. Be sure to see a doctor to get professional treatment. There is no point in trying to get rid of the disease on your own, and trying may make it worse. But how to treat an enlarged liver? What would such a symptom indicate? For what reason does this organ enlarge? We will talk about this and much more in the article.
Enlarged liver
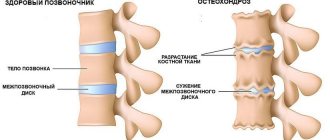
Before answering the question of how to treat an enlarged liver, it is necessary to understand in more detail what exactly this disease is. In the medical field, hepatomegaly is an increase in the size of the liver. However, it should be noted that this phenomenon is not considered a disease. Hepatomegaly is one of the characteristic symptoms that indicate problems in the hepatobiliary system.
The danger of organ enlargement lies not only in disruption of the liver and digestion - it can be a sign of abnormalities in organs and systems that are not related to the gastrointestinal tract: blood, heart. When a patient experiences liver swelling, it is important to stop such a symptom at the initial stage of its appearance, since it can provoke very serious consequences for the body. They are as follows:
- Liver failure, which can be fatal.
- The appearance of benign tumors.
- The development of diseases, the symptom of which is an enlarged liver.
- Hepatocarcinoma.
- Cirrhosis of the liver.
To avoid the complications described above, you need to know how to treat an enlarged liver. In addition, it is important to start treatment for this symptom on time. Be sure to contact your therapist, who will refer you to a specialist.
Prevention and prognosis
If the liver is enlarged, the prognosis depends on the etiology of hepatomegaly, the severity of the primary disease, the state of the immune system, and age. For viral diseases or helminthic infestations, a complete cure is possible. A sign of hepatomegaly in oncological diseases, cirrhosis, hepatosis can cause serious systemic disorders and death.
To avoid the development of pathology, you should lead a healthy and active lifestyle, give up bad habits, and engage in feasible sports. It is recommended to follow a diet, control weight and hormonal levels. In order not to become infected with worms - one of the causes of liver damage, you need to maintain hygiene, do not eat unwashed vegetables and fruits, unboiled water, or eat improperly cooked meat or fish. All medications must be taken only as prescribed by a doctor in a certain dose. All diseases that can provoke hepatomegaly must be treated promptly.
Causes of liver enlargement
The liver can become enlarged due to diseases that are associated with the organ, problems with blood circulation, and also due to certain infections. The most accurate diagnosis can only be made by a qualified specialist after carrying out some diagnostic measures. In addition, only a doctor can tell you how to treat an enlarged liver.
In most cases, the causes of this symptom are:
- Tumors: primary carcinoma, adenomas, metastatic cancer, focal nodular hyperplasia, cysts. In such a situation, the left or right lobe of the organ increases. With tumors, the liver will no longer grow completely.
- Inflammatory processes. First of all, this should include cirrhosis, as well as hepatitis of viral or drug etiology.
- Infiltrative processes: fatty degeneration, hepatosis, leukemia, amyloidosis, lymphoma, sarcoidosis or tuberculous hepatitis, hemochromatosis.
- Hereditary factor: congenital metabolic diseases, Gaucher disease.
- Damage to toxins. As a rule, this occurs against the background of drug treatment or alcohol addiction.
- Circulatory problems. This should include failure of the right heart, as well as blockage of the hepatic veins.
- Bacterial or viral infections that affect the hepatobiliary system.
- Helminthiasis.
- Gallstone disease, as well as lipid metabolism disorders.
An enlarged liver in a child is also considered an important point. If this happened to your baby, then the reason may lie in jaundice. This disease is very common among infants. She does not need therapy, as all the symptoms will go away on their own. The causes of jaundice are as follows:
- Disorders of the endocrine system in the mother, in particular diabetes.
- Birth injuries.
You should not be afraid of liver enlargement in preschool children, since pediatricians consider this phenomenon to be absolutely normal, because it is associated with the development of the body. If the organ is felt about 2 cm outside the ribs, then this is not dangerous. As the child gets older, the symptoms will go away. But it is still worth seeing a doctor.
But if the size of the organ does not change, and also exceeds the established norms, and is accompanied by other symptoms of any internal disorders, for example, fever, nausea, yellowness of the skin and mucous membranes, the appearance of rashes, weight loss, then the reasons may be as follows:
- Pathology of the metabolic process.
- Presence of metastases.
- Drug-induced or toxic liver damage.
- TORCH infections of a congenital nature.
- Blockage of the bile ducts.
- Biliary tract diseases.
Criteria for identifying hepatomegaly
As a rule, the most objective assessment of liver size is carried out by ultrasound or computed tomography. However, the initial signs of hepatomegaly are determined by the doctor using palpation and percussion.
- When examining an adult, it is considered normal if the percussion location of the diameter of the liver along the right midclavicular line does not exceed 12 cm. The lower border of the right lobe of the liver is palpated in incomplete people, it is soft and slides along the doctor’s fingertips.
- A protrusion of 1 - 2 cm is possible relative to the right costal arch. This is normal for people of asthenic body type. A protrusion of 3 cm is a deviation from the norm.
- The left lobe of the organ cannot be palpated. It is located behind the stomach above the epigastrium. If a dense formation is detected in this area, liver enlargement can be suspected.
Symptoms
If the liver is enlarged, how to treat it, what to do with this problem? First of all, it is necessary to diagnose the increased size of this organ. Therefore, you should become familiar with the symptoms that indicate an enlarged liver. Hepatomegaly will always be characterized by discomfort, which is localized in the right hypochondrium. There is also a feeling of heaviness and pressure. Additional symptoms may occur:
- Change in color of stool and urine.
- Yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes.
- Heartburn.
- Nausea, severe belching.
- Emotional instability, increased degree of irritability.
Diagnostic measures
Diagnostic indicators will help assess the activity of internal organs.
A hepatologist will be able to determine the cause of chronic enlargement and make the appropriate conclusion. You may also need to consult a gastroenterologist or oncologist. The doctor examines the medical history, listens to complaints and conducts a visual examination. On palpation, the liver is dilated and dense. The diagnosis is made after procedures such as:
- radiography of the organ;
- general blood and urine tests;
- biochemical blood test (increased alpha-amylase indicates problems with the digestive system);
- polymerase chain reaction for antibodies to the pathogen;
- CT or MRI.
Echosigns
Echoscopic ultrasound can help understand which liver diseases provoked hepatomegaly. A white liver on an ultrasound means that the organ is covered with fat cells. The causes and changes in the organ are shown in the table:
| Pathology | Hepatic changes |
| Hepatosis, cirrhosis, hepatitis | The structure is heterogeneous |
| Heart failure, helminthiasis, acute form of hepatitis | The structure is homogeneous |
| Neoplasms, abscesses | Areas of necrosis are visualized |
| The appearance of an inflammatory process | |
| The echo structure is disturbed |
Diagnostics
Only a qualified doctor can answer the question more accurately if the liver is enlarged, what to do, how to treat it. For this, specialists use some diagnostic procedures: CT, MRI, ultrasound. In the case of hepatomegaly in the clavicle area on the right line, the liver is more than 12 cm in length. In this case, it will be clearly palpable in the left lobe of the epigastric zone. It is imperative to monitor the following points:
- The presence of foreign tissue in the area of the right hepatic quadrant.
- Absence or presence of organ prolapse.
- Soreness, as well as the formation of a compaction, noticeable when palpating the organ.
Symptoms
It is worth understanding that liver enlargement may not appear for a long time. This is explained by the fact that the organ does not have nerve endings, therefore, it does not signal health problems with bright pain. Often, symptoms of liver enlargement are observed only when pathological processes are started. This is why it is much more difficult to cure the disease, because it is in the later stages.
Signs of liver enlargement:
- Discomfort in the area of the right ribs. It can manifest itself either periodically or constantly.
- The volume of the abdominal cavity has increased, this is caused by the accumulation of fluid in the abdomen.
- Digestive disorders. A person may often suffer from diarrhea and constipation, may also feel sick, vomit and have an unpleasant odor from the mouth.
- A feeling of heaviness in the body, which is especially aggravated in the body after taking fatty foods and alcoholic drinks.
- Change in skin color. The mucous membranes and epithelium become yellowish. The inner surfaces of the palms may become red and very itchy.
- Constant fatigue, insomnia, and mood swings. In general, a person’s emotional state is unstable, for this reason the quality of life deteriorates significantly.
- Losing weight. A person can lose kilos without following a diet.
- The appearance of rashes on the body in the form of small red dots on which blood vessels diverge.
All these signs indicate that a person has an enlarged liver. If symptoms are detected, you should immediately consult a doctor to normalize your health. You should not put off visiting a medical specialist and expect that your health will return to normal on its own.
It is impossible to say with certainty which symptoms are observed in a particular situation. The exact list depends on what kind of disease you are dealing with. After this, you will be able to decide what measures need to be taken to improve your well-being.
Features of treatment
So, we figured out why the liver is enlarged. How to treat such a symptom? In order to determine therapeutic measures, it is necessary to make an accurate diagnosis. In addition to the diagnostic methods described above, the specialist may additionally prescribe a biopsy to the patient if there is a suspicion of steatosis or cancer. A detailed blood test is also required. Additionally, the doctor must compile the patient’s verbal complaints, and, if necessary, send them for examination to other specialists.
The treatment regimen for an enlarged liver is often established not only by a gastroenterologist, but also by an infectious disease specialist and hepatologist. It is these doctors who will tell you how to treat an enlarged liver at home and what medications to take.
However, it is necessary to pay attention to the fact that whatever the cause of liver enlargement, the basis of therapy will be diet. The exact dietary restriction will be prescribed by the attending physician, but the essence of the diet will be to spare the organ. Speaking about how long such a diet will last, it is worth noting that this stage can last for several months or even years.
How to treat an enlarged liver? Medicines will necessarily be included in the basis of therapy. As a rule, for this purpose, drugs from the group of hepatoprotectors are prescribed, which have not so much a therapeutic effect as a preventive one. Such drugs are needed to maintain the organ, but they are not able to eliminate existing diseases.
We continue to look at how to treat an enlarged liver at home. Please note that no drug will work against this problem if the essence lies in advanced hepatitis. At its later stage, the only therapeutic measure will be transplantation. However, until this point, experts strive to prevent the development of complications.
How to understand that the liver is enlarged
The patient recognizes the problem mainly by unpleasant symptoms, which can also be observed when the organ is not too enlarged (when independent palpation brings almost no results). Hepatomegaly is always characterized by a feeling of discomfort in the right hypochondrium, among the unpleasant moments is a feeling of heaviness and pressure. Additionally there may be:
- yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes;
- changes in the color of urine and feces;
- heartburn;
- severe belching, nausea;
- increased irritability, emotional instability.
More accurate ways to detect an enlarged liver are classical methods of examining the hepatobiliary system - MRI, CT, ultrasound. With hepatomegaly along the right clavicular line, the organ is more than 12 cm in length and can be easily palpated in the left lobe of the epigastric zone. You should definitely keep track of the following points:
- presence or absence of organ prolapse;
- the presence of third-party tissues in the right hepatic quadrant;
- sensations during palpation - density of the palpated area, pain.
Diet
So, how to treat an enlarged liver at home? As mentioned earlier, the basis of therapy is diet. Whatever disease is the cause of hepatomegaly, hunger strike should not be allowed. This is no less dangerous for the liver than eating too much food. Any diet for organ enlargement requires compliance with simple rules. How to treat an enlarged liver in a child and an adult? How to eat food correctly?
First of all, you need to eat fractionally. This suggests that the patient should consume food in small portions, but often: in this way the organ is protected from overload and also stimulates the release of bile. It is advisable to eat at least 5 times in one day. The interval in this case should be no more than 2 hours. However, the exact figure will depend on the specific situation, as well as on the patient’s lifestyle.
Speaking about how to treat an enlarged liver in adults and children with diets, it should also be mentioned that it is necessary to reduce the amount of protein foods in the diet. This is especially important for those patients who suffer from cirrhosis, as they have a high likelihood of developing hepatic coma due to elevated levels of ammonia in the blood.
How else to treat an enlarged liver and fatty hepatosis? What nutritional rules must be followed? It is imperative to avoid fatty and spicy foods. The fact is that such dishes are the main sources of stress on the hepatobiliary system.
Causes of hepatomegaly and its classification
An increase in the size of the gland can occur in various pathologies, but the most common is a disruption of the functioning of the vascular system of the gland.
Most often, the development of the pathological condition is caused by damage to the portal and hepatic veins as a result of thrombus formation processes. In rare cases, a disorder occurs when the arterial part of the circulatory system of the liver is damaged.
The second most important cause of hepatomegaly is infectious viral damage to the organ, which results in damage to the parenchyma of the gland, portal vein and bile ducts.
Infectious viral lesions of the liver that provoke an increase in its volume include:
- viral hepatitis;
- Infectious mononucleosis;
- amoebic abscess;
- purulent thrombophlebitis of the portal vein;
- nonspecific cholangitis resulting from choledocholithiasis.
The development of hepatomegaly can be provoked by an oncological process, but it should be noted that primary tumor damage to the liver rarely leads to the development of pathology; most often the cause is malignant metastatic damage to the parenchyma.
In addition, adenomas and hemangiomas can be the reasons for an increase in the size of the gland.
Moderate hepatomegaly in an adult can often develop as a result of degenerative changes in the tissues of the gland. Such changes may be
- Steatohepatosis.
- Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
- Secondary changes in pathology of the cardiovascular system.
- Amyloidosis.
- Exposure to hepatotoxic compounds, which may be alcohol, drugs, some synthetic and natural compounds.
In some cases, the cause of the pathological condition may be congenital pathologies, autoimmune and endocrine disorders. Such ailments may be diabetes mellitus, endocrinopathy during pregnancy and traumatic damage to the liver parenchyma.
Main types of violation
Most often in medical practice, the etiological classification of this syndrome is used. Depending on the diseases that provoked liver enlargement, hepatomegaly is distinguished, which occurs due to circulatory disorders, metabolic disorders, primary liver diseases, infiltrative processes in the gland, some hematological diseases and local lesions.
In addition, when determining the type of disease, the anatomical and morphological classification is taken into account, which distinguishes pathologies with damage to the parenchyma, bile ducts, connective tissue or vascular network.
For differential diagnosis, a classification is used that reflects the compatibility of this disorder with splenomegaly, jaundice and ascites.
Depending on the degree of development of the pathological condition, three types of disorders are distinguished:
- moderate hepatomegaly - a slight change that does not fit into the normal range;
- pronounced - an increase of 10 cm from the norm;
- diffuse - an increase in the organ by more than 10 centimeters.
A separate form of hepatomegaly is distinguished, characterized by the fact that the patient has an uneven and heterogeneous enlargement of the liver.
What can't you eat?
So, we have looked at the reasons why the liver is enlarged. How to treat this symptom? What should you exclude from your diet to overcome this problem? As a rule, the following foods are prohibited:
- Dairy and fermented milk products, the fat content of which is more than 5%.
- Puff pastry products, baked goods.
- Sauces.
- Fatty fish.
- Fat meat.
- Egg yolks.
- Semi-finished products, fast food, sausages.
- Strong fish and meat broths.
- Legumes.
- Canned food.
- Spinach and sorrel.
- Cocoa, as well as its derivatives.
- Refined sugar.
- Confectionery.
- Carbonated drinks.
- Coffee.
Risk factors
A person must understand that the liver is often enlarged due to the fact that it is overloaded and cannot fully perform its functions. The organ is gradually depleted, which affects health. Similar phenomena can be observed under stress and significant loads. In such a situation, the organ begins to accumulate fat so that it can later be used to filter toxins, as well as to synthesize useful substances.
At the same time, certain factors that cannot be considered normal lead to changes in the size of the organ. They have different origins, but in most cases they are considered pathologies. It is important for a person to find out exactly what he can do in a particular situation. This is the only way to take timely measures and not trigger the existing pathology.
For what reasons can liver enlargement occur:
- Cirrhosis, viral hepatitis and hepatosis. All these dangerous diseases provoke a significant increase in liver size.
- Cysts, as well as neoplasms of various types. With them, a person may notice negative symptoms. Often the liver becomes enlarged, which impairs its functionality.
- Metabolic disruptions in the body. This factor leads to various problems, and it is often the liver that suffers.
- Taking alcoholic beverages and toxic medications. These factors have a destructive effect on the body. For this reason, they should be kept to a minimum to avoid extremely negative health consequences.
- Problems with the functioning of blood vessels and the heart.
- The presence of stones in the gallbladder, as well as obstructed outflow of bile.
It should be noted that in some situations, liver enlargement can be attributed to genetic pathologies. In this case, the cause of the disease can be a hereditary disease such as hemochromatosis.
It is extremely important to see a doctor in order to understand what exactly you are dealing with. In such a situation, it will be possible to significantly improve a person’s condition and avoid negative consequences. You should not wait until the pathology begins to progress and lead to a significant deterioration in well-being.
For this reason, it is recommended to contact a medical specialist in a timely manner so that you can restore your normal state of health.
What is allowed to eat?
The basis of the diet for the treatment of hepatomegaly will include vegetables, fruits, and herbs. It is allowed to eat cereals, vegetable milk soups, river fish, and dietary meat. Milk and dairy products should have a fat content of no more than 5%. You are allowed to eat one whole egg daily. It is advisable to prepare compotes based on dried fruits, but without adding sugar.
You can drink weak tea, freshly squeezed fruit and vegetable juices. You can include honey, berries, and marmalade in your diet. Rarely can you add olive oil or butter to dishes.
Prognosis and complications
An enlarged liver indicates the existence of a serious pathology in the body that requires medical intervention . The consequences of ignoring this problem in 1/3 of cases will lead to serious complications, including organ failure.
What are the dangers of liver enlargement and how dangerous is it? Viral and infectious hepatitis are reversible; timely treatment usually results in recovery and the return of the organ size back to normal limits. Damage caused by toxic substances, particularly alcohol, is usually irreversible. The prognosis for fatty hepatosis and fulminant forms of hepatitis will not be positive.
Preventing liver disease will help by switching to proper nutrition, giving up bad habits, regulating your sex life, and promptly consulting a doctor at the first symptoms of the disease.
Medicines
Enlarged liver: what to do, how to treat with medications? The selection of medications that will be used to treat an enlarged organ should be made only by an experienced doctor. Most patients are required to take hepatoprotectors, which protect the diseased organ, normalize its functioning, and also stop further cell changes. In addition, your doctor may prescribe the following medications:
- Enzyme medications: capsules, tablets that replenish the deficiency of digestive enzymes.
- Drugs that stimulate the flow of bile.
- Glucocorticosteroids, which are used in the late stages of liver cirrhosis as an anti-inflammatory agent.
- Antiviral medications are most often used in cases of viral hepatitis, but only at an early stage.
- Diuretics. These drugs are prescribed in case of ascites. They are contraindicated in the treatment of cirrhosis at an advanced stage, when there is a risk of developing hepatic coma.
Complications of hepatomegaly
Hepatomegaly is an alarming symptom of a disease that requires medication and, in some cases, surgical intervention. Ignoring the clinical picture in every third case leads to irreversible consequences, such as liver failure.
Timely treatment makes it possible to stop the development of pathological changes at the initial stages and return liver function to normal. In fulminant forms of the disease, the prognosis for patients is disappointing, especially if there is alcoholic liver damage, severe fatty hepatosis and fulminant hepatitis.
Attention. At the beginning of the development of liver pathologies, the problem can be dealt with by giving up alcohol, smoking and following the correct diet and regimen.
With further development, hepatomegaly can lead to enlargement of the portal vein and lymph nodes. These changes often indicate complex processes, for example the development of a malignant tumor.
Possible problems in the portal vein
The portal vein, also called the portal vein, is one of the largest vessels in the body. It plays a significant role in the processes of digestion and blood detoxification. Emerging pathological changes in the portal vein do not go away without leaving a trace, causing serious consequences.
The following problems are often diagnosed:
- portal vein thrombosis;
- portal hypertension of the vessel;
- pylephlebitis;
- cavernous transformation.
Diseases are acute and chronic, each of which has its own special symptoms.
One type of complication of hepatomegaly is hepatic portal vein thrombosis.
The acute form of the pathology is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- severe sharp pain in the abdomen;
- high body temperature, sometimes reaching critical levels;
- fever;
- an increase in the size of the spleen, which threatens the patient with organ rupture;
- nausea often progresses to vomiting;
- bowel disorders.
Chronic forms of the disease are dangerous due to their hidden course. A routine examination allows you to diagnose changes occurring in the body.
The absence of signs of pathology often causes the launch of compensatory mechanisms. Thus, to protect the body, the process of vasodilation is activated, which is characterized by an increase in the volume of the liver artery, as a result of the formation of a cavernoma.
As the disease processes further develop, the patient is able to notice the following symptoms:
- general weakness;
- lack of appetite;
- painful sensations in the right hypochondrium.
Portal hypertension poses a serious danger to human life and health.
The problem is expressed by the development of such conditions:
- ascites;
- dilation of the saphenous veins, localized in front of the abdominal wall;
- varicose veins of the esophagus.
Chronic thrombosis in the portal vein is accompanied by:
- dull constant pain in the abdomen on the right side;
- long-lasting low-grade body temperature;
- increase in the size of the spleen;
- hepatomegaly.
Enlarged lymph nodes at the porta hepatis
Possible enlargement of lymph nodes can only be determined through ultrasound diagnostics, but in addition, the patient can pay attention to emerging changes in health status.
Signs may be:
- sudden weight loss;
- increased body temperature (low-grade fevers are characteristic of the chronic form, high temperatures indicate an acute course);
- increased sweating, especially at night;
- when palpating the liver area, pain is felt;
- swelling of the limbs;
- chills, fever.
The photo shows an ultrasound image of enlarged lymph nodes at the porta hepatis.
The causes of inflammation of the lymph nodes at the porta hepatis can be:
- infectious liver lesions;
- proliferation of metastases from nearby cancer-affected organs;
- chlamydia;
- tuberculosis, syphilis, brucellosis virus;
- long-term use of drugs from the cephalosporins and sulfonamides group;
- fungi;
- systemic diseases, for example, rheumatoid arthritis, sarcoidosis, endocrinopathy;
- cytomegalovirus infection, HIV, various hepatitis;
- toxoplasmosis, giardiasis, toxocarosis, filariasis.
Fact. Damage to the lymph nodes at the porta hepatis due to the formation of a malignant tumor in the intestine and the growth of metastases to the liver is observed in 12% of all cases.
Folk remedies and liver treatment
How to treat an enlarged liver with folk remedies? To speed up the removal of toxins from the body, prevent deterioration of well-being, and also protect the organ from the effects of drugs, you can use traditional medicine recipes. As a rule, they do not have the same therapeutic effect as medications, but the result can be noticed if the disease occurs at the initial stage of development.
You should pay attention to the fact that home recipes must be used in combination with medications prescribed by the doctor. Most often, the following traditional medicine recipes are used for this purpose:
- Oatmeal broth. To prepare it, you need to thoroughly rinse one glass of oats, then fill the raw material with one liter of cold water. In a small container with thick walls, bring the oats to a boil, then simmer over low heat for 40 minutes. Then the pan is wrapped in a blanket and left for 6 hours. Use the finished product in an amount of 50 ml before meals. The duration of treatment is 1 month.
- Honey and turmeric. To prepare this healing remedy, you need to mix a quarter teaspoon of turmeric with one teaspoon of natural honey. Pour these ingredients into one glass of hot water, but not boiling water. Mix everything thoroughly and then consume before meals. This product should be used 4 times a day. The duration of treatment is 15 days.
How is the treatment carried out?
The most effective drugs
With hepatomegaly, heavy physical activity is prohibited, as this disrupts the blood supply to the liver, which leads to even greater swelling of the organ.
Effective treatment will require qualified medical assistance.
Drug treatment is prescribed by a doctor; self-medication is prohibited. Depending on the disease that caused the liver enlargement, drug therapy differs. For helminthiases, Albendazole, Mebendazole, Vormil, and Dekaris are recommended. For hepatitis, alpha and beta interferons are prescribed and detoxification measures are carried out. Heart failure requires complex treatment, including glycosides - Digoxin, Strophanthin, Korglikon. It is also recommended to use hepatoprotectors (drugs for the treatment and restoration of the liver), such as:
- "Gepabene";
- "Galstena";
- "Antral";
- "Essentiale";
- "Karsil";
- "Hofitol";
- "Gepamertz";
- "Hepatosan";
- "Milk thistle."
Therapeutic diet
Adhering to the principles of a healthy diet can speed up the healing process.
The diet for liver enlargement in adults should contain food that is steamed, stewed, boiled or baked. Alcohol, coffee, carbonated sweet drinks, as well as fatty, pickled, salty, fried, spicy foods and baked goods are strictly prohibited. You can eat no more than 5 g of salt per day. Meals should be divided into 5-6 small portions. A diet for an enlarged liver includes the following foods:
- low-fat dairy products;
- lean soups without frying;
- lean meats and fish;
- mild cheese;
- fresh vegetables, fruits and berries;
- fruit and berry jelly and compotes;
- dried white bread or crackers;
- pasta;
- cereal porridge;
- soft-boiled egg or steamed omelette;
- dried fruits;
- honey;
- legumes;
- vegetable oil;
- nuts.
Folk remedies
The use of traditional methods of treatment is agreed with the attending doctor.
If the liver is enlarged, folk remedies will help reduce its size. An effective herbal decoction is prepared as follows:
- Mix motherwort, St. John's wort, mint and immortelle inflorescences in equal proportions.
- Take 20 g of the mixture and add 500 ml of hot water.
- Let it brew for 40-60 minutes, filter.
- Take 100 ml before meals.
Treatment with folk remedies includes the following recipe:
- Take 20 g of honey and 20 ml of lemon juice.
- Add 200 ml a little warmed water.
- Drink 2 r. per day.
Treatment for an enlarged liver includes taking a medicine prepared as follows:
- Squeeze the juice from the apples to make 0.5 liters.
- Add 50-60 g of honey and mix thoroughly.
- Take 100 ml up to 5 p.m. in a day.
All means of alternative medicine should be agreed with a doctor, since herbal medicines have contraindications for various pathologies, against the background of which the liver could become enlarged.
The plant has powerful anti-inflammatory properties.
Hepatomegaly can be treated with herbal tea. Recipe:
- Take 5 g of dried sage herb.
- Pour in 300 ml of hot water.
- Leave for 30 minutes.
- Add 5 g of honey and let it brew for another half hour.
- Take on an empty stomach.
Chronic hepatomegaly can be cured with a decoction of dandelions. Do it like this:
- Dry a small amount of flowers, stems or leaves of the plant.
- Take 20 g of dandelion ingredients, pour 400 ml of water.
- Put on fire, bring to a boil and simmer for 15 minutes.
- Remove from heat, let steep for 30 minutes, filter.
- Take 4 tbsp. l. after every meal.
The organ will not be able to enlarge if it is treated with this remedy:
- Take 20 g of dried peppermint, pour into a heat-saving container and add 150 ml of hot water.
- Let it brew for 24 hours, filter.
- Drink 50 ml 3 times. per day for 7 days.
Herbs
There are a large number of different herbal preparations that help to gently restore the function of the hepatobiliary system. In addition, they stop the degenerative-dystrophic process. At the same time, venous circulation is normalized. The following recipes are effective in the treatment of hepatomegaly:
- Milk thistle powder. It should be taken one teaspoon at a time, preferably during meals. The powder must be chewed thoroughly and washed down with warm water. The duration of treatment is usually 1 month.
- A collection of calendula, celandine, St. John's wort, coltsfoot. All herbs are taken in equal proportions. After this, two tablespoons of the mixture are poured into two glasses of boiling water and infused for an hour. Take half a glass of the resulting product 20 minutes before eating. This product must be used 3 times a day. It is worth noting that the duration of treatment should be at least a month.
- Take St. John's wort leaves, mint leaves, immortelle flowers, and motherwort herb in equal proportions. All ingredients are mixed, after which two tablespoons of the mixture are boiled in 500 ml of water. Then the composition must be filtered. It should be consumed in an amount of 50 ml, and before eating. The duration of treatment is 1 month.
In conclusion, it is worth noting that to prevent hepatomegaly, it is necessary to monitor your body weight, avoiding excess weight. You should also reconsider your own lifestyle: eliminate nicotine and alcohol, normalize your rest and work schedule, go to the gym, and minimize stressful situations.
Briefly about the human liver and its indicators
As we have already noted, the liver is the largest organ; its part makes up 2.5% of the total human body weight. At the same time, a man’s liver is larger, on average its weight is 1.5 kg, and that of a woman – 1.2 kg.
The gland is located on the right side of the abdominal cavity; in a healthy state, the organ is not able to protrude from under the ribs, however, with pathological changes, an experienced doctor can easily palpate it.
The organ has a soft but dense structure, is dark red in color and consists of 4 lobes:
- large right;
- smaller left;
- an even smaller tailed one;
- square.
The tasks of the liver include performing more than 500 important functions (read more here), one of which is participation in blood circulation and hematopoiesis. The hepatic artery supplies oxygenated blood to the organ, and along the same path its outflow occurs, but already saturated with carbon dioxide.
In addition, a large volume of blood from all digestive organs enters the organ through the portal vein. The liver absorbs a huge amount of substances, both nutritious and non-nutritive, that enter the body through the digestive tract. Accordingly, the liver, as the main biochemical synthesizer in the body, is subject to all sorts of external influences.
The liver is a complex biological mechanism that performs numerous important functions.
Main functions of the liver:
- active participation in the digestive system;
- bile production;
- barrier function for the whole organism;
- neutralization of blood from toxins, poisons, microbes, bacteria, etc.;
- participation in metabolic processes;
- glycogen production;
- synthesis of hormones.
Important. With impaired liver function, various pathological changes occur throughout the body.
What does moderate hepatomegaly of the liver mean?
Liver enlargement for various reasons can come in several forms. According to statistics, the most common form is moderate hepatomegaly.
With a moderate form of pathology, the size of the organ is slightly changed. There are no signs of diffuse changes. The process is reversible, but requires proper diagnosis. Moderate hepatomegaly can “affect” both the left lobe of the liver and the right. In most cases, the right lobe is more often subject to changes due to the increased load on the right segment.
Note! Moderate enlargement of the liver can be caused by poor diet or medications. This condition is temporary and disappears after the cause is eliminated. BUT! More serious deviations cannot be excluded, which, if left untreated, go into the stage of “diffuse changes”.
To confirm the diagnosis, manual examination of the abdominal organ is not enough. This requires ultrasound diagnostics to obtain accurate data on the size of the organ and possible deviations in the structure of hepatocytes.
The disease does not bypass children of different ages (there is a congenital type of pathology). Pregnant women, people with obesity and alcohol dependence are at risk for moderate hepatomegaly.
How to diagnose hepatomegaly?
When visiting a doctor, the first step is a visual examination, tapping, and palpating of the anterior abdominal wall. This allows you to determine the relief and boundaries of the liver. The doctor is interested in information regarding previous diseases, operations, injuries, changes in stool, and digestive disorders.
By taking a detailed history, doctors can determine the root cause of hepatomegaly. When there is a suspicion of serious illness, the following must be prescribed:
- lab tests;
- instrumental studies;
- diagnostic procedures.
To understand the picture, the doctor needs the results of all studies.
Analyzes
The patient is recommended to donate a blood sample to determine markers of viral hepatitis, protein, bilirubin, and prothrombin index. The analysis may include research on 6-15 indicators.
Since helminthic infestations can cause malfunction and changes in the size of the liver, stool tests are also performed to check for worms. To most accurately and quickly determine the presence of parasites, you can donate blood from the ulnar vein instead of feces.
Research
It will be necessary to verify the integrity of the biliary tract; for this, patients need to undergo magnetic resonance imaging. If malignant neoplasms in the liver are suspected, a biopsy of the liver tissue is performed.
An ultrasound examination will be required to accurately represent the size, position and other characteristics of the liver. Thanks to an ultrasound, the doctor will see the state in which they are:
- gallbladder;
- The lymph nodes;
- intrahepatic veins.
The ratio of the parts of the gland is determined, how much the organ protrudes from under the costal arch.
No less important information regarding the structure of the liver, echogenicity, density. Additionally, the condition of the pancreas and spleen is diagnosed. Laparoscopy is recommended as an auxiliary method of checking the body. The technique allows you to determine the state of the hepatobiliary system.
Can hepatomegaly develop in only one lobe of the liver?
The liver consists of two lobes, each with its own innervation, blood supply, and bile ducts (central artery, vein, bile duct). Isolated hepatomegaly of the right lobe of the liver is observed more often than the left. Functionally, the right lobe is loaded more, performing 60% of the organ’s work, so any violations primarily affect it.
With uneven enlargement of the organ, they speak of partial hepatomegaly. The lower edge of the liver rarely changes, so ultrasound is necessary for detection. A characteristic echo sign is a change in the homogeneity of the tissue structure. Usually found in tumors, cysts, and abscesses.
Treatment
If no disease was detected during diagnosis, but the size of the organ is still increased, you need to resort to maintaining a correct, healthy lifestyle. Then the liver will slowly return to normal on its own. In most cases, the patient should lose weight (if there is excess body weight), stop drinking alcohol, smoking, eat right, and properly distribute physical activity.
Treatment also involves allocating sufficient time for sleep, walks, and rest. The entire course of therapy should only be carried out under the supervision of a physician. When this important organ enlarges, experts prescribe medications, homeopathic preparations that need to be taken for a long time. In addition, the doctor is obliged to prescribe therapy that will eliminate the causes of the disease.
Drugs for liver enlargement
- Chophytol, Artichoke, Artichol help improve the condition of hepatocytes and normalize their work.
- Essentiale is based on the effects of phospholipids. These fat-containing compounds (phospholipids) prevent the process of proliferation of fibrous tissue cells. Therefore, Essentiale reduces the risk of cirrhosis. This drug is prescribed for hepatitis, steatosis, necrosis, and toxic liver damage.
- Gepabene. This treatment is prescribed for hepatitis and liver poisoning by toxins. Gepabene consists of fume and milk thistle. Synonyms for this medicine are Karsil, Geparsil, Silegon.
- Galstena is a homeopathic medicine that is used to treat liver enlargement in gallstone disease (cholelithiasis) and hepatitis.
- Pancreatin, Mezim. These drugs contain enzymes that improve the functioning of the pancreas, intestines and normalize digestion.
Remember, treatment of an adult or child should only be carried out under the supervision of a doctor! Self-medication is strictly prohibited! Ask questions about the liver, its enlargement, share your problems with our specialist.
We recommend reading:
- Enlarged liver in a child
What is hepatomegaly
The liver is located in the upper right quadrant of the abdominal cavity. Consists of 2 lobes. The boundaries of the gland are an important diagnostic feature. The table below shows the figures for adults.
| Physical quantity | Dimensions (cm) |
| length | 14—18 |
| width | 20,1—22,5 |
| sagittal plane | 9—12 |
In obese people, the gland corresponds to the complexion and does not differ significantly from the norm . This is due to the characteristics of a particular individual. A healthy organ has sharp edges, smooth relief, soft consistency, and regular outlines. In various pathological conditions, for example, in heart failure, blood stagnates in the liver, it enlarges, and the structure becomes denser.
Causes
The causes of moderate liver enlargement can be either pathological or completely natural. Signs of small changes in the shape and tissues of the organ are observed when eating too fatty foods, smoked meats and other unhealthy foods. In addition, regular consumption of alcoholic beverages in large quantities leads to an increase in liver volume.
A moderate increase in organ size may also indicate the progression of pathological conditions. Usually the liver enlarges slightly at the initial stage of a particular disease. Most often this syndrome is observed when:
- hepatitis;
- metabolic disorders;
- liver fibrosis;
- cirrhosis;
- hemolytic disease (in newborns);
- parasitic organ damage;
- in the presence of congenital infections, for example, rubella, cytomegalovirus, etc.
Etiology
An enlarged liver can be observed in the following pathological processes:
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- fatty hepatosis;
- violation of the outflow of bile, cholelithiasis;
- viral hepatitis;
- infections of a viral or bacterial nature.
It should also be noted the reasons for liver enlargement that are not directly related to the functioning of this organ:
- cardiovascular failure;
- genetic diseases;
- vein blockage;
- disruption of fat metabolism and metabolic functioning;
- hemochromatosis;
- oncological processes;
- benign tumors;
- cysts;
- exposure to toxins, including alcohol and drugs.
Separately, we should highlight factors that can lead to liver enlargement in a child:
- inflammatory processes;
- toxic poisoning with heavy metals, chemical compounds, poisons;
- sepsis;
- abnormal development of the bile ducts;
- metabolic pathologies;
- poor nutrition of the child, which can lead to obesity or “fatty” liver syndrome;
- congenital infections;
- congestive liver pathologies.
It should also be noted that an enlarged liver in a child can be a signal of a blood disease - leukemia, hemolytic anemia, etc. Therefore, if an enlarged liver is noticed in a child, you should urgently seek medical help. Delay in this situation can lead to disability or death.
Symptoms of hepatomegaly
The first symptoms of an enlarged liver are noted almost immediately: this is a bursting feeling in the right side, as if something is interfering, and when you change the position of the body, a dense lump is noted in the abdominal cavity. Almost always, the disease is accompanied by bad breath, attacks of nausea, heartburn, and stool problems. Also, manifestations of the disease include yellowing of the sclera of the eyeballs, skin, and itching in the mucous membranes. All these are symptoms that characterize liver enlargement.
The causes of hepatomegaly are explained not only by inflammatory diseases, but also by the presence of bad habits in the patient (smoking, alcohol, poor diet), hereditary factors, and working conditions.
Causes of hepatomegaly
Provocateurs for enlargement of the digestive gland can be:
- Own pathological conditions (alcohol disease, cirrhosis, hepatitis), which go through 2 stages in their development. They begin with inflammation and swelling of the liver. After the death of hepatocytes, the size returns to normal. At the next stage, collagen tissue grows, filling the voids, which leads to repeated hepatomegaly.
- Hereditary metabolic abnormalities leading, in particular, to impaired glycogen formation. At the same time, the kidneys and spleen enlarge. Finely tuberous cirrhosis becomes a consequence of hemochromatosis - a malfunction in iron metabolism.
- Heart diseases with blood stagnation, swelling, compaction, and enlargement of parenchyma trigger mechanisms of fibrotic and necrotic phenomena.
Pain during palpation is often associated with inflammatory processes in hepatocytes, which can be provoked by protozoa, helminths, bacteria or viruses. Differential diagnosis does not give results, since schistosomes and echinococci in consistency and density are not much different from healthy liver tissue. Malignant neoplasms lead to infiltration, as well as an increase in the mass of the gland, sometimes up to 10 kg.
Reasons for development
Hepatomegaly is a common type of illness that is not a separate disease. Hepatic pathology in the form of changes in liver size accompanies a number of different pathological processes. Why does the “symptom” arise:
Liver pathology directly. This group includes infectious lesions of the structural unit of the organ, cirrhosis, hepatosis, inflammatory processes and helminthic infestations. Hepatomegaly of varying degrees is accompanied by amyloidosis, hepatitis of viral and non-viral etiology, and dystrophic changes due to metabolic disorders.
- Viral diseases affecting the condition of the organ. Mycoplasma, cytomegalovirus infection, mononucleosis, H1N influenza virus
- Enzymopathy, that is, it is impossible for liver cells to synthesize enzymes involved in the digestion process. Enzyme synthesis deficiency is also a combined disease.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract of varying degrees, for example, gastric ulcer, cholelithiasis, pancreatitis.
- Blood diseases in which red blood cells are destroyed, for example hemolytic anemia, Rh conflict in newborns. Extensive blood loss requiring transfusion of blood components or plasma.
- Thrombosis of the liver veins and varicose veins of the pelvic and abdominal organs.
- Alcohol addiction, in particular reactive changes in the organ under the influence of ethyl alcohol.
Echinococcosis is a parasitic disease in which Echinococcus infects the liver. The parasite is localized only in hepatocytes, causes enlargement of the liver, and enters hematogenously by eating food contaminated with echinococcus. Cases of mass infection with echinococcus have been identified. All patients had moderate and severe hepatomegaly.
- Intoxication and poisoning with various substances. The liver “filters” incoming substances along with the blood. In some cases, by producing special enzymes, it neutralizes poisons, toxins, and medicinal components. In case of severe or massive poisoning, the organ cannot cope, and due to this it increases in volume.
- Some cardiovascular pathologies are accompanied by various abnormalities. For example, with cardiovascular failure and arterial hypertension, hepatomegaly develops in 47% of cases.
There are many causes of hepatomegaly. Cases of physiological enlargement of the liver (congenital anomaly) have been reported.
Treatment method
Treatment is prescribed by a doctor depending on the diagnosis. If infections or parasites are detected, antibacterial and anthelmintic drugs are prescribed.
Oncology is treated comprehensively using surgery and radiation therapy. For genetic diseases, the attending physician prescribes the use of enzymatic agents to improve metabolism.
An important part of treatment, according to prokisheshnik, is maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Quitting alcohol, fatty, salty foods, and smoking will help. You need to adhere to a special diet.
Surgical intervention
Surgery is used for oncology and cyst formation. An open operation is performed to remove part of the liver.
Vascular embolization can be used to treat a tumor. This operation consists of blocking the access of oxygen to the malignant formation. Because of this, the tumor dies.
In difficult cases, an organ transplant will be needed. The liver is prone to regeneration, so it is enough to transplant only the affected part of the organ. The donor becomes a relative who is suitable for transplantation according to a number of parameters.
Medications
Medicines themselves cannot shrink the size of the liver. But in combination with general therapy, they have a positive effect on the condition of the organ. The most common medications for an enlarged liver are:
- Ovesol – improves the condition of the bile ducts and cleanses the filter organ;
- Essentiale – supports the proper functioning of blood vessels and the heart, and also reduces cholesterol levels;
- Hepatamine – restores normal liver function;
- Galstena – prescribed for the treatment of hepatitis and the formation of gallstones;
- Liv-52 - restores organ functions and protects it from toxins.
Proper nutrition for an enlarged liver
Proper nutrition
Diet is an invariable guide to the treatment of hepatomegaly. To reduce the size of the liver, it is necessary to exclude fatty, spicy and salty foods from the diet. Also, according to prokishecnik, it is necessary to exclude the intake of alcoholic beverages.
Nutrition must be comprehensive and must contain all the necessary minerals and vitamins. You need to eat in small portions 5-7 times a day. This promotes better digestion. For certain diseases, you need to exclude certain foods from your diet.
Sample menu for a week's diet
Write a menu for hepatomegaly with doses 5-6 times a day.
Monday:
- Rice, tea (green or herbal) with honey;
- Fresh apple juice with oatmeal;
- Boiled or steamed fish;
- Boiled carrots;
- Steamed vegetables.
Tuesday:
- Omelet without yolk, tea or rosehip decoction with baked goods;
- Dried fruits processed with boiling water;
- Beef or chicken broth with bran bread;
- Fresh vegetable juice with oatmeal baked goods;
- Skim cheese;
- Fresh vegetables and herbs.
Wednesday:
- Kefir or cottage cheese with 0% fat content;
- Rosehip decoction with baked goods;
- Steamed meatballs;
- Pumpkin puree, herbal tea;
- Cheesecakes with dried fruits;
- Juice with oatmeal baked goods.
Thursday:
- Oatmeal, tea;
- Dried fruit compote and dietary baked goods;
- Steamed fish with bran bread;
- Juice with biscuits;
- Vegetable casserole;
- Herbal tea.
Friday:
- Boiled spaghetti;
- Juice, biscuits;
- Buckwheat soup and bran bread;
- Dried apricots, raisins, prunes;
- Porridge with milk and baked goods;
- Tea, pastries.
Saturday:
- Buckwheat, tea;
- Fruits;
- Broth with bread;
- Sauerkraut;
- Marmalade.
Sunday:
- Cottage cheese with dried fruits and tea;
- Juice, biscuits;
- Boiled veal or poultry with vegetable puree;
- Rosehip infusion and bran bread;
- Kefir, biscuits;
- Fresh fruits or vegetables.
Hepatomegaly in children
In newborns, the weight of the liver is 4% of the total body weight. Exceeding metric parameters by 1-2 cm is considered normal, but can also be a consequence of serious conditions: infectious diseases, cholangitis, hereditary syndromes, for example, Debre. Additional signs: rapidly increasing jaundice, navel swelling, spider veins in the abdominal area, vomiting require urgent hospitalization.
In older children, this diagnosis means a restructuring of the body. The liver is moderately enlarged between the ages of 5 and 7 years. This is due to changes in metabolic processes. The symptom passes quickly, but can recur during puberty, when hormonal changes occur. The condition is considered dangerous if the child is bothered by frequent nausea and vomiting.
Complications
Hepatomegaly is a dangerous liver pathology that, without timely treatment, leads to complications: the development of renal failure and an increased risk of internal bleeding.
The disease can progress to a chronic stage, which requires constant maintenance therapy and a radical change in lifestyle and nutrition. The consequences of an enlarged liver are not always reversible.
In addition to the enlargement of the liver, the underlying cause of the disease worsens. The lack of therapy leads to the fact that hepatomegaly reaches a diffuse form, which cannot be treated, because it is caused by incurable diseases: the last stages of oncology, cirrhosis.